|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1797891
繊維廃棄物管理の2032年までの市場予測: 廃棄物タイプ別、素材タイプ別、サービス別、エンドユーザー別、地域別の世界分析Textile Waste Management Market Forecasts to 2032 - Global Analysis By Waste Type, Material Type, Service, End User and By Geography |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
|
|||||||
| 繊維廃棄物管理の2032年までの市場予測: 廃棄物タイプ別、素材タイプ別、サービス別、エンドユーザー別、地域別の世界分析 |
|
出版日: 2025年08月07日
発行: Stratistics Market Research Consulting
ページ情報: 英文 200+ Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
Stratistics MRCによると、世界の繊維廃棄物管理市場は2025年に115億8,000万米ドルを占め、予測期間中のCAGRは10.3%で成長し、2032年には230億米ドルに達する見込みです。
家庭やファッション・繊維産業から排出される繊維廃棄物を最小限に抑え、リサイクルし、適切に処分するために用いられる手法や技術を総称して繊維廃棄物管理と呼びます。ファストファッションによって繊維廃棄物は大きな環境問題となり、埋立地は溢れ、汚染は増加しています。衣類の再利用、繊維のリサイクル、古い布地の新製品へのアップサイクル、持続可能な生産方法の奨励などは、すべて効果的な繊維廃棄物管理技術の例です。さらに、繊維廃棄物を減らし、環境への悪影響を減らすには、消費者の意識と倫理的な買い方を促進することに大きく依存します。
米国環境保護庁(EPA)によると、2018年、米国では1,700万トンの繊維製品固形廃棄物が発生しました。そのうち1,130万トン(約66%)が埋め立てられ、320万トン(約19%)が焼却され、リサイクルされたのは250万トン(約14.7%)に過ぎませんでした。
ファッション業界の取り組みと循環型経済
繊維業界では、廃棄物への対応、資源の節約、環境への影響の軽減を目指し、循環型経済モデルが採用されています。製品のライフサイクルを長くするため、ファッションブランドは、衣類のレンタル、再販プラットフォーム、修理サービス、引き取りプログラムなどの循環型慣行を徐々に導入しています。Patagonia、Levi's、H&Mなど多くの企業が、衣料品の返却ポリシーを導入し、コレクションに含まれるリサイクル素材の量を増やすことを表明しています。さらに、こうした取り組みは、埋め立て地への依存を減らすだけでなく、リサイクルと再利用に焦点を当てた新たなバリューチェーンを確立することで、繊維廃棄物処理セクターの長期的成長の可能性を高めています。
高額な高度リサイクル技術
高度なリサイクル技術の初期コストが高いことは、繊維廃棄物管理の最大の障壁の一つです。解重合などのケミカルリサイクル手順は、高度なインフラ、特殊な酵素や溶剤、大量のエネルギーを必要とするため、従来の廃棄技術よりもコストがかかります。さらに、AIベースのシステムや近赤外分光法のような自動選別技術は、大規模に導入され、熟練した作業員によって維持管理される必要があります。中小企業(SME)や中低所得国では、こうした高コストが導入の制約となっています。
環境意識の高い消費者とサーキュラーファッションの成長
繊維廃棄物管理における最大の機会のひとつは、サーキュラーファッションへの動きです。消費者、特に若い世代における環境意識の高まりは、企業の持続可能な製品や倫理的なビジネス慣行への需要につながっています。その結果、アップサイクルブランドやレンタルサービス、再販プラットフォームの人気が高まっています。修理サービスや衣料品の返品プログラムは、付加価値の高いサービスと見なされるようになってきています。さらに、消費者の意識が高まるにつれ、企業はクローズドループのサプライチェーンを構築し、リサイクル可能な素材でイノベーションを起こし、回収インフラを構築する貴重な機会を手にしています。循環型社会への嗜好の高まりは、ブランドロイヤルティを支え、環境への影響を軽減する新たな収益源を生み出します。
