|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1678803
炭化ケイ素(SiC)半導体の世界市場 (2025年~2032年)Global Silicon Carbide (SiC) Semiconductor Market - 2025-2032 |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 炭化ケイ素(SiC)半導体の世界市場 (2025年~2032年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月11日
発行: DataM Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 205 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
- 全表示
- 概要
- 目次
炭化ケイ素(SiC)半導体の世界市場は、2024年に8億1,020万米ドルに達し、2032年には26億3,709万米ドルに達すると予測され、予測期間2025年のCAGRは15.9%で成長します。
炭化ケイ素(SiC)半導体市場は、ハイパワー、高効率用途の需要増加に牽引され、力強い成長を遂げています。SiC半導体は、従来のシリコンよりも熱伝導率が高く、エネルギー効率が高く、より高い電圧と温度で動作できるなど、優れた特性を備えています。同市場は、電気自動車(EV)、再生可能エネルギー、航空宇宙、産業用パワーエレクトロニクスなどの産業で勢いを増しています。
例えば、STマイクロエレクトロニクスは2024年、第4世代のSTPOWER炭化ケイ素(SiC)MOSFET技術を発表します。第4世代の技術は、電力効率、電力密度、堅牢性において新たなベンチマークをもたらします。この新技術は、自動車市場と産業市場の両方のニーズに対応する一方で、特に電気自動車(EV)パワートレインの主要部品であるトラクション・インバータ向けに最適化されています。
さらに、2025年には、インフィニオン・テクノロジーズAGは、200mm炭化ケイ素(SiC)ロードマップを大きく進展させました。インフィニオンは、2025年第1四半期に、先進的な200mm SiC技術に基づく最初の製品をすでに顧客にリリースする予定です。オーストリアのヴィラッハで製造されるこの製品は、再生可能エネルギー、鉄道、電気自動車などの高電圧用途向けに、第一級のSiCパワー技術を提供します。
さらに、再生可能エネルギー分野はSiC半導体から大きな恩恵を受けています。例えば、インフィニオン・テクノロジーズは、ソーラー・インバータ向けにSiCソリューションを供給し、エネルギー損失を低減し、電力密度を向上させています。航空宇宙産業でも進歩が見られ、NASAのグレン研究センターは、金星探査などのミッションに不可欠な、930°F(500℃)で数千時間動作可能なSiC回路を開発しています。これらの例は、性能の向上、システム・コストの削減、世界の持続可能性目標のサポートにおけるSiCの可能性を浮き彫りにしており、より環境に優しい未来への移行における重要な推進力となっています。
ダイナミクス
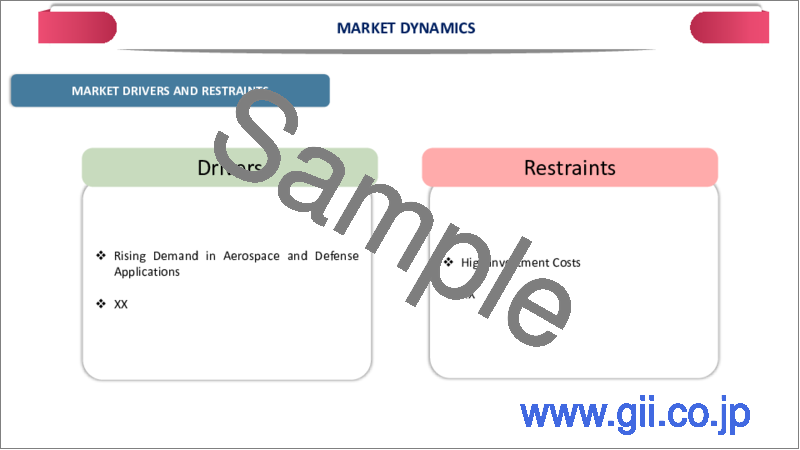
航空宇宙・防衛用途の増加
SiCベースのデバイスは、最新の航空宇宙および防衛システムに不可欠な独自の利点を提供するため、航空宇宙および防衛用途の台頭は、炭化ケイ素(SiC)半導体市場の重要な促進要因です。これらの産業は、高温、高電圧、過酷な環境といった過酷な条件下でも動作する高性能、高信頼性、高効率の電子部品を要求しています。
例えば、ドイツのPCIM Europe, 2024によると、航空宇宙用途におけるSiC技術の潜在的限界を分析し、CoolCAD Electronicsが開発した高高度および宇宙環境での使用ソリューションを提案しています。炭化ケイ素パワーデバイスは、従来のシリコンベースのコンポーネントに代わる潜在的な優れた代替品として登場し、宇宙船や電気航空機の高出力用途に大きなメリットをもたらします。
さらに2024年には、米国海軍の航空電子工学の専門家が、海軍の空母艦載偵察機E-2D Advanced Hawkeyeに搭載されるレーダー・パワー・エレクトロニクス用の炭化ケイ素部品の長期的かつ安定的な供給を確保するため、ノースロップ・グラマン社に注目しています。炭化ケイ素は、シリコンMOSFETや絶縁ゲート型バイポーラトランジスタ(IGBT)よりも優れたスイッチング性能を発揮し、温度に対する変動も最小限に抑えられます。
高出力用途の需要拡大
SiCの高熱伝導性、高耐圧、エネルギー効率などの優れた特性により、高出力用途への需要の高まりが炭化ケイ素(SiC)半導体市場を大きく牽引しています。これらの特性により、SiC半導体は電気自動車(EV)、再生可能エネルギーシステム、産業用電源に最適となっています。
