|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1744405
自動運転用地図(HD/LD/SDマップ、オンライン再構築、リアルタイム生成地図)産業(2025年)Autonomous Driving Map (HD/LD/SD MAP, Online Reconstruction, Real-time Generative Map) Industry Report 2025 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| 自動運転用地図(HD/LD/SDマップ、オンライン再構築、リアルタイム生成地図)産業(2025年) |
|
出版日: 2025年06月02日
発行: ResearchInChina
ページ情報: 英文 320 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
自動運転システムの主流となりつつある「マップレスNOA」。このソリューションは、開発が課題となっていたオフラインHDマップへの依存を軽減します。いわゆる「マップレス」は、ADASアルゴリズムが「ルールドリブン」ではなく「データドリブン」になる傾向がある一方で、本質的に「地図先行」から「リアルタイム地図構築」、そしてさらに「ワールドモデル」への発展へのシフトを意味します。
マップレスソリューションは、初期のSLAM技術と非常によく似ており、実際にオンラインでベクトルマップを構築し、それをオフラインLDマップと照合することで、測位とナビゲーションの情報を同時に取得します。初期のSLAM技術はLiDARに大きく依存していました。BEVの登場に伴い、SLAM技術は徐々に淘汰されましたが、地下駐車場などのシナリオではまだ使用されています。
自動運転用地図の進化
2022年以前:産業チェーンは幾何学的精度を重視するHDマップに注力し、従来のADASアルゴリズムは環境認識を処理するプリセットルールに依存していました。
2023年~2024年:マップレスNOAの開発に伴い、トポロジー、セマンティクス、鮮度を備えた軽量マップ(LDマップ)が推進され、利用されました。
2025年以降:3DガウススパッタリングやNeRF(Neural Radiance Fields)などの新技術の搭載により、自動運転用地図は「過去の記録」だけでなく「未来のプレビュー」が可能になります。「ワールドモデル」は、自己教師あり学習によって膨大な走行データから時空間パターンを抽出し、マルチモーダルなセンサーデータ(カメラ、LiDARなど)とリアルタイムのクラウドソースデータを統合し、動的に更新される環境知識ベースを構築し、道路トポロジー、意味情報、交通ルールのオンライン推論を達成します。
「ワールドモデル」は、過去のシナリオ情報とプリセット条件を活用し、将来のインテリジェントドライビングシナリオの変化と自車両の反応を予測します。
自動運転用地図の開発動向:低コスト自動地図、MapTRやVectorMapNetなどのベクトル化HDマップ構築技術の応用
Baidu MapAuto 6.5は、中国初の3D車線レベル地図と全シナリオの人間と機械の共同運転地図であり、包括的なデータサービスを提供します。Baidu MapAuto 6.5は、Baiduの統合データ収集車、マルチソースデータ入力、数十億のパラメーターを持つ地図生成基盤モデルに基づいており、地図作成の効率を飛躍的に向上させ、Baiduマップデータの迅速な更新を効果的にサポートし、強力で包括的なデータサービスを提供しています。
Baidu MapAuto 6.5は3種類のデータを提供できます。SD(ナビゲーションマップ)、LD(軽量自動運転用地図)、HD(HDマップ)です。2025年3月、LeapmotorはBaidu MapsのLDデータを搭載した技術アーキテクチャであるLEAP 3.5をリリースしました。
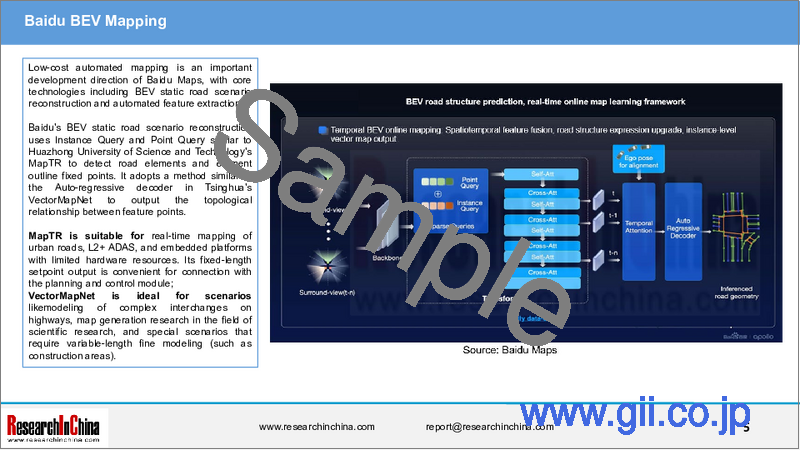
低コスト自動マッピングはBaidu Mapsの重要な開発方向であり、BEV静的道路シナリオ再構築と自動特徴抽出を含むコア技術です。
BaiduのBEV静的道路シナリオ再構築は、華中科技大学のMapTRと同様のInstance QueryとPoint Queryを使用し、道路要素と要素輪郭定点を検出します。また、清華大学のVectorMapNetのAuto-regressive decoderと同様の手法を採用し、特徴点間のトポロジー関係を出力します。
MapTRは、都市道路のリアルタイムマッピング、L2+ADAS、ハードウェアリソースが限られた組み込みプラットフォームに適しています。固定長セットポイント出力は、計画・制御モジュールとの接続に便利です。
VectorMapNetは、高速道路の複雑なインターチェンジのモデリング、科学研究分野の地図生成研究、可変長の微細なモデリングを必要とする特殊なシナリオ(工事現場など)に最適です。
当レポートでは、中国の自動運転用地図産業について調査分析し、市場規模、競合情勢、動向、新技術の応用などの情報を提供しています。
目次
第1章 自動運転用地図の定義と分類
- 自動運転用地図の定義と分類
- 自動運転用地図の分類(1):ナビゲーションマップ(SDマップ)
- 自動運転用地図の分類(2):軽量マップ(LDマップ)
- 自動運転用地図の分類(3):HDマップ
- 自動運転用地図の分類(4):NeRFオンライン再構築やリアルタイム生成地図などの新技術
- 自動運転用地図の分類(5):DWMへの進化
- 自動運転用地図の政策と規制
第2章 自動運転用地図市場の現状と競合情勢
- 自動車地図の市場規模
- 自動車地図市場の競合情勢
- 都市NOAの動向の中での自動運転用地図プロバイダーのビジネスモデルの変化
第3章 自動運転用地図産業の動向と新技術の応用
- エンドツーエンドの動向におけるインテリジェントドライビング用地図の進化
- 自動運転用地図の再構築:自動注釈システム、ビデオクリップ
- 自動運転用地図の再構築:NeRF技術の応用
- 自動運転用地図の再構築:ボクセルNeRFによるMVマップの作成
- 自動運転用地図の再構築:4D時空間特徴
- 自動運転用地図の再構築:3Dガウススプラッシュ
第4章 自動運転用地図の応用とOEMの技術レイアウト
- さまざまな自動運転シナリオにおける地図の需要
- OEMによる自動運転用地図の選択
- 自動運転用地図の搭載数:OEM別
- Tesla
- Xiaomi
- Xpeng
- Li Auto
- NIO
- Harmony Intelligent Mobility Alliance (HIMA)
- SAIC IM
- Leapmotor
- Geely & ZEEKR
- Dongfeng Voyah
- Changan Automobile
- Chery
- Great Wall Motor
- GAC Motor
- Volkswagen
- Mercedes-Benz
- BMW
- Toyota
第5章 自動運転用地図プロバイダー
- Baidu Maps
- NavInfo
- AutoNavi (amap.com)
