|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1290382
農業用プラスチックの世界市場-2023-2030Global Agricultural Plastics Market - 2023-2030 |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 農業用プラスチックの世界市場-2023-2030 |
|
出版日: 2023年06月12日
発行: DataM Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 195 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
- 全表示
- 概要
- 目次
市場概要
農業用プラスチックの世界市場は、2022年に106億米ドルに達し、2023年から2030年の予測期間中にCAGR 6.2%で成長し、2030年には171億米ドルに達すると予測されています。再生可能エネルギープロジェクトの成長は、中期的に農業用プラスチックの需要を促進する重要な要因になると思われます。
世界の農業用プラスチック市場は、農業技術の新たな進歩に伴い、継続的な進化を遂げています。特に先進国の都市部や半都市部における垂直農業の拡大は、そのニーズに独自に適合した新しいタイプのプラスチックを開発する新たな機会を創出するでしょう。
プラスチックメーカーは、業界の持続可能性を向上させるために、生産プロセスの変更を進めています。例えば、2023年5月、米国を拠点とする多国籍化学企業のダウは、再生可能なポリエチレンを製造するためのバイオベースのエチレン原料の長期供給を確保したと発表しました。
市場力学
新しい農業技術の人気の高まり
近年、都市化の進展により肥沃な耕作地が減少する中、垂直農法、水耕栽培、アクアポニックスなどの新しい農業技術の普及が進んでいます。UAE、シンガポール、イスラエルなどでは、耕作地がなくても新鮮な野菜や果物の国内生産を増やすために、垂直農法や水耕栽培を大規模に導入しています。
ほとんどすべての新しい農業技術は、断熱と微気候制御のために農業用プラスチックの使用を広範囲に頼っています。プラスチックは、悪天候、害虫、病気、紫外線から作物を守ります。さらに、プラスチックは水と栄養分の効率的な分配を促進し、作物の成長と生産性を最適化します。
気候変動の深刻化
気候変動は、干ばつ、洪水、異常気温など、予測不可能な気象現象の増加をもたらしています。また、気候変動の深刻化により、農業害虫や雑草の分布範囲が広がり、作物の損失が発生する可能性が高まっています。また、大気中の二酸化炭素濃度が上昇すると、農作物の栄養価が低下すると言われています。
農業用プラスチックは、ハウスやトンネルなど、農作物を悪天候から守るための構造物を提供することで、こうした気象条件による影響を軽減することができます。プラスチックは環境をコントロールすることで、農家はより安定した良好な気候の中で作物を栽培することができ、気候変動や予測不可能な気象パターンに関連するリスクを軽減することができます。
限られたリサイクルインフラ
プラスチックを多用する代替農法は近年急速に拡大していますが、リサイクルインフラはその成長に見合うだけの規模を備えていません。一部の国では、プラスチック廃棄物の発生とリサイクルに関して非常に厳しい規制が設けられています。これらの国の農業生産者は、プラスチック廃棄物を処理するためのインフラが限られているため、厳しい法的罰則に直面しています。
リサイクルの取り組みが活発化していますが、農業用プラスチックの分野では、リサイクルインフラが限られているため、課題に直面しています。多層フィルムや汚染物質など、農業用プラスチックの複雑な性質が、リサイクルをより困難にしています。適切な収集、選別、リサイクル施設がないため、農業用プラスチックのリサイクルオプションが制限され、廃棄物の増加に繋がっています。
COVID-19影響分析