例えば2025年、NASAグレン研究センターの研究開発者は、930°F(500℃)で数千時間、-310°F(-190℃)~1,490°F(812℃)の温度範囲で動作するなどの極限状態に耐える炭化ケイ素(SiC)回路を開発しました。これらの進歩は、金星探査にとって極めて重要であり、航空宇宙、電気自動車、再生可能エネルギー・システムなど、SiCがより高い電圧、温度、放射線を扱う能力を持つことで、性能と効率に大きな利点をもたらす、より広範な応用が可能です。
さらに、テスラは、モデル3のインバータに炭化ケイ素(SiC)MOSFETを使用した先駆者であり、従来のシリコンベースのトランジスタに比べて電力損失を最小限に抑えることでエネルギー効率を大幅に改善し、航続距離の延長に貢献しました。さらにシーメンスは、産業用ドライブにSiCコンポーネントを統合し、性能の向上とエネルギー消費の低減を実現しています。
高い投資コスト
炭化ケイ素(SiC)半導体は製造工程が複雑で資源集約的なため、製造コストが高いことが大きな足かせとなっています。SiCウエハーは従来のシリコンウエハーより高価で、6インチのSiCウエハーの価格は約1,000~2,000ドルであるのに対し、シリコンウエハーは25~50ドルです。この大幅なコスト差は、複雑な結晶成長プロセス(昇華)と高い欠陥率から生じ、歩留まりが低下します。
例えば、STマイクロエレクトロニクスやウルフスピードは、こうした高コストのためにSiCの生産規模を拡大するという課題に直面しており、電気自動車(EV)や再生可能エネルギー・システム向けのパワー・デバイスの価格設定に影響を及ぼしています。そのため、Lucid MotorsやRivianのようなEVメーカーは、SiCインバータやパワートレインを採用する際、生産コストが高くなる可能性があります。
目次
第1章 分析手法と分析範囲
第2章 定義と概要
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場力学
- 影響要因
- 促進要因
- 航空宇宙・防衛分野での応用が増加
- 高出力用途に対する需要の高まり
- 抑制要因
- 高い投資コスト
- 機会
- 影響分析
- 促進要因
第5章 産業分析
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- サプライチェーン分析
- 価格分析
- 規制分析
- 持続可能な分析
- DMIの見解
第6章 種類別
- SiCディスクリートデバイス
- SiCパワーモジュール
- SiC基板・ウエハー
- その他
第7章 ウエハーのサイズ別
- 2インチウエハー
- 4インチウエハー
- 6インチウエハー
- 8インチウエハー
第8章 技術別
- 平面SiC技術
- トレンチSiC技術
第9章 用途別
- 自動車
- 家電
- 産業
- 航空宇宙・防衛
- 通信
- エネルギー・電力
- その他
第10章 サスティナビリティ分析
- 環境分析
- 経済分析
- ガバナンス分析
第11章 地域別
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- メキシコ
- 欧州
- ドイツ
- 英国
- フランス
- イタリア
- スペイン
- その他欧州地域
- 南米
- ブラジル
- アルゼンチン
- その他南米
- アジア太平洋
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- オーストラリア
- その他アジア太平洋地域
- 中東・アフリカ
第12章 競合情勢
- 競合シナリオ
- 市況・シェア分析
- M&A分析
第13章 企業プロファイル
- Infineon Technologies
- 企業概要
- 製品ポートフォリオと概要
- 財務概要
- 主な動向
- Littelfuse
- ON Semiconductor
- Wolfspeed Inc
- Fuji Electric
- X-FAB
- GeneSiC Semiconductor
- Mitsubishi Electric
- STMicroelectronics
- ROHM Semiconductor
第14章 付録
Global Silicon Carbide (SiC) Semiconductor Market reached US$ 810.2 million in 2024 and is expected to reach US$ 2,637.09 million by 2032, growing with a CAGR of 15.9% during the forecast period 2025-2032.
