
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1851090
スモールセル5Gネットワーク:市場シェア分析、産業動向、統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Small Cell 5G Network - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| スモールセル5Gネットワーク:市場シェア分析、産業動向、統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年06月26日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 120 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
概要
スモールセル5Gネットワーク市場規模は、2025年に65億1,000万米ドルと推定され、予測期間(2025-2030年)のCAGRは32.54%で、2030年には266億3,000万米ドルに達すると予測されます。
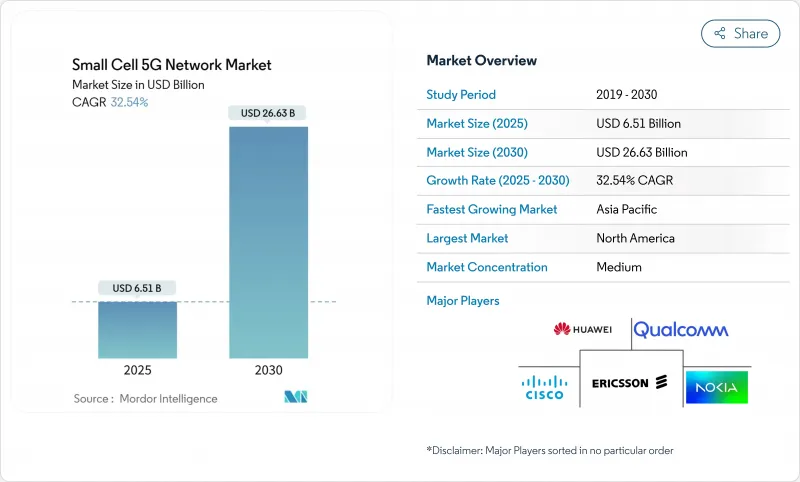
都市回廊で進む高密度化、企業のデジタル化、AIネイティブなネットワーク管理システムの展開により、通信事業者やプライベートネットワークの導入が加速しています。ピコセル、ニュートラルホストモデル、Release-17 NR-U機能は、周波数帯や敷地の制約を緩和することで、対応可能なユースケースを拡大しています。アジア太平洋地域はインフラ規模の拡大で注目を集めているが、北米はインフラをより効率的にプレミアム収入に変換しています。競合ダイナミクスとしては、AI対応チップメーカーやOpen RANのスペシャリストがニッチを切り開く一方で、既存の無線ベンダーがSoftware-Definedアーキテクチャに軸足を移しています。
世界のスモールセル5Gネットワーク市場の動向と洞察
都市部での5G展開における急速な高密度化のニーズ
通信事業者は、密集した都市ではマクロセルだけでは5Gのサービスレベル契約を満たせないことを確認しています。EEは英国全土で1,000以上のスモールセルを稼働させ、ロンドンの25サイトでは毎週7.5TBのデータを移動させ、従来のセクターの混雑を緩和しています。Virgin Media O2は、英国初の5Gスタンドアローン・スモールセルを導入し、マクロサイトでは対応できないネットワーク・スライシングと低遅延を実現した。スモールセル内のフラクショナル周波数再利用は、ARや産業用IoTのようなアップリンクを多用するアプリケーションが主流になるにつれて重要な周波数利用を改善します。自治体はお役所仕事から解放され、世界中で100以上のニュートラルホストが稼動しています。これらの要因が相まって、中期的な高密度化の必要性が高まっています。
企業のプライベートネットワーク需要(製造、物流)
政府の政策とインダストリー4.0のロードマップは、工場やロジスティクスの現場を決定論的な無線接続に向かわせつつあります。中国ではすでに約4,000の5G工場ネットワークが構築されており、2027年までに10,000を目標としています。ノキアは、2024年第4四半期までに5Gの個人顧客を850社数え、1四半期で55社を追加しました。タイの家電工場では、5Gによる自動化で生産性が15~20%向上したと報告されています。現在、欧州の7カ国が26GHz帯の免許を現地で取得し、6カ国が3.4~3.8GHz帯の100MHzを割り当てており、企業にとって周波数帯の調達が容易になっています。スモールセルは、狭いカバレッジ境界を強制し、エッジコンピューティングを統合し、同時ネットワークスライスをサポートするため、無線レイヤーとして依然として好まれています。
郊外や農村地帯におけるファイバー/バックホールの経済性への課題
空中光ファイバーの建設コストは、郊外では1マイルあたり6万米ドルから17万米ドルかかり、人口密度の低い地域では収益が落ち込みます。クラウン・キャッスルは、不利なバックホール計算を認識した後、米国の7,000のスモールセルサイトを棚上げし、将来の資本支出を8億米ドル節約しました。マイクロ波と衛星バックホールは設備投資を削減するが、5Gの容量や遅延の目標にはまだ対応できないです。連邦道路管理局のデータによると、マイクロトレンチを使用しても、郊外ではまだ6~8年の損益分岐点が残っています。そのため、事業者は、次世代ワイヤレスバックホールが商業的に実行可能であることが証明されるまで、収益性の高い大都市圏を超える高密度化を躊躇しています。
セグメント分析
ピコセルは2024年の売上高の41%を占め、混雑した都心部の通路における100~200mのカバレッジゾーンに適していることが確認されました。ピコセルのスモールセル5Gネットワーク市場規模は、ミッドバンドスペクトラムとマルチユーザーMIMOがサイトあたりの容量を増やすにつれて急拡大する傾向にあります。EdgeQのベースステーション・オンチップなどのシリコン・イノベーションは、電力、コスト、設置面積を縮小する統合型AIをもたらします。
フェムトセルは、ニッチな住宅や小規模オフィス向けですが、Wi-Fi 7からのプレッシャーに直面しており、マイクロセルは、ピコセル密度がコスト的に難しい郊外の広い区画をサポートします。Comba TelecomのORAN準拠マイクロ無線ユニットは、標準化されたマルチベンダー・エコシステムへの流れを反映しています。AIを活用した最適化によってフォームファクター間の性能格差が縮まるにつれ、事業者は運用効率を犠牲にすることなく、各サイトの容量要件に柔軟に対応できるようになります。
屋内サイトは2024年の展開の63%を占めたが、これはミッドバンド5Gの信号が最新の建築資材を通してフェードアウトするためです。ニュートラル・ホスト・システムとスマート・ビルディング管理は、オフィス、スタジアム、工場にまたがるサービス品質を求める企業にとって、屋内投資の説得力を維持します。屋外カテゴリーは、自治体による許可の迅速化、Release-17 NR-U、インフラの共有化によって設置の摩擦が軽減され、CAGR 33.01%で加速しています。マンチェスター中心部にあるVirgin Media O2の屋外セルなどの取り組みが、この軸足を強調しています。