再生繊維の需要変動
再生繊維の需要とコストは、特に不況時や原油安時には、安価なバージン代替繊維との競合が困難になることが多く、繊維廃棄物管理市場に大きな影響を与えます。例えば、原油価格が下落するとバージンポリエステルはより魅力的になり、再生ポリエステル(rPET)の市場は縮小します。さらに、一部の地域では入手可能な繊維が限られ、再生繊維の性能にばらつきがあるため、メーカーは品質に懸念を抱いています。ブランドは、リサイクル原料の信頼できる高品質のサプライチェーンに頼ることができなければ、従来の素材に切り替える可能性があります。繊維リサイクルのインフラと技術革新への収益性と長期投資は、こうした市場の変動によって深刻な脅威にさらされます。
COVID-19の影響
繊維廃棄物処理市場は、COVID-19の大流行によってさまざまな影響を受けましたが、そのほとんどはマイナスの影響でした。世界のサプライチェーンは操業停止中に混乱し、工場の閉鎖、消費者需要の減少、店舗の閉鎖によって繊維製品の生産は激減しました。そのため、生産くずなどの消費前繊維廃棄物の生産量は一時的に減少しました。しかし、オンラインショッピングの増加、ファストファッションのクリアランス、マスクのような使い捨ての個人用保護具(PPE)の増加の結果、使用済み繊維廃棄物(その大部分はリサイクル不可能なもの)は増加しました。労働力の制限と安全への懸念も、廃棄物収集とリサイクル活動の停滞を招きました。
予測期間中、使用済み廃棄物セグメントが最大になる見込み
予測期間中、使用済み廃棄物セグメントが最大の市場シェアを占めると予想されます。顧客が使用後に捨てる布地ベースの製品(家庭用繊維製品、古着、その他)がこのカテゴリーに含まれます。Ellen MacArthur Foundationによると、ファストファッションの台頭、製品ライフサイクルの短さ、消費者意識の高まりにより、毎年9,000万トン以上の繊維廃棄物が排出され、世界的に大規模な繊維廃棄物問題が発生しています。リサイクルプログラム、中古市場、引き取りプログラムにより、政府や業界の利害関係者はこの市場に関心を寄せています。さらに、汚染や素材の複雑さといった障害にもかかわらず、その量、環境への影響、繊維製品の循環経済ループを完成させる重要な役割から、使用済み繊維廃棄物は最大かつ最も重要なセグメントであり続けています。
予測期間中、小売業者セグメントがCAGRが最も高くなる見込み
予測期間中、小売業者セグメントが最も高い成長率を示すと予測されます。小売業者セグメント(百貨店、ショップ、オンラインマーケットプレース、ファッションブランドを含む)は、最も速い速度で拡大すると予測されます。衣料品返却プログラムの利用拡大、循環型ビジネスモデル(レンタルや再販など)、企業の持続可能性への取り組みが、この拡大の主な推進力となっています。小売業者は世界の拡大生産者責任(EPR)法により、消費者使用後の繊維製品を回収してリサイクルすることを余儀なくされており、消費者の循環型社会への欲求の高まりは、強力な再利用プログラムを持つ企業に報いるものとなっています。さらに、回収プログラムの迅速な拡大は、小売業者の強力な物流ネットワーク、マーケティングチャネル、消費者への直接的なリーチによって可能となっています。
最大のシェアを占める地域
予測期間中、持続可能な慣行の広範な採用、高度なリサイクルインフラ、厳格な環境規制によって、欧州地域が最大の市場シェアを占めると予想されます。持続可能で循環可能な繊維製品のためのEU戦略や、繊維製品の回収とリサイクルを義務付ける拡大生産者責任(EPR)法のような強力な政策の助けを借りて、この地域は循環経済の取り組みを先導しています。さらに、ドイツ、フランス、オランダのような国々が繊維製品の選別とリサイクル技術の開発で最先端を走っているため、市場規模やシステム効率という点では欧州が最も発展しており、支配的な地域となっています。
CAGRが最も高い地域