The Silicon Carbide (SiC) semiconductor market is experiencing robust growth, driven by the increasing demand for high-power, high-efficiency applications. SiC semiconductors offer superior properties over traditional silicon, including higher thermal conductivity, greater energy efficiency, and the ability to operate at higher voltages and temperatures. The market is gaining momentum across industries such as electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy, aerospace, and industrial power electronics.
For instance, in 2024, STMicroelectronics, introducing its fourth generation STPOWER silicon carbide (SiC) MOSFET technology. The Generation 4 technology brings new benchmarks in power efficiency, power density and robustness. While serving the needs of both the automotive and industrial markets, the new technology is particularly optimized for traction inverters, the key component of electric vehicle (EV) powertrains.
Additionally, in 2025, Infineon Technologies AG, has made significant progress on its 200 mm silicon carbide (SiC) roadmap. The company will already release the first products based on the advanced 200 mm SiC technology to customers in Q1 2025. The products, manufactured in Villach, Austria, provide first-class SiC power technology for high-voltage applications, including renewable energies, trains, and electric vehicles.
Moreover, the renewable energy sector benefits significantly from SiC semiconductors. For example, Infineon Technologies supplies SiC solutions for solar inverters, reducing energy losses and improving power density. The aerospace industry also sees advancements, with NASA's Glenn Research Center developing SiC circuits capable of operating at 930°F (500°C) for thousands of hours, critical for missions like Venus exploration. These instances highlight SiC's potential in enhancing performance, reducing system costs, and supporting global sustainability goals, making it a key driver in the transition toward a greener future.
Dynamics
Rising in Aerospace and Defense Applications
The rising aerospace and defense applications are significant drivers of the Silicon Carbide (SiC) Semiconductor Market, as SiC-based devices offer unique advantages that are critical for modern aerospace and defense systems. These industries demand high-performance, reliable, and efficient electronic components that can operate under extreme conditions, such as high temperatures, high voltages, and harsh environments.
For instance, according to PCIM Europe in Germany, 2024, analyzes the potential limits of SiC technology in aerospace applications, proposing the solutions developed by CoolCAD Electronics for usage in high-altitude and space environments. Silicon carbide power devices have emerged as a potentially superior alternative to conventional silicon-based components, offering substantial benefits for high-power applications on spacecraft and electric aircraft.
Additionally, in 2024, U.S. Navy avionics experts are looking to Northrop Grumman Corp. to ensure a long-term and steady supply of silicon carbide components for radar power electronics aboard the Navy's E-2D Advanced Hawkeye carrier-based surveillance aircraft. Silicon Carbide provides better switching performance than silicon MOSFETs and insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs) with minimal variation versus temperature.
Growing Demand for High-Power Applications
The growing demand for high-power applications significantly drives the Silicon Carbide (SiC) semiconductor market due to SiC's superior properties, including high thermal conductivity, high breakdown voltage, and energy efficiency. These attributes make SiC semiconductors ideal for electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy systems, and industrial power supplies.