- Tencent
- Lange Technology
- EMG
- MXNAVI
- Leador
- Heading Data Intelligence
- BrightMap
- Huawei
- Roadgrids Technology
- Mapbox
- Kuandeng Technology
Research on Autonomous Driving Maps: Evolve from Recording the Past to Previewing the Future with "Real-time Generative Maps"
"Mapless NOA" has become the mainstream solution for autonomous driving systems. This solution reduces the reliance on offline HD maps whose development has encountered challenges. The so-called "mapless" essentially means the shift from "map prior" to "real-time map construction" and then further development into "world models", while ADAS algorithms tend to be "data-driven" instead of being "rule-driven".
A mapless solution, very similar to the early SLAM technology, actually builds a vector map online and then matches it with offline LD maps to obtain positioning and navigation information at the same time. The early SLAM technology relied heavily on LiDAR. As BEV emerges, SLAM technology has been gradually eliminated, but it is still used in scenarios such as underground parking lots.
The evolution of autonomous driving maps:
Before 2022: The industry chain focused on HD maps that value geometric accuracy, while traditional ADAS algorithms relied on preset rules to process environmental perception;
2023-2024: With the development of mapless NOA, lightweight maps (LD maps) with topology, semantics and freshness were promoted and applied;
After 2025: With the introduction of new technologies such as 3D Gaussian sputtering and NeRF (Neural Radiance Fields), autonomous driving maps will "preview the future" instead of only "recording the past". "World models" extract spatiotemporal patterns from massive driving data through self-supervised learning, integrate multimodal sensor data (cameras, LiDAR, etc.) and real-time crowd-source data, build a dynamically updated environmental knowledge base, and accomplish online reasoning of road topology, semantic information and traffic rules.
"World models" leverage historical scenario information and preset conditions to predict the future changes in intelligent driving scenarios and the response of the ego vehicle.
Development trends of autonomous driving maps: Low-cost automated mapping, application of vectorized HD map construction technologies such as MapTR and VectorMapNet
Baidu MapAuto 6.5 is the first 3D lane-level map and all-scenario human-machine co-driving map in China, providing comprehensive data services. Baidu MapAuto 6.5, based on Baidu's integrated data collection vehicles, multi-source data input (closed loop of automotive and roadside data), and map generation foundation models with billions of parameters, has improved the efficiency of map production exponentially, effectively supported the rapid updates of Baidu map data, and offered powerful and comprehensive data services.
Baidu MapAuto 6.5 can provide three types of data: SD (navigation maps), LD (lightweight autonomous driving maps) and HD (HD maps). In March 2025, Leapmotor released LEAP 3.5, which is a technical architecture equipped with the LD data of Baidu Maps.
