|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1694625
自動車のコックピットにおけるAIの応用(2025年)Research Report on the Application of AI in Automotive Cockpits, 2025 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| 自動車のコックピットにおけるAIの応用(2025年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月02日
発行: ResearchInChina
ページ情報: 英文 310 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
音声認識やフェイスモニタリング機能が初めて自動車に搭載された2000年代初頭から、2023年の「大規模モデル統合」動向の台頭、さらには自動車メーカーが推論モデル「DeepSeek-R1」を広く採用する2025年まで、コックピットにおけるAIの応用は3つの重要なフェーズを経て進化してきました。
前大規模モデル時代:コックピットは機械式から電子式へ、そしてインテリジェントシステムへと移行し、顔認識や音声認識などのシナリオのために小規模AIモデルが統合されました。
ポスト大規模モデルの時代:AIの応用範囲は拡大し、量も増え、効果も大幅に改善されましたが、精度と適応性は依然として一貫性がありませんでした。
マルチモーダル大規模言語モデル(LLM)と推論モデル:コックピットは基本的な知能から「ディープインタラクションと自己進化」の段階へと進みました。
コックピットAI開発動向1:ディープインタラクション
ディープインタラクションは、「リンケージインタラクション」、「マルチモーダルインタラクション」、「パーソナライズドインタラクション」、「アクティブインタラクション」、「精密インタラクション」に反映されます。
「精密インタラクション」を例にとると、推論大規模モデルは音声インタラクションの精度、特に連続認識の精度を向上させるだけでなく、コンテキストの動的理解を通じて、センサー融合処理データと組み合わせ、マルチタスク学習アーキテクチャに依存して、ナビゲーション、音楽、その他の複合要求を同期処理し、応答速度は従来のソリューションに比べて40%向上します。2025年、推論モデル(DeepSeek-R1など)が大規模に搭載された後、エンドサイドの推論機能により、自動音声認識プロセスが高速化され、精度がさらに向上することが予測されます。
「マルチモーダルインタラクション」を例にとると、大規模モデルのマルチソースデータ処理能力を利用して、クロスモーダルコラボレーティブインテリジェントインタラクションシステムを構築することができます。3Dカメラとマイクアレイを深く統合することで、システムはジェスチャーコマンド、音声セマンティクス、環境特性を同時に分析し、マルチモーダルな意図理解を短時間で完了することができ、これは従来のソリューションよりも60%高速です。クロスモーダルアライメントモデルに基づき、ジェスチャー制御と音声コマンドを協調させることで、複雑な運転シナリオにおける誤操作率をさらに低減することができます。2025年~2026年に、マルチモーダルデータフュージョン処理機能が新世代のコックピットの標準になると予測されています。代表的なシナリオは以下の通りです。
ジェスチャー操作:ドライバーは、手を振る、指を指すなどの簡単なジェスチャーで、運転中の注意を散漫にすることなく、窓、サンルーフ、ボリューム、ナビゲーションなどの機能を便利に操作できます。
顔認識とパーソナライゼーション:顔認識技術によりドライバーを自動的に識別し、個人の選好に応じてシート、バックミラー、エアコン、音楽などの設定を自動的に調整し、「車に乗って楽しむ」というパーソナライズされた体験を実現します。
アイトラッキングとアテンションモニタリング:視線追跡技術により、ドライバーの視線方向と注意状態をモニターし、疲労運転や不注意などの危険行動をタイムリーに検出し、早期警告プロンプトを提供することで、運転の安全性を向上させます。
感情認識と感情的相互作用:AIシステムは、ドライバーの表情や声のトーンなどを通じて、不安、疲労、興奮などのドライバーの感情状態を判断し、それに応じて車内の環境照明、音楽、空調などを調整して、より親密な感情的サービスを提供することもできます。
コックピットAI開発動向2:自己進化
2025年、コックピットエージェントは、ユーザーがコックピットと対話するための媒体となり、その顕著な特徴が、「長期記憶」、「フィードバック学習」、「能動的認知」に反映される「自己進化」です。
当レポートでは、中国の自動車産業について調査分析し、国内外のメーカーによる、自動車のコックピットにおけるAIの応用に関する情報を提供しています。
目次
第1章 自動車のコックピットにおけるAIの応用シナリオ
- コックピットにおけるAIの応用の現状
- シナリオ1:音声認識
- シナリオ2:マルチモーダルインタラクション
- シナリオ3:IMS
- シナリオ4:HUD
- シナリオ5:レーダー検出
第2章 シナリオに基づいたコックピットエージェント
- コックピットエージェントの概要
- コックピットエージェントの応用の背景
第3章 サプライヤーのコックピットAI応用例
- サプライヤーのコックピットAI大規模モデルの機能
- Huawei
- Tencent
- Ali
- Baidu
- ByteDance (Volcano Engine)
- Zhipu AI
- SenseTime