COVID-19のパンデミックは世界のサプライチェーンを混乱させ、世界の農業に大きな影響を与えました。ロックダウンや労働力不足が農業活動に影響を与え、農業用プラスチックの需要減少につながっています。また、パンデミックによる規制のため、農業用プラスチックの生産にも支障をきたしました。
さらに、景気後退や個人消費の減少が農産物の需要に波及し、農業用プラスチックの需要にも間接的に影響を与えました。しかし、パンデミック後、農業セクターが回復し、農業用プラスチックの需要が回復しました。
AIによる影響
人工知能(AI)技術の進歩は、農業に革命を起こし、農業用プラスチックの使用量に影響を与える可能性があります。精密農業や自律型システムなど、AIを活用したソリューションは、資源配分、作物管理、収穫量予測を最適化します。この技術は、植物のニーズに基づいて正確に水を供給する精密灌漑システムなど、特定の用途における過剰なプラスチック使用の必要性を低減します。
AIはまた、農業用プラスチックの使用におけるより良いデータ駆動型の意思決定を促進し、その効率を向上させ、廃棄物を削減することができます。農業用プラスチックのデータ駆動型の使用は、マイクロプラスチック汚染が食糧生産に与える影響を抑制するのに役立ちます。また、AIは新しいプラスチックの研究開発プロセスの最適化にも応用することができます。
ウクライナ・ロシアへの影響
ウクライナ・ロシア戦争により、ウクライナとロシアの農業が崩壊し、両国の農業用プラスチックの需要が減少しました。EUと米国は、農業を含むロシア経済の主要部門に厳しい経済制裁を課しました。この制裁により、ロシアは農業用プラスチックの需要をアジアのサプライヤーに切り替えることになっています。
また、この戦争により、ロシアから地域への供給が途絶えたため、欧州のエネルギー価格が大きく跳ね上がりました。エネルギー価格の高騰は、欧州のプラスチックメーカーの競争力を低下させました。このシナリオは、アジアと北米のメーカーが欧州の犠牲の上に市場シェアを拡大する機会を作り出しました。
目次
第1章 調査手法とスコープ
- 調査手法
- 調査目的および調査範囲
第2章 定義と概要
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場力学
- 影響要因
- 促進要因
- 作物収量向上のための世界の推進力
- 垂直農法の採用拡大
- 新しい農法への注目の高まり
- 気候変動の深刻化
- 抑制要因
- 食物連鎖におけるマイクロプラスチック汚染に対する懸念の高まり
- リサイクルインフラが限られている
- 機会
- 影響分析
- 促進要因
第5章 産業分析
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- サプライチェーン分析
- 価格分析
- 法規制の分析
第6章 COVID-19の分析
第7章 材料別
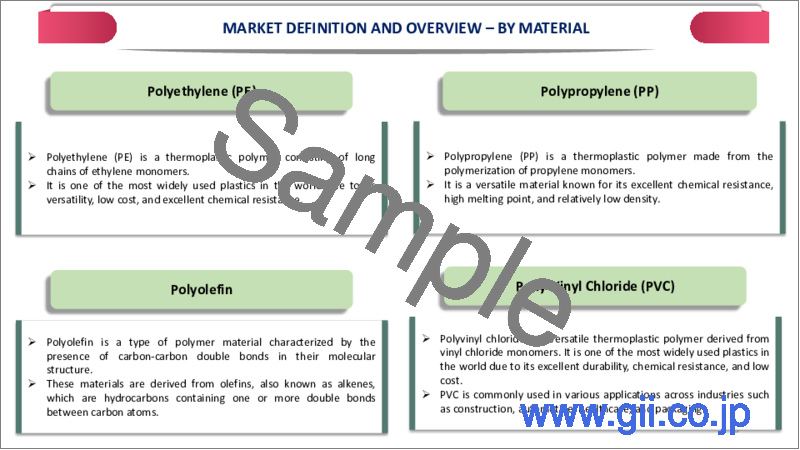
- ポリエチレン(PE)
- ポリプロピレン(PP)
- ポリオレフィン
- ポリ塩化ビニル(PVC)
- エチレン-酢酸ビニル共重合体(EVA)
- その他
第8章 用途別
- 植物保護フィルム
- 温室
- マルチング
- トンネル
- その他
- 水管理
- プラスチック製貯水タンク
- 灌漑システム
- サイレージ
- 遮光ネット
- 育苗ポット
- その他
第9章 地域別
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- メキシコ
- 欧州
- ドイツ
- 英国
- フランス
- イタリア
- スペイン
- その他欧州
- 南米
- ブラジル
- アルゼンチン
- その他南米地域
- アジア太平洋地域
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- オーストラリア
- その他アジア太平洋地域
- 中東・アフリカ地域
第10章 競合情勢
- 競合シナリオ
- 市況/シェア分析
- M&A(合併・買収)分析
第11章 企業プロファイル
- AEP Industries Inc.