Low-cost automated mapping is an important development direction of Baidu Maps, with core technologies including BEV static road scenario reconstruction and automated feature extraction.
Baidu's BEV static road scenario reconstruction uses Instance Query and Point Query similar to Huazhong University of Science and Technology's MapTR to detect road elements and element outline fixed points. It adopts a method similar to the Auto-regressive decoder in Tsinghua's VectorMapNet to output the topological relationship between feature points.
MapTR is suitable for real-time mapping of urban roads, L2+ ADAS, and embedded platforms with limited hardware resources. Its fixed-length setpoint output is convenient for connection with the planning and control module;
VectorMapNet is ideal for scenarios likemodeling of complex interchanges on highways, map generation research in the field of scientific research, and special scenarios that require variable-length fine modeling (such as construction areas).
Development trends of autonomous driving maps: Integration with driving world models (DWMs)
NavInfo has proposed to add the spatiotemporal cognition capability of maps to the intelligent driving technology driven by world models, that is, "let world models inherit the spatiotemporal cognition of maps" - "Maps have evolved from static layers to dynamic data engines that are indispensable in the world-model-driven stage. They are irreplaceable "prior sensors" in application scenarios such as improving the intelligence level of a single vehicle, reducing computing power constraints and responding to emergency warnings."
DWMs are the core components of the next-generation autonomous driving systems. By predicting the spatiotemporal evolution of dynamic driving scenarios, they help vehicles perceive the environment more accurately, understand interaction logic, and optimize decision-making.
DWMs build continuous learning and prediction capabilities for the physical world by integrating HD map data, real-time sensor information (such as cameras, LiDAR), vehicle status data (such as speed, steering), and external environment data (such as traffic flow, weather). The goal is to enable autonomous driving systems to secure the trinity of "understanding, prediction, and planning" through a closed data loop.
Core functions of DWMs:
Environmental understanding: Accurately locate the vehicle position through autonomous driving maps and real-time perception data, and recognize key information such as lane lines, traffic signs, and obstacles.
Dynamic prediction: Predict the behavior trajectory of other traffic participants (vehicles, pedestrians), and predict potential risks (such as cutting in, sudden braking).
Global planning: Generate the optimal driving path and driving strategy based on long-term environment simulation (such as generalization of scenarios under different weather and road conditions).
Technical features of DWMs:
Continuously optimize the models based on data, continuous input of massive high-quality data and AI algorithms (such as deep learning and reinforcement learning).
Achieve closed-loop iteration and self-evolution of the models through a complete closed loop of data collection -> model training -> simulation verification -> deployment optimization.
Integrate reality with virtuality and accelerate model generalization by combining simulation environments (such as digital twins) with real road test data.
Core value of DWMs:
Scenario deduction: Generate the physical rationality and spatiotemporal consistency of future scenarios based on historical observations, and support autonomous driving systems to predict potential risks (such as bizarre accidents (for example, when there is a vehicle or obstacle blocking the view ahead, a non-motorized vehicle or pedestrian suddenly jumps out from the roadside, and the driver fails to avoid it in time, often causing an accident), dynamic changes in construction areas);
Multimodal fusion: Integrate multimodal data such as 2D images, 3D point clouds, and Occupancy grids to improve environmental modeling accuracy (such as 98.7% BEV geometric consistency in nuScenes data set tests);
Decision-making optimization: Achieve human-like driving capabilities through reinforcement learning and prediction, real difference fine-tuning (The measured traffic efficiency on Beijing's Fifth Ring Road increased by 28%).
Development trends of autonomous driving maps: OEMs explore and deploy NeRF technology in autonomous driving map reconstruction
At present, many OEMs have begun to explore or deploy NeRF technology in the field of autonomous driving maps, especially in dynamic scenario reconstruction and HD map generation.
NeRF technology can reconstruct 2D images into 3D scenarios, and then produce HD maps to achieve high-precision vehicle positioning and map matching;
NeRF technology can synthesize complex autonomous driving scenarios, enrich autonomous driving training data, and help autonomous driving systems perform efficient data enhancement;
NeRF technology can simulate harsh scenarios such as extreme weather and serious traffic accidents, and use simulated data to restore real harsh scenarios to improve the safety of autonomous driving
The AD Max 3.0 of Li Auto has built a triple perception architecture consisting of "static BEV + dynamic BEV + NeRF enhanced occupancy". By deeply combining NeRF technology with occupancy networks, it handles insufficient long-distance perception resolution which exists in traditional pure vision solutions:
Static BEV network: Transformer fuses data from multiple cameras to generate a bird's-eye view of the road structure. When some cameras fail, NeRF helps reconstruct the road edges and lane lines in the missing areas.
Dynamic BEV network: Thanks to the spatiotemporal attention mechanism tracking traffic participants and NeRF's spatiotemporal continuity modeling, the speed and acceleration estimation error of moving objects is less than 0.3m/s.
