|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1684190
個別化がんワクチンの世界市場:市場の機会と臨床試験見通し(2025年)Global Personalized Cancer Vaccine Market Opportunity & Clinical Trials Outlook 2025 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| 個別化がんワクチンの世界市場:市場の機会と臨床試験見通し(2025年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月01日
発行: KuicK Research
ページ情報: 英文 130 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
個別化がんワクチンは、バイオテクノロジーの進歩や標的治療に対する需要の高まりに後押しされ、次世代がん治療法における変革的な力として台頭してきており、商業的な可能性も出てきています。これらのワクチンは、がん治療に対するオーダーメイドのアプローチであり、がん細胞を特異的に標的として排除するワクチンを作るために、患者固有の遺伝的体質を利用します。このアプローチの成功は支持を集めており、個別化がんワクチン市場は2030年までに大きく成長すると予想されています。BioNTech、Moderna、そしてmyNEO Therapeuticsのような中小企業が、COVID-19パンデミックの際に磨かれたmRNA技術の専門知識を駆使して最前線にいます。
個別化がんワクチンの台頭は、個々の患者の特性に合わせた治療を行う精密医療革命によるところが大きいです。これらのワクチンは、従来の治療法よりも特異性や有効性が高いなど、いくつかの利点があります。例えば、BioNTechは、特に製薬大手Genentechとの膵臓がんをターゲットとした共同研究を通じて、個別化mRNAがんワクチンの研究で注目を集めています。この提携は、BioNTechのiNeST技術プラットフォームに基づく自己遺伝子セブメランの開発につながっています。自己遺伝子セブメランは現在、膵管腺がん、メラノーマ、大腸がんを対象とした臨床試験中です。この共同研究は、先進的なmRNA技術と個別化治療を組み合わせることで、これまで治療が困難であったがんに対処できる可能性を示しています。
個別化がんワクチンへの投資も急増しており、ベンチャーキャピタルや製薬会社は新興企業や提携企業に多額の資金を注いでいます。たとえば、MerckとModernaの共同研究はすでに有望な結果を示しており、がんワクチンの将来に対する楽観的な見方が広がっています。しかし、この技術を取り巻く興奮とは裏腹に、課題は残っています。個別化がんワクチンは各個人に合わせたオーダーメイド治療であるため、製造コストは患者1人当たり10万米ドルを超えることもあります。この高コストは、近い将来、こうしたワクチンの普及を制限しかねない大きなハードルのひとつです。
朗報としては、AIによる新抗原選択やロボットによるワクチン合成など、自動化技術の継続的な進歩により、製造コストの長期的な削減が期待されることです。これらの技術革新は、ワクチン開発を合理化し、より幅広い患者層が治療にアクセスできるようにするのに役立つとみられています。さらに、規模の経済が発揮されるにつれ、製造コストは低下し、長期的には個別化がんワクチンの費用対効果が高まることが予想されます。
前述の課題にもかかわらず、個別化がんワクチンは今後数年でがん治療ポートフォリオの要になると予想されます。コンパニオン診断の利用可能性が高まることで、患者選択の精度が向上し、こうしたワクチンの恩恵を受ける可能性が最も高い患者が確実にワクチンを受けられるようになります。これにより、がんの治療方法が再定義され、画一的なモデルから、個別化され、正確で、より効果的なモデルへと移行する可能性があります。
結論として、個別化がんワクチンを取り巻く商業的エコシステムは急速に進化しており、イノベーションと収益性の大きな機会があります。がん治療に革命をもたらすワクチンの有望性は明らかですが、製造、知的財産、償還などの複雑な問題をうまく切り抜けられるかどうかが、その可能性をフルに発揮するための鍵となるでしょう。技術の進歩が続き、この分野が成熟すれば、個別化がんワクチンが標準的な治療選択肢となり、世界中の患者に希望を与え、がん治療の未来を再構築する可能性があります。
当レポートは、世界の個別化がんワクチン市場について調査し、市場の概要とともに、薬剤動向、臨床試験動向、地域別動向、および市場に参入する企業の競合情勢などを提供しています。
目次
第1章 次世代免疫療法アプローチとしての個別化がんワクチン
第2章 個別化がんワクチンの作用機序
- 腫瘍新抗原とヒト白血球抗原の役割
- 個別化がんワクチンの作用メカニズム
- 薬理ゲノム学における遺伝子多型
- がん薬理ゲノム学と体細胞変異
第3章 個別化ワクチンにおけるバイオマーカーの役割
- 薬理ゲノムバイオマーカー
- 予後および予測バイオマーカー
第4章 Provenge-初めて承認された個別化がんワクチン
- 概要と特許情報
- 価格と投与量の洞察
第5章 個別化がんワクチン開発者、適応症、相別の臨床的洞察
第6章 現在の臨床開発と将来の商業化の見通し
- 現在の市場開拓シナリオ
- 今後の市場見通し
第7章 個別化がんワクチンの臨床傾向と開発適応症別の洞察
- 悪性黒色腫
- 肺がん
- 乳がん
- 前立腺がん
- 消化器がん
- 婦人科がん
- 脳腫瘍
- 造血悪性腫瘍
第8章 地域別の個別化がんワクチンの臨床および市場洞察
- 米国
- 欧州連合
- 中国
- インド
- オーストラリア
- 韓国
- 台湾
- 英国
第9章 個別化がんワクチンの独自開発プラットフォーム
第10章 個別化がんワクチン市場力学
- 市場促進要因と機会
- 市場の課題と抑制要因
第11章 競合情勢
- BioNtech AG
- CureVac AG
- Evaxion Biotech
- Geneos Therapeutics
- Genentech
- Merck
- Moderna Therapeutics
- NeoCura
- Transgene
- TuHURA Biosciences
List of Figures
- Figure 1-1: Cancer Vaccine Types
- Figure 1-2: Advantages Of Targeting Neoantigens In Cancer Vaccine Development
- Figure 2-1: Personalized Cancer Vaccine - Mechanism
- Figure 2-2: Demonstrating Genomic Polymorphism In Pharmacogenomics