For instance, in 2025, Engineers at NASA's Glenn Research Center have developed silicon carbide (SiC) circuits capable of withstanding extreme conditions, including 930°F (500°C) for thousands of hours and operating across a -310°F (-190°C) to 1,490°F (812°C) temperature range. These advancements are crucial for Venus exploration and have broader applications in aerospace, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems, where SiC's ability to handle higher voltages, temperatures, and radiation offers significant performance and efficiency benefits.
Additionally, Tesla pioneered the use of Silicon Carbide (SiC) MOSFETs in the inverters of its Model 3, significantly improving energy efficiency and contributing to increased driving range by minimizing power losses compared to traditional silicon-based transistors; this made the Model 3 one of the first electric vehicles to widely adopt SiC technology in its powertrain. Moreover, Siemens integrates SiC components in industrial drives, enhancing performance and lowering energy consumption.
High Investment Costs
The high manufacturing cost of Silicon Carbide (SiC) semiconductors is a significant restraint due to the complex and resource-intensive production processes. SiC wafers are more expensive than traditional silicon wafers, with 6-inch SiC wafers costing around $1,000-$2,000, compared to $25-$50 for silicon wafers. This substantial cost difference arises from the intricate crystal growth process (sublimation) and higher defect rates, resulting in lower yields.
For instance, STMicroelectronics and Wolfspeed face challenges in scaling SiC production due to these high costs, affecting the pricing of power devices for electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy systems. Therefore, EV manufacturers like Lucid Motors and Rivian may encounter higher production expenses when adopting SiC inverters and powertrains.
Segment Analysis
The global silicon carbide (sic) semiconductor market is segmented based on type, wafer size, technology, application and region.
SiC Power Modules: Leading the Charge in High-Efficiency Semiconductor Applications
The SiC power modules segment dominates the Silicon Carbide (SiC) semiconductor market due to its ability to handle higher voltages, temperatures, and switching frequencies with improved energy efficiency and power density compared to silicon-based modules. These advantages make SiC power modules ideal for electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy systems, and industrial power applications, where efficiency and compact designs are critical.
For instance, in 2023, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation had agreed with Coherent Corp to invest USD 500 million (approx. 75 billion yen1) in a new silicon carbide (SiC) business to be carved out from Coherent, aiming to expand its SiC power device business by strengthening vertical collaboration with Coherent, who has been a supplier of SiC substrates to Mitsubishi Electric.
Additionally, in 2022, Fuji Electric Co., announce that it has made a decision to carry out capital investment in Fuji Electric Tsugaru Semiconductor Co., Ltd, one of power semiconductor production bases, for an increase in the production of SiC power semiconductors. Mass production is planned to begin in fiscal 2024. These real-world applications demonstrate how SiC power modules lead the market by supporting the global push for energy-efficient, high-performance power solutions across key industries.
Geographical Penetration
Advancing EVs, Renewables, and Aerospace in North America
North America dominates the Silicon Carbide (SiC) semiconductor market due to the presence of leading industry players, robust electric vehicle (EV) adoption, and significant investments in renewable energy and aerospace sectors. The region's focus on energy efficiency, advanced manufacturing, and technological innovation drives the demand for SiC semiconductors in high-power applications.
For instance, Wolfspeed, a key player based in the U.S., opened the world's largest SiC materials factory in New York to meet the growing demand for SiC power devices. In the EV sector, Tesla, headquartered in California, uses SiC MOSFETs in its Model 3 inverters, improving energy efficiency and extending vehicle range.
The aerospace industry also plays a pivotal role, with NASA's Glenn Research Center developing SiC circuits capable of withstanding extreme temperatures for space exploration missions, such as those targeting Venus. These developments underline North America's leadership in leveraging SiC technology across diverse, high-growth sectors.
Competitive Landscape
The major global players in the market include Infineon Technologies, Littelfuse, ON Semiconductor, Wolfspeed Inc, Fuji Electric, X-FAB, GeneSiC Semiconductor, Mitsubishi Electric, STMicroelectronics, ROHM Semiconductor, and among others.
Key Developments
- In 2023, Vitesco Technologies, a leading international manufacturer of modern drive technologies and electrification solutions, has secured strategically important capacities in energy-efficient silicon carbide power semiconductors through a long-term supply partnership with ROHM - worth over one billion US dollars until 2030.
- In 2025, Onsemi, had completed its acquisition of the Silicon Carbide Junction Field-Effect Transistor (SiC JFET) technology business, including the United Silicon Carbide subsidiary, from Qorvo for $115 million in cash. The addition of SiC JFET technology will complement onsemi's extensive EliteSiC power portfolio and enable the company to address the need for high energy efficiency and power density in the AC-DC stage in power supply units for AI data centers.
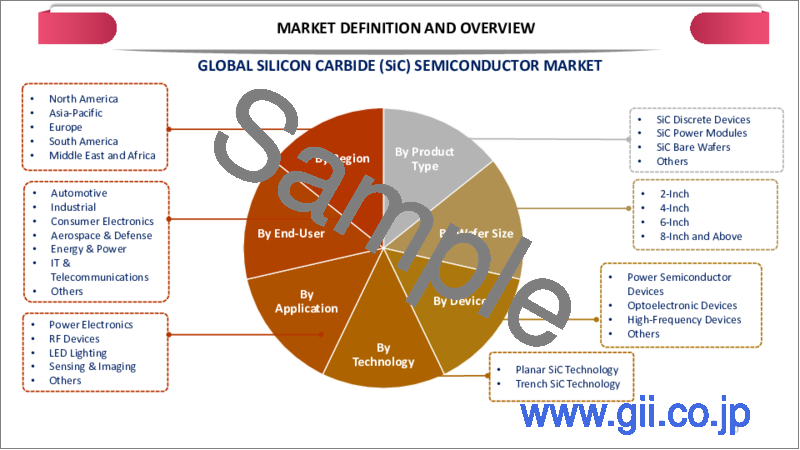
By Type
- SiC Discrete Devices
- SiC Power Modules
- SiC Substrates and Wafers
- Others
By Wafer Size
- 2-inch Wafers
- 4-inch Wafers
- 6-inch Wafers
- 8-inch Wafers
By Technology
- Planar SiC Technology
- Trench SiC Technology
By Application
- Automotive
- Consumer Electronics
- Industrial
- Aerospace & Defense
- Telecommunications
- Energy & Power
- Others
By Region
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- UK
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of South America
- Asia-Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
- Middle East and Africa
Why Purchase the Report?
- To visualize the global silicon carbide (sic) semiconductor market segmentation based on type, wafer size, technology, application and region.
- Identify commercial opportunities by analyzing trends and co-development.
- Excel data sheet with numerous data points at the silicon carbide (sic) semiconductor market level for all segments.
- PDF report consists of a comprehensive analysis after exhaustive qualitative interviews and an in-depth study.
- Product mapping available as excel consisting of key products of all the major players.
The global Silicon Carbide (SiC) Semiconductor market report would provide approximately 70 tables, 61 figures and 205 pages.
Target Audience 2024
- Manufacturers/ Buyers
- Industry Investors/Investment Bankers
- Research Professionals
- Emerging Companies
Table of Contents
1. Methodology and Scope
- 1.1. Research Methodology
- 1.2. Research Objective and Scope of the Report
2. Definition and Overview
3. Executive Summary
- 3.1. Snippet by Type
- 3.2. Snippet by Wafer Size
- 3.3. Snippet by Technology
- 3.4. Snippet by Application
- 3.5. Snippet by Region
4. Dynamics
- 4.1. Impacting Factors
- 4.1.1. Drivers
- 4.1.1.1. Rising in Aerospace and Defense Applications
- 4.1.1.2. Growing Demand for High-Power Applications
- 4.1.2. Restraints
- 4.1.2.1. High Investment Costs
- 4.1.3. Opportunity
- 4.1.4. Impact Analysis
- 4.1.1. Drivers
5. Industry Analysis
- 5.1. Porter's Five Force Analysis
- 5.2. Supply Chain Analysis
- 5.3. Pricing Analysis
- 5.4. Regulatory Analysis
- 5.5. Sustainable Analysis
- 5.6. DMI Opinion
6. By Type
- 6.1. Introduction
- 6.1.1. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Type
- 6.1.2. Market Attractiveness Index, By Type
- 6.2. SiC Discrete Devices*
- 6.2.1. Introduction
- 6.2.2. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%)
- 6.3. SiC Power Modules
- 6.4. SiC Substrates and Wafers
- 6.5. Others
7. By Wafer Size
- 7.1. Introduction
- 7.1.1. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Wafer Size
- 7.1.2. Market Attractiveness Index, By Wafer Size
- 7.2. 2-inch Wafers*
- 7.2.1. Introduction
- 7.2.2. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%)
- 7.3. 4-inch Wafers
- 7.4. 6-inch Wafers
- 7.5. 8-inch Wafers
8. By Technology
- 8.1. Introduction
- 8.1.1. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Technology
- 8.1.2. Market Attractiveness Index, By Technology
- 8.2. Planar SiC Technology*
- 8.2.1. Introduction
- 8.2.2. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%)