Occupancy network upgrade: The original Occupancy output resolution improves from 0.2m to 0.1m, sub-pixel details are generated through NeRF's radiation field rendering, and 30cm high curbstones and 5cm diameter manhole covers can be recognized
OEMs such as Xpeng, Mercedes-Benz, and Li Auto have taken the lead in mass production and application of NeRF technology, while Tesla, BMW, etc. are exploring deeper application through technical cooperation. In the future, with the improvement of hardware computing power (such as the Blackwell architecture) and open source ecology, NeRF is expected to become the underlying standard technology of autonomous driving maps, promoting the industry to evolve towards "real-time generative maps".
Table of Contents
1 Definition and Classification of Autonomous Driving Maps
- 1.1 Definition and Classification of Autonomous Driving Maps
- Definition of Autonomous Driving Maps
- Autonomous Driving Maps Evolve from Recording the Past to Previewing the Future with "Real-time Generative Maps"
- Evolution of Autonomous Driving Algorithms and Map Construction, 2020-2026E
- 1.2 Classification of Autonomous Driving Maps (1): Navigation Maps (SD Maps)
- Definition of Autonomous Driving Maps: Navigation Maps (SD Maps)
- Installations of Navigation Maps (SD Maps) in Vehicles
- 1.3 Classification of Autonomous Driving Maps (2): Lightweight Maps (LD Maps)
- Definition of Lightweight Maps (LD Maps)
- Lightweight Maps (LD Maps) Are Required to Provide Basic Data for "Mapless" Intelligent Driving Solutions
- Classification of Lightweight Maps (LD Maps)
- Development of Lightweight Maps (LD Maps): Integration of SD Maps and HD/LD Maps
- Lightweight Map (LD Map) Solutions: Map Providers Reduce Costs and Increase Update Frequency
- Lightweight Map (LD Map) Solutions: Some Providers Build Maps Online via Algorithms (1)
- Lightweight Map (LD Map) Solutions: Some Providers Build Maps Online via Algorithms (2)
- Application Cases of Urban NOA Based on Lightweight Maps (LD Maps): QCraft's Urban NOA Adopts NavInfo HD Lite
- Application Cases of Urban NOA Based on Lightweight Maps (LD Maps): MAXIEYE's Automatic Mapping Memory
- Installations of Lightweight Maps (LD Maps) in Vehicles (1)
- Installations of Lightweight Maps (LD Maps) in Vehicles (2)
- 1.4 Classification of Autonomous Driving Maps (3): HD Maps
- Definition of Autonomous Driving Maps: HD Maps
- Complementarity between HD Maps and Perception Can Improve the Safety of Urban NOA
- HD Map Development Path (1)
- HD Map Development Path (2)
- Application of HD Maps in "Light Map" Solutions
- OEMs' Attitude towards HD Maps
- 1.5 Classification of Autonomous Driving Maps (4): New Technologies such as NeRF Online Reconstruction and Real-time Generative Maps
- Application Trends of New Online Mapping Technologies (1)
- Application Trends of New Online Mapping Technologies (2)
- Application Trends of New Online Mapping Technologies (3)
- Application Trends of New Online Mapping Technologies (4)
- 1.6 Classification of Autonomous Driving Maps (5): Evolution to DWMs
- Summary of DWMs Worldwide as of January 2025
- Technical Features of DWMs
- Impact of DWMs on Autonomous Driving Maps (1)
- Impact of DWMs on Autonomous Driving Maps (2)
- 1.7 Autonomous Driving Map Policies and Regulations
- National Regulations (1)
- National Regulations (2)
- National Regulations (3)
- Local Regulations (1)
- Local Regulations (2)
- Local Regulations (3)
2 Status Quo and Competitive Landscape of Autonomous Driving Map Market
- 2.1 Automotive Map Market Size
- Global Automotive Map Market Size
- Global Automotive Map Market for Passenger Cars and Commercial Vehicles
- Global Automotive Map Market Landscape (by Type)
- Global Automotive Map Market Landscape (by Region)
- Map Installations of Chinese Passenger Cars by Autonomous Driving Level (by Price Range), 2023-2024
- Autonomous Driving Level of Chinese Passenger Cars, 2024-2030E
- SD/LD/HD Map Installations of Chinese Passenger Cars, 2024-2030E
- SD/LD/HD Map Market Size for Chinese Passenger Cars, 2024-2030E
- Autonomous Driving Level of Chinese Passenger Cars by Autonomous Driving Level, 2024-2030E
- 2.2 Competitive Landscape of Automotive Map Market
- Competitive Landscape of Chinese Urban NOA Map Market for Passenger Cars, 2024
- Major Players in Autonomous Driving Map Market
- Players in Autonomous Driving Map Market (1): Domestic Map Providers (1)
- Players in Autonomous Driving Map Market (1): Domestic Map Providers (2)
- Players in Autonomous Driving Map Market (2): OEMs