Freshwave社は、英国の4つの通信事業者すべてを1つの屋外・屋内スモールセル筐体に統合し、以前のシステムに比べてコストを65%、エネルギーを60%削減しています。屋内プロバイダーは現在、Wi-Fiが及ばない確定的な遅延、セキュリティ、スライス管理を強調することで、理論速度46Gbpsを宣伝するWi-Fi 7を防御しなければならないです。
スモールセル5Gネットワーク市場レポートは、セルタイプ(フェムトセル、ピコセル、マイクロセル、メトロセル)、動作環境(屋内、屋外)、周波数帯(6GHz未満、Mmwave[24 GHz以上]、1GHz未満)、エンドユーザー(通信事業者、企業、住宅)、地域別に分類されています。
地域分析
アジア太平洋は2024年の売上高の38%を占め、2030年までのCAGRは32.60%です。これは中国の440万の5G基地局と、300都市での5G-Advancedオーバーレイに充てられる30億人民元によって推進されます。チャイナユニコム北京とファーウェイは、人口1,000万人規模で11.2Gbpsのダウンリンクピークを達成し、将来の高密度オーバーレイの基準点を設定しました。日本と韓国は企業向けmmWaveを推進し、インドはオークション後に官民パートナーシップによる高密度化の余地を提供しました。
北米は収益実現の効率性を示します。エリクソンの地域別売上高は、AT&Tの140億米ドルの契約を背景に前年比55%増となり、堅調な投資収益を実証しました。米国では50以上のニュートラルホスト・プロジェクトがCBRSで運用されており、カナダのTELUSは初の商用仮想化Open RANを展開し、この地域をクラウドネイティブRAN実験の最前線に位置付けています。しかし、クラウン・キャッスルの導入中止は、郊外における経済性が根強いハードルであることを浮き彫りにしています。
欧州は明確な周波数政策を享受しているが、単体での5Gカバレッジは遅れており、2024年後半までに普及率はわずか2%にしか達していないです。ヴァージン・メディアO2やEEはスモールセルのフットプリントを増強しているが、多くの事業者はデバイスの普及率が上がれば、ビジネス・ケースが変転するのを待っています。中東では、UAEが30.5Gbpsの5G通信速度を記録し、duがハイパースケールデータセンターに20億AEDを投入しました。ラテンアメリカでは、ブラジルのBrisanetとウルグアイのAntelが公共5Gを拡大しているが、マクロ経済の制約と周波数帯の不足がスモールセルの展開を抑制しています。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリストサポート
よくあるご質問
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場の定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- 都市部での5G展開における急速な高密度化ニーズ
- 企業のプライベートネットワーク需要(製造、物流)
- リリース17 5G NR-Uは免許不要のスモールセル・スペクトラムを可能にする
- 規制当局の支持を得るニュートラルホスト・ビジネスモデル
- AIによる自己最適化ネットワークがOpExを削減(過少報告)
- 市場抑制要因
- 郊外や農村地帯におけるファイバー/バックホールの経済的課題
- 自治体の用地取得遅延と手数料
- オープンRANスモールセルをめぐる根強いセキュリティ懸念(過少報告)
- サプライチェーン分析
- 規制情勢
- テクノロジーの展望
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 買い手の交渉力
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 代替品の脅威
- ライバルの激しさ
第5章 市場規模と成長予測
- セルタイプ別
- フェムトセル
- ピコセル
- マイクロセル
- メトロセル
- 使用環境別
- インドア
- アウトドア
- 周波数帯域別
- サブ6 GHz
- mmWave(24GHz以上)
- サブ1 GHz
- エンドユーザー別
- 電気通信事業者
- 企業
- 住宅用
- 地域別
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- メキシコ
- 南米
- ブラジル
- アルゼンチン
- その他南米
- 欧州
- ドイツ
- 英国
- フランス
- ロシア
- その他欧州地域
- アジア太平洋地域
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- 韓国
- その他アジア太平洋地域
- 中東
- サウジアラビア
- アラブ首長国連邦
- トルコ
- その他中東
- アフリカ
- 南アフリカ
- その他アフリカ
- 北米
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度
- 戦略的動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業プロファイル
- Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- Nokia Corporation
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
- ZTE Corporation
- Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd
- Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- Airspan Networks Inc.
- CommScope Inc.
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- NEC Corporation
- Baicells Technologies Co. Ltd
- Qucell Inc.
- JMA Wireless
- Parallel Wireless
- Mavenir Systems
- Casa Systems
- Corning Inc.
- Sercomm Corporation
- Comba Telecom Systems Holdings Ltd
- American Tower Corporation
- Boingo Wireless Inc.


