
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1444670
日本の糖尿病ケア機器:市場シェア分析、業界動向と統計、成長予測(2024-2029)Japan Diabetes Care Devices - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 日本の糖尿病ケア機器:市場シェア分析、業界動向と統計、成長予測(2024-2029) |
|
出版日: 2024年02月15日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 99 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
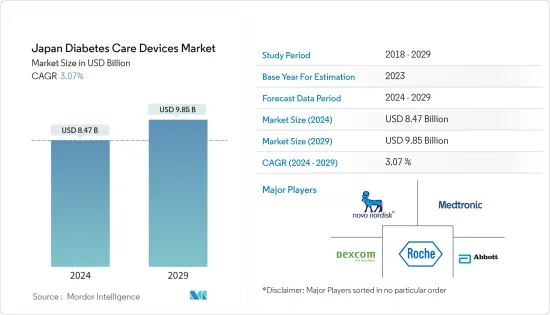
日本の糖尿病ケア機器市場規模は2024年に84億7,000万米ドルと推定され、2029年までに98億5,000万米ドルに達すると予測されており、予測期間(2024年から2029年)中に3.07%のCAGRで成長します。
COVID-19のパンデミックは、糖尿病ケア機器市場に大きな影響を与えています。COVID-19感染症で入院した患者における糖尿病の有病率と、血糖コントロールの改善により、SARS-CoV-2患者の転帰が改善し、入院期間が短縮される可能性があるという認識により、糖尿病治療機器の重要性が強調されています。第81回米国糖尿病協会(ADA)のバーチャル科学セッションで遡及的分析が発表され、糖尿病が日本人のCOVID-19症患者の重症化加速の主な危険因子であることが示された
パンデミックの間中、糖尿病はCOVID-19の重大な危険因子として存続しました。糖尿病とCOVID-19を患う入院患者では、10人に1人が入院後7日以内に死亡しました。
パンデミックはまた、ヘルスケア提供者と糖尿病患者との間の仮想相談や糖尿病テクノロジーの利用を通じて、糖尿病ケアの提供におけるイノベーションを継続および拡大する機会を浮き彫りにしました。危機管理により、患者と医療提供者の両方から遠隔医療に対する前例のない関心が生まれ、長年にわたる多くの規制障壁が取り除かれました。このように、COVID-19感染症の発生により、日本の糖尿病ケア機器市場の成長が加速しました。
糖尿病は世界の流行病として浮上しており、IDF 2021データによると、日本には約1,100万人が糖尿病を患っています。 1型糖尿病は免疫系の機能不全によって引き起こされますが、2型糖尿病は座りっぱなしのライフスタイルを導くことに関連しており、その結果インスリンに対する固有の抵抗力が発現します。したがって、1型糖尿病はインスリン要求性糖尿病として特徴付けられ、2型糖尿病はインスリン依存性糖尿病として特徴付けられます。日本は世界でも有数の高齢者人口を抱えており、2型糖尿病を発症しやすい国です。日本では高齢化が進み、糖尿病の有病率も増加しています。心血管疾患、腎臓障害、その他多くの症状などの悪影響を回避するために、血糖値の監視と管理が増加しています。
日本の糖尿病ケア機器市場動向
継続的グルコースモニタリングセグメントは、予測期間中に最も高い成長率を示すことが予想されます
継続的血糖モニタリングセグメントは、予測期間中に11%以上のCAGRで推移すると予想されます。
CGMを使用するには、皮膚の最上層を貫通する小さなプラスチック製のカニューレを使用して、小さなセンサーを腹部または腕に挿入します。粘着パッチがセンサーを所定の位置に保持し、昼夜を問わず間質液中のグルコースの測定を可能にします。通常、センサーは7~14日ごとに交換する必要があります。センサーに接続された小型の再利用可能な送信機により、システムは血糖データを表示するモニターデバイスにリアルタイムの測定値をワイヤレスで送信できます。専用のモニターを備えたシステムや、スマートフォンのアプリを介して情報を表示するシステムもあります。
連続グルコース監視センサーは、グルコースオキシダーゼを使用して血糖値を検出します。グルコースオキシダーゼはグルコースを水素ペルオキシダーゼに変換し、これがセンサー内のプラチナと反応して、送信機に伝達される電気信号を生成します。センサーは、継続的な血糖値監視装置の最も重要な部分です。研究者たちは、電気化学ベースのグルコースセンサーの代替品を見つけて開発し、より手頃な価格で侵襲性が最小限に抑えられたユーザーフレンドリーなCGMセンサーを作成しようとしています。光学測定は、グルコースセンシングのための有望なプラットフォームです。分光法、蛍光、ホログラフィック技術など、継続的なグルコースセンシングで高い可能性を秘めたいくつかの技術が報告されています。Senseonics Companyが開発した蛍光センシングに基づくCGMセンサーであるEversenseは、電気化学センサーよりもはるかに長い寿命を示します。センサーの精度を向上させる技術の進歩により、予測期間中のセグメントの成長が促進されると予想されます。
血糖値をモニタリングする頻度は糖尿病の種類によって異なり、患者ごとに異なります。 1型糖尿病患者は、血糖値を定期的にチェックして血糖値を監視し、それに応じてインスリン投与量を調整する必要があります。現在のCGMデバイスは、設定された間隔での血糖値の日常的なチェックと比較して、血糖のパターンと傾向を詳細に表示します。さらに、現在の連続血糖監視装置は、データをダウンロードすることで血糖値の動向を遡及的に表示したり、受信機のディスプレイを通じて血糖値のリアルタイム画像を表示したりすることができます。携帯電話の統合などの新技術により、継続的な血糖値モニタリング装置が安価になりつつあります。これは、予測期間中のセグメントの成長を促進する可能性があります。
