|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1403147
次世代電池用リチウム金属負極材料の技術開発状況と市場予測(2024年)<2024> Technology Development Status and Market Forecast of Lithium Metal Anode Materials for Next-Gen Batteries |
||||||
|
|||||||
| 次世代電池用リチウム金属負極材料の技術開発状況と市場予測(2024年) |
|
出版日: 2023年12月11日
発行: SNE Research
ページ情報: 英文 271 Pages
納期: お問合せ
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
21世紀の気候変動が深刻化する中、再生可能でクリーンなエネルギー技術開発の必要性がますます高まっています。さまざまな規制が設けられ、環境規制を通じて環境保護と持続可能な社会の実現に積極的に取り組む中、二次電池産業は環境にやさしいエネルギー産業を先導しています。輸送がICEから電気自動車に移行する中、各種リチウムイオン二次電池の研究が活発に進められています。
1990年代に実用化されて以来、リチウムイオン二次電池はさまざまな電子機器や電気自動車の電源として大きな成功を収めてきました。しかし、黒鉛負極を用いた従来のリチウムイオン電池は、負極の理論容量(~372 mAh/g)と体積あたりの容量(~735 mAh/cm3)が低いため、高いエネルギー密度を達成するには限界があります。増大するリチウム二次電池の需要を満たすには、従来のリチウムイオン電池を超える新たな電池技術を開発する必要があります。
リチウム金属は理論容量が非常に高く(~3,860 mAh/g)、電気化学的電位がもっとも低く(-3.04 V vs. SHE)、密度がもっとも低い(0.53 g/cm3)です。これらの特徴から、リチウム金属は単位重量と単位体積あたりの高いエネルギー密度と出力密度を達成するためのもっとも有望な材料と考えられています。
さらに、負極にリチウムを含まない材料を使用したり、少量のリチウムしか使用しない無負極技術も活発に研究されています。負極材料は電池の充電速度や寿命に影響するため、負極材料をなくす、または減らすことで、電池のエネルギー密度を高め、寿命を延ばせるという利点があります。
当レポートでは、リチウム金属負極市場について調査し、リチウム金属技術や無負極技術、リチウム金属関連企業や研究機関の技術と開発状況などの情報を提供しています。また、2030年までのリチウム金属負極材料市場の需要と規模を予測しています。
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
第2章 負極材料技術と開発状況
- リチウムイオン二次電池負極材料の概要
- リチウムイオン二次電池負極材料の開発動向
- 負極材料(リチウム金属負極)の将来の発展
- 負極材料(無負極)の将来の発展
第3章 リチウム金属の製造技術と供給状況
- リチウムの生産と供給状況
- 世界のリチウム埋蔵量
- 世界のリチウム生産量
- リチウム資源:鉱物
- リチウム資源:鉱石
- リチウム資源:塩水
- リチウム材料供給構造
- リチウム需要の見通し
- リチウム金属製造技術
- リチウム材料技術
- リチウム薄膜技術
- リチウム薄膜技術
- リチウム薄膜化プロセスの制限
- 高コスト構造
第4章 リチウム金属負極の研究開発動向と主な課題
- リチウム金属負極の開発史
- 開発履歴の概要
- リチウム金属電池(LMB)の歴史
- リチウム金属電池(LMB)の初期開発
- リチウムイオン電池の開発と市場独占
- リチウム金属電池(LMB)需要の拡大
- リチウム金属負極の主な問題
- リチウム樹状突起の成長
- SEIレイヤーの問題
- リチウム金属負極の研究開発動向
- 人工SEI
- 新構造設計
- 電解質修飾
- 無負極設計
第5章 リチウム金属負極の開発状況:企業別
- 概要
- アジアの企業
- Samsung SDI
- LGES
- SK on
- CATL
- EVE
- Prologium
- Qingtao Energy
- Welion
- Hyundai Motors
- POSCO
- Neba Corporation
- Ulvac Inc
- Santoku
- Honjo metal
- Wuxi Sunenergy Lithium Industrial
- China Energy Lithium
- Ganfeng Lithium
- Tianqi Lithium
- Montavista
- Shenzen Inx Technology
- BTR
- SoftBank Next-Generation Battery Lab
- National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
- National Institute for Materials Science-ALCA SPRING
- 欧州の企業
- Blue Solutions
- Volkswagen
- Mercedes-Benz
- SIDRABE
- IMEC
- 北米の企業
- SES
- QuantumScape
- Solid Power
- Factorial Energy
- Soelect
- TeraWatt
- Hydro Quebec
- Brightvolt
- Sion Power
- SEEO
- Cuberg
- Enpower Greentech
- PolyPlus
- Sepion Technologies Inc
- Ion Storage Systems
- Sakuu
- GM
- Ford
- Li Metal Corp
- Ionic Materials
- Albemarle
- SQM
- Livent Corp
- Pure Lithium Corp
- 主要企業のサマリー
第6章 リチウム金属負極市場の見通し
- リチウム金属負極市場の見通しの概要
- リチウム金属負極電池の種類とコスト構造
- リチウム金属負極の採用ロードマップ
- リチウム金属負極電池の商業化シナリオ
- リチウム金属負極市場の見通し
- リチウム金属負極の需要の見通し
- リチウム金属負極の価格の見通し
- リチウム金属負極の価格予測の根拠
- リチウム金属電池(SLMB)の市場規模の予測
- リチウム金属電池(SLMB)の採用の予測
- リチウム金属電池(SLMB)の利用の見通し
With the growing seriousness of climate change in the 21st century, the need for renewable and clean energy technology development has become increasingly urgent. Amidst various regulations and active efforts to achieve environmental protection and a sustainable society through environmental regulations, the secondary battery industry is a leading eco-friendly energy industry. As transportation shifts from internal combustion engines to electric vehicles, research on various types of lithium-ion batteries is actively underway.