- Players in Autonomous Driving Map Market (3): Foreign Map Providers
- Layout Concept of Map Providers Driven by Urban NOA
- Layout Strategy of Map Providers Driven by Urban NOA (1)
- Layout Strategy of Map Providers Driven by Urban NOA (2)
- Layout Strategy of Map Providers Driven by Urban NOA (3)
- 2.3 Changes in Business Models of Autonomous Driving Map Providers amid the Trend of Urban NOA
- Classification of Autonomous Driving Map Business Models
- Summary of Autonomous Driving Map Business Models: Domestic Map Providers (1)
- Summary of Autonomous Driving Map Business Models: Domestic Map Providers (2)
- Summary of Autonomous Driving Map Business Models: Foreign Map Providers
- The Focus Of Competition in the Autonomous Driving Map Industry Shifts to Comprehensive Capabilities under Urban NOA
- Changes in Business Models of Map Suppliers amid the Development of Urban NOA
3 Trends and New Technology Application in Autonomous Driving Map Industry
- 3.1 Evolution of Intelligent Driving Maps amid the End-to-end Trend
- Maps Are the Carriers of Standardized Location Data
- Integration of Maps and Scenarios in Intelligent Driving
- Evolution of Intelligent Driving Maps: Solutions with Maps VS Solutions without Maps
- Evolution of Intelligent Driving Maps: Advantages of Mapless Solutions
- The Value of Intelligent Driving Maps Is Re-evaluated amid the End-to-end Trend
- How to Access Intelligent Driving Maps in End-to-end Technology (1): SD Map Features Are the Key and Value Input
- How to Access Intelligent Driving Maps in End-to-end Technology (2): Initial Query Input
- 3.2 Autonomous Driving Map Reconstruction: Automatic Annotation System and Video Clips
- Automatic Annotation System (Tesla as an Example)
- Pavement Reconstruction Process (1)
- Pavement Reconstruction Process (2)
- Pavement Reconstruction Process (3)
- Automatic Annotation Can Solve the Occlusion Problem of Moving Objects
- 3.3 Autonomous Driving Map Reconstruction: Application of NeRF Technology
- Application of NeRF in Autonomous Driving Includes Perception, 3D Reconstruction, Positioning and Map Construction, etc.
- NeRF's Application Potential in Autonomous Driving: Data Enhancement
- NeRF's Application Potential in Autonomous Driving: Model Training
- NeRF's Application Potential in Autonomous Driving: SLAM
- Technical Comparison between NeRF Static Maps and Dynamic Generative Maps
- The Combined Application of NeRF and Generative Maps Brings the Best Solution
- HD Map Technology Evolution: NeRF Reconstruction and Real-time Generative Map Application Will See a Turning Point in 2027-2028
- Accelerated Application of NeRF in Autonomous Vehicles
- 3.4 Autonomous Driving Map Reconstruction: Voxel NeRF Produces MV-Map
- MV-Map Can Significantly Improve the Quality of HD Maps
- MV-Map Framework
- MV-Map Production Steps
- 3.5 Autonomous Driving Map Reconstruction: 4D Spatiotemporal Features
- Application of 4D Spatiotemporal Features in Autonomous Driving: Combined with Intelligent Driving Maps to Improve Prediction Capabilities
- DriveWorld: a 4D Spatiotemporal Pre-training Algorithm for Autonomous Driving
- Application of 4D Spatiotemporal Features in Vehicles
- 3.6 Autonomous Driving Map Reconstruction: 3D Gaussian Splashing
- Autonomous Driving Algorithms Need "Intermediate Expression Maps"
- 3D Gaussian Splashing (Intermediate Expression Maps for Autonomous Driving) (1)
- 3D Gaussian Splashing (Intermediate Expression Maps for Autonomous Driving) (2)
4 Autonomous Driving Map Application and Technology Layout of OEMs
- 4.1 Demand for Maps in Different Autonomous Driving Scenarios
- Main Application Scenarios of Autonomous Driving Maps
- Main Application Scenarios of Autonomous Driving Maps: Demand of Passenger Car NOA for Autonomous Driving Maps
- Main Application Scenarios of Autonomous Driving Maps: Demand of Autonomous Passenger Cars (L3/L4) for Autonomous Driving Maps
- Main Application Scenarios of Autonomous Driving Maps: Demand of Passenger Cars with Low-speed Automated Parking for Autonomous Driving Maps
- Main Application Scenarios of Autonomous Driving Maps: Demand of Unmanned Cargo Transport for Autonomous Driving Maps
- 4.2 OEMs' Choice of Autonomous Driving Maps
- OEMs' Choice of Autonomous Driving Maps (1)
- OEMs' Choice of Autonomous Driving Maps (2)
- OEMs' Choice of Autonomous Driving Maps (3)
- OEMs' Choice of Autonomous Driving Maps (4)
- OEMs' Choice of Autonomous Driving Maps (5)
- 4.3 Installations of Autonomous Driving Maps by OEMs
- Installations of Intelligent Driving Maps in Production Passenger Cars of Independent Brands (1)
