
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1636207
欧州のバイオ医療廃棄物管理:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Europe Bio-Medical Waste Management - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 欧州のバイオ医療廃棄物管理:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年01月05日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 150 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
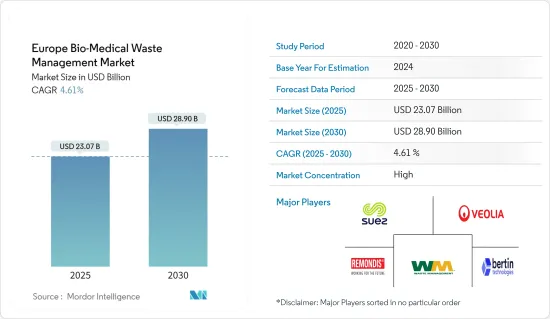
欧州のバイオ医療廃棄物管理の市場規模は2025年に230億7,000万米ドルと推定され、予測期間(2025-2030年)のCAGRは4.61%で、2030年には289億米ドルに達すると予測されます。
欧州のバイオ医療廃棄物管理市場は、厳しい規制措置、ヘルスケア活動の急増、バイオ医療廃棄物の適切な処理への重点化によって拍車がかかり、廃棄物管理産業において極めて重要な役割を果たしています。
欧州の病院では年間約600万トンの医療廃棄物が発生し、その約3分の1は手術室から排出されます。この固形廃棄物のほとんどは、体液で汚染されていない限りリサイクル可能です。感染性廃棄物は病院廃棄物のわずか2~3%で、バイオハザード廃棄物の50~70%に比べればかなり少ないです。
ドイツのヘルスケア産業が排出する廃棄物のうち、特殊な処理を必要とするものはごく一部です。年間約5,000キログラム(最大5%)が感染性廃棄物に該当します。この廃棄物は感染の危険性があるため危険物とみなされ、AVV(Abfallverzeichnisverordnung:廃棄物ディレクトリ規制)に分類されています。
ヘルスケア廃棄物(HCW)の発生率は様々です。廃棄物管理の慣行、ヘルスケア施設の性質とその専門性、再利用可能な器材の有無、1日の患者数などに影響されます。開発途上国では一般的に、登録されたHCW排出量は先進国よりも少ないと報告されています。例えば欧州では、HCW生産量は3.5~4.4kg/床/日であり、ノルウェーは3.9kg/床/日、ギリシャは0.3~3.6kg/床/日、フランスは2.7~3.3kg/床/日です。
欧州のバイオ医療廃棄物管理市場は一貫して成長しているが、これは主にヘルスケア施設、研究センター、診断ラボの拡大による医療廃棄物の増加によるものです。この成長傾向は、特にCOVID-19期間中のヘルスケア需要の急増に後押しされ、効果的なバイオ医療廃棄物管理の重要性が浮き彫りになることで、今後も続くと予想されます。
欧州連合や各国政府のような機関による規制は、公衆衛生と環境保護を重視し、バイオ医療廃棄物の適切な処分と処理の必要性を強調しています。オートクレーブ、焼却、化学処理などの廃棄物処理における技術革新も含め、技術の進歩はバイオ医療廃棄物管理の効率と安全性を高めています。
病院、診療所、調査施設の数が増加し、高齢化も進むにつれて、バイオ医療廃棄物の量も増加しています。さらに、不適切なバイオ医療廃棄物処理に伴うリスクに対する意識の高まりが、専門的な廃棄物管理サービスへの需要に拍車をかけています。
このような高度な廃棄物処理技術や規制遵守は極めて重要であるが、特に小規模のヘルスケア事業体にとっては大きなコストがかかります。廃棄物管理サービスのプロバイダーは、欧州各国に蔓延する複雑で多様な規制をうまく乗り切るという課題に直面しています。
欧州のバイオ医療廃棄物管理市場の動向
バイオ医療廃棄物管理市場は大幅な成長へ
ヘルスケア産業の拡大により、特に開発途上国では医療廃棄物の発生が大幅に増加しています。パンデミック(世界的大流行)時の入院患者数の急増に伴い、バイオ医療廃棄物の発生量は増加の一途をたどっています。典型的な発展途上国では、医療廃棄物の発生量はベッド1台あたり1日平均0.5~2.5kgで、人口統計とヘルスケア・サービスに大きく左右されます。感染症が増加するにつれ、バイオ医療廃棄物管理市場は大幅な成長を遂げようとしています。さらに、微生物学的廃棄物、人体解剖学的廃棄物、動物性廃棄物の蓄積は、この市場をさらに拡大すると思われます。
2004年、WHOの政策文書とストックホルム条約は、重金属、酸性ガス、一酸化炭素、有機化合物、病原体に焦点を当て、ヘルスケア廃棄物の焼却のリスクを強調しました。開発途上国で一般的な方法は、依然として小規模焼却か埋め立てです。対照的に、多くの先進諸国は、ダイオキシンを含まない技術を優先し、医療焼却炉を段階的に廃止しています。特にアイルランド、ポルトガル、ドイツのような国では、二酸化炭素排出削減目標や廃棄物エネルギー化ソリューションへのシフトを背景に、焼却炉を閉鎖するか、モラトリアム(一時停止)措置をとっています。
急速に高齢化が進み、ヘルスケア廃棄物規制が厳しい欧州は、バイオ医療廃棄物管理市場にとって有利な状況を示しています。例えば西欧では、1ベッドあたり3~6kgのバイオ医療廃棄物統計が報告されており、日常的な廃棄物発生量の世界的リーダーとなっています。廃棄物処理インフラがしっかりしており、廃棄物排出量も多いことから、これらの先進地域が世界のバイオ医療廃棄物管理市場を独占することになると思われます。
バイオ医療廃棄物管理市場は、特に発展途上国における医療廃棄物の急増に後押しされ、大幅な成長が見込まれています。さらに、特に欧州などの先進地域では、廃棄物管理における厳しい規制と技術革新が市場の見通しを強めています。