- 会社概要
- 製品ポートフォリオと説明
- 財務概要
- 主な発展状況
- BASF SE
- Dow
- EYYonMobil Chemical
- Novamont S.p.A.
- Trioplast Group
- Berry Global
- Grupo Armando Alvarez
- Ab Rani Plast Oy
- BioBag International AS
第12章 付録
Market Overview
The Global Agricultural Plastics Market reached US$ 10.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to reach US$ 17.1 billion by 2030 growing with a CAGR of 6.2% during the forecast period 2023-2030. The growth of renewable energy projects will be a key factor in driving the demand for agricultural plastics in the medium term.
The global agricultural plastics market is witnessing continuous evolution, with new advances in farming technology. The expansion of vertical farming, especially in urban and semi-urban areas in developed countries will create new opportunities for the development of new types of plastics uniquely suited to its needs.
Plastic manufacturers are modifying their production processes to improve sustainability in the industry. For instance, in May 2023, Dow, the U.S.-based multinational chemical company, announced that it secured a long-term supply of bio-based ethylene feedstock for the production of renewable polyethylene.
Market Dynamics
Growing Popularity of New Farming Techniques
New farming techniques such as vertical farming, hydroponics and aquaponics have become increasingly popular in recent years, as growing urbanization shrinks the availability of fertile and arable land. Countries such as the UAE, Singapore and Israel are adopting vertical farming and hydroponics on a large scale to increase domestic production of fresh fruits and vegetables in the absence of arable land.
Almost all new farming techniques extensively rely on the usage of agricultural plastics for insulation and microclimate control. Plastics protect crops from adverse weather conditions, pests, diseases and UV radiation. Furthermore, plastics also facilitate efficient water and nutrient distribution, optimizing crop growth and productivity.
Increasing Severity of Climate Change
Climate change has resulted in the rise of unpredictable weather events, including droughts, floods, and extreme temperatures. Furthermore, the rising severity of climate change has increased the range of distribution of agricultural pests and weeds, thus creating more potential for crop loss. Rising atmospheric CO2 levels are also purported to reduce the nutritional value of food crops.
Agricultural plastics help mitigate the impact of these weather events by providing protective structures, such as greenhouses and tunnels, which shield crops from adverse weather conditions. By creating a controlled environment, plastics enable farmers to cultivate crops in a more stable and favorable climate, reducing the risks associated with climate change and unpredictable weather patterns.
Limited Recycling Infrastructure
Alternative farming methods that extensively use plastic have grown tremendously in recent years, however, recycling infrastructure hasn't scaled up to account for this growth. Some countries have extremely stringent regulations on the generation and recycling of plastic waste. Agricultural producers in these countries face tough legal penalties due to the limited infrastructure available for handling plastic waste.
Although recycling initiatives are gaining momentum, the agricultural plastics sector faces challenges due to limited recycling infrastructure. The complex nature of agricultural plastics, such as multi-layer films and contaminated materials, makes recycling more difficult. The lack of proper collection, sorting and recycling facilities limits the recycling options for agricultural plastics, leading to increased waste.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis
The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted global supply chains and had a significant impact on the global agricultural industry. Lockdowns and labor shortages affected agricultural activities which led to a reduction in demand for agricultural plastics. The production of agricultural plastics was also disturbed due to pandemic restrictions.
Furthermore, the economic downturn and reduced consumer spending had a ripple effect on the demand for agricultural products, indirectly affecting the demand for agricultural plastics. However, in the aftermath of the pandemic, the agricultural sector rebounded, leading to a resurgence in the demand for agricultural plastics.
AI Impact
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) technologies have the potential to revolutionize agriculture and impact the usage of agricultural plastics. AI-powered solutions, such as precision farming and autonomous systems, optimize resource allocation, crop management and yield prediction. The technologies reduce the need for excessive plastic use in certain applications, such as precision irrigation systems that precisely deliver water based on plant needs.
