
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1431053
種子:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2024年~2030年)Seed - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 種子:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2024年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2024年02月15日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 937 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
概要
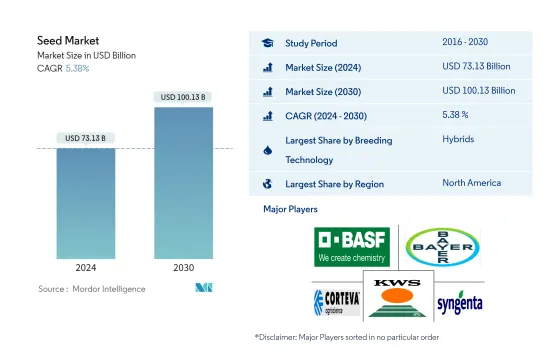
種子市場規模は2024年に731億3,000万米ドルと推定され、2030年には1,001億3,000万米ドルに達すると予測され、予測期間中(2024-2030年)のCAGRは5.38%で成長します。
主なハイライト
- 作物ファミリー別最大セグメント:穀物・穀類:栽培農家にとって高収益をもたらし、食料として大量消費され、バイオ燃料生産用の潤滑油産業による需要が増加していることから、最大セグメントとなっています。
- 国別最大セグメント:米国:トウモロコシ、大豆、キュウリなど高価値作物の主要生産国であり、バイオ作物やハイブリッド種子の導入が世界的に最も進んでいます。
- 作物ファミリー別急成長セグメント-根菜類・球根類: 市場価値の増加、加工産業による需要の増加、市場における高収量品種の入手可能性により、最も急成長しています。
- 国別急成長セグメント:イタリア:サラダ消費の増加、世界のエンドウ豆の主要生産国、酪農家の飼料需要の増加により急成長しています。
種子市場の動向
ハイブリッドが最大の育種技術
- 有機栽培農家、家畜飼料、食品、バイオ燃料産業からのハイブリッド種子と開放受粉種子の需要の高まりが、市場成長の原動力となっています。
- ハイブリッド種子は、高い生産性、幅広い適応性、生物学的・生物学的ストレスに対する高い耐性など、さまざまな利点があるため、主に主要な農業生産国から高い伸びを示しています。例えば、綿花では、ハイブリッドは従来品種より50%多い収量をもたらします。その幅広い適応性は、主に環境の変動に対する高い緩衝能力によるものです。
- 新しい植物育種技術は、種子や植物細胞のDNAを改変することによって、望ましい形質を持つ新品種の開発を可能にしています。植物育種における革新は、農家が日々現場で直面する課題の解決に役立っています。
- さまざまな気候条件に適応し、高い収量ポテンシャルを持ち、病気に強く、干ばつに強い高度な改良品種への需要が高まっているため、企業は新しい植物技術に多額の投資を行っています。例えば、バイエルは2020年、アリゾナ州マラナに初の完全自動化温室を開設しました。この温室には、独自の種子チップ化、先進マーカー技術、自動化、データサイエンスなどの革新的な進歩が含まれています。
- 改良された開放受粉品種を採用することは、収量が多い、現地の環境に適応している、作物が強く育つなど、多くの利点があります。需要の増加により、OPVのシェアは2021年に前年比4.1%増加しました。
北米が最大の地域
- 世界的に見ると、アジア太平洋は生産量最大の農業地域であり、主要作物の作付面積の増加と種子交換率の上昇により、世界の種子市場で大きなシェアを占めています。例えば、穀物の収穫面積は2019年の3億3,300万ヘクタールから2020年には3億4,100万ヘクタールに増加しています。
- 北米は世界有数の種子生産地域です。米国は最大の種子市場であり、トウモロコシが大きなシェアを占め、2021年の米国種子市場の52.8%を占める。これは主にバイオ作物の導入によるものです。
- 欧州は飼料の主要生産国で、2021年の世界の飼料用種子市場におけるシェアは32.7%です。フォレージ種子市場の主な促進要因としては、飼料製品に対する需要の高まりと放牧地の縮小が挙げられます。
- アフリカでは、連作作物が最大のシェアを占め、2021年には79.2%を占める。連作作物が大きなシェアを占める主な理由は、耕作面積の増加に伴う消費の増加です。
- 南米では2022年から2028年にかけてハイブリッド種子の採用率が開放受粉種子品種を上回ると予想されるが、これは収量が10~15%増加し、品質が良く、投資収益率が良いためです。そのため、ハイブリッド種子は2021年から2028年にかけて38.7%の増加が見込まれます。
- 中東ではハイブリッド種子の使用率が低いため、中東の種子市場は2022年から2028年にかけて緩やかに成長すると予想されます。生産者は遺伝子組換え種子の使用に関心がなく、国内需要を満たすためには、作物の約30~50%を他国から輸入しなければならないです。
種子産業の概要
種子市場は細分化されており、上位5社で38.08%を占めています。この市場の主要企業は、BASF SE、Bayer AG、Corteva Agriscience、KWS SAAT SE &Co.KGaA、Syngenta Group(アルファベット順)です。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主な調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 栽培面積
- 最も人気のある形質
- 規制の枠組み
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 育種技術
- ハイブリッド
- 非トランスジェニック・ハイブリッド
- 遺伝子組み換え雑種
- 除草剤耐性
- 昆虫抵抗性
- その他の形質
- 開放受粉品種とハイブリッド派生品種