ドイツの高度に規制されたバイオ医療廃棄物処理システム
ドイツは、バイオ医療廃棄物を管理するための高度で厳格な規制システムを誇っています。その中核となるのが廃棄物管理法で、廃棄物の予防、リサイクル、再利用、廃棄を監督しています。さらに、国内のヘルスケア機関は、感染制御と安全に関する義務を遵守しなければならないです。
例えば病院では、廃棄物処理の監督者を任命し、安全性と法的基準の遵守を保証する責任を負う。また、廃棄物処理を施設の品質管理に組み込んでいます。特に、医療廃棄物の75~90%は家庭ごみであり、リサイクルや焼却に適しています。
施設では、針やメスなどの危険物は、耐穿刺性、防漏性、施錠可能な容器で処理します。廃棄物の分別は発生源から開始され、個別の容器や袋がそのプロセスを支援します。病原体汚染に配慮し、廃棄物の処理は専門業者が行っています。
ドイツでは、バイオ医療廃棄物を管理する主な技術として、焼却、化学消毒、湿式熱処理(蒸気滅菌)、マイクロ波照射、土地処分、収益化などがあります。
バイオ医療廃棄物管理に関する国の戦略は、細心の分別、安全な取り扱い、環境に配慮した廃棄方法に重点を置いています。また、リサイクルとコスト効率も重視しています。この包括的なシステムは、医療従事者、一般市民、そして環境を、医療廃棄物に関連するリスクから守ることを目的としています。
厳しい規制と先進技術に支えられたドイツのバイオ医療廃棄物管理システムは、環境と公衆の安全に主眼を置きながら、医療廃棄物の確実な処分とリサイクルを保証しています。
欧州のバイオ医療廃棄物管理産業の概要
欧州のバイオ医療廃棄物管理市場は、市場の集中度が中程度から高水準で、主要企業が優位性を発揮しています。これらの企業は最先端技術を活用し、厳格な規制を遵守し、総合的な廃棄物管理ソリューションを提供しています。主なプレーヤーには、SUEZ Group、Veolia Environmental Services、Remondis Medison、WM Intellectual Property Holdings LLC、Bertin Technologiesなどがあります。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリスト・サポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の成果
- 調査の前提
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場力学
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- ヘルスケアサービス需要の急増
- 外科手術の増加
- 市場抑制要因
- 高い運用コスト
- 市場機会
- 政府はヘルスケアインフラの強化と廃棄物管理プログラムの強化に多額の資金を割り当てています。
- バリューチェーン/サプライチェーン分析
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 買い手/消費者の交渉力
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係
- 市場における技術革新に関する洞察
- 地政学とパンデミックが市場に与える影響
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 廃棄物タイプ別
- 有害
- 非有害
- サービスタイプ別
- 回収
- 輸送と保管
- 処理と処分
- その他のサービスタイプ
- 国別
- ドイツ
- 英国
- フランス
- ロシア
- スペイン
- その他欧州
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度の概要
- 企業プロファイル
- SUEZ Group
- Veolia Environmental Services
- Remondis Medison
- WM Intellectual Property Holdings LLC
- Bertin Technologies
- Cleansing Service Group(CSG)
- Rhenus Group
- Initial Medical Services
- Biffa
- Cannon Hygiene
- Cleanaway
- Grundon Waste Management
- Viridor
第7章 今後の動向
The Europe Bio-Medical Waste Management Market size is estimated at USD 23.07 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 28.90 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.61% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

The European bio-medical waste management market plays a pivotal role in the waste management industry, spurred by strict regulatory measures, a surge in healthcare activities, and an amplified focus on properly disposing of bio-medical waste.