AI can also facilitate better data-driven decision-making in the use of agricultural plastics, improving their efficiency and reducing waste. Data-driven usage of agricultural plastics will help to curb the impact of microplastic pollution on food production. AI can also be applied to optimize the research and development process for new plastics.
Ukraine-Russia Impact
The Ukraine-Russia war disrupted the agricultural industries of Ukraine and Russia, thus leading to a reduced demand for agricultural plastics from both countries. Stringent economic sanctions were imposed by the EU and the U.S., on all major sectors of the Russian economy, including agriculture. The sanctions caused Russia to switch towards Asian suppliers to fulfill its demand for agricultural plastics.
The war also caused a major jump in European energy prices, as Russia disrupted supplies to the region. High energy prices have eroded the competitiveness of European plastic manufacturers. The scenario has created opportunities for Asian and North American manufacturers to increase their market shares at Europe's expense.
Segment Analysis
The global agricultural plastics market is segmented based on material, application and region.
Due to its High Versatility and Durability, Polyethylene is the Most Widely Used Agricultural Plastic
Polyethylene accounts for nearly a third of the market share of plastic materials. Polyethylene is a highly versatile plastic that can be easily molded, extruded, or formed into various shapes and sizes. The versatility allows for various agricultural plastic products such as films, sheets, bags, tubes, and pipes to be produced from polyethylene.
Polyethylene exhibits excellent durability and longevity, which are essential characteristics for agricultural applications. Agricultural plastics need to withstand harsh environmental conditions, including exposure to sunlight, moisture and chemicals. Polyethylene resists degradation from UV radiation, moisture and many agricultural chemicals, ensuring prolonged use in the field without significant deterioration.
Geographical Analysis
Strong Government Incentives Enable North America to Garner Major Market Share
North America occupies a share of nearly a quarter of the global agricultural plastics market. U.S. and Canada have encouraged innovation in their agriculture industries through strong government incentives. The U.S. federal government spends nearly US$ 20 billion annually on subsidies for farm businesses.
The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) also grants preferential grants and loans for new agricultural innovations. Agricultural R&D in the U.S. mainly focuses on areas such as biodegradable plastics, reducing plastic waste and enhancing the functional properties of agricultural plastics. In December 2022, the USDA announced a grant of US$ 9.5 million to develop new bioproducts and bioplastics for the agricultural industry.
Competitive Landscape
The major global players include: AEP Industries Inc., BASF SE, Dow, EYYonMobil Chemical, Novamont S.p.A., Trioplast Group, Berry Global, Grupo Armando Alvarez, Ab Rani Plast Oy and BioBag International AS.
Why Purchase the Report?
- To visualize the global agricultural plastics market segmentation based on material, application and region, as well as understand key commercial assets and players.
- Identify commercial opportunities by analyzing trends and co-development.
- Excel data sheet with numerous data points of agricultural plastics market-level with all segments.
- PDF report consists of a comprehensive analysis after exhaustive qualitative interviews and an in-depth study.
- Product mapping available as Excel consisting of key products of all the major players.
The global agricultural plastics market report would provide approximately 50 tables, 53 figures and 195 Pages.