予測期間中、アジア太平洋地域が最も高いCAGRを示すと予想されますが、これは環境意識の高まり、繊維生産の増加、急速な都市化が背景にあります。バングラデシュ、ベトナム、中国、インドといった国々は、重要な繊維生産国であるだけでなく、繊維廃棄物も大量に生産しています。この地域で増大する廃棄物問題に対処するため、各国政府はより強力な環境法を制定し、リサイクル支出を増やし、循環経済の原則を提唱しています。さらに、アジア太平洋地域は、中流階級の人口増加、ファストファッション消費の増加、国内外のブランドが持続可能性の枠組みを導入するなどの要因により、組織化された繊維廃棄物管理ソリューションの成長率が最も高い地域です。
無料カスタマイズサービス
本レポートをご購読の顧客には、以下の無料カスタマイズオプションのいずれかをご利用いただけます。
- 企業プロファイル
- 追加市場プレイヤーの包括的プロファイリング(3社まで)
- 主要企業のSWOT分析(3社まで)
- 地域セグメンテーション
- 顧客の関心に応じた主要国の市場推計・予測・CAGR(注:フィージビリティチェックによる)
- 競合ベンチマーキング
- 製品ポートフォリオ、地理的プレゼンス、戦略的提携に基づく主要企業のベンチマーキング
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第2章 序文
- 概要
- ステークホルダー
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
- データマイニング
- データ分析
- データ検証
- 調査アプローチ
- 調査資料
- 一次調査資料
- 二次調査情報源
- 前提条件
第3章 市場動向分析
- 促進要因
- 抑制要因
- 機会
- 脅威
- エンドユーザー分析
- 新興市場
- COVID-19の影響
第4章 ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 買い手の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係
第5章 世界の繊維廃棄物管理市場:廃棄物タイプ別
- 使用済み廃棄物
- 産業後廃棄物
- 消費前廃棄物
- 売れ残り商品
- 非有害性技術繊維製品
第6章 世界の繊維廃棄物管理市場:素材タイプ別
- 天然繊維
- コットン
- ウール
- シルク
- ジュート
- 動物繊維
- 合成繊維
- ポリエステル
- ナイロン
- アクリル
- 混紡生地
- セルロースおよび再生繊維
- ビスコース
- リヨセル
- モーダル
第7章 世界の繊維廃棄物管理市場:サービス別
- 収集・物流
- 選別・等級分け
- 堆肥作り
- リサイクル
- 機械的リサイクル
- 化学/酵素リサイクル
- 再利用/再生
第8章 世界の繊維廃棄物管理市場:エンドユーザー別
- 住宅/家庭
- 商業・公共施設
- 工業製造業
- 繊維メーカー
- 小売業者
- リサイクル業者
- その他
第9章 世界の繊維廃棄物管理市場:地域別
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- メキシコ
- 欧州
- ドイツ
- 英国
- イタリア
- フランス
- スペイン
- その他欧州
- アジア太平洋
- 日本
- 中国
- インド
- オーストラリア
- ニュージーランド
- 韓国
- その他アジア太平洋地域
- 南米
- アルゼンチン
- ブラジル
- チリ
- その他南米
- 中東・アフリカ
- サウジアラビア
- アラブ首長国連邦
- カタール
- 南アフリカ
- その他中東・アフリカ
第10章 主な発展
- 契約、パートナーシップ、コラボレーション、ジョイントベンチャー
- 買収と合併
- 新製品発売
- 事業拡大
- その他の主要戦略
第11章 企業プロファイリング
- Infinited Fiber Company
- Aquafil S.p.A.
- Patagonia Inc.
- Suez SA
- TOMRA Sorting Solutions
- Lenzing AG
- Fabscrap Inc.
- Hyosung TNC Corporation
- Indorama Ventures PLC
- Renewcell AB
- Boer Group
- RETEXTIL Deutschland GmbH
- Textile Recycling International
- Veolia Environnement S.A.