再利用可能なペン型インスリンカートリッジは、今年度の管理デバイス部門で最高のシェアを占めました
再利用可能なペン型インスリンカートリッジは、今年度の管理デバイス部門で約68%という最高の市場シェアを占めました。これは、インスリンバイアルのアップグレードバージョンです。ほとんどの種類のインスリンはカートリッジの形で製造されているため、簡単に入手できます。これらのデバイスには、再利用可能なペンの機能上の利点がすべて含まれており、長期的にはこれらのカートリッジは使い捨てインスリンペンに比べて安価であるため、費用対効果が高くなります。
インスリンカートリッジの需要の増加により、ほとんどのインスリン装置メーカーは、さまざまなインスリンメーカーのカートリッジと互換性のある再利用可能なインスリンペンを製造しました。これらのインスリンカートリッジは、従来のバイアルと注射器に比べて小さく目立たないため、より消費者に優しいと考えられています。これらのデバイスは消費者にとっても持ち運びが容易です。オープンカートリッジは冷蔵する必要がないため、消費者にとって保管が容易になります。したがって、使い捨てペンとは異なり、再利用可能なペンは一度限りの投資で済むため、カートリッジは最も費用効果の高いインスリンの使用方法です。
糖尿病は厚生労働省によって重点ヘルスケアとして位置づけられています。 2型糖尿病の罹患率の高さは、重大な経済的負担と関連しています。糖尿病の費用は、高血圧や高脂血症などの併存疾患がある患者や合併症を発症した患者では増加します。合併症の数が増えると費用も増加します。日本では、医療保険制度が整備され、糖尿病の医療費は全額負担され、糖尿病患者は自由に医師の診察を受けることができます。また、自己注射によるインスリン療法も合法となり、健康保険が適用されます。このような利点が、これらの製品が日本市場で採用されるのに役立ちました。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3か月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場の定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場力学
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- 市場抑制要因
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 消費者の交渉力
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 代替製品やサービスの脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係の激しさ
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 管理デバイス
- インスリンポンプ
- テクノロジー
- テザー付きインスリンポンプ
- チューブレスインスリンポンプ
- 成分
- インスリンポンプ装置
- インスリンポンプリザーバー
- 輸液セット
- インスリンペン
- 再利用可能なペン型インスリンカートリッジ
- 使い捨てのペン型インスリンカートリッジ
- インスリン注射器
- ジェットインジェクター
- インスリンポンプ
- 監視デバイス
- 血糖の自己モニタリング
- 血糖計デバイス
- 血糖テストストリップ
- ランセット
- 継続的なグルコースモニタリング
- センサー
- 耐久財(受信機および送信機)
- 血糖の自己モニタリング
- エンドユーザー
- 病院・診療所
- ホーム/個人
第6章 市場指標
- 1型糖尿病人口
- 2型糖尿病の人口
第7章 競合情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- Abbott Diabetes Care
- Roche Diabetes Care
- LifeScan(Johnson &Johnson)
- Sanofi
- Medtronic
- Novo Nordisk A/S
- Terumo
- Eli Lilly
- Arkray
- Becton Dickinson
- 企業シェア分析
- Self-monitoring Blood Glucose Devices
- Abbott Diabetes Care
- LifeScan
- Others
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices
- Abbott Diabetes Care
- Medtronic PLC
- Others
- Insulin Devices
- Medtronic
- Novo Nordisk A/S
- Others
- Self-monitoring Blood Glucose Devices
第8章 市場機会と将来の動向
The Japan Diabetes Care Devices Market size is estimated at USD 8.47 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 9.85 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 3.07% during the forecast period (2024-2029).