- ハイブリッド
- 栽培メカニズム
- 露地栽培
- 保護栽培
- 作物タイプ
- 畑作物
- 繊維作物
- 綿花
- その他の繊維作物
- 飼料作物
- アルファルファ
- 飼料用トウモロコシ
- 飼料用ソルガム
- その他の飼料作物
- 穀物
- トウモロコシ
- 米
- ソルガム
- 小麦
- その他の穀物
- 油糧種子
- キャノーラ、菜種、マスタード
- 大豆
- ひまわり
- その他の油糧種子
- 豆類
- 繊維作物
- 野菜
- アブラナ
- キャベツ
- ニンジン
- カリフラワー&ブロッコリー
- その他のアブラナ
- ウリ科
- キュウリ・ガーキン
- かぼちゃ・カボチャ
- その他ウリ科
- 根菜・球根
- ニンニク
- タマネギ
- ジャガイモ
- その他の根菜類
- ナス科
- 唐辛子
- ナス科
- トマト
- その他ナス科
- その他の野菜
- アスパラガス
- レタス
- オクラ
- エンドウ豆
- ほうれん草
- その他
- 畑作物
- 産地
- アフリカ
- 育種技術別
- 栽培メカニズム別
- 作物別
- 国別
- エジプト
- エチオピア
- ガーナ
- ケニア
- ナイジェリア
- 南アフリカ
- タンザニア
- その他のアフリカ
- アジア太平洋
- 育種技術別
- 栽培メカニズム別
- 作物別
- 国別
- オーストラリア
- バングラデシュ
- 中国
- インド
- インドネシア
- 日本
- ミャンマー
- パキスタン
- フィリピン
- タイ
- ベトナム
- その他アジア太平洋地域
- 欧州
- 育種技術別
- 栽培メカニズム別
- 作物別
- 国別
- フランス
- ドイツ
- イタリア
- オランダ
- ポーランド
- ルーマニア
- ロシア
- スペイン
- トルコ
- ウクライナ
- 英国
- その他欧州
- 中東
- 育種技術別
- 栽培メカニズム別
- 作物別
- 国別
- イラン
- サウジアラビア
- その他中東
- 北米
- 育種技術別
- 栽培メカニズム別
- 作物別
- 国別
- カナダ
- メキシコ
- 米国
- 北米その他
- 南米
- 育種技術別
- 栽培メカニズム別
- 作物別
- 国別
- アルゼンチン
- ブラジル
- その他南米地域
- アフリカ
第6章 競合情勢
- 主要な戦略動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- Advanta Seeds-UPL
- BASF SE
- Bayer AG
- Corteva Agriscience
- DLF
- Groupe Limagrain
- KWS SAAT SE & Co. KGaA
- Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel BV
- Sakata Seeds Corporation
- Syngenta Group
第7章 CEOへの主な戦略的質問CEOへの主な戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界・バリューチェーン分析
- 世界市場規模とDRO
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表リスト
- 主要洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
目次
Product Code: 92492
The Seed Market size is estimated at USD 73.13 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 100.13 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 5.38% during the forecast period (2024-2030).

Key Highlights
- Largest Segment by Crop Family - Grains & Cereals : It is the largest segment as it provides high profit for growers, high consumption as food, and an increase in the demand by the lubricants industry for biofuel production.
- Largest Segment by Country - United States : It is a leading producer of high-value crops such as corn, soybean, and cucumber, and the adoption of biotech crops, as well as hybrid seeds is the highest globally.
- Fastest-growing Segment by Crop Family - Roots & Bulbs : It is the fastest growing due to the increase in market value, increase in the demand by processing industries, and the availability of high-yielding varieties in the market.
- Fastest-growing Segment by Country - Italy : It is the fastest growing because of the increase in the consumption of salad, the leading producer of peas globally, and the increase in the demand for feed by dairy farmers.