- Installations of Intelligent Driving Maps in Production Passenger Cars of Independent Brands (2)
- Installations of Intelligent Driving Maps in Production Passenger Cars of Independent Brands (3)
- Installations of Intelligent Driving Maps in Production Passenger Cars of Independent Brands (10)
- Installations of Intelligent Driving Maps in Production Passenger Cars of Independent Brands (11)
- Installations of Intelligent Driving Maps in Production Passenger Cars of Independent Brands (12)
- Installations of Intelligent Driving Maps in Production Passenger Cars of Joint Venture Brands (1)
- Installations of Intelligent Driving Maps in Production Passenger Cars of Joint Venture Brands (2)
- 4.4 Tesla
- Evolution of Autonomous Driving Software and Map Solutions
- Online Map Construction and Real-time Generative Map Layout
- Autonomous Driving Software: "End-to-end" Technology Route
- Autonomous Driving Software: Algorithm Iteration
- Autonomous Driving Software: Perception Technology of Occupancy Networks
- Autonomous Driving Software: Pure Visual Solutions (1)
- Autonomous Driving Software: Pure Visual Solutions (2)
- Real-time Construction and Updates of HD Maps with AI Technology
- FSD Uses SD Maps (1)
- FSD Uses SD Maps (2)
- 4.5 Xiaomi
- Evolution of Autonomous Driving Software and Map Solutions
- Online Map Construction and Real-time Generative Map Layout
- SU7 Uses HD Maps as Safety Redundancy
- Autonomous Driving Maps: From HD Maps to End-to-end
- End-to-end Foundation Models Use a "Three-layer Modeling" Architecture to Build Physical World Models
- End-to-end Foundation Models Use a "Three-layer Modeling" Architecture
- Data Closed Loop: Physical World Modeling
- 4.6 Xpeng
- Evolution of Autonomous Driving Software and Map Solutions
- Online Map Construction and Real-time Generative Map Layout
- XNGP Is Upgraded to a "Mapless" Solution (1)
- Autonomous Driving Software: Next-generation Perception Architecture - "X Net"
- XNGP Is Upgraded to a "Mapless" Solution (2)
- XNGP Is Upgraded to a "Mapless" Solution (3)
- Autonomous Driving Software: Self-developed Fully Automatic Annotation System Based on XNet
- HD Map Solutions
- Autonomous Driving Software: Cloud Foundation Models
- Cloud Training Base: "World Base Model" R&D (1)
- Cloud Training Base: "World Base Model" R&D (2)
- Cloud Training Base: "World Base Model" R&D (3)
- Cloud Training Base: "World Base Model" R&D (4)
- Cloud Training Base: "World Base Model" R&D (5)
- 4.7 Li Auto
- Evolution of Autonomous Driving Software and Map Solutions
- Online Map Construction and Real-time Generative Map Layout
- AD Max 3.0 Is Upgraded to a "Mapless" Solution
- Online Mapping Technology (1)
- Online Mapping Technology (2)
- Closed Loop Simulation System (1)
- Closed Loop Simulation System (2)
- Closed Loop Simulation System (3)
- 4.8 NIO
- Evolution of Autonomous Driving Software and Map Solutions
- Online Map Construction and Real-time Generative Map Layout
- Autonomous Driving Software: Navigation World Models (NWMs) (1)
- Autonomous Driving Software: Navigation World Models (NWMs) (2)
- 4.9 Harmony Intelligent Mobility Alliance (HIMA)
- Evolution of Autonomous Driving Software and Map Solutions
- Online Map Construction and Real-time Generative Map Layout
- Autonomous Driving Software: ADS 4.0 (1)
- Autonomous Driving Software: ADS 4.0 (2)
- Autonomous Driving Software: Features of ADS 3.0 (1)
- Autonomous Driving Software: Features of ADS 3.0 (2)
- Autonomous Driving Software: ADS SE
- Autonomous Driving Software: Comparison between ADS SE and ADS (Advanced Version)
- Autonomous Driving Software: Mapless Solutions
- Autonomous Driving Software: Petal Maps
- Autonomous Driving Software: Mapless Solutions
- Autonomous Driving Software: Petal Maps
- AI Technology Application: Automotive World Behavior Models
- 4.10 SAIC IM
- Evolution of Autonomous Driving Software and Map Solutions
- Online Map Construction and Real-time Generative Map Layout
- Autonomous Driving Software: Cooperate Deeply with Momenta in NOA
- Autonomous Driving Software: IM AD 3.0 (1)
- Autonomous Driving Software: IM AD 3.0 (2)
- Autonomous Driving Software: IM AD 3.0 (3)
- Autonomous Driving Software: "Production-ready" Robotaxi 3.0
- HD Map Application
- Online Mapping Technology
- 4.11 Leapmotor
- Evolution of Autonomous Driving Software and Map Solutions
- Online Map Construction and Real-time Generative Map Layout
- Automotive Autonomous Driving Software: LEAP 3.5
- Gradual Evolution towards Light Map Solutions
- Low-cost Map Solutions
