|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1618223
非動物代替検査市場の成長機会、成長促進要因、産業動向分析、2024~2032年予測Non-animal Alternative Testing Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2024 - 2032 |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
|
|||||||
| 非動物代替検査市場の成長機会、成長促進要因、産業動向分析、2024~2032年予測 |
|
出版日: 2024年10月25日
発行: Global Market Insights Inc.
ページ情報: 英文 137 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
2023年に18億米ドルと評価された世界の非動物代替検査市場は、2024~2032年にかけてCAGR 11.9%で拡大すると予測されています。
この成長の原動力となっているのは、代替検査法を推進する投資や研究助成金の増加です。動物実験をめぐる倫理的懸念の高まりに加え、米国FDAや欧州連合(EU)などの機関による規制イニシアチブが、人道的な代替検査へのシフトを加速させています。こうした施策は、実行可能で倫理的な検査ソリューションを提供する革新的技術への投資を促進します。近年、技術の進歩により、研究者は従来の動物実験よりも正確なヒトの生理学的反応をシミュレートできるようになりました。
こうした技術革新は医薬品開発と安全性検査を一変させ、ヒトの生物学に関する予測的洞察を記載しています。製品タイプ別に分類すると、臓器オンチップ、細胞株、組織モデルがあります。細胞株は2023年に主要セグメントとして浮上し、12億米ドルの市場規模を獲得しました。これらのモデルは、ヒトの様々な生理機能を模倣する適応性の高さから、薬効検査や毒性検査などのセグメントで貴重な存在となっています。
また、大量生産が可能であることから、高スループットスクリーニングプロセスにも適しており、規制や科学的検証に不可欠な一貫した再現性のある結果が得られます。非動物代替検査市場は、技術別に細胞培養技術、高性能技術、分子イメージング、オミクスに区分されます。細胞培養技術は、検査管内でヒト細胞を培養・操作できるため、疾患や薬剤反応の研究により適切な生物学的モデルを提供することができ、2023年のシェアは49.4%で市場をリードしました。この技術は、検査結果の信頼性を高めるだけでなく、細胞株のスケーラブルな生産をサポートし、創薬に不可欠な膨大な数の化合物の検査を効率化します。
| 市場範囲 | |
|---|---|
| 開始年 | 2023年 |
| 予測年 | 2024~2032年 |
| 開始価格 | 18億米ドル |
| 予想価格 | 48億米ドル |
| CAGR | 11.9% |
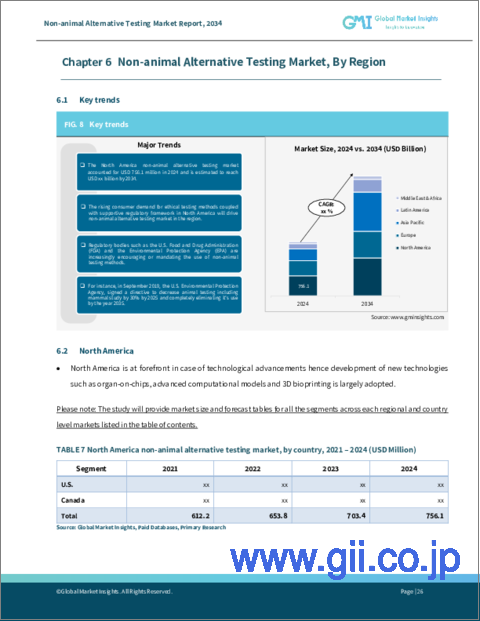
米国の非動物実験代替品市場は、動物実験に対する国民の高い意識と倫理的懸念の高まりに牽引され、2032年までに19億米ドルに達すると予測されます。2023年には、米国が北米で最大の売上シェアを占め、その総額は6億5,660万米ドルでした。人道的な研究プラクティスを求める社会的要求が製薬会社に非動物実験の採用を促し、その背景には国立衛生ラボ(NIH)からの寄付を含む強力な資金と研究助成金があります。このような資金の流入は、各セグメントにおける非動物実験法の研究と応用に拍車をかけ、動物実験モデルからのサステイナブル移行を支えています。
目次
第1章 調査手法と調査範囲
第2章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第3章 産業洞察
- エコシステム分析
- 産業への影響要因
- 促進要因
- 医薬品開発における技術の進歩
- 代替技術開発への投資と研究助成の拡大
- 研究目的での動物モデルの使用禁止の増加
- 産業の潜在的リスク・課題
- 安全性、有効性、品質に関する厳しい規制
- 促進要因
- 成長可能性分析
- 規制状況
- 米国
- 欧州
- ポーター分析
- PESTEL分析
第4章 競合情勢
- イントロダクション
- 企業マトリックス分析
- 主要市場参入企業の細胞ラインの競合分析
- 主要市場参入企業の組織ラインの競合分析
- 臓器オンチップ主要市場競争分析
- 競合のポジショニングマトリックス
- 戦略ダッシュボード
- 戦略展望マトリックス