- 8.3. Trench SiC Technology
9. By Application
- 9.1. Introduction
- 9.1.1. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Application
- 9.1.2. Market Attractiveness Index, By Application
- 9.2. Automotive*
- 9.2.1. Introduction
- 9.2.2. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%)
- 9.3. Consumer Electronics
- 9.4. Industrial
- 9.5. Aerospace & Defense
- 9.6. Telecommunications
- 9.7. Energy & Power
- 9.8. Others
10. Sustainability Analysis
- 10.1. Environmental Analysis
- 10.2. Economic Analysis
- 10.3. Governance Analysis
11. By Region
- 11.1. Introduction
- 11.1.1. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Region
- 11.1.2. Market Attractiveness Index, By Region
- 11.2. North America
- 11.2.1. Introduction
- 11.2.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 11.2.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Type
- 11.2.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Wafer Size
- 11.2.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Technology
- 11.2.6. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Application
- 11.2.7. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 11.2.7.1. US
- 11.2.7.2. Canada
- 11.2.7.3. Mexico
- 11.3. Europe
- 11.3.1. Introduction
- 11.3.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 11.3.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Type
- 11.3.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Wafer Size
- 11.3.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Technology
- 11.3.6. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Application
- 11.3.7. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 11.3.7.1. Germany
- 11.3.7.2. UK
- 11.3.7.3. France
- 11.3.7.4. Italy
- 11.3.7.5. Spain
- 11.3.7.6. Rest of Europe
- 11.4. South America
- 11.4.1. Introduction
- 11.4.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 11.4.3. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 11.4.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Type
- 11.4.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Wafer Size
- 11.4.6. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Technology
- 11.4.7. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Application
- 11.4.8. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 11.4.8.1. Brazil
- 11.4.8.2. Argentina
- 11.4.8.3. Rest of South America
- 11.5. Asia-Pacific
- 11.5.1. Introduction
- 11.5.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 11.5.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Type
- 11.5.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Wafer Size
- 11.5.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Technology
- 11.5.6. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Application
- 11.5.7. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 11.5.7.1. China
- 11.5.7.2. India
- 11.5.7.3. Japan
- 11.5.7.4. Australia
- 11.5.7.5. Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 11.6. Middle East and Africa
- 11.6.1. Introduction
- 11.6.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 11.6.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Type
- 11.6.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Wafer Size
- 11.6.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Technology
- 11.6.6. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Application
12. Competitive Landscape
- 12.1. Competitive Scenario
- 12.2. Market Positioning/Share Analysis
- 12.3. Mergers and Acquisitions Analysis
13. Company Profiles
- 13.1. Infineon Technologies*
- 13.1.1. Company Overview
- 13.1.2. Product Portfolio and Description
- 13.1.3. Financial Overview
- 13.1.4. Key Developments
- 13.2. Littelfuse
- 13.3. ON Semiconductor
- 13.4. Wolfspeed Inc
- 13.5. Fuji Electric
- 13.6. X-FAB
- 13.7. GeneSiC Semiconductor
- 13.8. Mitsubishi Electric
- 13.9. STMicroelectronics
- 13.10. ROHM Semiconductor
LIST NOT EXHAUSTIVE
14. Appendix
- 14.1. About Us and Services
- 14.2. Contact Us