The COVID-19 pandemic has had a substantial impact on the diabetes care devices market. The prevalence of diabetes in people hospitalized with COVID-19 infection and the recognition that improved glycemic control might improve outcomes and reduce the length of stay in patients with SARS-CoV-2 have underlined the importance of diabetes care devices. A retrospective analysis was presented at the virtual 81st Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association?iR) (ADA) which showed diabetes was the main risk factor for the accelerated advancement to a severe state in Japanese COVID-19 patients.
Throughout the pandemic, diabetes has persisted as a significant risk factor for COVID-19. In hospitalized patients with diabetes and COVID-19, one in 10 people died within seven days of admission.
The pandemic also highlighted opportunities for continuing and expanding innovations in the delivery of diabetes care, through virtual consultations between healthcare providers and people with diabetes, and the use of diabetes technology. Crisis management has created unprecedented interest in remote care from both patients and providers and removed many long-standing regulatory barriers. Thus, the COVID-19 outbreak increased the Japanese diabetes care device market's growth.
Diabetes has emerged as a global epidemic, Japan has around 11 million people with diabetes according to IDF 2021 data. While Type 1 diabetes is caused by an immune system malfunction, Type 2 diabetes is linked to leading a sedentary lifestyle, which results in the development of inherent resistance to insulin. Hence, Type 1 diabetes can be characterized as insulin-requiring, while Type 2 diabetes can be characterized as insulin-dependent diabetes. Japan has one of the largest elderly populations in the world which is more susceptible to the onset of type 2 diabetes. As Japan's population continues to age, the prevalence of diabetes increases as well. The monitoring and management of blood glucose levels are on the rise, to avoid negative consequences, such as cardiovascular diseases, kidney disorders, and many other conditions.
Japan Diabetes Care Devices Market Trends
The continuous glucose monitoring segment is expected to witness the highest growth rate over the forecast period
The continuous glucose monitoring segment is expected to register a CAGR of more than 11% over the forecast period.
To use a CGM, a small sensor is inserted into the abdomen or arm with a tiny plastic cannula penetrating the top skin layer. An adhesive patch holds the sensor in place, allowing it to take glucose readings in interstitial fluid throughout the day and night. Generally, the sensors must be replaced every 7 to 14 days. A small, reusable transmitter connected to the sensor allows the system to send real-time readings wirelessly to a monitor device that displays blood glucose data. Some systems contain a dedicated monitor, and some display the information via a smartphone app.
Continuous glucose monitoring sensors use glucose oxidase to detect blood sugar levels. Glucose oxidase converts glucose to hydrogen peroxidase, which reacts with the platinum inside the sensor, producing an electrical signal to be communicated to the transmitter. Sensors are the most important part of continuous glucose monitoring devices. Researchers are trying to find and develop alternatives to electrochemical-based glucose sensors and create more affordable, minimally invasive, and user-friendly CGM sensors. Optical measurement is a promising platform for glucose sensing. Some technologies with high potential in continuous glucose sensing are reported, including spectroscopy, fluorescence, holographic technology, etc. Eversense, a CGM sensor based on fluorescence sensing developed by Senseonics Company, presents a much longer lifespan than electrochemical sensors. Technological advancements to improve the sensor's accuracy are expected to drive segment growth during the forecast period.
The frequency of monitoring glucose levels depends on the diabetes type, which varies from patient to patient. Type-1 diabetic patients need to check their blood glucose levels regularly to monitor their blood glucose levels and adjust the insulin dosing accordingly. The current CGM devices show a detailed representation of blood glucose patterns and tendencies compared to a routine check of glucose levels at set intervals. Furthermore, the current continuous glucose monitoring devices can either retrospectively display the trends in blood glucose levels by downloading the data or give a real-time picture of glucose levels through receiver displays. Continuous glucose monitoring devices are becoming cheaper with new technologies, like cell phone integration. It is likely to drive the segment growth during the forecast period.
