|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1448840
AIとRAN:どれだけの速度で動いているのか?AI and RAN - How Fast Will They Run? |
||||||
|
|||||||
| AIとRAN:どれだけの速度で動いているのか? |
|
出版日: 2024年03月11日
発行: Insight Research Corporation
ページ情報: 英文 169 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
当レポートでは、人工知能 (AI) と無線アクセスネットワーク (RAN) の融合点を掘り下げ、両者の進化する関係性に光を当て、将来の軌道を予測しています。
サンプルビュー
図1-1:RAN向けAIの最終用途:収益シェアの推移
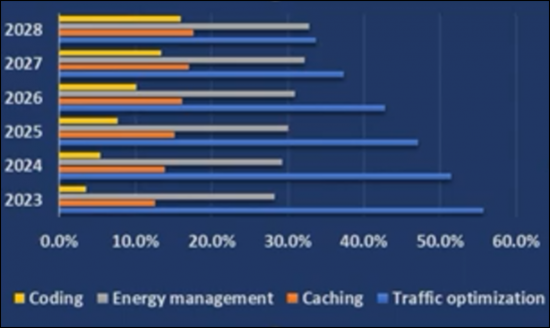
出典:Insight Research
近年、AIは業界全体のイノベーションを推進する極めて重要な力として浮上しています。特に電気通信分野では、RANアーキテクチャへのAIの統合による変革的な影響を目の当たりにしています。当レポートでは、この相乗効果を探り、両者の融合の背後にあるダイナミクスと通信業界への影響を明らかにしています。
分析概要
- RAN向けAIのアドレッサブル市場 (獲得可能な市場規模) は、2023年から2028年にかけて毎年45%という驚異的な成長を遂げます。
- 5G RANにおけるAIのアドレッサブル市場は、それ以前の電話通信の世代よりも急速に成長します。
- アジア太平洋地域が、RANキャッシュ・アプリケーション向けAIの最大市場となります。
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第2章 AI/ML/DL:主要な概念の説明
- 人工知能 (AI)
- 機械学習 (ML)
- 教師あり機械学習
- 教師なし機械学習
- 強化された機械学習
- k近傍法
- ディープラーニング・ニューラルネットワーク (DLNN)
- 注目すべきML・DLアルゴリズム
- 異常検出
- 人工ニューラルネットワーク (ANN)
- バグングされた決定木
- CART・SVMアルゴリズム
- クラスタリング
- 条件付き変分オートエンコーダ
- 畳み込みニューラルネットワーク
- 相関・クラスタリング
- 進化アルゴリズムと分散学習
- フィードフォワード・ニューラルネットワーク (FNN)
- グラフニューラルネットワーク (GNN)
- ハイブリッドコグニティブエンジン (HCE)
- カルマンフィルター
- マルコフの意思決定プロセス
- 多層パーセプトロン (MLP)
- 単純ベイズ
- 放射基底関数
- ランダムフォレスト
- 再起型ニューラルネットワーク
- 強化型ニューラルネットワーク
- SOMアルゴリズム
- スパースベイズ学習
第3章 RANの仮想化
- RANとその進化
- E-UTRANの詳細
- 5G-NR、NSA、SA
- MEC
- リジッドCPRI
- RANからvRANへの進化
- VMベースのvRANとコンテナベースのvRANを比較する方法は?