European hospitals generate around 6 million tons of medical waste yearly, about one-third of which originates in operating rooms. Most of this solid waste is potentially recyclable unless contaminated by bodily fluids. Infectious waste, constituting only 2-3% of hospital waste, is significantly less than the 50-70% found in biohazard waste streams.
Germany's healthcare industry generates a small portion of waste that requires specialized handling. Approximately 5,000 kilograms, or up to 5%, of the country's annual healthcare waste falls under the category of infectious waste. This subset is deemed hazardous due to its infection risk and is thus classified under the Abfallverzeichnisverordnung (AVV), or waste directory regulation.
The production rate of healthcare waste (HCW) varies. It is influenced by waste management practices, the nature of healthcare facilities and their specializations, the availability of reusable equipment, and the daily patient load. Developing nations typically report lower registered HCW production than their developed counterparts. For instance, in Europe, HCW production rates range from 3.5 to 4.4 kg/bed/day, with specific figures like Norway at 3.9 kg/bed/day, Greece varying from 0.3 to 3.6 kg/bed/day, and France at 2.7 to 3.3 kg/bed/day.
Europe's bio-medical waste management market is consistently growing, primarily fueled by the mounting medical waste from expanding healthcare setups, research centers, and diagnostic labs. This growth trend is expected to persist, bolstered by the surging healthcare demands, especially during COVID-19, underscoring the criticality of effective bio-medical waste management.
Regulations from entities like the European Union and national governments underscore the need for proper disposal and treatment of bio-medical waste, emphasizing public health and environmental protection. Technological advancements, including innovations in waste treatment like autoclaving, incineration, and chemical treatments, are boosting the efficiency and safety of bio-medical waste management.
As the number of hospitals, clinics, and research facilities rises, along with the aging demographic, the volume of bio-medical waste also increases. Moreover, a heightened awareness of the risks associated with improper bio-medical waste disposal is spurring the demand for professional waste management services.
While these advanced waste treatment technologies and regulatory compliance are crucial, they come at a significant cost, especially for smaller healthcare entities. Waste management service providers face challenges in navigating the intricate and varied regulations prevalent across European nations.
Europe Bio-Medical Waste Management Market Trends
The Bio-medical Waste Management Market is Set for Significant Growth
The healthcare industry's expansion has significantly boosted medical waste generation, especially in developing nations. With the surge in hospital admissions during the pandemic, the production of bio-medical waste is set to escalate. In a typical developing country, the volume of medical waste generated, averaging 0.5-2.5 kg per bed per day, hinges largely on demographics and healthcare services. As infectious diseases increase, the bio-medical waste management market is primed for substantial growth. Furthermore, the mounting accumulation of microbiological, human anatomical, and animal waste will further expand this market.
In 2004, a WHO policy paper and the Stockholm Convention underscored the risks of incinerating healthcare waste, highlighting heavy metals, acid gases, carbon monoxide, organic compounds, and pathogens. The prevalent methods in developing nations remain small-scale incineration or landfilling. In contrast, many developed countries are phasing out healthcare incinerators favoring dioxin-free technologies. Notably, nations like Ireland, Portugal, and Germany have either shuttered incinerators or placed moratoriums on them, driven by their carbon emission reduction goals and a shift toward waste-to-energy solutions, which, in turn, augments the bio-medical waste management market's potential.