- Figure 2-3: Source of Pharmacological & Pharmacogenetic Variability
- Figure 3-1: Biomarkers In Personalized Medicine
- Figure 3-2: Roadmap For Developing Predictive Biomarkers
- Figure 4-1: Provenge - Approval Year By Region
- Figure 4-2: Provenge - Cost Per Unit & Supply (US$), March'2025
- Figure 6-1: Global Personalized Cancer Vaccines Market - Future Outlook
- Figure 7-1: KEYNOTE-942 Phase 2 Study (NCT03897881) - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 7-2: BNT111-01 Phase 2 Study (NCT04526899) - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 7-3: KEYNOTE-D36 Phase 2 Study (NCT05309421) - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 7-4: MC210102 Phase 1 Study (NCT05269381) - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 7-5: INTerpath-002 Phase 3 Study (NCT06077760) - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 7-6: INTerpath-009 Phase 3 Study (NCT06623422) - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 7-7: KEYNOTE-603 Phase 1 Study (NCT03313778) - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 7-8: MCC-20915 Phase 2 Study (NCT05325632) - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 7-9: FK-PC101-01 Phase 2 Study (NCT06636682) - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 7-10: 19-039 Phase 1 Study (NCT04161755) - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 7-11: IMCODE003 Phase 2 Study (NCT05968326) - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 7-12: GT-30 Phase 1/2 Study (NCT04251117) - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 7-13: QUILT 502 Phase 1/2 Study (NCT06253494) - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 9-1: BioNTech - iNeST
- Figure 9-2: BioVaxys - DPX & Haptenix Platforms
- Figure 9-3: CureVac - proprietary mRNA technology
- Figure 9-4: Evaxion -Proprietary Technologies
- Figure 9-5: Geneos - GT-EPIC Platform
- Figure 9-6: Moderna - mRNA Design Studio Features
- Figure 9-7: myNEO Therapeutics - ImmunoEngine
- Figure 9-8: Nouscom - Unnamed Technology
- Figure 9-9: Nykode Therapeutics - Vaccibody Structure
- Figure 9-10: Nykode Therapeutics - Vaccibody Mechanism Of Action
- Figure 9-11: Transgene - myvac Platform
- Figure 10-1: Global Personalized Cancer Vaccines Market - Drivers & Opportunities
- Figure 10-2: Global Personalized Cancer Vaccines Market - Challenges & Restraints
List of Tables
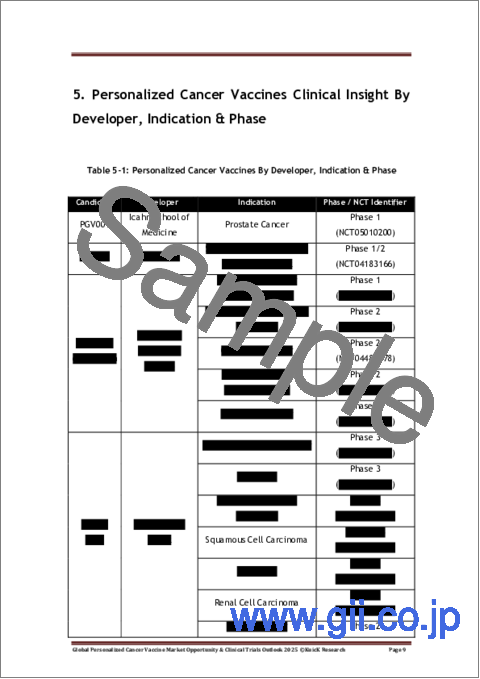
- Table 5-1: Personalized Cancer Vaccines By Developer, Indication & Phase
- Table 7-1: Melanoma - Personalized Vaccines In Clinical Trials
- Table 7-2: Lung Cancer - Personalized Vaccines In Clinical Trials
- Table 7-3: Breast Cancer - Personalized Vaccines In Clinical Trials
- Table 7-4: Prostate Cancer - Personalized Vaccines In Clinical Trials
- Table 7-5: Gastrointestinal Cancer - Personalized Vaccines In Clinical Trials
- Table 7-6: Gynecological Cancer - Personalized Vaccines In Clinical Trials
- Table 7-7: Brain Cancer - Personalized Vaccines In Clinical Trials