- NFVのアーキテクチャ
- コンテナの必要性
- マイクロサービス
- コンテナの形態
- コンテナの導入方法
- ステートフルコンテナとステートレスコンテナ
- アドバンテージコンテナ
- コンテナが直面する課題
- RAN仮想化:アライアンスの物語
- O-RANアーキテクチャの概要
- O-RANの歴史
- O-RANのワークグループ
- オープンvRAN (O-vRAN)
- TIP (通信インフラプロジェクト) OpenRAN
第4章 RANにおけるAIの最終用途
- O-RANとAI
- イントロダクション
- RIC、xApp、rApp
- WG2とML
- AIの利用事例:トラフィックの最適化
- 背景
- 方法論と課題
- AIベースのアプローチ
- AIの利用事例:キャッシング
- AIの利用事例:エネルギー管理
- AIの利用事例:コーディング
第5章 RANにおけるAI:ベンダー各社の取り組み
- イントロダクション
- 主な分析結果
- 企業・組織概要
- Aira Channel Prediction xApp
- Aira Dynamic Radio Network Management rApp
- AirHop Auptim
- Aspire Anomaly Detection rApp
- Cisco Ultra Traffic Optimization
- Capgemini RIC
- Cohere MU-MIMO Scheduler
- DeepSig OmniSig
- Deepsig OmniPHY
- Ericsson Radio System
- Ericsson RIC
- Fujitsu Open RAN Compliant RUs
- HCL iDES rApp
- Huawei PowerStar
- Juniper RIC/Rakuten Symphony Symworld
- Mavenir mMIMO 64TRX
- Mavenir RIC
- Net AI xUPscaler Traffic Predictor xApp
- Nokia RAN Intelligent Controller
- Nokia AVA
- Nokia ReefShark Soc
- Nvidia AI-on-5G platform
- Opanga Networks
- P.I. Works Intelligent PCI Collision and Confusion Detection rApp
- Qualcomm RIC
- Qualcomm Cellwize CHIME
- Qualcomm Traffic Management Solutions
- Rimedo Policy-controlled Traffic Steering xApp
- Samsung Network Slice Manager
- ZTE PowerPilot
- VMware RIC
第6章 RANにおけるAI:通信企業各社の取り組み
- イントロダクション
- 主な分析結果
- 企業・組織概要
- AT&T Inc
- Axiata Group Berhad
- Bharti Airtel
- China Mobile
- China Telecom
- China Unicom
- CK Hutchison Holdings
- Deutsche Telekom
- Etisalat
- Globe Telecom Inc
- NTT DoCoMo
- MTN Group
- Ooredoo
- Orange
- PLDT Inc
- Rakuten Mobile
- Reliance Jio
- Saudi Telecom Company
- Singtel
- SK Telecom
- Softbank
- Telefonica
- Telenor
- Telkomsel
- T-Mobile US
- Verizon
- Viettel Group
- Vodafone
第7章 定量的分析と予測
- 分析手法
- 予測用の分類法
- 世界市場
- 市場全体
- 携帯電話の世代別
- 地域区分別
- トラフィック最適化
- 市場全体
- 携帯電話の世代別
- 地域区分別
- キャッシング
- 市場全体
- 携帯電話の世代別
- 地域区分別
- エネルギー管理
- 市場全体
- 携帯電話の世代別
- 地域区分別
- コーディング
- 市場全体
- 携帯電話の世代別
- 地域区分別
This report delves into the intersection of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Radio Access Network (RAN), shedding light on their evolving relationship and forecasting their future trajectories.
SAMPLE VIEW
Figure 1-1: Progression of revenue shares of AI end-applications in the RAN

Source: Insight Research
In recent years, AI has emerged as a pivotal force driving innovation across industries. The telecom sector, in particular, has witnessed a transformative impact with the integration of AI into RAN architecture. The report explores this synergy, uncovering the dynamics behind their convergence and the implications for the telecommunication landscape.
"At Insight Research, we recognize the seismic shifts occurring within the telecommunications industry, and our latest report elucidates the symbiotic relationship between AI and RAN," remarked Kaustubha Parkhi, Principal Analyst at Insight Research. "We're witnessing a paradigm shift in RAN architecture, with AI playing a pivotal role in driving efficiency, agility, and performance."
Key Highlights from the Report:
- The addressable market for AI in RAN will grow by an impressive 45% annually during 2023-2028
- The addressable market for AI in 5G RAN will grow faster than earlier telephony generations
- The APAC region will be the largest market for AI in RAN caching applications
With a meticulous breakdown of the market by application, region, and telephony generations, the report offers unparalleled quantitative insights, empowering stakeholders to make informed decisions in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Insight Research's "AI and RAN - How Fast Will They Run?" report is essential reading for telecom operators, technology providers, policymakers, and investors seeking to navigate the evolving landscape of AI-driven telecommunications infrastructure.
Table of Contents
1. Executive Summary
- 1.1. Key observations
- 1.2. Quantitative Forecast Taxonomy
- 1.3. Report Organization
2. AI/ML/DL - Key Concepts Explainer
- 2.1. Artificial Intelligence
- 2.2. Machine Learning (ML)
- 2.2.1. Supervised Machine Learning
- 2.2.2. Unsupervised Machine Learning
- 2.2.3. Reinforced Machine Learning
- 2.2.4. K-Nearest Neighbor
- 2.3. Deep Learning Neural Network (DLNN)
- 2.4. Noteworthy ML and DL Algorithms
- 2.4.1. Anomaly Detection
- 2.4.2. Artificial Neural Networks (ANN)
- 2.4.3. Bagged Trees
- 2.4.4. CART and SVM Algorithms
- 2.4.5. Clustering
- 2.4.6. Conditional Variational Autoencoder
- 2.4.7. Convolutional Neural Network
- 2.4.8. Correlation and Clustering
- 2.4.9. Evolutionary Algorithms and Distributed Learning
- 2.4.10. Feed Forward Neural Network
- 2.4.11. Graph Neural Networks
- 2.4.12. Hybrid Cognitive Engine (HCE)
- 2.4.13. Kalman Filter
- 2.4.14. Markov Decision Processes
- 2.4.15. Multilayer Perceptron
- 2.4.16. Naïve Bayes
- 2.4.17. Radial Basis Function
- 2.4.18. Random Forest
- 2.4.19. Recurrent Neural Network
- 2.4.20. Reinforced Neural Network
- 2.4.21. SOM Algorithm
- 2.4.22. Sparse Bayesian Learning
3. Virtualization of the RAN
- 3.1. The RAN and its Evolution
- 3.1.1. Closer Look at E-UTRAN
- 3.1.2. 5G- NR, NSA and SA
- 3.1.3. MEC
- 3.1.4. The Rigid CPRI
- 3.2. The Progression of the RAN to the vRAN
- 3.3. How VM-based and Container-based vRANs Compare?
- 3.3.1. NFV architecture
- 3.3.2. The Need for Containers
- 3.3.3. Microservices
- 3.3.4. Container Morphology
- 3.3.5. Container Deployment Methodologies
- 3.3.6. Stateful and Stateless Containers
- 3.3.7. Advantage Containers
- 3.3.8. Challenges Confronting Containers
- 3.4. RAN Virtualization - A Story of Alliances
- 3.4.1. O-RAN Architecture Overview
- 3.4.2. History of O-RAN
- 3.4.3. Workgroups of O-RAN
- 3.4.4. Open vRAN (O-vRAN)
- 3.4.5. Telecom Infra Project (TIP) OpenRAN
4. End-applications for AI in the RAN
- 4.1. O-RAN and AI
- 4.1.1. Introduction
- 4.1.2. RIC, xApps and rApps
- 4.1.3. WG2 and ML
- 4.2. AI Use-Case - Traffic Optimization
- 4.2.1. Background
- 4.2.2. Methodologies and Challenges
- 4.2.3. AI-based Approaches
- 4.3. AI Use-Case - Caching
- 4.3.1. Background
- 4.3.2. Methodologies and Challenges
- 4.3.3. AI-based Approaches
- 4.4. AI Use-Case - Energy Management
- 4.4.1. Background
- 4.4.2. Methodologies and Challenges
- 4.4.3. AI-based Approaches
- 4.5. AI Use-Case - Coding
- 4.5.2. AI-based Approaches
5. Vendor Initiatives for AI in the RAN
- 5.1. Introduction
- 5.2. Salient Observations
- 5.3. Company and Organization Summary
- 5.4. Aira Channel Prediction xApp
- 5.5. Aira Dynamic Radio Network Management rApp
- 5.6. AirHop Auptim
- 5.7. Aspire Anomaly Detection rApp
- 5.8. Cisco Ultra Traffic Optimization
- 5.9. Capgemini RIC
- 5.10. Cohere MU-MIMO Scheduler
- 5.11. DeepSig OmniSig
- 5.12. Deepsig OmniPHY
- 5.13. Ericsson Radio System
- 5.14. Ericsson RIC
- 5.15. Fujitsu Open RAN Compliant RUs
- 5.16. HCL iDES rApp
- 5.17. Huawei PowerStar
- 5.18. Juniper RIC/Rakuten Symphony Symworld
- 5.19. Mavenir mMIMO 64TRX
- 5.20. Mavenir RIC
- 5.21. Net AI xUPscaler Traffic Predictor xApp
- 5.22. Nokia RAN Intelligent Controller
- 5.23. Nokia AVA
- 5.24. Nokia ReefShark Soc
- 5.25. Nvidia AI-on-5G platform
- 5.26. Opanga Networks
- 5.27. P.I. Works Intelligent PCI Collision and Confusion Detection rApp
- 5.28. Qualcomm RIC
- 5.29. Qualcomm Cellwize CHIME
- 5.30. Qualcomm Traffic Management Solutions
- 5.31. Rimedo Policy-controlled Traffic Steering xApp
- 5.32. Samsung Network Slice Manager
- 5.33. ZTE PowerPilot
- 5.34. VMware RIC
6. Telco Initiatives for AI in the RAN
- 6.1. Introduction
- 6.2. Salient Observations
- 6.3. Company and Organization Summary
- 6.4. AT&T Inc
- 6.5. Axiata Group Berhad
- 6.6. Bharti Airtel
- 6.7. China Mobile
- 6.8. China Telecom
- 6.9. China Unicom
- 6.10. CK Hutchison Holdings
- 6.11. Deutsche Telekom
- 6.12. Etisalat
- 6.13. Globe Telecom Inc
- 6.14. NTT DoCoMo
- 6.15. MTN Group
- 6.16. Ooredoo
- 6.17. Orange
- 6.18. PLDT Inc
- 6.19. Rakuten Mobile
- 6.20. Reliance Jio
- 6.21. Saudi Telecom Company
- 6.22. Singtel
- 6.23. SK Telecom
- 6.24. Softbank
- 6.25. Telefonica
- 6.26. Telenor
- 6.27. Telkomsel
- 6.28. T-Mobile US
- 6.29. Verizon
- 6.30. Viettel Group
- 6.31. Vodafone
7. Quantitative Analysis and Forecasts
- 7.1. Research Methodology
- 7.2. Forecast Taxonomy
- 7.3. Global Market
- 7.3.1. Overall Market
- 7.3.2. Mobile Telephony Generations
- 7.3.3. Geographical Regions
- 7.4. Traffic Optimization
- 7.4.1. Overall Market
- 7.4.2. Mobile Telephony Generations
- 7.4.3. Geographical Regions
- 7.5. Caching
- 7.5.1. Overall Market
- 7.5.2. Mobile Telephony Generations
- 7.5.3. Geographical Regions
- 7.6. Energy Management
- 7.6.1. Overall Market
- 7.6.2. Mobile Telephony Generations
- 7.6.3. Geographical Regions
- 7.7. Coding
- 7.7.1. Overall Market
- 7.7.2. Mobile Telephony Generations
- 7.7.3. Geographical Regions
Figures & Tables
- Figure 1-1: Progression of revenue shares of AI end-applications in the RAN
- Figure 3-1: VNF versus CNF Stacks
- Figure 3-2: O-RAN High-Level Architecture
- Figure 3-3: O-RAN High-Level Architecture
- Figure 3-4: Architecture of vRAN Base Station as Visualized by TIP.