- Le Relais Group
- SOEX Group
- Worn Again Technologies
List of Tables
- Table 1 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Region (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 2 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Waste Type (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 3 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Post-Consumer Waste (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 4 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Post-Industrial Waste (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 5 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Pre-Consumer Waste (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 6 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Unsold Goods (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 7 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Non-Hazardous Technical Textiles (2024-2032) ($MN)
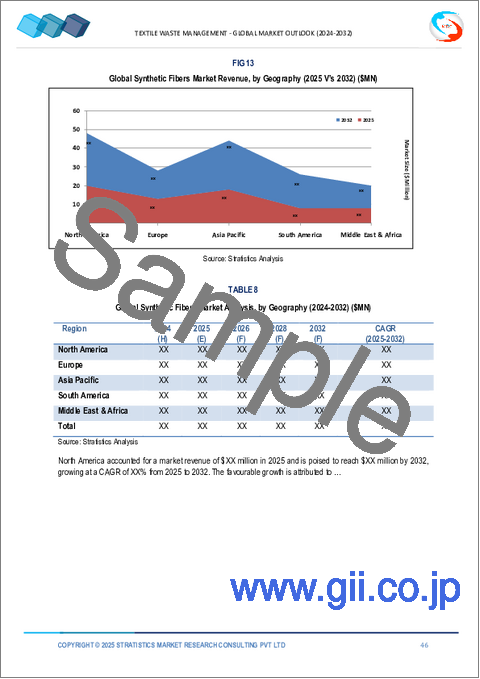
- Table 8 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Material Type (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 9 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Natural Fibers (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 10 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Cotton (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 11 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Wool (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 12 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Silk (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 13 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Jute (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 14 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Animal Fibre (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 15 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Synthetic Fibers (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 16 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Polyester (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 17 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Nylon (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 18 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Acrylic (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 19 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Blended Fabrics (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 20 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Cellulosic & Regenerated Fibers (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 21 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Viscose (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 22 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Lyocell (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 23 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Modal (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 24 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Service (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 25 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Collection & Logistics (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 26 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Sorting & Grading (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 27 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Composting (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 28 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Recycling (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 29 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Mechanical Recycling (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 30 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Chemical/Enzymatic Recycling (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 31 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Reuse/Refurbishment (2024-2032) ($MN)
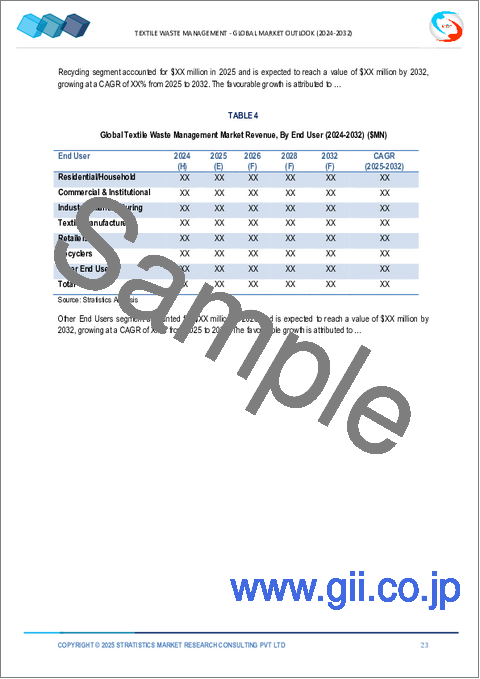
- Table 32 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By End User (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 33 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Residential/Household (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 34 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Commercial & Institutional (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 35 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Industrial Manufacturing (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 36 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Textile manufacturers (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 37 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Retailers (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 38 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Recyclers (2024-2032) ($MN)
- Table 39 Global Textile Waste Management Market Outlook, By Other End Users (2024-2032) ($MN)
Note: Tables for North America, Europe, APAC, South America, and Middle East & Africa Regions are also represented in the same manner as above.
According to Stratistics MRC, the Global Textile Waste Management Market is accounted for $11.58 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach $23.00 billion by 2032 growing at a CAGR of 10.3% during the forecast period. The methods and techniques used to minimize, recycle, and appropriately dispose of textile waste produced by homes and the fashion and textile industries are collectively referred to as textile waste management. Fast fashion has made textile waste a major environmental issue, causing landfills to overflow and pollution to rise. Reusing clothing, recycling fibers, upcycling old fabrics into new products, and encouraging sustainable production methods are all examples of effective textile waste management techniques. Additionally, reducing textile waste and its negative effects on the environment depends heavily on promoting consumer awareness and ethical buying practices.
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), in 2018 the United States generated 17 million tons of textile municipal solid waste. Of that, 11.3 million tons (≈ 66%) were landfilled, 3.2 million tons were incinerated (≈ 19%), and only 2.5 million tons (≈ 14.7%) were recycled.
Market Dynamics:
Driver:
Fashion industry initiatives and circular economy
A circular economy model is being adopted by the textile industry in an effort to address waste, conserve resources, and lessen its impact on the environment. In order to prolong product life cycles, fashion brands are progressively implementing circular practices such as clothing rental, resale platforms, repair services, and take-back programs. A number of businesses, such as Patagonia, Levi's, and H&M, have pledged to introduce clothing return policies and increase the amount of recycled materials in their collections. Moreover, these initiatives are increasing the textile waste management sector's potential for long-term growth by not only decreasing reliance on landfills but also establishing new value chains focused on recycling and reuse.