Since their commercialization in the 1990s, lithium-ion batteries have been highly successful in powering various electronic devices and electric vehicles. However, conventional lithium-ion batteries with graphite anodes have limitations in achieving high energy density due to the low theoretical capacity (~372 mAh/g) and volumetric capacity (~735 mAh/cm3) of the anode. Meeting the growing demand for lithium secondary batteries requires the development of new battery technologies beyond conventional lithium-ion batteries.
Lithium metal has a very high theoretical capacity (~3860 mAh/g), the lowest electrochemical potential (-3.04 V vs. SHE), and the lowest density (0.53 g/cm3). Due to these characteristics, lithium metal is considered the most promising material for achieving high energy and power density per unit weight and volume.
In addition, anode-less/anode-free technologies, which use lithium-free materials for the anode or apply only a small amount of lithium, are also being actively researched. Since the anode material affects the charging speed and lifespan of the battery, eliminating or reducing it has the advantage of increasing the energy density of the battery and increasing its lifespan.
This report covers the latest trends centered on lithium metal and anode-free technologies, which are considered promising anode materials for the future. It also examined the technology and development status of more than 50 lithium metal-related companies and research institutes in Korea, China, Japan, North America, and Europe. Lastly, the market analysis section predicts the demand and size of the lithium metal anode material market by 2030, taking into account the utilization in xEVs and other emerging applications within the next-generation battery market landscape.
Strong Points of this report:
- 1. Li metal manufacturing technologies and issues
- 2. Understanding the overall R&D trends of Li metal anode and anodeless
- 3.Technology trends and strategies of major players related to Li metal anodes
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
- 1.1. Required Characteristics of Li-Ion Secondary Batteries
- 1.2. Development Trends of Li-Ion Secondary Batteries
2. Anode Material Technology and Development Status
- 2.1. Overview of Li-Ion Secondary Battery Anode Materials
- 2.2. Development Trends in Li-Ion Secondary Battery Anode Materials
- 2.2.1. Future Developments in Anode Materials (Li-metal anode)
- 2.2.2. Future Developments in Anode Materials (Anodeless)
3. Li Metal Manufacturing Technology and Supply Status
- 3.1. Lithium Production and Supply Status
- 3.1.1. Global Li reserves
- 3.1.2. Global Li production
- 3.1.3. Li resources: Mineral
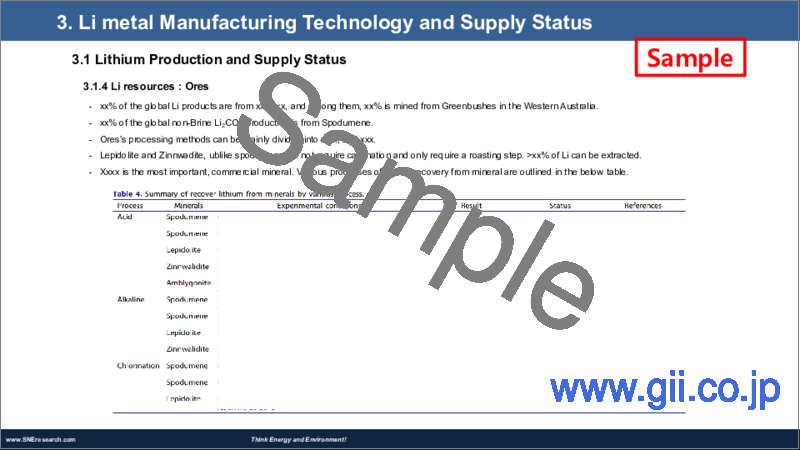
- 3.1.5. Li resources: Ores
- 3.1.6. Li resources: Brines