Insulin cartridges in reusable pens occupied the highest share in the management devices segment in the current year
Insulin cartridges in reusable pens occupied the highest market share of about 68% in the management devices segment in the current year.
Insulin cartridges in reusable pens are an upgraded version of insulin vials. Most types of insulins are manufactured in the form of cartridges, making them easily accessible. These devices include all the functional benefits of reusable pens and are cost-effective, as these cartridges are less expensive compared to disposable insulin pens in the long run.
Due to the increasing demand for insulin cartridges, most insulin device manufacturers produced reusable insulin pens compatible with various insulin manufacturers' cartridges. These insulin cartridges are considered more consumer-friendly, as they are smaller and less noticeable than the classic vial-and-syringe. These devices are also more portable for consumers. Open cartridges do not need to be refrigerated, making storage easy for consumers. Thus, cartridges are the most cost-effective insulin use, as reusable pens are a one-time investment, unlike disposable pens.
Diabetes is identified as a healthcare priority by the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare. The high prevalence of type 2 diabetes is associated with a significant economic burden. The costs of diabetes are increased in patients with co-morbidities such as hypertension and hyperlipidemia and in patients who develop complications. Costs increase with an increasing number of complications. Well-organized medical insurance systems cover all medical fees for diabetes mellitus, and people with diabetes can visit doctors freely in Japan. Also, insulin therapy by self-injection became legal and is covered by health insurance. Such advantages helped the adoption of these products in the Japanese market.
Japan Diabetes Care Devices Industry Overview
The Japanese diabetes care devices market is semi-consolidated, with major manufacturers like Roche, Abbott, Novo Nordisk, Dexcom, Medtronic, etc., and other region-specific manufacturers.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products and Services
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Management Devices
- 5.1.1 Insulin Pump
- 5.1.1.1 Technology
- 5.1.1.1.1 Tethered Insulin Pump
- 5.1.1.1.2 Tubeless Insulin Pump
- 5.1.1.2 Component
- 5.1.1.2.1 Insulin Pump Device
- 5.1.1.2.2 Insulin Pump Reservoir
- 5.1.1.2.3 Infusion Set
- 5.1.2 Insulin pens
- 5.1.2.1 Cartridges in Reusable Pens
- 5.1.2.2 Insulin Disposable Pens
- 5.1.3 Insulin Syringes
- 5.1.4 Jet Injectors
- 5.1.1 Insulin Pump
- 5.2 Monitoring Devices
- 5.2.1 Self-monitoring Blood Glucose
- 5.2.1.1 Glucometer Devices
- 5.2.1.2 Blood Glucose Test Strips
- 5.2.1.3 Lancets
- 5.2.2 Continuous Glucose Monitoring
- 5.2.2.1 Sensors
- 5.2.2.2 Durables (Receivers and Transmitters)
- 5.2.1 Self-monitoring Blood Glucose
- 5.3 End User
- 5.3.1 Hospital/Clinics
- 5.3.2 Home/Personal
6 MARKET INDICATORS
- 6.1 Type 1 Diabetes Population
- 6.2 Type 2 Diabetes Population
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 Abbott Diabetes Care
- 7.1.2 Roche Diabetes Care
- 7.1.3 LifeScan (Johnson & Johnson)
- 7.1.4 Sanofi
- 7.1.5 Medtronic
- 7.1.6 Novo Nordisk A/S
- 7.1.7 Terumo
- 7.1.8 Eli Lilly
- 7.1.9 Arkray
- 7.1.10 Becton Dickinson
- 7.2 Company Share Analysis
- 7.2.1 Self-monitoring Blood Glucose Devices
- 7.2.1.1 Abbott Diabetes Care
- 7.2.1.2 LifeScan
- 7.2.1.3 Others
- 7.2.2 Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices
- 7.2.2.1 Abbott Diabetes Care
- 7.2.2.2 Medtronic PLC
- 7.2.2.3 Others
- 7.2.3 Insulin Devices
- 7.2.3.1 Medtronic
- 7.2.3.2 Novo Nordisk A/S
- 7.2.3.3 Others
- 7.2.1 Self-monitoring Blood Glucose Devices


