|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1469300
PLK標的治療の世界市場:市場機会、臨床試験動向(2024年)Global PLK Targeted Therapies Market Opportunity & Clinical Trials Insight 2024 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| PLK標的治療の世界市場:市場機会、臨床試験動向(2024年) |
|
出版日: 2024年04月01日
発行: KuicK Research
ページ情報: 英文 84 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
ポロ様キナーゼ(PLK)は、セリン/スレオニンキナーゼの一群で、細胞周期の調節、有糸分裂、DA損傷応答、細胞質分裂など、様々な細胞プロセスにおいて重要な役割を果たしています。これらの重要なプロセスにおける役割から、PLKはがんや他の疾患における有望な治療標的として浮上してきました。PLK標的治療の市場はまだ初期段階にあるが、いくつかの製薬会社は様々な一般的疾患の治療を改善する目的で、その研究に投資しています。
PLKは、有糸分裂、中心体成熟、紡錘体形成、染色体分離、細胞質分裂など、細胞周期のいくつかの段階を制御しています。また、DNA損傷応答やチェックポイント制御システムにも関与しています。PLKの過剰発現と調節異常は様々なタイプのがんで観察されており、制御不能な細胞増殖、ゲノム不安定性、化学療法や放射線療法に対する抵抗性の一因となっています。PLKを阻害すると、有糸分裂のカタストロフィーが誘導され、がん細胞では細胞周期の停止とアポトーシスが引き起こされます。
また、PLKが免疫細胞の機能と炎症の制御に関与している可能性を示唆する証拠も出てきており、ループス、関節リウマチ、多発性硬化症などの自己免疫疾患の潜在的な標的となっています。さらに、ヒト免疫不全ウイルス(HIV)やB型肝炎ウイルス(HBV)のように、宿主のPLKをハイジャックして複製や発症を行うウイルスもあり、PLKを標的とした治療が、これらのプロセスを抑制することによって抗ウイルス効果を発揮する可能性が示唆されています。
今後、製薬業界におけるPLK標的治療の将来は有望です。継続的な研究開発、新しい創薬技術、臨床の進歩により、有効性と安全性を高めた次世代のPLK標的治療の開発が推進されるとみられています。PLK阻害剤は、治療効果を向上させ、耐性メカニズムを克服するために、他の抗がん剤と併用される可能性があります。さらに、様々ながんや疾患の遺伝的・分子的プロファイルの理解が進むにつれて、PLK標的治療はバイオマーカーや遺伝的フィンガープリントを用いて特定の患者集団にカスタマイズされる可能性があります。
当レポートは、世界のPLK標的治療市場について調査し、市場の概要とともに、薬剤動向、臨床試験動向、地域別動向、および市場に参入する企業の競合情勢などを提供しています。
目次
第1章 調査手法
第2章 PLK標的治療のイントロダクション
第3章 PLK標的治療の臨床アプローチ
- 低分子阻害剤
- RNA干渉
- アンチセンスオリゴヌクレオチド
- PROTAC分解剤
第4章 PLK標的治療の臨床応用、適応症別
- がん
- 微生物感染症
- 自己免疫疾患
第5章 PLK標的治療の併用戦略
- 化学療法との併用
- 免疫療法との併用
- 標的療法との併用
第6章 PLK標的治療市場概要
- 現在の市場動向
- 今後の商業化の見通し
第7章 PLK標的治療市場力学
- 市場の促進要因と機会
- 市場の課題と抑制要因
第8章 世界のPLK標的治療の臨床試験の概要
- 相別
- 国別
- 企業別
- 適応症別
- 優先度別
- 患者セグメント
第9章 PLK標的治療の臨床試験に関する企業、国、適応症別の考察
- 研究
- 前臨床
- 第I相
- 第I/II相
- 第II相
- 第III相
第10章 競合情勢
- Biogenera
- Boehringer Ingelheim
- Cardiff Oncology
- Cyclacel Pharmaceutical
- Korea United Pharm
- ORIC Pharmaceuticals
- Pdx Pharmaceuticals
- Repare Therapeutics
- SillaJen Biotherapeutics
- Treadwell Therapeutics
List of Figures
- Figure 2-1: Some Biological Functions of PLKs
- Figure 2-2: PLK-Targeted Therapies - Chronology of Events
- Figure 4-1: Rigosertib Early Phase 1 (NCT04177498) Study - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 4-2: Rigosertib Phase 1/2a (NCT04263090) Study - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 4-3: Rigosertib Phase 2 (NCT05764395) Study - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 4-4: Onvansertib Phase 2 (NCT06106308) Study - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 4-5: Onvansertib Phase 2 (NCT05450965) Study - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 4-6: Onvansertib Phase 1 (NCT05549661) Study - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 4-7: Ocifisertib Phase 1/2 (NCT04730258) Study - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 4-8: Ocifisertib Phase 2 (NCT03624543) Study - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 4-9: Ocifisertib Phase 1 (NCT03187288) Study - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 4-10: RP-1664 Phase 1 (NCT06232408) Study - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 4-11: Plogosertib Phase 1 (NCT05358379) Study - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 4-12: BAL0891 Phase 1 (NCT05768932) Study - Initiation & Completion Year