Seed Market Trends
Hybrids is the largest Breeding Technology
- The growing demand for hybrid and open-pollinated seeds from organic growers, animal feed, food, and biofuel industries is driving the market's growth.
- Hybrid seeds have witnessed high growth, mainly from the major agriculture-producing countries, because of their various benefits, including higher productivity, wider adaptability, and a high degree of resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses. For instance, in cotton, hybrids give 50% more yield than conventional varieties. Their wider adaptability is mainly due to their high buffering capacity to environmental fluctuations.
- New plant breeding techniques are allowing the development of new plant varieties with desired traits by modifying the DNA of the seeds and plant cells. Innovations in plant breeding are helping address the challenges farmers face in the field every day.
- Companies are heavily investing in new plant technologies due to the increasing demand for advanced improved varieties that are adaptable to different climatic conditions, have high yield potential, are resistant to diseases, and are drought tolerant. For instance, in 2020, Bayer opened its first fully automated greenhouse in Marana, Arizona, which includes innovative advancements in proprietary seed chipping, advanced marker technology, automation, and data science.
- Adopting improved open-pollinated varieties has many benefits, such as high yield, being well adapted to the local environment, and allowing crops to grow stronger. Due to the increase in demand, the share value of OPV increased by 4.1% in 2021 from the previous year.
North America is the largest Region
- Globally, Asia-Pacific is the largest agricultural region in terms of production, which holds the major share in the global seed market due to the increase in area under major crops and the increase in seed replacement rate. For instance, the area harvested in cereals increased to 341 million hectares in 2020 from 333 million hectares in 2019.
- North America is one of the world's leading seed-producing regions. The United States is the largest seed market, with corn contributing a major share and accounting for 52.8% of the US seed market in 2021. This is mainly because of the adoption of biotech crops.
- Europe is a major producer of forages, with a share value of 32.7% in the global forage seed market in 2021. Major driving factors of the forage seed market include growing demand for feed products and shrinking land for grazing animals.
- In Africa, row crops held the largest share, accounting for 79.2% in 2021. The main reason for holding the major share of row crops is the increasing consumption with an increasing acreage under cultivation.
- South America's hybrid adoption rate is expected to be more than that of open-pollinated seed varieties from 2022 to 2028 because of an increase in the yield by 10-15%, good quality, and better return on investment. Therefore, hybrid seeds are expected to increase by 38.7% from 2021 to 2028.
- The seed market in the Middle East is expected to grow moderately from 2022 to 2028 because of the lower usage of hybrid seeds in the Middle East. The growers are not interested in using transgenic seeds, and to meet domestic demand, they must import about 30-50% of crops from other countries.
Seed Industry Overview
The Seed Market is fragmented, with the top five companies occupying 38.08%. The major players in this market are BASF SE, Bayer AG, Corteva Agriscience, KWS SAAT SE & Co. KGaA and Syngenta Group (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Area Under Cultivation
- 4.2 Most Popular Traits
- 4.3 Regulatory Framework
- 4.4 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Breeding Technology
- 5.1.1 Hybrids
- 5.1.1.1 Non-Transgenic Hybrids