- Latest Application Dynamics of Baidu LD Maps: Access to LEAP 3.5
- 4.12 Geely & ZEEKR
- Evolution of Autonomous Driving Software and Map Solutions
- Online Map Construction and Real-time Generative Map Layout
- Autonomous Driving Software: Pan-World Models
- Autonomous Driving Software: G-Pilot
- Autonomous Driving Software: Multimodal Foundation Models
- Autonomous Driving Software: G-AES
- Autonomous Driving Software: SEA 2.0 (1)
- Autonomous Driving Software: SEA 2.0 (2)
- Autonomous Driving Software: ZeekrXMapbox Real-time Cloud Navigation System
- 4.13 Dongfeng Voyah
- Evolution of Autonomous Driving Software and Map Solutions
- Online Map Construction and Real-time Generative Map Layout
- Intelligent Driving Solutions Based on Navigation Maps (SD Maps)
- Autonomous driving software: Baidu Maps V20 Visual Lane-level Navigation
- Intelligent Driving Map Application
- Application of Intelligent Driving Maps in Dongfeng Forthing StarSea
- 4.14 Changan Automobile
- Evolution of Autonomous Driving Software and Map Solutions
- Online Map Construction and Real-time Generative Map Layout
- Autonomous Driving Software: Dubhe Intelligent Driving (1)
- Autonomous Driving Software: Dubhe Intelligent Driving (2)
- Autonomous Driving Software: Dubhe Intelligent Driving (3)
- Avita's Autonomous Driving Software: Huawei Petal Maps
- 4.15 Chery
- Evolution of Autonomous Driving Software and Map Solutions
- Online Map Construction and Real-time Generative Map Layout
- Chery STERRA's Intelligent Driving Solution Tends to "Get Rid of Maps"
- Autonomous Driving Software: Intelligent Driving Software Business Layout and Planning
- Autonomous Driving Software: Technical Features of Chery Pilot 4.0
- Autonomous Driving Software: Falcon Intelligent Driving Series (1)
- Autonomous Driving Software: Falcon Intelligent Driving Series (2)
- Autonomous Driving Software: Falcon Intelligent Driving Series (3)
- Autonomous Driving Software: Falcon Intelligent Driving Series (4)
- 4.16 Great Wall Motor
- Evolution of Autonomous Driving Software and Map Solutions
- Online Map Construction and Real-time Generative Map Layout
- Autonomous Driving Software: Coffee Pilot Ultra
- Autonomous Driving Software: SEE End-to-end Foundation Models
- Autonomous Driving Software: AutoNavi Map X Great Wall Motor Joint Mobility Innovation Lab
- 4.17 GAC Motor
- Evolution of Autonomous Driving Software and Map Solutions
- Online Map Construction and Real-time Generative Map Layout
- Autonomous Driving Software: Five Major Intelligent Driving Platforms
- Autonomous Driving Software: VLA
- Autonomous Driving Software: Perception Algorithm of ADiGO PILOT
- Autonomous Driving Software: "Edge-cloud" Light Map Solutions
- "Mapless Intelligent Driving" Solutions Relying on Navigation Maps (SD Maps)
- Aion's HD Map Solution
- Aion's Electronic Vision System
- Aion's HD Map Curvature and Slope
- Online Mapping Patent Application
- 4.18 Volkswagen
- Evolution of Autonomous Driving Software and Map Solutions
- Online Map Construction and Real-time Generative Map Layout
- Autonomous Driving Software: Self-developed High-Level AI Intelligent Driving System
- Autonomous Driving Software: Product Route for "Smart Driving Equality" (1)
- Autonomous Driving Software: Product Route for "Smart Driving Equality" (2)
- Autonomous Driving Software: Product Route for "Smart Driving Equality" (3)
- Autonomous Driving Software: Product Route for "Intelligent Driving Equality" (4)
- 4.19 Mercedes-Benz
- Evolution of Autonomous Driving Software and Map Solutions
- Online Map Construction and Real-time Generative Map Layout
- Autonomous Driving Software: Autonomous Driving Software Development Model
- Autonomous Driving Software: L2++ "Mapless" Advanced Intelligent Driving
- 4.20 BMW
- Autonomous Driving Software Solution and Supply Chain Construction
- Online Map Construction and Real-time Generative Map Layout
- Autonomous Driving Software: Features of L3 Personal Pilot
- Autonomous Driving Software: L2+ and L3 Autonomous Driving Systems
- Autonomous Driving Software: Intelligent Driving Planning for BMW Vision Neue Klasse
- 4.21 Toyota
- Autonomous Driving Software Solution and Supply Chain Construction
- Online Map Construction and Real-time Generative Map Layout
- Autonomous Driving Software: All-scenario Intelligent Driving of bZ3X
- Autonomous Driving Software: L4 Autonomous Driving Evolution
5 Autonomous Driving Map Providers
- 5.1 Baidu Maps
- Committed to Building Maps Suitable for Autonomous Driving
- Automotive Map System
- Automotive Maps (1): Navigation Maps (SD Maps)
