
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1693945
衛星部品・コンポーネント:市場シェア分析、産業動向、成長予測(2025~2030年)Satellite Parts and Components - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 衛星部品・コンポーネント:市場シェア分析、産業動向、成長予測(2025~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 169 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
概要
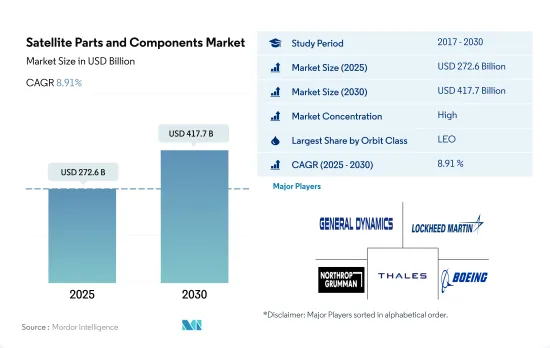
衛星部品・コンポーネント市場規模は2025年に2,726億米ドルと推定され、2030年には4,177億米ドルに達すると予測され、予測期間(2025~2030年)のCAGRは8.91%で成長します。
新しい衛星製造技術の適応が新たなビジネス機会を開くと予想される
- 世界の衛星部品・コンポーネント産業は、近年いくつかの動向を経験しています。技術の進歩に伴い、小型衛星の性能とコスト効率が向上し、様々な用途にとって魅力的な選択肢となっています。衛星の小型化の動向は、推進システム、電力システム、アンテナなどの小型衛星部品・コンポーネントの需要の増加をもたらしました。
- アディティブ・マニュファクチャリング(3Dプリンティング)は、複雑な部品の製造と製造コストの削減が可能なため、衛星産業で人気を集めています。この技術は、アンテナ、ブラケット、エンジン部品などの衛星部品・コンポーネントの製造に利用されています。NASAや欧州宇宙機関といった主要な宇宙機関がそれを強調しています。世界の宇宙産業の主要企業のひとつである米国は、衛星通信、リモートセンシング、宇宙探査のための先端技術開発における動向セッターです。これらの革新的技術には、高性能エレクトロニクス、先進センサ、軽量材料、推進システムなどが含まれます。もうひとつの動向は、衛星の設計・開発において、既存のコンポーネントやサブシステムの商用オフザシェルフ(COTS)の利用が増加していることです。COTSコンポーネントは、信頼性と性能を向上させながら、開発時間とコストを大幅に削減することができます。
- 2017~2022年5月までの間に、世界中で約4,300機以上の衛星が製造され、打ち上げられました。全体として、このような動向は世界の衛星部品・コンポーネント産業の将来を形成しており、各社は絶えず変化する市場の需要に対応しながら、このセグメントの技術革新を推進しています。世界の衛星部品・コンポーネント市場は、2023~2029年にかけて40%の成長が見込まれています。
世界の衛星部品・コンポーネント市場の動向
衛星小型化の重要性の高まりが衛星質量に影響すると予想される
- 最近では衛星の小型化が進んでおり、小型衛星は従来の衛星の数分の一のコストで、従来の衛星ができるほとんどすべてのことができるため、小型衛星コンステレーションの構築、打ち上げ、運用がますます現実的になっています。それに応じて、小型衛星への信頼も飛躍的に高まっています。小型衛星は通常、開発サイクルが短く、開発チームも小規模で、打ち上げコストもはるかに低いです。
- 質量によって大きく分類されるのは、1,000kgを超える大型衛星です。2017~2022年の間に打ち上げられた大型衛星のうち、北米の組織が所有するものは約44機です。中型衛星は質量が500~1,000kg。世界全体では、320機以上の衛星が打ち上げられました。衛星は質量によって分類されます。質量が500kg以下の衛星は小型衛星と呼ばれ、全世界で約3,800機以上の小型衛星が打ち上げられています。
- 開発期間が短く、ミッション全体のコストを削減できることから、この地域では小型衛星への動向が高まっています。小型衛星によって、科学的技術的成果を得るために必要な時間を大幅に短縮することが可能になりました。小型衛星のミッションは柔軟であるため、新たな技術的機会やニーズへの対応も容易です。米国の小型衛星産業は、特定の用途に合わせた小型衛星を設計・製造するための強固な枠組みに支えられています。北米地域における衛星部品・コンポーネントの需要は、商業・軍事宇宙セグメントでの需要増加により、2023~2029年に急増すると予想されています。
様々な宇宙機関の支出の増加は衛星産業にプラスの影響を与えると予想されます。
- 通信、ナビゲーション、地球観測など様々な用途で衛星技術の利用が増加しているため、新しくて革新的な衛星コンポーネントへのニーズが高まっています。各社は、これらの用途に特有の要件を満たす部品を開発するため、研究開発に投資しています。AIや機械学習、積層造形、先端材料の利用といった技術の進歩が、衛星部品・コンポーネント産業における研究開発投資の必要性を後押ししています。こうした進歩は、革新的な部品開発の新たな機会を生み出しています。
- 2022年11月、欧州宇宙機関(ESA)は、地球観測における欧州のリードを維持し、航法サービスを拡大し、米国との探査パートナーであり続けることを目的として、今後3年間で宇宙資金を25%増額することを提案したと発表しました。欧州宇宙機関(ESA)は、2023~2025年にかけての約185億ユーロの予算を支持するよう22カ国に求めています。同様に、フランスは2022年9月、国家と欧州の宇宙プログラムへの支出を増加させる見込みであると発表しました。
- 北米では、宇宙計画のための世界政府支出が2021年に過去最高の約1,030億に達しました。この地域は、世界最大の宇宙機関であるNASAが存在する、宇宙イノベーションと研究の震源地です。2022年、米国政府は宇宙プログラムに約620億米ドルを費やし、世界で最も宇宙開発費を支出する国となりました。米国では、連邦政府機関は毎年政府から資金援助を受けており、その子会社のために323億3,000万米ドルが使われています。宇宙と調査助成金に対する支出はこの地域で急増し、世界経済のあらゆる領域でこのセグメントの重要性が増すと予想されます。
衛星部品・コンポーネント産業概要