- Figure 6-1: PLK Targeted Therapies - Future Opportunities
- Figure 7-1: PLK Targeted Therapies Market - Drivers & Opportunities
- Figure 7-2: PLK Targeted Therapies Market - Challenges & Restraints
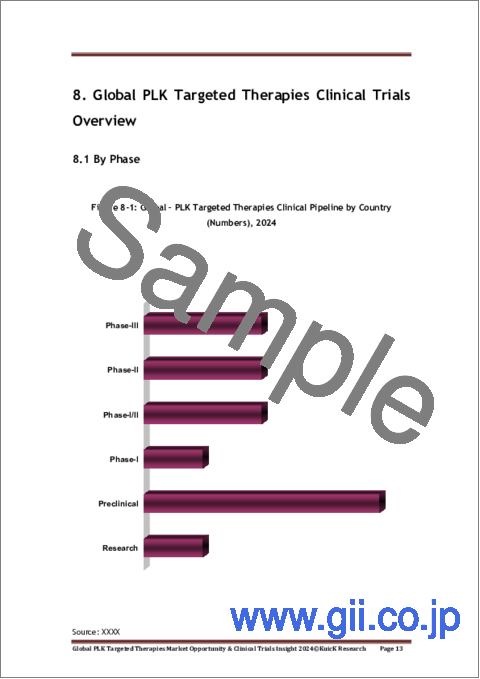
- Figure 8-1: Global - PLK Targeted Therapies Clinical Pipeline by Country (Numbers), 2024
- Figure 8-2: Global - PLK Targeted Therapies Clinical Pipeline by Country (Numbers), 2024
- Figure 8-3: PLK Targeted Therapies Clinical Pipeline by Company (Numbers), 2024
- Figure 8-4: Global - PLK Targeted Therapies Clinical Pipeline by Indication (Numbers), 2024
- Figure 8-5: Global - PLK Targeted Therapies Clinical Pipeline by Fast Track Designation (Numbers), 2024
- Figure 8-6: Global - PLK Targeted Therapies Clinical Pipeline by Patient Segment (Numbers), 2024
List of Tables
- Table 5-1: PLK Inhibitor & Chemotherapy Combinations in Clinical Trials, April'2024
Global PLK Targeted Therapies Market Opportunity & Clinical Trials Insight 2024 Report Highlights:
- PLK Targeted Therapies In Clinical Trials: > 10 Therapies
- USA Domination PLK Therapies Clinical Development Landscape: > 5 Therapies
- Breast Cancer Targeted Therapies In Clinical Trials: > 5 Therapies
- PLK Targeted Therapies Clinical Trials Insight By Company, Country, Indication & Phase
- Insight On Key Companies Involved In Development Of PLK Therapies
- PLK Targeted Therapy Combination Strategies With Chemotherapies, Immunotherapies & Targeted Therapies
Polo-like kinases (PLKs) are a group of serine/threonine kinases that play important roles in a variety of cellular processes, including cell cycle regulation, mitosis, DA damage response, and cytokinesis. Because of their role in these crucial processes, PLKs have emerged as promising therapeutic targets in cancer and other diseases. Though the market for PLK targeted therapies is still in its early stages, several pharmaceutical companies are investing in their research with the objective of improving the treatment of a variety of common ailments.
PLKs regulate several stages of the cell cycle, including mitosis, centrosome maturation, spindle assembly, chromosomal segregation, and cytokinesis. They also take part in DNA damage response and checkpoint control systems. Overexpression and dysregulation of PLKs have been observed in various types of cancer, contributing to uncontrolled cell proliferation, genomic instability, and resistance to chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Inhibition of PLKs can induce mitotic catastrophe, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in cancer cells.
Emerging evidence also suggests that PLKs may be involved in the regulating of immune cell function and inflammation, making them potential targets for autoimmune diseases such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis. Further, some viruses, like human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and hepatitis B virus (HBV), hijack host PLKs for their replication and pathogenesis, suggesting that PLK targeted therapies may have antiviral effects by dampening these processes.
