|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1109318
世界の水素市場 : 規制枠組みおよび成長機会Global Hydrogen Regulatory Frameworks and Growth Opportunities |
||||||
| 世界の水素市場 : 規制枠組みおよび成長機会 |
|
出版日: 2022年07月07日
発行: Frost & Sullivan
ページ情報: 英文 125 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
- 全表示
- 概要
- 目次
産業セクターの脱炭素化とカーボンニュートラル目標が、水素経済への政府投資を促進すると予測されています。
当レポートでは、世界の水素市場について調査分析し、戦略的必須要件、成長機会、各国の水素戦略や規制等の情報を提供しています。
目次
戦略的必須要件
成長環境と範囲
- 水素国家戦略のタイムライン
- 各国の水素政策や規制の概要
成長機会分析
- 調査の目的
- 調査範囲と除外
- この調査が答える主な質問
- 脱炭素化への5つの重要な柱
- 水素未来ゼロカーボンエネルギーキャリア
- 水素に対する政府の対応
- 水素の色スペクトルと生成経路
- 水素バリューチェーン
- 水素エコシステム
- 成長促進要因
- 成長抑制要因
国別プロファイル - オーストラリア
- オーストラリア
- オーストラリア - 水素戦略
国別プロファイル - カナダ
- カナダ
- カナダ - 水素戦略
国別プロファイル - チリ
- チリ
- チリ - 水素戦略
国別プロファイル - 中国
- 中国
- 中国 - 水素戦略
国別プロファイル - デンマーク
- デンマーク
- デンマーク - 水素戦略
国別プロファイル - フランス
- フランス
- フランス - 水素戦略
国別プロファイル - ドイツ
- ドイツ
- ドイツ - 水素戦略
国別プロファイル - インド
- インド
- インド - 水素戦略
国別プロファイル - イタリア
- イタリア
- イタリア - 水素戦略
国別プロファイル - 日本
- 日本
- 日本 - 水素戦略
国別プロファイル - オランダ
- オランダ
- オランダ - 水素戦略
国別プロファイル - ノルウェー
- ノルウェー
- ノルウェー - 水素戦略
国別プロファイル - サウジアラビア
- サウジアラビア
- サウジアラビア - 水素戦略
国別プロファイル - 韓国
- 韓国
- 韓国 - 水素戦略
国別プロファイル - スペイン
- スペイン
- スペイン - 水素戦略
国別プロファイル - アラブ首長国連邦
- アラブ首長国連邦
- アラブ首長国連邦 - 水素戦略
国別プロファイル - 英国
- 英国
- 英国 - 水素戦略
国プロファイル - 米国
- 米国
- 米国 - 水素戦略
全世界における成長機会
- 成長機会1 - 二酸化炭素排出量を削減するための水素/アンモニアと石炭の混焼
- 成長機会2 - 二酸化炭素排出量を削減するための水素の既存天然ガスパイプラインへの混合
- 成長機会3 - 商品またはサービスとしての水素をもたらす地理的拡大
- 成長機会4 - オフグリッドおよび重要インフラ用の主要電源・バックアップ電源
- 成長機会5 - 電力貯蔵削減率の低減
- 成長機会6 - 産業用および商業用の熱電併給 (CHP) 燃料電池
- 成長機会7 - 原子力のライフラインとしての水素
- 成長機会8 - 二酸化炭素回収・貯留 (CCS) への新たな関心を促す水素
- 成長機会9 - 水素市場を牽引する主な利害関係者間の合併とパートナーシップ
- 展示物一覧
- 免責事項
Decarbonization of Industrial Sectors and Carbon Neutrality Goals Driving Government Investments in the Hydrogen Economy
Our pathway toward decarbonization and achieving the 1.5° Celsius target necessitates supportive regulatory frameworks mandating energy-efficiency measures across the commercial, industrial, and residential segments. It also requires significant economic investments driving renewables and the switch to nuclear low-carbon and large-scale CCUS technologies. Interest in hydrogen as a low- or zero-carbon energy carrier has grown in recent years. Many governments acknowledge that a hydrogen-based economy could be the best alternative to the present fossil fuels-based economy and an answer to concerns over carbon emissions, energy security, and climate change.
Hydrogen helps curb carbon emissions by:
- Decarbonizing the carbon-intensive automotive, maritime, aviation, and industrial sectors
- Integrating more RES to produce hydrogen, reducing the curtailment rate
- Providing resiliency and reliability to the electric grid as an ESS and supplementing RES during low-demand periods
Though the promise of hydrogen as an essential tool in catalyzing the transition toward a sustainable energy economy is huge, its current application is mostly limited to the industrial sector. Many projects across power generation, transport, and other segments are still in their pilot stages and require technological and cost breakthroughs for increased adoption. There is still a long way to go, and it will likely take another 10 to 20 years before the hydrogen economy becomes mainstream across the global power sector and other segments.
For the hydrogen economy to become a reality, decisive government actions in four areas are necessary:
- Supporting R&D activities related to technologies involved in the production, storage, transport, and utilization of hydrogen
- Providing incentives to companies for developing the hydrogen and CCUS infrastructure
- Addressing socioeconomic barriers inhibiting the growth of the technology and mandating policies toward decarbonization
- Developing a roadmap toward a hydrogen economy
In the past five years, many countries have developed a hydrogen strategy prioritizing targets and investments running into billions over the next decade. While some nations are focused on production and export, others are making domestic and foreign investments to ensure future supply. There are also specific targets relating to production, in terms of cost or quantity, or particular areas targeted for decarbonizing, such as industries, heating, power, or mobility.
The primary aim of this research study is to analyze the policies and roadmaps implemented by various countries toward hydrogen adoption to achieve a sustainable energy future. The study also identifies growth opportunities for the hydrogen market and the countries and companies active in this space.
Table of Contents
The Strategic Imperative
- Why Is It Increasingly Difficult to Grow?
- The Strategic Imperative 8™
- Impact of the Top 3 Strategic Imperatives on the Global Hydrogen Industry
- Growth Opportunities Fuel the Growth Pipeline Engine™
Growth Environment and Scope
- Timeline of Hydrogen National Strategies
- Summary of Hydrogen Policies and Regulations by Country
- Summary of Hydrogen Policies and Regulations by Country (continued)
- Summary of Hydrogen Policies and Regulations by Country (continued)
- Summary of Hydrogen Policies and Regulations by Country (continued)
- Summary of Hydrogen Policies and Regulations by Country (continued)
Growth Opportunity Analysis
- Research Aim
- Study Coverage and Exclusions
- Key Questions this Study Will Answer
- 5 Key Decarbonization Pillars
- Hydrogen-Future Zero-carbon Energy Carrier
- Government Action for Hydrogen
- Hydrogen Color Spectrum and Production Pathways
- Hydrogen Value Chain
- Hydrogen Ecosystem
- Growth Drivers
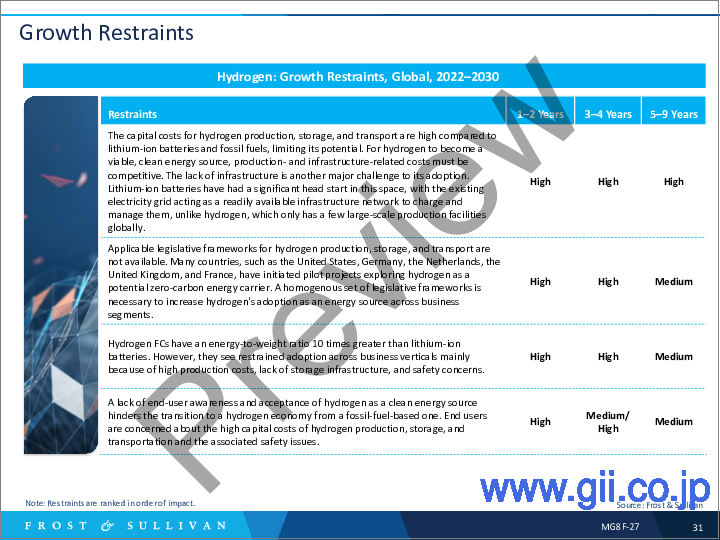
- Growth Restraints
Country Profile-Australia
- Australia
- Australia (continued)
- Australia-Hydrogen Strategy
Country Profile-Canada
- Canada
- Canada-Hydrogen Strategy
- Canada-Hydrogen Strategy (continued)
Country Profile-Chile