衛星部品・コンポーネント市場はかなり統合されており、上位5社で90.12%を占めています。この市場の主要企業は、General Dynamics、Lockheed Martin Corporation、Northrop Grumman Corporation、Thales、The Boeing Companyです。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主要調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 衛星の小型化
- 衛星質量
- 宇宙開発への支出
- 規制の枠組み
- 世界
- オーストラリア
- ブラジル
- カナダ
- 中国
- フランス
- ドイツ
- インド
- イラン
- 日本
- ニュージーランド
- ロシア
- シンガポール
- 韓国
- アラブ首長国連邦
- 英国
- 米国
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 地域
- アジア太平洋
- 欧州
- 北米
- その他
第6章 競合情勢
- 主要な戦略動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- AAC Clyde Space
- BAE Systems
- General Dynamics
- Innovative Solutions in Space BV
- Jena-Optronik
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- OHB SE
- SENER Group
- Sitael S.p.A.
- Thales
- The Boeing Company
第7章 CEOへの主要戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界のバリューチェーン分析
- 市場力学(DROs)
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表一覧
- 主要な洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
目次
Product Code: 50001258
The Satellite Parts and Components Market size is estimated at 272.6 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 417.7 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 8.91% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

The adaptation of new satellite manufacturing techniques is expected to open new scope of opportunities
- The global satellite parts and components industry has been experiencing several trends in recent years. With the advancements in technology, small satellites have become more capable and cost-effective, making them an attractive option for various applications. The trend of satellite miniaturization resulted in an increasing demand for small satellite components, such as propulsion systems, power systems, and antennas.
- Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, has been gaining popularity in the satellite industry due to its ability to produce complex parts and reduce manufacturing costs. This technology is being used to produce satellite components such as antennas, brackets, and engine parts. The major space agencies such as NASA and the European Space Agency have emphasized that. One of the major players in the global space industry, the United States, is a trendsetter in the development of advanced technologies for satellite communications, remote sensing, and space exploration. These innovative technologies include high-performance electronics, advanced sensors, lightweight materials, and propulsion systems. Another trend is the increasing use of pre-existing components and subsystems commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) in satellite design and development. COTS components can significantly reduce development time and costs while improving reliability and performance.