- iFLYTEK
- AISpeech
- Unisound AI Technology Co, Ltd
- Upjohn technology
- ThunderSoft
- Z-One
- Desay SV
- TINNOVE
- PATEO
- Cerence
- MediaTek
- Minieye
- oToBrite
- Smart Eye
第4章 自動車メーカーのコックピットAI応用例
- OEMの大規模モデル応用の概要
- NIO
- Li Auto
- XPeng
- Xiaomi
- Leapmotor
- BYD
- SAIC
- GAC
- BAIC
- Chang'an
- Great Wall
- Chery
- Geely
- Jianghuai
- Applications of Jianghuai AI Cockpit
- BMW
- Mercedes Benz
- VW
第5章 コックピットにおけるAIの応用の動向と技術的リソース
- コックピットにおけるAIの応用の動向
- 動向1:
- 動向2:大規模モデルからエージェントへ
- 動向3:
- 動向4:
- 動向5:
- 動向6:
- 動向7:
- コックピットへのAI技術実装に向けたリソース計算
- リソース計算
- さまざまなコックピットAIアルゴリズムの長所と短所
Cockpit AI Application Research: From "Usable" to "User-Friendly," from "Deep Interaction" to "Self-Evolution"
From the early 2000s, when voice recognition and facial monitoring functions were first integrated into vehicles, to the rise of the "large model integration" trend in 2023, and further to 2025 when automakers widely adopt the reasoning model DeepSeek-R1, the application of AI in cockpits has evolved through three key phases:
Pre-large model era: Cockpits transitioned from mechanical to electronic and then to intelligent systems, integrating small AI models for scenarios like facial and voice recognition.
Post-large model era: AI applications expanded in scope and quantity, with significant improvements in effectiveness, though accuracy and adaptability remained inconsistent.
Multimodal large language models (LLMs) and reasoning models: Cockpits advanced from basic intelligence to a stage of "deep interaction and self-evolution."
Cockpit AI Development Trend 1: Deep Interaction
Deep interaction is reflected in "linkage interaction", "multi-modal interaction", "personalized interaction", "active interaction" and "precise interaction".
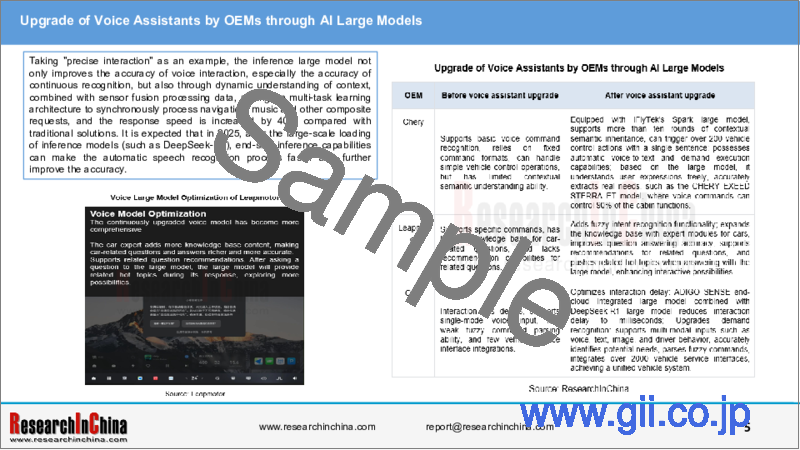
Taking "precise interaction" as an example, the inference large model not only improves the accuracy of voice interaction, especially the accuracy of continuous recognition, but also through dynamic understanding of context, combined with sensor fusion processing data, relying on multi-task learning architecture to synchronously process navigation, music and other composite requests, and the response speed is increased by 40% compared with traditional solutions. It is expected that in 2025, after the large-scale loading of inference models (such as DeepSeek-R1), end-side inference capabilities can make the automatic speech recognition process faster and further improve the accuracy.