- 5.1.1.2 Transgenic Hybrids
- 5.1.1.2.1 Herbicide Tolerant
- 5.1.1.2.2 Insect Resistant
- 5.1.1.2.3 Other Traits
- 5.1.2 Open Pollinated Varieties & Hybrid Derivatives
- 5.1.1 Hybrids
- 5.2 Cultivation Mechanism
- 5.2.1 Open Field
- 5.2.2 Protected Cultivation
- 5.3 Crop Type
- 5.3.1 Row Crops
- 5.3.1.1 Fiber Crops
- 5.3.1.1.1 Cotton
- 5.3.1.1.2 Other Fiber Crops
- 5.3.1.2 Forage Crops
- 5.3.1.2.1 Alfalfa
- 5.3.1.2.2 Forage Corn
- 5.3.1.2.3 Forage Sorghum
- 5.3.1.2.4 Other Forage Crops
- 5.3.1.3 Grains & Cereals
- 5.3.1.3.1 Corn
- 5.3.1.3.2 Rice
- 5.3.1.3.3 Sorghum
- 5.3.1.3.4 Wheat
- 5.3.1.3.5 Other Grains & Cereals
- 5.3.1.4 Oilseeds
- 5.3.1.4.1 Canola, Rapeseed & Mustard
- 5.3.1.4.2 Soybean
- 5.3.1.4.3 Sunflower
- 5.3.1.4.4 Other Oilseeds
- 5.3.1.5 Pulses
- 5.3.2 Vegetables
- 5.3.2.1 Brassicas
- 5.3.2.1.1 Cabbage
- 5.3.2.1.2 Carrot
- 5.3.2.1.3 Cauliflower & Broccoli
- 5.3.2.1.4 Other Brassicas
- 5.3.2.2 Cucurbits
- 5.3.2.2.1 Cucumber & Gherkin
- 5.3.2.2.2 Pumpkin & Squash
- 5.3.2.2.3 Other Cucurbits
- 5.3.2.3 Roots & Bulbs
- 5.3.2.3.1 Garlic
- 5.3.2.3.2 Onion
- 5.3.2.3.3 Potato
- 5.3.2.3.4 Other Roots & Bulbs
- 5.3.2.4 Solanaceae
- 5.3.2.4.1 Chilli
- 5.3.2.4.2 Eggplant
- 5.3.2.4.3 Tomato
- 5.3.2.4.4 Other Solanaceae
- 5.3.2.5 Unclassified Vegetables
- 5.3.2.5.1 Asparagus
- 5.3.2.5.2 Lettuce
- 5.3.2.5.3 Okra
- 5.3.2.5.4 Peas
- 5.3.2.5.5 Spinach
- 5.3.2.5.6 Other Unclassified Vegetables
- 5.3.1 Row Crops
- 5.4 Region
- 5.4.1 Africa
- 5.4.1.1 By Breeding Technology
- 5.4.1.2 By Cultivation Mechanism
- 5.4.1.3 By Crop
- 5.4.1.4 By Country
- 5.4.1.4.1 Egypt
- 5.4.1.4.2 Ethiopia
- 5.4.1.4.3 Ghana
- 5.4.1.4.4 Kenya
- 5.4.1.4.5 Nigeria
- 5.4.1.4.6 South Africa
- 5.4.1.4.7 Tanzania
- 5.4.1.4.8 Rest of Africa
- 5.4.2 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.2.1 By Breeding Technology
- 5.4.2.2 By Cultivation Mechanism
- 5.4.2.3 By Crop
- 5.4.2.4 By Country
- 5.4.2.4.1 Australia
- 5.4.2.4.2 Bangladesh
- 5.4.2.4.3 China
- 5.4.2.4.4 India
- 5.4.2.4.5 Indonesia
- 5.4.2.4.6 Japan
- 5.4.2.4.7 Myanmar
- 5.4.2.4.8 Pakistan
- 5.4.2.4.9 Philippines
- 5.4.2.4.10 Thailand
- 5.4.2.4.11 Vietnam
- 5.4.2.4.12 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 By Breeding Technology
- 5.4.3.2 By Cultivation Mechanism
- 5.4.3.3 By Crop
- 5.4.3.4 By Country
- 5.4.3.4.1 France
- 5.4.3.4.2 Germany
- 5.4.3.4.3 Italy
- 5.4.3.4.4 Netherlands
- 5.4.3.4.5 Poland
- 5.4.3.4.6 Romania
- 5.4.3.4.7 Russia
- 5.4.3.4.8 Spain
- 5.4.3.4.9 Turkey
- 5.4.3.4.10 Ukraine
- 5.4.3.4.11 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.4.12 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.4 Middle East
- 5.4.4.1 By Breeding Technology
- 5.4.4.2 By Cultivation Mechanism
- 5.4.4.3 By Crop
- 5.4.4.4 By Country
- 5.4.4.4.1 Iran
- 5.4.4.4.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.4.4.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.4.5 North America
- 5.4.5.1 By Breeding Technology
- 5.4.5.2 By Cultivation Mechanism
- 5.4.5.3 By Crop
- 5.4.5.4 By Country
- 5.4.5.4.1 Canada
- 5.4.5.4.2 Mexico
- 5.4.5.4.3 United States
- 5.4.5.4.4 Rest of North America
- 5.4.6 South America
- 5.4.6.1 By Breeding Technology
- 5.4.6.2 By Cultivation Mechanism
- 5.4.6.3 By Crop
- 5.4.6.4 By Country
- 5.4.6.4.1 Argentina
- 5.4.6.4.2 Brazil
- 5.4.6.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.1 Africa
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 Advanta Seeds - UPL
- 6.4.2 BASF SE
- 6.4.3 Bayer AG
- 6.4.4 Corteva Agriscience
- 6.4.5 DLF
- 6.4.6 Groupe Limagrain
- 6.4.7 KWS SAAT SE & Co. KGaA
- 6.4.8 Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel BV
- 6.4.9 Sakata Seeds Corporation
- 6.4.10 Syngenta Group
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SEEDS CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Global Market Size and DROs
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms


