|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1308049
標的タンパク質分解 (TPD) 治療薬の新たな情勢Emerging Landscape of Targeted Protein Degradation Therapeutics |
||||||
|
|||||||
| 標的タンパク質分解 (TPD) 治療薬の新たな情勢 |
|
出版日: 2023年06月29日
発行: Frost & Sullivan
ページ情報: 英文 69 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
- 全表示
- 概要
- 目次
急速な技術進歩が強力な治療パイプラインを強化
Frost & Sullivanの調査レポートは、新たな標的タンパク質分解 (TPD) 分野を詳細に分析しています。TPD戦略は、病気の原因となるタンパク質を制御された方法で攻撃し、副作用のリスクを低減することで、従来のアプローチではまだ治療不可能な様々な病気の治療を可能にします。
細胞のプロテオームの80%は、低分子阻害剤、ASO、モノクローナル抗体といった従来のアプローチでは標的とできないと推定されており、これがTPDアプローチの開発につながっています。実際、TPDはこの20年間で非常に進歩し、PROTACはこれまで研究されてきた中で最も一般的なタンパク質分解酵素として登場しました。新しい技術が登場するにつれ、いくつかのタイプのタンパク質分解剤が開発されてきました。
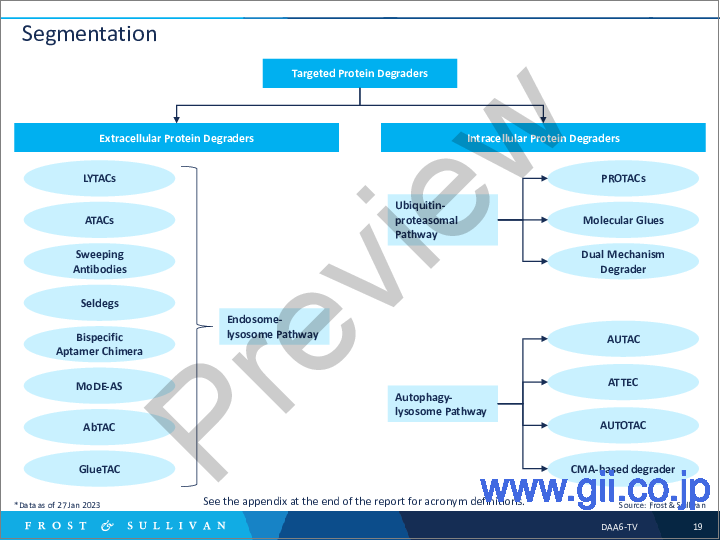
細胞内分解剤と細胞外分解剤の二つが、主な種類となっています。これまで、細胞内タンパク質分解剤が最も広く研究されてきました。これらはユビキチン-プロテアソーム分解経路を利用して細胞内タンパク質を分解しますが、細胞外タンパク質や膜関連タンパク質をコードする遺伝子の推定40%は細胞内タンパク質分解剤の標的とすることができないため、それが細胞外タンパク質分解剤の開発につながっています。
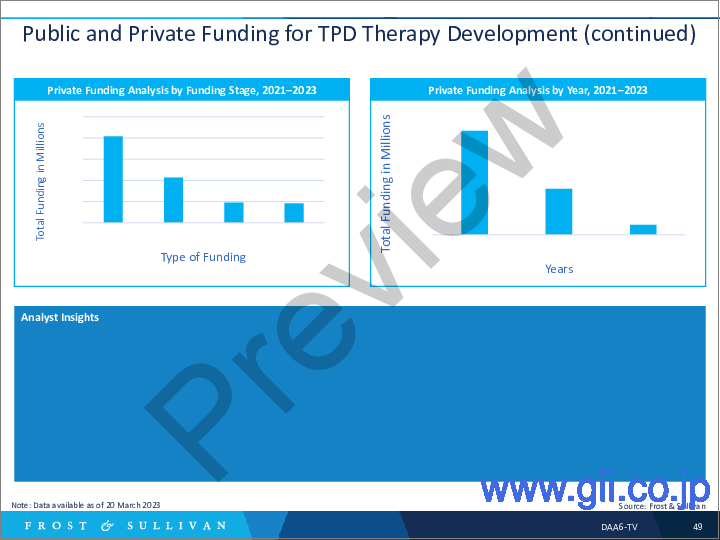
民間・公的資金の増加は、標的タンパク質分解技術の成長を促進する重要な要因です。本レポートでは、TPD分野における資金動向の分析を含みます。
本レポートでは、細胞外・細胞内タンパク質分解剤の種類と研究開発の重点分野について論じています。また、様々な疾患における様々な分解剤の適用可能性を分析し、その臨床応用と関連する主要プレイヤーを特定しています。最後にFrost &Sullivanは、市場を変革する可能性のあるTPDの4つの成長機会を特定しました。
本レポートが答えようとする疑問は以下の通りである:
- 1. TPD開発の主な促進要因や課題は何か?
- 2. TPDに対する民間の資金提供やパートナーシップの状況はどうなっているか?
- 3. 標的タンパク質分解酵素を開発している主な業界関係者は?
- 4. タンパク質分解酵素の開発を促進する可能性のある、TPDの研究開発動向はどのようなものか?
目次
戦略的課題
- なぜ成長が難しくなっているのか?
- The Strategic Imperative 8 (TM)
- 標的タンパク質分解業界における戦略的重要課題:上位3項目のインパクト
- 成長機会によるGrowth Pipeline Engine (TM) の促進
- 調査手法
- イントロダクション
成長機会分析
- 成長促進要因
- 成長促進要因分析
- 成長抑制要因
- 成長抑制要因分析
- 分析範囲
- セグメンテーション
- 標的タンパク質分解剤のニーズ
研究開発とイノベーションのエコシステム
- TPDの進化と臨床的側面
- 臨床開発中の細胞内標的タンパク質分解薬
- 細胞内標的タンパク質分解薬:PROTACs
- 新たな細胞内標的タンパク質分解薬
- イノベーション・スポットライト:細胞内タンパク質分解
- 細胞外タンパク質分解治療薬の開発
- 細胞外タンパク質分解治療薬の開発の課題
- 細胞外タンパク質分解アプローチ
- 細胞外タンパク質分解剤の新たなクラス
- イノベーション・スポットライト:細胞外タンパク質分解
- 細胞外タンパク質の標的と、細胞内タンパク質の標的の主な違い
- 標的タンパク質分解:技術スナップショット
研究開発の焦点と応用情勢
- 研究開発・イノベーションの動向
- 医療におけるタンパク質分解とその先
- さまざまな疾患領域におけるタンパク質分解剤
- 主要企業と注目される治療分野
- タンパク質分解剤のイノベーションの展望
市場力学
- TPD治療薬開発のための公的・民間資金調達
- TPD治療薬開発におけるバイオ製薬企業の提携状況
- TPD治療薬開発のためのTPD企業のパートナーシップ
成長機会ユニバース
- 成長機会1:効率的で組織特異的な分解剤の送達
- 成長機会2:新規E3リガーゼの発見と設計
- 成長機会3:先進的PROTACの開発
- 成長機会4:次世代TPD治療薬開発のための研究開発パートナーシップ
付録
- 付録
- 付録
次のステップ
- 次のステップ
- なぜFrost & Sullivanなのか、なぜ今なのか
- 免責事項
Rapid Technology Advances Bolster a Robust Therapeutic Pipeline
This Frost & Sullivan research report provides an in-depth analysis of the emerging targeted protein degradation (TPD) space. TPD strategies enable treating various diseases not yet treatable via conventional approaches by attacking disease-causing proteins in a controlled manner, thus reducing the risk of side effects.
It is estimated that 80% of a cell's proteome cannot be targeted via traditional approaches such as small molecule inhibitors, ASO, or monoclonal antibodies, which has led to the development of TPD approaches. Indeed, TPD has advanced enormously in the last two decades, and PROTACs have emerged as the most common protein degrader researched until now. As new technologies emerge, several types of protein degraders have been developed.
Two main types exist: intracellular and extracellular degraders. Until now, intracellular protein degraders have been the most extensively studied. These degrade intracellular proteins by leveraging the ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation pathway, but an estimated 40% of genes encoding extracellular and membrane-associated proteins cannot be targeted by intracellular protein degraders, leading to the development of extracellular protein degradation.
Increased private and public funding is an important factor driving the growth of targeted protein degradation technology. This report includes an analysis of funding trends in the TPD space.
This report discusses the different types of extracellular and intracellular protein degraders and R&D focus areas; it analyses the applicability of different degraders across various diseases and identifies their clinical translation and related key players. Finally, Frost & Sullivan has identified four growth opportunities for TPD that could potentially transform the market.
Questions that this report seeks to answer include:
- 1. What are the key drivers or challenges for TPD development?
- 2. How do the private funding and partnership landscapes look for TPD?
- 3. Who are the key industry participants developing targeted protein degraders?
- 4. What are the R&D trends emerging across TPD that could further shape the development of protein degraders?
Table of Contents
Strategic Imperatives
- Why Is It Increasingly Difficult to Grow?
- The Strategic Imperative 8™
- The Impact of the Top 3 Strategic Imperatives on the Targeted Protein Degradation Industry
- Growth Opportunities Fuel the Growth Pipeline Engine™
- Research Methodology
- Introduction
Growth Opportunity Analysis
- Growth Drivers
- Growth Driver Analysis
- Growth Restraints
- Growth Restraints Analysis
- Scope of Analysis
- Segmentation
- The Need for Targeted Protein Degraders
R&D and Innovation Ecosystem
- TPD-Evolution and Clinical aspect
- Intracellular Targeted Protein Degraders in Clinical Development
- Intracellular Targeted Protein Degraders-PROTACs
- Emerging Intracellular Targeted Protein Degraders
- Innovation Spotlight-Intracellular Protein Degradation
- Development of Extracellular Protein Degradation Therapeutics
- Challenges for Extracellular Protein Degrader Development
- Extracellular Protein Degradation Approaches
- Emerging Classes of Extracellular Protein Degraders
- Innovation Spotlight-Extracellular Protein Degradation
- Key Differences Between Extracellular and Intracellular Protein Targeting
- Targeted Protein Degradation Technology Snapshot
R&D Focus and Application Landscape
- R&D Innovation Trends
- Protein Degraders in Healthcare and Beyond
- Protein Degraders across Different Disease Areas
- Key Players and Therapeutics Areas of Focus
- Protein Degraders Innovation Landscape
Market Dynamics
- Public and Private Funding for TPD Therapy Development
- Partnership Landscape of Biopharma Companies in TPD Therapeutics Development
- TPD Companies' Partnerships for Developing TPD Therapeutics
Growth Opportunity Universe
- Growth Opportunity 1: Efficient and Tissue-specific Degrader Delivery
- Growth Opportunity 2: Novel E3 Ligases Discovery and Design
- Growth Opportunity 3: Advanced PROTACs Development
- Growth Opportunity 4: Research and Product Development Partnerships to Develop Next-gen TPD Therapeutics
Appendix
- Appendix
- Appendix
Next Steps
- Your Next Steps
- Why Frost, Why Now?
- Legal Disclaimer