Taking "multi-modal interaction" as an example, using the multi-source data processing capabilities of large models, a cross-modal collaborative intelligent interaction system can be built. Through the deep integration of 3D cameras and microphone arrays, the system can simultaneously analyze gesture commands, voice semantics and environmental characteristics, and complete multi-modal intent understanding in a short time, which is 60% faster than traditional solutions. Based on the cross-modal alignment model, gesture control and voice commands can be coordinated to further reduce the misoperation rate in complex driving scenarios. It is expected that in 2025-2026, multi-modal data fusion processing capabilities will become standard in the new generation of cockpits. Typical scenarios include:
Gesture control: Drivers can conveniently control functions such as windows, sunroof, volume, navigation, etc. through simple gestures, such as waving, pointing, etc., without distracting their driving attention.
Facial recognition and personalization: The system can automatically identify the driver through facial recognition technology, and automatically adjust the settings of seats, rearview mirrors, air conditioners, music, etc. according to their personal preferences, to achieve a personalized experience of "get in the car and enjoy".
Eye tracking and attention monitoring: Through eye tracking technology, the system can monitor the driver's gaze direction and attention state, detect risk behaviors such as fatigue driving and inattention in a timely manner, and provide early warning prompts to improve driving safety.
Emotional recognition and emotional interaction: AI systems can even identify the driver's emotional state, such as judging whether the driver is anxious, tired or excited through facial expressions, voice tone, etc., and adjust the ambient lighting, music, air conditioning, etc. in the car accordingly to provide more intimate emotional services.
Cockpit AI Development Trend 2: self-evolution
In 2025, the cockpit agent will become the medium for users to interact with the cockpit, and one of its salient features is "self-evolution", reflected in "long-term memory", "feedback learning", and "active cognition".
"Long-term memory", "feedback learning", and "active cognition" are gradual processes. AI constructs user portraits through voice communication, facial recognition, behavior analysis and other data to achieve "thousands of people and thousands of faces" services. This function uses reinforcement learning and reasoning related technology implementation, and the system relies on data closed-loop continuous learning of user behavior. Under the reinforcement learning mechanism, each user feedback becomes the key basis for optimizing the recommendation results.
With the continuous accumulation of data, the large model can more quickly discover the law of user interest point transfer, and can anticipate user requests in advance. It is expected that in the next two years, with the help of more advanced reinforcement learning algorithms and efficient reasoning architecture, the system will increase the mining speed of users' new areas of interest by 50%, and the accuracy of recommended results will be further improved. Such as:
BMW's cockpit system remembers driver seat preferences, frequented locations, and automatically dims ambient lights to relieve anxiety on rainy days;
Mercedes-Benz's voice assistant can recommend restaurants based on the user's schedule and reserve charging stations in advance.
BMW Intelligent Voice Assistant 2.0 is based on Amazon's Large Language Model (LLM) and combines the roles of personal assistant, vehicle expert and accompanying occupant to generate customized suggestions by analyzing the driver's daily route, music preferences and even seat adjustment habits. For example, if the system detects that the driver often stops at a coffee shop every Monday morning, it will proactively prompt in a similar situation: "Are you going to a nearby Starbucks?" In addition, the system can also adjust recommendations based on weather or traffic conditions, such as recommending indoor parking on rainy days; when the user says "Hello BMW, take me home", "Hello BMW, help me find a restaurant", the personal assistant can quickly plan a route and recommend a restaurant.
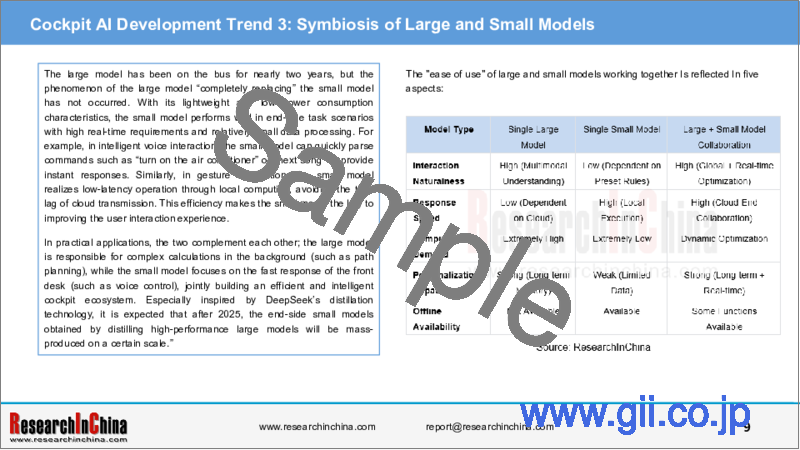
Cockpit AI Development Trend 3: Symbiosis of Large and Small Models
The large model has been on the bus for nearly two years, but the phenomenon of the large model "completely replacing" the small model has not occurred. With its lightweight and low power consumption characteristics, the small model performs well in end-side task scenarios with high real-time requirements and relatively small data processing. For example, in intelligent voice interaction, the small model can quickly parse commands such as "turn on the air conditioner" or "next song" to provide instant responses. Similarly, in gesture recognition, the small model realizes low-latency operation through local computing, avoiding the time lag of cloud transmission. This efficiency makes the small model the key to improving the user interaction experience.