第5章 市場推定・予測:製品タイプ別、2021~2032年
- 主要動向
- 臓器オンチップ
- 細胞ライン
- 組織ライン
第6章 市場推定・予測:メソッド別、2021~2032年
- 主要動向
- 生体外検査
- コンピューターモデリング
- 細胞アッセイ
- 生化学アッセイ
第7章 市場推定・予測:技術別、2021~2032年
- 主要動向
- 細胞培養技術
- 高性能技術
- 分子イメージング技術
- オミクス技術
第8章 市場推定・予測:用途別、2021~2032年
- 主要動向
- 感染症
- 免疫疾患
- 腫瘍学的疾患
- 心血管疾患
- 糖尿病
- 遺伝性疾患
- 神経疾患
第9章 市場推定・予測:最終用途別、2021~2032年
- 主要動向
- 製薬企業
- バイオテクノロジー企業
- 研究機関と学術機関
- CRO
- その他最終用途
第10章 市場推定・予測:地域別、2021~2032年
- 主要動向
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- 欧州
- ドイツ
- 英国
- フランス
- イタリア
- スペイン
- アジア太平洋
- 中国
- 日本
- インド
- オーストラリア
- 韓国
- ラテンアメリカ
- ブラジル
- メキシコ
- 中東・アフリカ
- 南アフリカ
- サウジアラビア
第11章 企業プロファイル
- AlveoliX
- BICO GROUP
- CN Bio Innovations
- Emulate
- Hesperos
- InSphero
- Lonza Group
- Merck
- MIMETAS
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- TissUse
- VITROCELL Systems
The Global Non-Animal Alternative Testing Market, valued at USD 1.8 billion in 2023, is projected to expand at a CAGR of 11.9% from 2024 to 2032. This growth is driven by rising investments and research grants advancing alternative testing methods. Heightened ethical concerns surrounding animal testing, alongside regulatory initiatives from agencies such as the U.S. FDA and European Union, have accelerated the shift toward humane testing alternatives. These policies foster investment in innovative technologies that offer viable, ethical testing solutions. In recent years, technological advancements have allowed researchers to simulate human physiological responses with more accuracy than traditional animal testing methods.
These innovations transform drug development and safety testing, providing predictive insights into human biology. The market, categorized by product type, includes organ-on-chips, cell lines, and tissue models. Cell lines emerged as the leading segment in 2023, capturing a market value of USD 1.2 billion. These models have become invaluable in fields like drug efficacy and toxicity testing due to their adaptability in mimicking various human physiological functions.