Restraint:
Expensive advanced recycling technologies
The high initial cost of sophisticated recycling technologies is one of the largest barriers to textile waste management. Chemical recycling procedures, such as depolymerization, are more costly than conventional disposal techniques because they require sophisticated infrastructure, specialized enzymes or solvents, and a large amount of energy. Furthermore, automated sorting technologies like AI-based systems and near-infrared spectroscopy need to be deployed on a large scale and maintained by skilled workers. Adoption is constrained by these high costs in small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) and low- and middle-income nations.
Opportunity:
Growth of eco-conscious consumers and circular fashion
One of the biggest opportunities in textile waste management is the move toward circular fashion. Growing environmental consciousness among consumers, particularly among younger generations, has led to a demand for sustainable products and ethical business practices from companies. As a result, upcycling brands, rental services, and resale platforms have grown in popularity. Repair services and clothing return programs are becoming more and more seen as value-added services. Moreover, businesses have a rare opportunity to build closed-loop supply chains, innovate with recyclable materials, and build collection infrastructure as consumer awareness rises. This growing preference for circularity creates new revenue streams that support brand loyalty and lessen the impact on the environment.
Threat:
Demand variability for recycled fibers
The demand and cost of recycled fibers, which frequently find it difficult to compete with less expensive virgin alternatives, particularly during recessions or times of low oil prices, have a significant impact on the textile waste management market. For instance, virgin polyester becomes more attractive, and the market for recycled polyester (rPET) contracts when oil prices fall. Additionally, manufacturers are concerned about quality due to limited availability in some areas and inconsistent performance in recycled fibers. Brands may switch back to traditional materials if they are unable to rely on reliable, high-quality supply chains for recycled inputs. The profitability and long-term investment in textile recycling infrastructure and innovation are seriously threatened by these market swings.
Covid-19 Impact:
The market for textile waste management was affected by the COVID-19 pandemic in a variety of ways, but mostly negatively. Global supply chains were upset during lockdowns, and factory closures, decreased consumer demand, and store closures caused a dramatic drop in textile production. This led to a brief decrease in the production of pre-consumer textile waste, such as production scraps. However, post-consumer textile waste-a large portion of which was non-recyclable-rose as a result of the rise in online shopping, fast fashion clearances, and disposable personal protective equipment (PPE) like masks. Workforce limitations and safety concerns also caused waste collection and recycling activities to slow down.
The post-consumer waste segment is expected to be the largest during the forecast period
The post-consumer waste segment is expected to account for the largest market share during the forecast period. Home textiles, used clothing, and other fabric-based products that customers throw away after using them are included in this category. According to the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, the rise in fast fashion, short product lifecycles, and increased consumerism has led to a massive global textile waste problem, with over 90 million tonnes produced each year. With recycling programs, secondhand markets, and take-back programs, governments and industry stakeholders are paying more attention to this market. Moreover, post-consumer waste continues to be the largest and most important segment due to its volume, environmental impact, and crucial role in completing the textile circular economy loop, despite obstacles like contamination and material complexity.
The retailers segment is expected to have the highest CAGR during the forecast period
Over the forecast period, the retailers segment is predicted to witness the highest growth rate. The Retailers segment-which includes department stores, shops, online marketplaces, and fashion brands-is anticipated to expand at the fastest rate. The growing use of clothing return programs, circular business models (such as renting and reselling), and corporate sustainability initiatives are the main drivers of this expansion. Retailers are being forced by global Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) laws to gather and recycle post-consumer textiles, and consumers' increasing desire for circularity is rewarding companies with strong reuse programs. Additionally, fast collection program scaling is made possible by retailers' strong logistics networks, marketing channels, and direct consumer reach.
Region with largest share:
During the forecast period, the Europe region is expected to hold the largest market share, driven by its extensive adoption of sustainable practices, sophisticated recycling infrastructure, and strict environmental regulations. With the help of robust policies like the EU Strategy for Sustainable and Circular Textiles and Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) laws that require textile collection and recycling, the region is leading the way in circular economy initiatives. Furthermore, Europe is the most developed and dominant region in terms of market size and system efficiency because nations like Germany, France, and the Netherlands are at the forefront of developing textile sorting and recycling technologies.