In practical applications, the two complement each other; the large model is responsible for complex calculations in the background (such as path planning), while the small model focuses on the fast response of the front desk (such as voice control), jointly building an efficient and intelligent cockpit ecosystem. Especially inspired by DeepSeek's distillation technology, it is expected that after 2025, the end-side small models obtained by distilling high-performance large models will be mass-produced on a certain scale."
Taking NIO as an example, it runs its AI application in a two-wheel drive manner for large and small models as a whole, with a focus on large models, but it does not ignore the application of small models.
Table of Contents
Relevant Definitions
1 Application Scenarios of AI in Automotive Cockpits
- 1.1 Current Status of AI Applications in Cockpits
- Characteristics of the New Generation Cockpit after AI Integration
- Application Scenarios of AI in Cockpits: Current Status
- 1.2 Scenario 1: Speech Recognition
- AI Large Model Integration into Speech Recognition Development Roadmap
- Sub-Scenario 1: Voiceprint Recognition
- Sub-Scenario 2: External Vehicle Speech Recognition
- Speech Interaction Suppliers Integrating AI Large Models
- 1.3 Scenario 2: Multimodal Interaction
- AI Large Model Integration into Facial Recognition Development Roadmap
- Small Model Integration in Lip Movement Recognition Scenarios
- Small Model Integration in Iris Recognition Scenarios
- Vehicle Models with Iris Recognition Function
- 1.4 Scenario 3: IMS
- Functions Implemented by In-cabin Monitoring Systems
- Development of AI in In-cabin Monitoring Scenarios
- Examples of AI Algorithms in In-cabin Monitoring
- AI Technology Applications in In-cabin Monitoring Chip Suppliers
- AI Technology Applications in In-cabin Monitoring: Algorithm Suppliers
- 1.5 Scenario 4: HUD
- Applications of AI algorithms in HUDs
- 1.6 Scenario 5: Radar Detection
- AI algorithms in Radar (1)
- AI algorithms in Radar (2)
2 Cockpit Agents Based on Scenarios
- 2.1 Overview of Cockpit Agents
- Introduction to AI Agents
- Classification of Cockpit AI agents
- Evolution Direction of Cockpit AI agents: Cognition-driven
- Process of AI Agents Landing in Cockpits: From Large Models to AIOS
- Program for AI Agents Landing in Cockpits based on LLMs
- Interaction Mechanism of Cockpit AI Agents
- Classification of Application Scenarios for Cockpit AI Agents (1)
- Classification of Application Scenarios for Cockpit AI Agents (2)
- Evolution Direction of AI Agents: Active Interaction
- Evolution Direction of AI Agents: Reflective Optimization
- 2.2 Application Background of Cockpit Agents
- Application Background (1): Multimodal Interaction Spurs Agent Landing
- Application Background (2): Scenario Creation as an Important Approach for Agent Evolution
- Application Background (3): Agent Scenarios Drive Demand for High-Performance Computing Chips
- Application Background (4): Performance of Large Models Determines the Upper Limit of Agents
- Application Background (5): Parallel Development of Large and Small Models
3 Cockpit AI Application Cases of Suppliers
- Overview of Cockpit AI Large Model Functions of Suppliers
- 3.1 Huawei
- Huawei's AI Application Planning in Cockpits
- Function Construction of Huawei HarmonySpace Intelligent Cockpit
- Huawei Xiaoyi's Voice Capabilities based on Large Models
- AI Functions of Huawei Harmony OS
- Two Implementation Methods of Huawei Harmony OS "See and Say"
- Case: Xiaoyi Assistant Interaction Scenario in Harmony OS vehicles
- 3.2 Tencent