Target Audience 2023
- Plastics Manufacturers
- Petrochemical Companies
- Manufacturers/ Buyers
- Industry Investors/Investment Bankers
- Research Professionals
- Emerging Companies
Table of Contents
1. Methodology and Scope
- 1.1. Research Methodology
- 1.2. Research Objective and Scope of the Report
2. Definition and Overview
3. Executive Summary
- 3.1. Snippet by Material
- 3.2. Snippet by Application
- 3.3. Snippet by Region
4. Dynamics
- 4.1. Impacting Factors
- 4.1.1. Drivers
- 4.1.1.1. Global Drive for Improving Crop Yields
- 4.1.1.2. Growing Adoption of Vertical Farming
- 4.1.1.3. Growing Popularity of New Farming Techniques
- 4.1.1.4. Increasing Severity of Climate Change
- 4.1.2. Restraints
- 4.1.2.1. Growing Concerns about the Microplastic Contamination of the Food Chain
- 4.1.2.2. Limited Recycling Infrastructure
- 4.1.3. Opportunity
- 4.1.4. Impact Analysis
- 4.1.1. Drivers
5. Industry Analysis
- 5.1. Porter's Five Force Analysis
- 5.2. Supply Chain Analysis
- 5.3. Pricing Analysis
- 5.4. Regulatory Analysis
6. COVID-19 Analysis
- 6.1. Analysis of COVID-19
- 6.1.1. Scenario Before COVID
- 6.1.2. Scenario During COVID
- 6.1.3. Scenario Post COVID
- 6.2. Pricing Dynamics Amid COVID-19
- 6.3. Demand-Supply Spectrum
- 6.4. Government Initiatives Related to the Market During Pandemic
- 6.5. Manufacturers Strategic Initiatives
- 6.6. Conclusion
7. By Material
- 7.1. Introduction
- 7.1.1. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Material
- 7.1.2. Market Attractiveness Index, By Material
- 7.2. Polyethylene (PE)*
- 7.2.1. Introduction
- 7.2.2. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%)
- 7.3. Polypropylene (PP)
- 7.4. Polyolefin
- 7.5. Polly-Vinyl Chloride (PVC)
- 7.6. Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer (EVA)
- 7.7. Others
8. By Application
- 8.1. Introduction
- 8.1.1. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Application
- 8.1.2. Market Attractiveness Index, By Application
- 8.2. Plant Protection Films*
- 8.2.1. Introduction
- 8.2.2. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%)
- 8.2.3. Greenhouse
- 8.2.4. Mulching
- 8.2.5. Tunnels
- 8.2.6. Others
- 8.3. Water Management
- 8.3.1. Plastic Reservoirs
- 8.3.2. Irrigation Systems
- 8.4. Silage
- 8.5. Shading Nets
- 8.6. Nursery Pots
- 8.7. Others
9. By Region
- 9.1. Introduction
- 9.1.1. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Region
- 9.1.2. Market Attractiveness Index, By Region
- 9.2. North America
- 9.2.1. Introduction
- 9.2.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 9.2.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Material
- 9.2.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Application
- 9.2.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 9.2.5.1. The U.S.
- 9.2.5.2. Canada
- 9.2.5.3. Mexico
- 9.3. Europe
- 9.3.1. Introduction
- 9.3.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 9.3.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Material
- 9.3.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Application
- 9.3.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 9.3.5.1. Germany
- 9.3.5.2. The UK
- 9.3.5.3. France
- 9.3.5.4. Italy
- 9.3.5.5. Spain
- 9.3.5.6. Rest of Europe
- 9.4. South America
- 9.4.1. Introduction
- 9.4.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 9.4.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Material
- 9.4.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Application
- 9.4.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 9.4.5.1. Brazil
- 9.4.5.2. Argentina
- 9.4.5.3. Rest of South America
- 9.5. Asia-Pacific
- 9.5.1. Introduction
- 9.5.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 9.5.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Material
- 9.5.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Application
- 9.5.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 9.5.5.1. China
- 9.5.5.2. India
- 9.5.5.3. Japan
- 9.5.5.4. Australia
- 9.5.5.5. Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 9.6. Middle East and Africa
- 9.6.1. Introduction
- 9.6.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 9.6.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Material
- 9.6.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Application
10. Competitive Landscape
- 10.1. Competitive Scenario
- 10.2. Market Positioning/Share Analysis
- 10.3. Mergers and Acquisitions Analysis
11. Company Profiles
- 11.1. AEP Industries Inc.*
- 11.1.1. Company Overview
- 11.1.2. Product Portfolio and Description
- 11.1.3. Financial Overview
- 11.1.4. Key Developments
- 11.2. BASF SE
- 11.3. Dow
- 11.4. EYYonMobil Chemical
- 11.5. Novamont S.p.A.
- 11.6. Trioplast Group
- 11.7. Berry Global
- 11.8. Grupo Armando Alvarez
- 11.9. Ab Rani Plast Oy
- 11.10. BioBag International AS
LIST NOT EXHAUSTIVE
12. Appendix
- 12.1. About Us and Services
- 12.2. Contact Us