Region with highest CAGR:
Over the forecast period, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to exhibit the highest CAGR, driven by rising environmental consciousness, growing textile production, and fast urbanization. In addition to being significant textile producers, nations like Bangladesh, Vietnam, China, and India also produce a lot of textile waste. To combat the region's growing waste problems, governments are enacting stronger environmental laws, boosting recycling expenditures, and advocating for circular economy principles. Moreover, Asia-Pacific is the region with the fastest rate of growth for organized textile waste management solutions due to factors like growing middle-class populations, rising fast fashion consumption, and local and international brands implementing sustainability frameworks.
Key players in the market
Some of the key players in Textile Waste Management Market include Infinited Fiber Company, Aquafil S.p.A., Patagonia Inc., Suez SA, TOMRA Sorting Solutions, Lenzing AG, Fabscrap Inc., Hyosung TNC Corporation, Indorama Ventures PLC, Renewcell AB, Boer Group, RETEXTIL Deutschland GmbH, Textile Recycling International, Veolia Environnement S.A., Le Relais Group, SOEX Group and Worn Again Technologies.
Key Developments:
In December 2024, Hyosung TNC Corp said it will acquire the specialty gas division of Hyosung Chemical Corp. for 920 billion won ($642 million). The textile subsidiary of Hyosung Group approved the plan at its board meeting earlier in the day. Hyosung TNC, the world's largest spandex manufacturer, received a letter of intent for the acquisition from Hyosung Chemical and has reviewed the takeover.
In November 2024, Tomra Recycling and Redwave have announced an agreement that will see the two firms offer each other's complementary metal sorting technologies directly to their respective customers. The alliance focuses specifically on the X-ray fluorescence (XRF) sorting devices made by Redwave and X-ray transmission (XRT) technology in which Tomra specializes.
In October 2024, Aquafil and Asahi Kasei collaborate on cellulose nanofiber and regenerated ECONYL(R) Polymer for 3D printing applications. The two companies agreed to develop a novel material for 3D printing (3DP) applications utilizing Aquafil's ECONYL(R) Polymer chemically recycled PA6 and Asahi Kasei's cellulose nanofiber (CNF), with the support of ITOCHU Corporation, which has made a capital investment in Aquafil.
Waste Types Covered:
- Post-Consumer Waste
- Post-Industrial Waste
- Pre-Consumer Waste
- Unsold Goods
- Non-Hazardous Technical Textiles
Material Types Covered:
- Natural Fibers
- Synthetic Fibers
- Blended Fabrics
- Cellulosic & Regenerated Fibers
Services Covered:
- Collection & Logistics
- Sorting & Grading
- Composting
- Recycling
End Users Covered:
- Residential/Household
- Commercial & Institutional
- Industrial Manufacturing
- Textile manufacturers
- Retailers
- Recyclers
- Other End Users
Regions Covered:
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- UK
- Italy
- France
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- India
- Australia
- New Zealand
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Chile
- Rest of South America
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Qatar
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
What our report offers:
- Market share assessments for the regional and country-level segments
- Strategic recommendations for the new entrants
- Covers Market data for the years 2024, 2025, 2026, 2028, and 2032
- Market Trends (Drivers, Constraints, Opportunities, Threats, Challenges, Investment Opportunities, and recommendations)
- Strategic recommendations in key business segments based on the market estimations
- Competitive landscaping mapping the key common trends