- 3.1.7. Lithium Material Supply Structure
- 3.1.8. Li Demand Outlook
- 3.2. Li Metal Manufacturing Technology
- 3.2.1. Li Material Technology
- 3.2.2. Li Thin-Film Technology
- 3.3. Li Thin-Film Technology
- 3.3.1. Li Thinning Process Limitations
- 3.3.2. High-Cost Structure
4. Li Metal Anode R&D Trend and Main Issue
- 4.1. Li Metal Anode Development History
- 4.1.1. Development History Overview
- 4.1.2. Li metal battery(LMB) History
- 4.1.3. Initial Development of the Li Metal Battery (LMB)
- 4.1.4. Li Ion Battery Development and Market Dominance
- 4.1.5. Growing Need for Lithium Metal Batteries (LMBs)
- 4.2. Li Metal Anode Main Issue
- 4.2.1. Li Dendritic Growth
- 4.2.2. SEI Layer issue
- 4.3. Li Metal Anode R&D Trends
- 4.3.1. Artificial SEI
- 4.3.2. New structure design
- 4.3.3. Electrolyte modification
- 4.3.4. Anodeless design
5. Development Status of Li Metal Anode by Company
- 5.1. Overview
- 5.2. Asian Companies
- 5.2.1. Samsung SDI
- 5.2.2. LGES
- 5.2.3. SK on
- 5.2.4. CATL
- 5.2.5. EVE
- 5.2.6. Prologium
- 5.2.7. Qingtao Energy
- 5.2.8. Welion
- 5.2.9. Hyundai Motors
- 5.2.10. POSCO
- 5.2.11. Neba Corporation
- 5.2.12. Ulvac Inc
- 5.2.13. Santoku
- 5.2.14. Honjo metal
- 5.2.15. Wuxi Sunenergy Lithium Industrial
- 5.2.16. China Energy Lithium
- 5.2.17. Ganfeng Lithium
- 5.2.18. Tianqi Lithium
- 5.2.19. Montavista
- 5.2.20. Shenzen Inx Technology
- 5.2.21. BTR
- 5.2.22. SoftBank Next-Generation Battery Lab
- 5.2.23. National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
- 5.2.24. National Institute for Materials Science-ALCA SPRING
- 5.3. European Companies
- 5.3.1. Blue Solutions
- 5.3.2. Volkswagen
- 5.3.3. Mercedes-Benz
- 5.3.4. SIDRABE
- 5.3.5. IMEC
- 5.4. North American Companies
- 5.4.1. SES
- 5.4.2. QuantumScape
- 5.4.3. Solid Power
- 5.4.4. Factorial Energy
- 5.4.5. Soelect
- 5.4.6. TeraWatt
- 5.4.7. Hydro Quebec
- 5.4.8. Brightvolt
- 5.4.9. Sion Power
- 5.4.10. SEEO
- 5.4.11. Cuberg
- 5.4.12. Enpower Greentech
- 5.4.13. PolyPlus
- 5.4.14. Sepion Technologies Inc
- 5.4.15. Ion Storage Systems
- 5.4.16. Sakuu
- 5.4.17. GM
- 5.4.18. Ford
- 5.4.19. Li Metal Corp
- 5.4.20. Ionic Materials
- 5.4.21. Albemarle
- 5.4.22. SQM
- 5.4.23. Livent Corp
- 5.4.24. Pure Lithium Corp
- 5.5. Summary of Key Companies
6. Li Metal Anode Market Outlook
- 6.1. Overview of Li Metal Anode Market Outlook
- 6.1.1. Li Metal Anode Battery Types and Cost Structure
- 6.1.2. Li Metal Anode Adoption Roadmap
- 6.1.3. Commercialization Scenarios of Li Metal Anode Battery
- 6.2. Li Metal Anode Market Outlook
- 6.2.1. Li Metal Anode Demand Outlook
- 6.2.2. Li Metal Anode Price Outlook
- 6.2.3. Li Metal Anode Price Forecast Rationale
- 6.2.4. Li Metal Battery (SLMB) Market Size Forecast
- 6.2.5. Forecast of Li Metal Battery (SLMB) Adoption
- 6.2.6. Outlook by Li Metal Battery (SLMB) Application