- Chile
- Chile (continued)
- Chile-Hydrogen Strategy
Country Profile-China
- China
- China-Hydrogen Strategy
- China-Hydrogen Strategy (continued)
Country Profile-Denmark
- Denmark
- Denmark-Hydrogen Strategy
- Denmark-Hydrogen Strategy (continued)
Country Profile-France
- France
- France-Hydrogen Strategy
- France-Hydrogen Strategy (continued)
Country Profile-Germany
- Germany
- Germany-Hydrogen Strategy
- Germany-Hydrogen Strategy (continued)
Country Profile-India
- India
- India-Hydrogen Strategy
- India-Hydrogen Strategy (continued)
Country Profile-Italy
- Italy
- Italy-Hydrogen Strategy
- Italy-Hydrogen Strategy (continued)
Country Profile-Japan
- Japan
- Japan-Hydrogen Strategy
- Japan-Hydrogen Strategy (continued)
Country Profile-Netherlands
- Netherlands
- Netherlands-Hydrogen Strategy
- Netherlands-Hydrogen Strategy (continued)
Country Profile-Norway
- Norway
- Norway (continued)
- Norway-Hydrogen Strategy
Country Profile-Saudi Arabia
- Saudi Arabia
- Saudi Arabia-Hydrogen Strategy
- Saudi Arabia-Hydrogen Strategy (continued)
Country Profile-South Korea
- South Korea
- South Korea-Hydrogen Strategy
- South Korea-Hydrogen Strategy (continued)
Country Profile-Spain
- Spain
- Spain-Hydrogen Strategy
- Spain-Hydrogen Strategy (continued)
Country Profile-UAE
- United Arab Emirates
- United Arab Emirates-Hydrogen Strategy
- United Arab Emirates-Hydrogen Strategy (continued)
Country Profile-United Kingdom
- United Kingdom
- United Kingdom-Hydrogen Strategy
- United Kingdom-Hydrogen Strategy (continued)
Country Profiles-United States
- United States
- United States-Hydrogen Strategy
- United States-Hydrogen Strategy (continued)
Growth Opportunity Universe
- Growth Opportunity 1-Co-firing Hydrogen/Ammonia with Coal to Reduce CO2 Emissions
- Growth Opportunity 1-Co-firing Hydrogen/Ammonia with Coal to Reduce CO2 Emissions (continued)
- Growth Opportunity 2-Blending Hydrogen into Existing NG Pipelines to Reduce CO2 Emissions
- Growth Opportunity 2-Blending Hydrogen into Existing NG Pipelines to Reduce CO2 Emissions (continued)
- Growth Opportunity 3-Geographic Expansion Resulting in Hydrogen as a Commodity or Service
- Growth Opportunity 3-Geographic Expansion Resulting in Hydrogen as a Commodity or Service (continued)
- Growth Opportunity 4-Primary and Backup Power Source for Off-grid and Critical Infrastructures
- Growth Opportunity 4-Primary and Backup Power Source for Off-grid and Critical Infrastructures (continued)
- Growth Opportunity 5-Electricity Storage Reducing Curtailments Ratio
- Growth Opportunity 5-Electricity Storage Reducing Curtailments Ratio (continued)
- Growth Opportunity 6-Combined Heat and Power (CHP) FCs for Industrial and Commercial Applications
- Growth Opportunity 6-Combined Heat and Power (CHP) FCs for Industrial and Commercial Applications (continued)
- Growth Opportunity 7-Hydrogen as a Lifeline for Nuclear Energy
- Growth Opportunity 7-Hydrogen as a Lifeline for Nuclear Energy (continued)
- Growth Opportunity 8-Hydrogen to Drive Renewed Interest in CCS
- Growth Opportunity 8-Hydrogen to Drive Renewed Interest in CCS (continued)
- Growth Opportunity 9-Mergers and Partnerships Between Key Stakeholders to Drive the Hydrogen Market
- Growth Opportunity 9-Mergers and Partnerships Between Major Stakeholders to Drive the Hydrogen Market (continued)
- List of Exhibits
- List of Exhibits (continued)
- Legal Disclaimer