- Company profiling with detailed strategies, financials, and recent developments
- Supply chain trends mapping the latest technological advancements
Free Customization Offerings:
All the customers of this report will be entitled to receive one of the following free customization options:
- Company Profiling
- Comprehensive profiling of additional market players (up to 3)
- SWOT Analysis of key players (up to 3)
- Regional Segmentation
- Market estimations, Forecasts and CAGR of any prominent country as per the client's interest (Note: Depends on feasibility check)
- Competitive Benchmarking
- Benchmarking of key players based on product portfolio, geographical presence, and strategic alliances
Table of Contents
1 Executive Summary
2 Preface
- 2.1 Abstract
- 2.2 Stake Holders
- 2.3 Research Scope
- 2.4 Research Methodology
- 2.4.1 Data Mining
- 2.4.2 Data Analysis
- 2.4.3 Data Validation
- 2.4.4 Research Approach
- 2.5 Research Sources
- 2.5.1 Primary Research Sources
- 2.5.2 Secondary Research Sources
- 2.5.3 Assumptions
3 Market Trend Analysis
- 3.1 Introduction
- 3.2 Drivers
- 3.3 Restraints
- 3.4 Opportunities
- 3.5 Threats
- 3.6 End User Analysis
- 3.7 Emerging Markets
- 3.8 Impact of Covid-19
4 Porters Five Force Analysis
- 4.1 Bargaining power of suppliers
- 4.2 Bargaining power of buyers
- 4.3 Threat of substitutes
- 4.4 Threat of new entrants
- 4.5 Competitive rivalry
5 Global Textile Waste Management Market, By Waste Type
- 5.1 Introduction
- 5.2 Post-Consumer Waste
- 5.3 Post-Industrial Waste
- 5.4 Pre-Consumer Waste
- 5.5 Unsold Goods
- 5.6 Non-Hazardous Technical Textiles
6 Global Textile Waste Management Market, By Material Type
- 6.1 Introduction
- 6.2 Natural Fibers
- 6.2.1 Cotton
- 6.2.2 Wool
- 6.2.3 Silk
- 6.2.4 Jute
- 6.2.5 Animal Fibre
- 6.3 Synthetic Fibers
- 6.3.1 Polyester
- 6.3.2 Nylon
- 6.3.3 Acrylic
- 6.4 Blended Fabrics
- 6.5 Cellulosic & Regenerated Fibers
- 6.5.1 Viscose
- 6.5.2 Lyocell
- 6.5.3 Modal
7 Global Textile Waste Management Market, By Service
- 7.1 Introduction
- 7.2 Collection & Logistics
- 7.3 Sorting & Grading
- 7.4 Composting
- 7.5 Recycling
- 7.5.1 Mechanical Recycling
- 7.5.2 Chemical/Enzymatic Recycling
- 7.5.3 Reuse/Refurbishment
8 Global Textile Waste Management Market, By End User
- 8.1 Introduction
- 8.2 Residential/Household
- 8.3 Commercial & Institutional
- 8.4 Industrial Manufacturing
- 8.5 Textile manufacturers
- 8.6 Retailers
- 8.7 Recyclers
- 8.8 Other End Users
9 Global Textile Waste Management Market, By Geography
- 9.1 Introduction
- 9.2 North America
- 9.2.1 US
- 9.2.2 Canada
- 9.2.3 Mexico
- 9.3 Europe
- 9.3.1 Germany
- 9.3.2 UK
- 9.3.3 Italy
- 9.3.4 France
- 9.3.5 Spain
- 9.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 9.4 Asia Pacific
- 9.4.1 Japan
- 9.4.2 China
- 9.4.3 India
- 9.4.4 Australia
- 9.4.5 New Zealand
- 9.4.6 South Korea
- 9.4.7 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 9.5 South America
- 9.5.1 Argentina
- 9.5.2 Brazil
- 9.5.3 Chile
- 9.5.4 Rest of South America
- 9.6 Middle East & Africa
- 9.6.1 Saudi Arabia
- 9.6.2 UAE
- 9.6.3 Qatar
- 9.6.4 South Africa
- 9.6.5 Rest of Middle East & Africa
10 Key Developments
- 10.1 Agreements, Partnerships, Collaborations and Joint Ventures
- 10.2 Acquisitions & Mergers
- 10.3 New Product Launch
- 10.4 Expansions
- 10.5 Other Key Strategies
11 Company Profiling
- 11.1 Infinited Fiber Company
- 11.2 Aquafil S.p.A.
- 11.3 Patagonia Inc.
- 11.4 Suez SA
- 11.5 TOMRA Sorting Solutions
- 11.6 Lenzing AG
- 11.7 Fabscrap Inc.
- 11.8 Hyosung TNC Corporation
- 11.9 Indorama Ventures PLC
- 11.10 Renewcell AB
- 11.11 Boer Group
- 11.12 RETEXTIL Deutschland GmbH
- 11.13 Textile Recycling International
- 11.14 Veolia Environnement S.A.
- 11.15 Le Relais Group
- 11.16 SOEX Group
- 11.17 Worn Again Technologies