With its rapidly aging population and stringent healthcare waste regulations, Europe presents a favorable landscape for the bio-medical waste management market. Western Europe, for instance, reports bio-medical waste statistics of 3-6 kg per bed, making it a global leader in daily waste generation. Given their robust waste disposal infrastructure and higher waste output, these developed regions are poised to dominate the global bio-medical waste management market.
The bio-medical waste management market is poised for substantial growth, fueled by a surge in medical waste, especially in developing nations. Additionally, stringent regulations and technological innovations in waste management, notably in advanced regions such as Europe, are bolstering the market's prospects.
Germany's Highly Regulated System for Handling Bio-medical Waste
Germany boasts a sophisticated and tightly regulated system for managing bio-medical waste. At its core is the Closed Substance Cycle Waste Management Act, which oversees waste prevention, recycling, reuse, and disposal. In addition, healthcare institutions in the country must adhere to infection control and safety mandates.
Hospitals, for instance, appoint a waste disposal overseer responsible for ensuring compliance with safety and legal standards. They also integrate waste disposal into the facility's quality management. Notably, 75-90% of healthcare waste mirrors domestic waste, making it suitable for recycling or incineration via municipal channels.
Facilities handle hazardous items like needles and scalpels in puncture-resistant, leak-proof, and lockable containers. Waste separation begins at the source, with distinct bins and sacs aiding the process. Given its pathogen contamination, specialized companies handle the disposal of this waste.
In Germany, the primary technologies for managing bio-medical waste encompass incineration, chemical disinfection, wet thermal treatment (steam sterilization), microwave irradiation, land disposal, and monetization.
The nation's strategy for bio-medical waste management centers on meticulous segregation, secure handling, and eco-conscious disposal practices. It also underscores recycling and cost-efficiency. This comprehensive system aims to shield healthcare professionals, the public, and the environment from the risks linked to medical waste.
Germany's bio-medical waste management system, supported by stringent regulations and advanced technologies, ensures the secure disposal and recycling of medical waste, with a primary focus on environmental and public safety.
Europe Bio-Medical Waste Management Industry Overview
The European bio-medical waste management market exhibits a moderate to high level of market concentration, with key players wielding dominance. They leverage cutting-edge technologies, adhere to strict regulations, and offer holistic waste management solutions. Some key players are SUEZ Group, Veolia Environmental Services, Remondis Medison, WM Intellectual Property Holdings LLC, and Bertin Technologies.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Deliverables
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
- 1.3 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surging Demand for Healthcare Services
- 4.2.2 Rise in Surgical Procedures
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Operational Costs
- 4.4 Market Opportunities
- 4.4.1 The Government is Allocating Significant Funds to Bolster Healthcare Infrastructure and Enhance Waste Management Programs
- 4.5 Value Chain / Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.6 Porter's Five Force Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.7 Insights on Technology Innovation in the Market.
- 4.8 Impact of Geopolitics and Pandemics on the Market
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Waste Type
- 5.1.1 Hazardous
- 5.1.2 Non-hazardous
- 5.2 By Service Type
- 5.2.1 Collection
- 5.2.2 Transportation and Storage
- 5.2.3 Treatment and Disposal
- 5.2.4 Other Service Types
- 5.3 By Country
- 5.3.1 Germany
- 5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.3 France
- 5.3.4 Russia
- 5.3.5 Spain
- 5.3.6 Rest of Europe
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 SUEZ Group
- 6.2.2 Veolia Environmental Services
- 6.2.3 Remondis Medison
- 6.2.4 WM Intellectual Property Holdings LLC
- 6.2.5 Bertin Technologies
- 6.2.6 Cleansing Service Group (CSG)
- 6.2.7 Rhenus Group
- 6.2.8 Initial Medical Services
- 6.2.9 Biffa
- 6.2.10 Cannon Hygiene
- 6.2.11 Cleanaway
- 6.2.12 Grundon Waste Management
- 6.2.13 Viridor