- Figure 4-1: Reinforcement learning model training and actor locations per O-RAN WG2
- Figure 4-2: AI/ML Workflow in the O-RAN RIC as proposed O-RAN WG2
- Figure 4-3: AI/ML deployment scenarios
- Table 5-1: AI in RAN Product and Solution Vendor Summary
- Figure 5-1: The Aira channel detection xApp functional blocks
- Figure 5-2: Modules of the Aspire Anomaly Detection rApp
- Figure 5-3: OmniPHY Module Drop in Typical vRAN Stack Overview
- Figure 5-4: Ericsson IAP
- Figure 5-5: HCL iDES rApp Architecture
- Figure 5-6: Working of the Net Ai xUPscaler
- Figure 5-7: Nokia RIC programmability via AI/ML and Customized Applications
- Figure 5-8: Timesharing the GPU in Nvidia Aerial A100
- Figure 5-8: Rimedo TS xApp in the O-RAN architecture
- Figure 5-9: Rimedo TS xApp in the VMware RIC
- Figure 5-10: PowerPilot Solution Evolution
- Table 6-1: AI in RAN Telco Profile Snapshot
- Figure 7-1: AI in the RAN Market Forecast Taxonomy
- Table 7-1: Addressable Market in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies 2023-2028 ($ million)
- Table 7-2: Addressable Market in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Mobile Telephony Generation 2023-2028 ($ million)
- Figure 7-2: Share of Addressable Market in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Mobile Telephony Generation 2023-2028
- Table 7-3: Addressable Market in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Geographical Region 2023-2028 ($ million)
- Figure 7-3: Share of Addressable Market in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Geographical Region 2023-2028
- Table 7-4: Addressable Market in Traffic Optimization End-Application in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies 2023-2028 ($ million)
- Table 7-5: Addressable Market in Traffic Optimization Application in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Mobile Telephony Generation 2023-2028 ($ million)
- Figure 7-4: Share of Addressable Market in Traffic Optimization End-Application in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Mobile Telephony Generation 2023-2028
- Table 7-6: Addressable Market in Traffic Optimization End-Application Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Geographical Region 2023-2028 ($ million)
- Figure 7-5: Share of Addressable Market in Traffic Optimization End-Application Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Geographical Region 2023-2028
- Table 7-7: Addressable Market in Caching End-Application in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies 2023-2028 ($ million)
- Table 7-8: Addressable Market in Caching End-Application in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Mobile Telephony Generation 2023-2028 ($ million)
- Figure 7-6: Share of Addressable Market in Caching End-Application in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Mobile Telephony Generation 2023-2028
- Table 7-9: Addressable Market in Caching End-Application in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Geographical Region 2023-2028 ($ million)
- Figure 7-7: Share of Addressable Market in Caching End-Application in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Geographical Region 2023-2028
- Table 7-10: Addressable Market in Energy Management End-Application in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies 2023-2028 ($ million)
- Table 7-11: Addressable Market in Energy Management End-Application in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Mobile Telephony Generation 2023-2028 ($ million)
- Figure 7-8: Share of Addressable Market in Energy Management End-Application in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Mobile Telephony Generation 2023-2028
- Table 7-12: Addressable Market in Energy Management End-Application in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Geographical Region 2023-2028 ($ million)
- Figure 7-9: Share of Addressable Market in Energy Management End-Application in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Geographical Region 2023-2028
- Table 7-13: Addressable Market in Coding End-Application in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies 2023-2028 ($ million)
- Table 7-14: Addressable Market in Coding End-Application in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Mobile Telephony Generation 2023-2028 ($ million)
- Figure 7-10: Share of Addressable Market in Coding End-Application in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Mobile Telephony Generation 2023-2028
- Table 7-15: Addressable Market in Coding End-Application in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Geographical Region 2023-2028 ($ million)
- Figure 7-11: Share of Addressable Market in Coding End-Application in Mobile RAN for AI and Related Technologies; by Geographical Region 2023-2028