- Automotive Maps (1): Navigation Maps (SD Maps) V21 Is Upgraded to Intelligent Driving Navigation
- Automotive Maps (2): Autonomous Driving Maps (1)
- Automotive Maps (2): Autonomous Driving Maps (2)
- Automotive Maps (2): The First Intelligent Parking Navigation System Seamlessly Connects to Parking Spaces
- Automotive Maps (3): HD Maps
- Maps Are One of the Core Competitiveness of Autonomous Driving Systems
- Core Value of "Familiar Route Mode" (1): Safety
- Core Value of "Familiar Route Mode" (2): Comfort
- Core Value of "Familiar Route Mode" (3): Efficiency
- Low-cost Intelligent Driving Map Construction Technology (1): Map Construction
- Low-cost Intelligent Driving Map Construction Technology (1): BEV Static Road Scenario Reconstruction (1)
- Low-cost Intelligent Driving Map Construction Technology (1): BEV Static Road Scenario Reconstruction (2)
- Low-cost Intelligent Driving Map Construction Technology (2): Automated Feature Extraction
- Compared with HD Maps, Autonomous Driving Maps Are Less Burdensome
- The Latest Application of HD Maps: Access to Tesla
- The Latest Application of LD Maps: Access to LEAP 3.5
- 5.2 NavInfo
- Transformation of Autonomous Driving Map Business Models
- Redefined Role of Autonomous Driving Maps: From Automotive Charging to Training
- Redefined Role of Autonomous Driving Maps: Safe Redundant Configuration
- Automotive Map System
- Automotive Maps (1): Navigation Maps (SD Maps)
- Automotive Maps (2): Scenario Maps (1)
- Automotive Maps (2): Scenario Maps (2)
- Automotive Maps (3): HD Maps (1)
- Automotive Maps (3): HD Maps (2)
- Automotive Maps (3): HD Maps (3)
- Automotive Maps (3): HD Maps (4)
- 5.3 AutoNavi (amap.com)
- Automotive Maps (1): Navigation Maps (SD Maps)
- Automotive Maps (2): The Latest Technological Progress of Autonomous Driving Maps
- Automotive Maps (2): HQ Live MAP
- Automotive Maps (2): All-domain Lane-level Navigation Installed on NIO ET9
- Automotive Maps (3): HD Maps
- Matching between HD Maps and SD Maps
- 5.4 Tencent
- Automotive Maps (1): Navigation Maps (SD Maps)
- Automotive Maps (2): Autonomous Driving Maps (Intelligent Driving Cloud Maps)
- Automotive Maps (2): Autonomous Driving Maps (Intelligent Driving Maps)
- Automotive Maps (2): Autonomous Driving Maps (Intelligent Driving Maps 8.0)
- Automotive Maps (3): HD Maps
- Application of Automotive Maps in Urban NOA: Horizon Continental Technology's L2+ Intelligent Driving Solution - Astra
- 5.5 Lange Technology
- Intelligent Driving Map System
- Competitive Advantages in Intelligent Driving Maps
- Four-layer Intelligent Driving Map Model
- Data Intelligence System with Weekly Updates
- Intelligent Driving Map Mass Production and Delivery Solutions
- 5.6 EMG
- Automotive Map Layout: Technology-driven + Ecological Binding
- Automotive Maps (1): Parking Lot HD Maps (1)
- Automotive Maps (1): Parking Lot HD Maps (2)
- Automotive Maps (2): Autonomous Driving Maps (Vehicle-road-cloud Integrated Maps)
- Automotive Maps (3): HD Map Cloud Platforms
- Automotive Map Application: Autonomous Driving Simulation Testing
- 5.7 MXNAVI
- Business Layout
- Industrial Qualifications
- Intelligent Driving Solutions in Urban Areas: Vehicle-cloud Integrated Route Memory
- Automotive Maps (1): Crowd-source Map Technology
- Automotive Maps (1): Progress of Crowd-source Map Platforms
- Automotive Maps (1): Crowd-source Map Platforms Empower Urban NOA
- Automotive Maps (1): Application Effect of Crowd-source Map Platforms
- Automotive Maps (2): HD Map Fusion Platforms
- 5.8 Leador
- Autonomous Driving Technology Based on HD Maps
- Application of Parking Lot HD Maps: Changan Automobile
- 5.9 Heading Data Intelligence
- Map-based Product Line
- Automotive Maps (1): HD Map Data
- Automotive Maps (2): HD Map Engines
- 5.10 BrightMap
- Automotive Maps (1): AVP HD Maps (1)
- Automotive Maps (2): AVP HD Maps (1)
- 5.11 Huawei
- Automotive Maps (1): Navigation Maps (SD Maps)
- Automotive Maps (2): Online Mapping
- Automotive Maps (3): Autonomous Driving Map Data
- Automotive Map Application: ADS
- 5.12 Roadgrids Technology
- Automatic Construction and Updates of Light HD Maps
- Trade-offs of Light HD Map Elements
- Light Map Closed-loop Solutions (1)
- Light Map Closed-loop Solutions (2)
- 5.13 Mapbox
- Automotive Maps: Navigation Maps (SD Maps)
- Automotive Maps: HD Maps
- 5.14 Kuandeng Technology
- "Automotive Crowd-sourced Update" Solutions
- "Roadside Crowd-sourced Update" Solutions
- HD Lite Maps
- Solutions for Matching between HD Maps and SD Maps: vehicles
- Solutions for Matching between HD Maps and SD Maps: Cloud