- Tencent's Intelligent Cockpit Large Model Framework
- Enhancing Interaction Functions with Tencent's Large Model
- Applications of Tencent's Intelligent Cockpit Large Model (1)
- Applications of Tencent's Intelligent Cockpit Large Model (2)
- Interaction Features of Tencent's Cockpit (1)
- Interaction Features of Tencent's Cockpit (2)
- 3.3 Ali
- Alibaba Qwen Large Model and OS Integration
- Ali's AI-based Voice Scenario
- Ali NUI End-cloud Integrated Platform Architecture
- Alibaba's E2E Large Model Combined with Cloud Computing
- Functional Application of Qwen Large Model End Side on IVI
- Qwen Large Model Mounted on IVI
- 3.4 Baidu
- Baidu Smart Cabin is Built based on ERNIE Bot Model
- Baidu AI Native Operating System
- 3.5 ByteDance (Volcano Engine)
- Volcano Engine Cockpit Function Highlights
- 3.6 Zhipu AI
- Cockpit Design Architecture Based on AI Large Model
- Scenario Design of AI Large Model
- Design of AI Large Model for Cockpit Interaction Pain Points
- 3.7 SenseTime
- Six Features of SenseTime Smart Cabin
- Influence of SenseTime SenseNova on Cockpit Interaction
- SenseTime Multimodal Processing Capability Framework
- Multimodal Interactive Application Case of SenseAuto
- In-cabin Monitoring Products of SenseAuto
- 3.8 iFLYTEK
- Spark Large Model Function List
- Development History of iFLYTEK Spark Model
- Upgrade Content of iFLYTEK Spark Model 4.0
- Spark Model Core Capability
- Large Model Deployment Solution
- Car Assistant based on Spark Model
- Spark Voice Model
- Spark Large Model Function List
- How does iFLYTEK's Spark Cockpit Integrate into AI Services?
- Application Technology of Spark Large Model
- Full-stack Intelligent Interaction Technology
- Smart Car AI Algorithm Chip Compatibility
- Characteristics of Multimode Perception System
- Multimodal Interaction
- 3.9 AISpeech
- Large Model Details
- DUI 2.0 products based on DFM
- DFM "1 + N" layout
- AISpeech Fusion Large Model Solution
- Development History AI Speech Technology
- Multi-modal Interaction Solution of AI Speech Technology
- Features of AISpeech Car Voice Assistant
- 3.10 Unisound AI Technology Co, Ltd
- Vehicle Large Model solution
- Large Model Details
- Application of Shanhai Large Model in Cockpit
- Vehicle Voice Solution Business Model
- Voice Basic Technology
- 3.11 Upjohn technology
- Voice Large Model Solution
- Intelligent Cabin Large Model (Hybrid Architecture + Fusion Open)
- Vehicle Voice Solution
- 3.12 ThunderSoft
- Large Model Layout
- Rubik Model in Cockpit Interaction
- 3.13 Z-One
- AI Service Structure is Built according to 4 Levels
- AI's Changes to Hardware Layer
- AI's Changes to the Software Layer
- AI Changes to Cloud/Vehicle Deployment
- 3.14 Desay SV
- Four Main Application Scenarios of Cockpit Large Model
- Multimodal Interaction of Cockpit Large Model
- Multimode Interaction of Cockpit Large Model: Smart Solution 2.0
- Research History of Vehicle Voice
- Voice Large Model Solution Overview
- Solutions to Pain Points in Voice Industry
- Large Model Voice Future Planning
- 3.15 TINNOVE
- AI Models Empower Three Levels of Cockpit
- Four Stages of Smart Cockpit Planning
- AI Cockpit Architecture Design
- AI Large Model Service Form
- AI Large Model Application Scenario
- Combination of TTI OS and Digital Human
- 3.16 PATEO
- Voice Interaction Technology
- PATEO AI Voice Capability Configuration
- 3.17 Cerence
- Automotive Language Large Model Solution
- Voice Assistant and Large Model Integration Solution
- Voice Assistant
- Vehicle-Outside Voice Interaction
- Core Technology of Speech Based on Large Model
- 3.18 MediaTek
- MediaTek Cockpit Interaction Features