Their capability for high-volume production also makes them a preferred choice for high throughput screening processes, ensuring consistent, reproducible results essential for regulatory and scientific validation. By technology, the non-animal alternative testing market segments into cell culture technology, high-throughput technology, molecular imaging, and omics. Cell culture technology led the market in 2023, with a 49.4% share, due to its capacity to grow and manipulate human cells in vitro, offering a more relevant biological model for studying diseases and drug responses. This technology not only enhances the reliability of test outcomes but also supports the scalable production of cell lines, streamlining the testing of vast numbers of compounds essential for drug discovery.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2024-2032 |
| Start Value | $1.8 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $4.8 Billion |
| CAGR | 11.9% |
U.S. non-animal alternative testing market is expected to reach USD 1.9 billion by 2032, led by high public awareness and mounting ethical concerns over animal testing. In 2023, the U.S. accounted for the largest revenue share in North America, totaling USD 656.6 million. Public demand for humane research practices has prompted pharmaceutical companies to adopt non-animal testing, backed by robust funding and research grants, including contributions from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). This influx of funding is fueling both research and application of non-animal testing methods across sectors, supporting a sustainable transition away from animal-based models.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology & Scope
- 1.1 Market scope & definition
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Base estimates & calculations
- 1.3.1 Base year calculation
- 1.3.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.4 Forecast model
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.5.2 Data mining sources
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry 360° synopsis
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.2 Industry impact forces
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.2.1.1 Technological advances in drug development
- 3.2.1.2 Growing investments and research grants for developing alternative technologies
- 3.2.1.3 Increasing ban on using animal models for research purposes
- 3.2.2 Industry pitfalls & challenges
- 3.2.2.1 Stringent regulations related to safety, efficacy and quality
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.3 Growth potential analysis
- 3.4 Regulatory landscape
- 3.4.1 U.S.
- 3.4.2 Europe
- 3.5 Porter's analysis
- 3.6 PESTEL analysis
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2023
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company matrix analysis
- 4.3 Competitive analysis of major market players cell line
- 4.4 Competitive analysis of major market players tissue line
- 4.5 Competitive analysis of major market players organ-on-chips
- 4.6 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.7 Strategy dashboard
- 4.8 Strategy outlook matrix
Chapter 5 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Product Type, 2021 - 2032 ($ Mn)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Organ-on-chips
- 5.3 Cell lines
- 5.4 Tissue lines
Chapter 6 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Method, 2021 - 2032 ($ Mn)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Ex vivo testing
- 6.3 Computer modelling
- 6.4 Cellular assay
- 6.5 Biochemical assay
Chapter 7 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Technology, 2021 - 2032 ($ Mn)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Cell culture technology
- 7.3 High throughput technology
- 7.4 Molecular imaging technology
- 7.5 Omics technology
Chapter 8 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Application, 2021 - 2032 ($ Mn)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 Infectious diseases
- 8.3 Immunological diseases
- 8.4 Oncology
- 8.5 Cardiovascular diseases
- 8.6 Diabetes
- 8.7 Genetic diseases
- 8.8 Neurological diseases
Chapter 9 Market Estimates and Forecast, By End Use, 2021 - 2032 ($ Mn)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 Pharmaceutical companies
- 9.3 Biotechnological companies
- 9.4 Research institutes and academics
- 9.5 CROs
- 9.6 Other End Use
Chapter 10 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Region, 2021 - 2032 ($ Mn)
- 10.1 Key trends
- 10.2 North America
- 10.2.1 U.S.
- 10.2.2 Canada
- 10.3 Europe
- 10.3.1 Germany
- 10.3.2 UK
- 10.3.3 France
- 10.3.4 Italy
- 10.3.5 Spain
- 10.4 Asia Pacific
- 10.4.1 China
- 10.4.2 Japan
- 10.4.3 India
- 10.4.4 Australia
- 10.4.5 South Korea
- 10.5 Latin America
- 10.5.1 Brazil
- 10.5.2 Mexico
- 10.6 Middle East and Africa
- 10.6.1 South Africa
- 10.6.2 Saudi Arabia
Chapter 11 Company Profiles
- 11.1 AlveoliX
- 11.2 BICO GROUP
- 11.3 CN Bio Innovations
- 11.4 Emulate
- 11.5 Hesperos
- 11.6 InSphero
- 11.7 Lonza Group
- 11.8 Merck
- 11.9 MIMETAS
- 11.10 Thermo Fisher Scientific
- 11.11 TissUse
- 11.12 VITROCELL Systems