- Table 7-8: Hematological Malignancies - Personalized Vaccines In Clinical Trials
Global Personalized Cancer Vaccine Market Opportunity & Clinical Trials Outlook 2025 Report Highlights & Findings:
- Commercially Approved Personalized Cancer Vaccine: Provenge
- Provenge Patent , Price & Dosage Insight
- Global Clinical Research Trends By Region & Indication
- Insight On More Than 18 Personalized Cancer Vaccines In Clinical Trials
- Personalized Cancer Vaccines Clinical Insight By Developer, Indication & Phase
- Insight On Key Personalized Cancer Vaccines Proprietary Development Platforms
- Competitive Landscape
Personalized cancer vaccines are emerging as a transformative force in next generation cancer treatment methodology, with emergent commercial potential fueled by advancements in biotechnology and an increasing demand for targeted therapies. These vaccines represent a tailored approach to cancer treatment, utilizing a patient's unique genetic makeup to craft vaccines that specifically target and eliminate cancer cells. The success of this approach is gaining traction, and the market for personalized cancer vaccines is expected to grow significantly by 2030. Companies like BioNTech, Moderna, and smaller players such as myNEO Therapeutics are at the forefront, using their expertise in mRNA technology, which was initially honed during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The rise of personalized cancer vaccines is largely driven by the precision medicine revolution, which tailors treatments to individual patient characteristics. These vaccines offer several advantages over traditional therapies, including greater specificity and efficacy. BioNTech, for example, has gained attention for its work on personalized mRNA cancer vaccines, particularly through its collaboration with pharmaceutical giant Genentech to target pancreatic cancer. This partnership has led to the development of autogene cevumeran, which is based on BioNTech's iNeST technology platform. Autogene cevumeran is currently being tested in clinical trials for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, melanoma, and colorectal cancer. The collaboration demonstrates the potential of combining advanced mRNA technology with personalized treatments to address cancers that have historically been difficult to treat.
Investment in personalized cancer vaccines is also soaring, with venture capital firms and pharmaceutical companies pouring significant funds into startups and partnerships. The collaboration between Merck and Moderna, for example, has already demonstrated promising results, contributing to the growing optimism around the future of cancer vaccines. However, despite the excitement surrounding the technology, challenges remain-particularly in manufacturing. Since personalized cancer vaccines are bespoke treatments tailored to each individual, production costs can exceed $100,000 per patient. This high cost is one of the major hurdles that could limit the widespread adoption of these vaccines in the near term.
The good news is that ongoing advancements in automation technologies, including AI-driven neoantigen selection and robotic vaccine synthesis, are expected to reduce production costs over time. These innovations will help streamline vaccine development and make the treatment more accessible to a broader patient population. Furthermore, as economies of scale come into play, the cost of production is likely to decrease, helping to make personalized cancer vaccines more cost-effective in the long term.
Despite the aforementioned challenges, personalized cancer vaccines are anticipated to become a cornerstone of oncology treatment portfolios in the coming years. The increasing availability of companion diagnostics will help refine patient selection, ensuring that those most likely to benefit from these vaccines receive them. This could potentially redefine how cancers are treated, shifting from a one-size-fits-all model to one that is personalized, precise, and more effective.
In conclusion, the commercial ecosystem surrounding personalized cancer vaccines is evolving rapidly, with significant opportunities for innovation and profitability. The promise of these vaccines to revolutionize cancer treatment is clear, but successful navigation of the complexities of manufacturing, intellectual property, and reimbursement will be key to realizing their full potential. As technology continues to advance and the field matures, personalized cancer vaccines could become a standard treatment option, offering hope for patients worldwide and reshaping the future of cancer care.
Table of Contents
1. Personalized Cancer Vaccines As Next Generation Immunotherapeutic Approach
- 1.1 Approach To Cancer Vaccine Strategy
- 1.2 Cancer Vaccines - Current Progress & Challenges
2. Personalized Cancer Vaccine Mechanism Of Action
- 2.1 Role of Tumor Neoantigens & Human Leukocyte Antigen
- 2.2 Personalized Cancer Vaccine Working Mechanism
- 2.3 Genetic Polymorphism In Pharmacogenomics
- 2.4 Cancer Pharmacogenomics & Somatic Mutations
3. Role of Biomarkers In Personalized Vaccines
- 3.1 Pharmacogenomic Biomarkers
- 3.2 Prognostic & Predictive Biomarkers
4. Provenge - 1st Approved Personalized Cancer Vaccine
- 4.1 Overview & Patent Insight
- 4.2 Pricing & Dosing Insight
5. Personalized Cancer Vaccines Clinical Insight By Developer, Indication & Phase
6. Current Clinical Development & Future Commercialization Outlook
- 6.1 Current Market Development Scenario
- 6.2 Future Market Outlook
7. Personalized Cancer Vaccines Clinical Tends & Developments Insight By Indication
- 7.1 Melanoma
- 7.2 Lung Cancer
- 7.3 Breast Cancer
- 7.4 Prostate Cancer
- 7.5 Gastrointestinal Cancers
- 7.6 Gynecological Cancers
- 7.7 Brain Tumor
- 7.8 Hematological Malignancies
8. Personalized Cancer Vaccines Clinical & Market Insight By Region
- 8.1 US
- 8.2 EU
- 8.3 China
- 8.4 India
- 8.5 Australia
- 8.6 South Korea
- 8.7 Taiwan
- 8.8 UK
9. Personalized Cancer Vaccines Proprietary Development Platforms
- 9.1 BioNTech - iNeST
- 9.2 BioVaxys - DPX & Haptenix Platforms
- 9.3 CureVac - proprietary mRNA technology
- 9.4 Evaxion - PIONEER & ObsERV Technologies
- 9.5 Geneos - GT-EPIC(TM) platform
- 9.6 Moderna - mRNA Design Studio
- 9.7 myNEO Therapeutics - ImmunoEngine
- 9.8 Nouscom - Unnamed Technology
- 9.9 Nykode Therapeutics - Vaccibody
- 9.10 Transgene - myvac
10. Personalized Cancer Vaccine Market Dynamics
- 10.1 Market Drivers & Opportunities
- 10.2 Market Challenges & Restraints
11. Competitive Landscape
- 11.1 BioNtech AG
- 11.2 CureVac AG
- 11.3 Evaxion Biotech
- 11.4 Geneos Therapeutics
- 11.5 Genentech
- 11.6 Merck
- 11.7 Moderna Therapeutics
- 11.8 NeoCura
- 11.9 Transgene
- 11.10 TuHURA Biosciences