- 3.19 Minieye
- I-CS Intelligent Cockpit Adopts CV Technology
- 3.20 oToBrite
- Vision AI Driver Monitoring System
- 3.21 Smart Eye
- AI Scenario of Driver Monitoring System
- LLM Powers Smart Eye DMS/OMS System
4 Cockpit AI Application Cases of OEMs
- Overview of OEM Large Model Applications
- 4.1 NIO
- Multimodal Perception Large Model: NOMI GPT
- Multimodal Interaction Applications based on NOMI GPT
- LeDao intelligent Cockpit Interaction Scenarios based on NOMI GPT
- 4.2 Li Auto
- Lixiang Tongxue: Building Multiple Scenarios
- Lixiang Tongxue: Thinking Chain Explainability
- Mind GPT: Building AI Agent as Core of Large Model
- Mind GPT: Multimodal Perception
- Large Model Training Platform Adopts 4D Parallel Mode
- Cooperation with NVIDIA on Inference Engine
- Lixiang Tongxue's Multimodal Interaction Case in MEGA Ultra
- 4.3 XPeng
- Intelligent Cockpit Solution: XOS Tianji system
- 4.4 Xiaomi
- Xiaomi Vehicle Large Model: MiLM
- Voice Large Model Gets on
- XiaoAi Covers the Scene through Voice Commands
- Voice Task Analysis and Execution Process
- XiaoAi Accurately Match through RAG
- Xiaomi HyperOS Launches DeepSeek R1 Model
- Mi SU7 Self-developed Sound Model
- 4.5 Leapmotor
- Large Model 1.0: Tongyi Large Model
- Large Model 2.0: Enhancing Cockpit Large Model Capabilities with DeepSeek R1
- 4.6 BYD
- Functional Scenario of BYD Xuanji AI Large Model in Cockpit
- Case of BYD Xuanji AI Large Model in Cockpit
- 4.7 SAIC
- Application of IM Large Model in Vehicle Voice
- IM Large Model Application Case
- IM Large Model Builds Active Perception Scenario
- 4.8 GAC
- Intelligent Cockpit Solution
- Cockpit Application of GAC AI Large Model
- Application of DeepSeek in GAC Cockpit
- 4.9 BAIC
- Three Development Stages of BAIC Large Model
- Large Model Specific Scenario
- BAIC Agent Platform Architecture
- Planning Ideas for Large Model Products
- AI Application Case
- 4.10 Chang'an
- Improvement of Cockpit Interaction by Changan Xinghai Large Model
- Changan Integrates AI into SOA Architecture Layer
- Chang'an's Planning of "Digital Intelligence" Cockpit
- Changan Realizes Automatic Switching of Cockpit Scenarios and Functions
- AI Application Case
- 4.11 Great Wall
- Cockpit Application of Great Wall Large Model
- 4.12 Chery
- Chery LION AI base
- EXEED STERRA ET is Equipped with Lion AI Large Model
- 4.13 Geely
- Geely Xingrui AI Large Model
- Geely Xingrui AI Large Model Access DeepSeek
- Smart Cockpit Solution
- Flyme Auto Voice Interaction Capability
- ZEEKR Smart Cockpit Solution: ZEEKR AI OS
- Two Forms of Large Model Cockpit Application
- Large Model Installation Situation
- Large Model Installation Situation: Geely Galaxy E8
- Large Model Installation Situation: ZEEKR 7X
- ZEEKR Cockpit Agent Scenario: Life Service
- ZEEKR Cockpit Agent Scenario: Multimodal Perception
- 4.14 Jianghuai
- 4 Applications of Jianghuai AI Cockpit
- Jianghuai AI Large Model Installation Case
- 4.15 BMW
- BMW Intelligent Voice Assistant 2.0 based on LLM
- 4.16 Mercedes Benz
- MB. OS Digital World - Personalized Services with MBUX Virtual Assistant
- Cockpit Large Model Cooperation Dynamics
- 4.17 VW
- Upgrade Dynamics of Voice Interaction System
- Volkswagen and Baidu Cooperate on Voice Model
5 Trends and Technical Resources of AI Applications in Cockpits
- 5.1 Trends of AI Applications in Cockpits
- Trend 1:
- Trend 2: From Large Models to Agents
- Trend 3:
- Trend 4:
- Trend 5:
- Trend 6:
- Trend 7:
- 5.2 Resource Calculation for AI Technology Implementation in Cockpits
- Resource calculation
- Advantages and disadvantages of different Cockpit AI algorithms