As a result of these growing investigations, various small molecule inhibitors of PLKs have been found and are being developed, with some currently in clinical trials. Onvansertib, a PLK1 inhibitor developed by Cardiff Oncology, is currently the most advanced candidate in clinical trials. Onvansertib is being studied in a phase 2 trial to determine its safety and efficacy in patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC) who have not responded to or are unable to tolerate chemotherapy. Aside from being researched in several solid malignancies, Onvansertib is currently undergoing a phase 1 trial to determine its efficacy and safety in the treatment of patients with recurrent or refractory chronic myelomonocytic leukemia.
Other candidates in the pipeline include RP-1664 and BAL0891, which are being assessed in solid cancers and CFI-400945, being studied for various hematological cancers. The progression of these candidates through the pipeline reflects the growing interest and confidence in PLK targeted therapies.
In addition to small molecule inhibitors, antisense oligonucleotides and PROTACs (proteolysis-targeting chimeras) are being investigated as potential PLK targets. Antisense oligonucleotides can selectively reduce PLK mRNA expression, whereas PROTACs cause proteasomal breakdown of PLK proteins, providing alternative methods to conventional kinase inhibitors. While these methods have shown promise in research and preclinical trials, their clinical implementation has proven difficult for a variety of reasons. However, ongoing research seeks to create more selective and powerful alternatives with better safety profiles.
As interest in PLK targeted therapies grows, pharmaceutical companies will have an opportunity to create and commercialize innovative PLK inhibitors or other PLK-targeting modalities. PLK inhibitors, degraders, and silencers have the potential to meet unmet medical needs in cancer, autoimmune disorders, and viral diseases, making them a valuable market opportunity. Established pharmaceutical corporations may seek alliances and partnerships with academic institutions or biotech companies to work on PLK targeted therapies, leveraging their experience and accelerating the development of novel treatments.
Looking ahead, the future of PLK targeted therapies in the pharmaceutical sector is promising. Continued research efforts, novel drug discovery techniques, and clinical advances will propel the development of next-generation PLK targeted therapies with enhanced efficacy and safety profiles. PLK inhibitors may be used in combination with other anticancer treatments to improve therapeutic efficacy and overcome resistance mechanisms. Furthermore, as our understanding of the genetic and molecular profiles of various cancers and disorders grows, PLK-targeted therapies may be customized to specific patient populations using biomarkers or genetic fingerprints.
In conclusion, PLK targeted therapies are a rapidly developing field with revolutionary promise across a wide range of disease areas. While significant progress has been made in the development of small molecule inhibitors and alternative modalities targeting PLKs, ongoing research and clinical trials are required to address challenges and unlock the full potential of this promising therapeutic approach. As research progresses and clinical data accumulate, the pharmaceutical industry is poised to capitalize on the therapeutic promise of PLK inhibition, shaping the future landscape of precision medicine and patient care.
Table of Contents
1. Research Methodology
2. Introduction to PLK Targeted Therapy
- 2.1 Overview
- 2.2 Development & Evolution
3. PLK Targeted Therapy Clinical Approaches
- 3.1 Small Molecule Inhibitors
- 3.2 RNA Interference
- 3.3 Antisense Oligonucleotides
- 3.4 PROTAC Degraders
4. PLK Targeted Therapy Clinical Application by Indication
- 4.1 Cancer
- 4.1.1 Overview
- 4.1.2 Ongoing Research & Development
- 4.2 Microbial Infections
- 4.3 Autoimmune Diseases
5. PLK Targeted Therapy Combination Strategies
- 5.1 Combination with Chemotherapies
- 5.2 Combination with Immunotherapies
- 5.3 Combination with Targeted Therapies
6. PLK Targeted Therapies Market Overview
- 6.1 Current Market Trends
- 6.2 Future Commercialization Outlook
7. PLK Targeted Therapies Market Dynamics
- 7.1 Market Drivers & Opportunities
- 7.2 Market Challenges & Restraints
8. Global PLK Targeted Therapies Clinical Trials Overview
- 8.1 By Phase
- 8.2 By Country
- 8.3 By Company
- 8.4 By Indication
- 8.5 By Priority Status
- 8.6 Patient Segment
9. PLK Targeted Therapies Clinical Trials insight By Company, Country & Indication
- 9.1 Research
- 9.2 Preclinical
- 9.3 Phase I
- 9.4 Phase I/II
- 9.5 Phase II
- 9.6 Phase III
10. Competitive Landscape
- 10.1 Biogenera
- 10.2 Boehringer Ingelheim
- 10.3 Cardiff Oncology
- 10.4 Cyclacel Pharmaceutical
- 10.5 Korea United Pharm
- 10.6 ORIC Pharmaceuticals
- 10.7 Pdx Pharmaceuticals
- 10.8 Repare Therapeutics
- 10.9 SillaJen Biotherapeutics
- 10.10 Treadwell Therapeutics