- Between 2017 and May 2022, around 4300+ satellites were manufactured and launched globally. Overall, these trends are shaping the future of the global satellite parts and components industry as companies work to meet the demands of an ever-changing market while also driving innovation in the field. The global satellite parts and components market is expected to grow by 40% between 2023 and 2029.
Global Satellite Parts and Components Market Trends
The increased importance of satellite miniaturization is expected to affect the satellite mass
- Satellites are getting smaller nowadays, and a small satellite can do almost everything that a conventional satellite can at a fraction of the cost of the conventional satellite, which has made the building, launching, and operation of small satellite constellations increasingly viable. Correspondingly, reliance on them has been growing exponentially. Small satellites typically have shorter development cycles, smaller development teams, and cost much less for launch.
- The major classification types according to mass are large satellites that are more than 1,000 kg. During 2017-2022, around 44 large satellites launched were owned by North American organizations. A medium-sized satellite has a mass between 500 and 1000 kg. Globally, organizations operated more than 320 satellites launched. Satellites are classified according to mass. Satellites with a mass of less than 500 kg are considered small satellites, and around 3800+ small satellites were launched globally.
- There is a growing trend toward small satellites in the region because of their shorter development time, which can reduce overall mission costs. They have made it possible to significantly reduce the time required to obtain scientific and technological results. Small spacecraft missions tend to be flexible and can, therefore, be more responsive to new technological opportunities or needs. The small satellite industry in the United States is supported by a robust framework for designing and manufacturing small satellites tailored to serve specific application profiles. The demand for satellite parts and components in the North American region is expected to surge during 2023-2029 due to increasing demand in the commercial and military space sector.
The increasing expenditures of different space agencies is expected to positively impact the satellite industry
- The increasing use of satellite technology in various applications, including communication, navigation, and earth observation, has created a need for new and innovative satellite components. Companies are investing in R&D to develop components that meet the specific requirements of these applications. Technological advancements, such as the use of AI and machine learning, additive manufacturing, and advanced materials, are driving the need for R&D investment in the satellite parts and components industry. These advancements are creating new opportunities for the development of innovative components.
- In November 2022, ESA announced that it proposed a 25% boost in space funding over the next three years designed to maintain Europe's lead in Earth observation, expand navigation services, and remain a partner in exploration with the United States. The European Space Agency (ESA) is asking its 22 nations to back a budget of some EUR 18.5 billion for 2023-2025. Likewise, in September 2022, France announced that it is expecting to increase spending on national and European space programs.
- In North America, global government expenditure for space programs hit a record of approximately 103 billion in 2021. The region is the epicenter of space innovation and research, with the presence of NASA, the world's biggest space agency. In 2022, the US government spent nearly USD 62 billion on its space programs, making it the highest spender on space in the world. In the United States, federal agencies receive aid from the government every year, known as funding, USD 32.33 billion for its subsidiaries. The spending on space and research grants is expected to surge in the region, growing the sector's importance in every domain of the global economy.
Satellite Parts and Components Industry Overview
The Satellite Parts and Components Market is fairly consolidated, with the top five companies occupying 90.12%. The major players in this market are General Dynamics, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Thales and The Boeing Company (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Satellite Miniaturization
- 4.2 Satellite Mass
- 4.3 Spending On Space Programs
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.4.1 Global
- 4.4.2 Australia
- 4.4.3 Brazil
- 4.4.4 Canada
- 4.4.5 China
- 4.4.6 France
- 4.4.7 Germany
- 4.4.8 India
- 4.4.9 Iran
- 4.4.10 Japan
- 4.4.11 New Zealand
- 4.4.12 Russia
- 4.4.13 Singapore
- 4.4.14 South Korea
- 4.4.15 United Arab Emirates
- 4.4.16 United Kingdom
- 4.4.17 United States
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Region
- 5.1.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.1.2 Europe
- 5.1.3 North America
- 5.1.4 Rest of World
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 AAC Clyde Space
- 6.4.2 BAE Systems
- 6.4.3 General Dynamics
- 6.4.4 Innovative Solutions in Space BV
- 6.4.5 Jena-Optronik
- 6.4.6 Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 6.4.7 Northrop Grumman Corporation
- 6.4.8 OHB SE
- 6.4.9 SENER Group
- 6.4.10 Sitael S.p.A.
- 6.4.11 Thales
- 6.4.12 The Boeing Company
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SATELLITE CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms


