|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1553393
全身性エリテマトーデス - 市場の洞察、疫学、市場予測:2034年Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Market Insight, Epidemiology, and Market Forecast - 2034 |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
|
|||||||
| 全身性エリテマトーデス - 市場の洞察、疫学、市場予測:2034年 |
|
出版日: 2024年08月01日
発行: DelveInsight
ページ情報: 英文 180 Pages
納期: 1~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
主要7ヶ国市場における全身性エリテマトーデスの市場規模は、2023年に約32億米ドルとなりました。EU4ヶ国(ドイツ、スペイン、イタリア、フランス)、英国、日本に比べて米国が最大(約26億米ドル)となっています。EU4ヶ国と英国の中では、スペインが最も市場規模が大きく、次いで英国でした。
全身性エリテマトーデスは、身体の様々な部位に影響を及ぼす慢性の自己免疫疾患です。通常、感染や病気から体を守る免疫系が、自分自身の組織を攻撃することで発症します。この攻撃は炎症を引き起こし、場合によっては皮膚、関節、心臓、肺、腎臓、循環血液細胞、脳など広範囲に及ぶ永久的な組織損傷を引き起こします。
全身性エリテマトーデスの診断は、臨床所見と検査所見の組み合わせに基づいて行われます。診断基準に精通していることは、臨床医が全身性エリテマトーデスを認識し、標的臓器症状のパターンに基づいてこの複雑な疾患を下位分類するのに役立ちます。ACR/EULARの分類では、HEp-2細胞で少なくとも1:80の抗核抗体(ANA)力価、またはそれに相当する陽性反応が少なくとも1回必要です。それがあれば、7つの臨床領域(体質、血液学的、神経精神医学的、粘膜皮膚、漿液性、筋骨格系、腎臓)と3つの免疫学的領域(抗リン脂質抗体、補体蛋白、SLE特異的抗体)からなる22の「加算加重」分類基準が考慮されます。各基準は2点から10点の範囲で点数化されます。臨床的基準が少なくとも1つあり、10点以上の患者は全身性エリテマトーデスに分類されます。
当レポートでは、主要7ヶ国における全身性エリテマトーデス市場について調査し、市場の概要とともに、疫学、患者動向、新たな治療法、2034年までの市場規模予測、および医療のアンメットニーズなどを提供しています。
目次
第1章 重要な洞察
第2章 レポートのイントロダクション
第3章 全身性エリテマトーデスのエグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 疫学と市場予測の調査手法
第5章 SLE市場概要
第6章 疾患の背景と概要
- イントロダクション
- 原因とリスク要因
- 兆候と症状
- 病態生理学
- 診断
- 治療
第7章 疫学と患者人口
- 主な調査結果
- 前提と根拠
- 主要7ヶ国におけるSLEの診断済み有病者総数
- 米国
- EU4ヶ国と英国
- 日本
- 患者動向
第8章 上市済み治療法
第9章 新たな治療法
第10章 全身性エリテマトーデス(SLE):主要7ヶ国分析
- 主な調査結果
- 市場見通し
- コンジョイント分析
- 主要な市場予測の前提条件
- 主要7ヶ国におけるSLEの総市場規模
- 米国の市場規模
- EU4ヶ国と英国の市場規模
- 日本
第11章 アンメットニーズ
第12章 SWOT分析
第13章 KOLの見解
第14章 市場アクセスと償還
- 米国
- EU4ヶ国と英国
- 日本
- 市場アクセスと償還
- 付録
- 文献
- レポートの調査手法
- DelveInsightのサービス内容
- 免責事項
- DelveInsightについて
List of Tables
- Table 1: Summary of SLE Market and Epidemiology (2020-2034)
- Table 2: EULAR/ACR Classification Criteria for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Table 3: EULAR Recommendations for the Management of SLE
- Table 4: Levels of Evidence and Grades of Recommendation for Diagnosis, Assessment, and Monitoring of nonrenal SLE
- Table 5: Management of SLE Patients With Renal Involvement
- Table 6: Recommendations for Clinical and Serological Features Prompting Consideration of a Diagnosis of SLE
- Table 7: Recommendations for cSLE - Diagnostic Procedures
- Table 8: Recommendations for NP-cSLE - Diagnostic Procedures
- Table 9: EULAR Recommendations for the Management of SLE
- Table 10: Levels of Evidence and Grades of Recommendation for Medications Used in the Treatment of Nonrenal SLE
- Table 11: Recommendations for the Management of Mild SLE
- Table 12: Recommendations for the Management of Moderate SLE
- Table 13: Recommendations for the Management of Severe SLE
- Table 14: Recommendations for cSLE - Management and Treatment
- Table 15: Recommendations for NP-cSLE - Treatment
- Table 16: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in the 7MM, in thousands (2020-2034)
- Table 17: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in the US, in thousands (2020-2034)
- Table 18: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE by Gender in the US, in thousands (2020-2034)
- Table 19: Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE by Age in the US, in thousands (2020-2034)
- Table 20: Severity-based Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in the US, in thousands (2020-2034)
- Table 21: Total Treated Cases of SLE in the US, in thousands (2020-2034)
- Table 22: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in EU4 and the UK, in thousands (2020-2034)
- Table 23: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE by Gender in EU4 and the UK, in thousands (2020-2034)
- Table 24: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE by Age in EU4 and the UK, in thousands (2020-2034)
- Table 25: Severity-Based Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in EU4 and the UK, in thousands (2020-2034)
- Table 26: Total Treated Cases of SLE in EU4 and the UK, in thousands (2020-2034)
- Table 27: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in Japan, in thousands (2020-2034)
- Table 28: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE by Gender in Japan, in thousands (2020-2034)
- Table 29: Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE by Age in Japan, in thousands (2020-2034)
- Table 30: Severity-Based Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in Japan, in thousands (2020-2034)
- Table 31: Total Treated Cases of SLE in Japan, in thousands (2020-2034)
- Table 32: Comparison of Marketed Drugs
- Table 33: BENLYSTA (belimumab) Clinical Trial Description, 2024
- Table 34: SAPHNELO (anifrolumab) Clinical Trial Description, 2024
- Table 35: Comparison of Emerging Drugs Under Development
- Table 36: Litifilimab, Clinical Trial Description, 2024
- Table 37: Ianalumab, Clinical Trial Description, 2024
- Table 38: Cenerimod, Clinical Trial Description, 2024
- Table 39: Telitacicept, Clinical Trial Description, 2024
- Table 40: Dapirolizumab pegol, Clinical Trial Description, 2024
- Table 41: Obinutuzumab, Clinical Trial Description, 2024
- Table 42: Deucravacitinib, Clinical Trial Description, 2024
- Table 43: Upadacitinib, Clinical Trial Description, 2024
- Table 44: Key Market Forecast Assumptions of SLE in the United States
- Table 45: Key Market Forecast Assumptions of SLE in EU4 and the UK
- Table 46: Key Market Forecast Assumptions of SLE in Japan
- Table 47: Market Size of SLE in the US, USD million (2020-2034)
- Table 48: Market Size of SLE in the US, USD million (2020-2034)
- Table 49: Market Size of SLE by Therapies in the US, USD million (2020-2034)
- Table 50: Market Size of SLE in EU4 and the UK, in USD million (2020-2034)
- Table 51: Market Size of SLE by Therapies in Germany, USD million (2020-2034)
- Table 52: Market Size of SLE by Therapies in France, USD million (2020-2034)
- Table 53: Market Size of SLE by Therapies in Italy, USD million (2020-2034)
- Table 54: Market Size of SLE by Therapies in Spain, USD million (2020-2034)
- Table 55: Market Size of SLE by Therapies in the UK, USD million (2020-2034)
- Table 56: Market Size of SLE in Japan, USD million (2020-2034)
- Table 57: Market Size of SLE by Therapies in Japan, USD million (2020-2034)
- Table 58: NICE Assessment for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Therapies
- Table 59: IQWiG Assessment for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Therapies
- Table 60: HAS Assessment for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Therapies
- Table 61: AEMPS Assessment for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Therapies
- Table 62: AIFA Assessment for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Therapies
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Pathophysiology of SLE
- Figure 2: Diagnostic Approach to a Patient With Suspected SLE
- Figure 3: Management of SLE
- Figure 4: EULAR Recommendations for the Management of SL? Drugs, Treatment Strategy, Targets of Therapy and Adjunct Therapy
- Figure 5: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in the 7MM (2020-2034)
- Figure 6: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in the US (2020-2034)
- Figure 7: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE by Gender in the US (2020-2034)
- Figure 8: Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE by Age in the US (2020-2034)
- Figure 9: Severity-based Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in the US (2020-2034)
- Figure 10: Total Treated Cases of SLE in the US (2020-2034)
- Figure 11: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in EU4 and the UK (2020-2034)
- Figure 12: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE by Gender in EU4 and the UK (2020-2034)
- Figure 13: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE by Age in EU4 and the UK (2020-2034)
- Figure 14: Severity-Based Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in EU4 and the UK (2020-2034)
- Figure 15: Total Treated Cases of SLE in EU4 and the UK (2020-2034)
- Figure 16: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in Japan (2020-2034)
- Figure 17: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE by Gender in Japan (2020-2034)
- Figure 18: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE by Age in Japan, in thousands (2020-2034)
- Figure 19: Severity-Based Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in Japan (2020-2034)
- Figure 20: Total Treated Cases of SLE in Japan(2020-2034)
- Figure 21: Market Size of SLE in the 7MM, USD million (2020-2034)
- Figure 22: Market Size of SLE in the US, USD million (2020-2034)
- Figure 23: Market Size of SLE by Therapies in the US, USD million (2020-2034)
- Figure 24: Market Size of SLE in EU4 and the UK, in USD million (2020-2034)
- Figure 25: Market Size of SLE by Therapies in EU4 and the UK, USD million (2020-2034)
- Figure 26: Market Size of SLE in Japan, USD million (2020-2034)
- Figure 27: Market Size of SLE by Therapies in Japan, USD million (2020-2034)
- Figure 28: Health Technology Assessment
- Figure 29: Reimbursement Process in Germany
- Figure 30: Reimbursement Process in France
- Figure 31: Reimbursement Process in Italy
- Figure 32: Reimbursement Process in Spain
- Figure 33: Reimbursement Process in the United Kingdom
- Figure 34: Reimbursement Process in Japan
Key Highlights:
- Systemic lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disorder characterized by antibodies to nuclear and cytoplasmic antigens, multisystem inflammation, protean clinical manifestations, and a relapsing and remitting course.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus mostly affects women. Approximately, 90% of women seem to be affected by the prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Among 7MM, the US accounted for the highest number of cases approximately 50% and approximately 51% of the cases accounted for moderate severity.
- Treatments of systemic lupus erythematosus include NSAIDs and antimalarial agents, which are the first-line therapies for mild systemic lupus erythematosus. In addition, glucocorticoids and cytotoxic or immunosuppressive agents. BENLYSTA and SAPHNELO are approved by the FDA for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus.
- In May 2024, the US FDA approved a 200 mg subcutaneous route of administration of BENLYSTA for patients five years of age and older with active SLE who are receiving standard therapy. This option provides pediatric patients the possibility to receive the treatment at home.
- The US accounts for approximately 82% of systemic lupus erythematosus market share, with BENLYSTA occupying the largest market among therapies.
- Leading pharmaceutical companies such as Novartis/MorphoSys, Idorsia Pharmaceuticals/Viatris, RemeGen, and Biogen are actively working to improve the treatment landscape for systemic lupus erythematosus. In August 2023, AbbVie initiated its Phase III Select-SLE study to evaluate RINVOQ for moderate to severe SLE.
- The collaboration between Idorsia Pharmaceuticals and Viatris for the global development and commercialization of two Phase III assets, selatogrel and cenerimod, signifies significant progress in research and development.
- The future is certainly hopeful for an improved treatment a better disease understanding and a growing market.
DelveInsight's "Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - Market Insights, Epidemiology and Market Forecast - 2034" report delivers an in-depth understanding of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, historical and forecasted epidemiology as well as the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus market trends in the United States, EU4 (Germany, Spain, Italy, and France) and the United Kingdom, and Japan.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus market report provides real-world prescription pattern analysis, emerging drugs, market share of individual therapies, and historical and forecasted 7MM Systemic Lupus Erythematosus market size from 2020 to 2034. The report also covers current Systemic Lupus Erythematosus treatment practices/algorithms and unmet medical needs to curate the best opportunities and assess the market's underlying potential.
Geography Covered:
The United States
EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom
Japan
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Understanding and Treatment Algorithm
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Overview, Country-Specific Treatment Guidelines and Diagnosis
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect many parts of the body. Lupus occurs when the immune system, which normally helps protect the body from infection and disease, attacks its own tissues. This attack causes inflammation, and in some cases permanent tissue damage, which can be widespread - affecting the skin, joints, heart, lung, kidneys, circulating blood cells, and brain.
The diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus is based on a combination of clinical findings and laboratory evidence. Familiarity with the diagnostic criteria helps clinicians to recognize systemic lupus erythematosus and to subclassify this complex disease based on the pattern of target-organ manifestations. The ACR/EULAR classification requires an antinuclear antibody (ANA) titer of at least 1:80 on HEp-2 cells or an equivalent positive test at least once. If that is present, 22 "additive weighted" classification criteria are considered, comprising seven clinical domains (constitutional, hematologic, neuropsychiatric, mucocutaneous, serosal, musculoskeletal, renal) and three immunologic domains (antiphospholipid antibodies, complement proteins, SLE-specific antibodies). Each criterion is assigned points, ranging from 2 to 10. Patients with at least one clinical criterion and 10 or more points are classified as having systemic lupus erythematosus.
The systemic lupus erythematosus report provides an overview of systemic lupus erythematosus pathophysiology, diagnostic approaches, and detailed treatment algorithm along with a real-world scenario of a patient's journey beginning from the first symptom, the time taken for diagnosis to the entire treatment process.
Further details related to country-based variations in diagnosis are provided in the report
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Treatment
Treatment in systemic lupus erythematosus aims to prevent organ damage and achieve remission. The choice of treatment is dictated by the organ system/systems involved and the severity of involvement and ranges from minimal treatment (NSAIDs, antimalarials) to intensive treatment (cytotoxic drugs, corticosteroids). Patient education, physical and lifestyle measures, and emotional support play a central role in managing systemic lupus erythematosus.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Epidemiology
The Systemic Lupus Erythematosus epidemiology chapter in the report provides historical as well as forecasted in the 7MM covering the United States, EU4 countries (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the United Kingdom, and Japan from 2024 to 2034. The Systemic Lupus Erythematosus epidemiology is segmented with detailed insights into Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus by Gender, and Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus by Age, Severity-Based Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, and Total Treated Cases of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
- Between EU4 and the UK, Spain accounted for the highest number of diagnosed prevalent cases followed by the UK and Germany.
- The age group most affected by the prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus is 40-59 years. In 2023, among 7MM, approximately 40% of cases belonged to the 40-59 years age group.
- In 2023, approximately 50% of cases were found to be moderate cases in Spain.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Drug Chapters
The drug chapter segment of the systemic lupus erythematosus report encloses a detailed analysis of systemic lupus erythematosus marketed drugs and late-stage (Phase III and Phase II) pipeline drugs. It also deep dives into the systemic lupus erythematosus pivotal clinical trial details, recent and expected market approvals, patent details, the latest news, and recent deals and collaborations.
Marketed Drugs
BENLYSTA (belimumab): GlaxoSmithKline
BENLYSTA (belimumab), a B-lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) specific inhibitor, is a fully human monoclonal antibody that binds to soluble BLyS, which is found to be increased in patients with systemic autoimmune diseases like SLE and lupus nephritis (LN). ABy bding BLyS, BENLYSTA inhibits the prolonged survival of B cells, including autoreactive B cells, and reduces the differentiation of B cells into immunoglobulin-producing plasma cells. BENLYSTA does not bind B cells directly. The US FDA first approved BENLYSTA for the treatment of active systemic lupus erythematosus; it is the first and only approved biologic for both SLE and LN in more than 50 years, including for the pediatric population. It was first approved by the US FDA in 2011.
SAPHNELO (anifrolumab): AstraZeneca
SAPHNELO (anifrolumab) is a first in class, fully human monoclonal antibody that binds to subunit 1 of the type I interferon (IFN) receptor, blocking the activity of type I IFN. Type I IFNs, such as IFN-alpha, IFN-beta and IFN-kappa, are cytokines involved in regulating the inflammatory pathways implicated in SLE. The majority of adults with SLE have increased type I IFN signaling, which is associated with increased disease activity and severity. SAPHNELO is approved to treat systemic lupus erythematosus in more than 60 countries worldwide including the US, EU and Japan, with reviews ongoing in other countries.
Emerging Drugs
Cenerimod: Idorsia Pharmaceuticals/Viatris
Cenerimod is a highly selective sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1P1) receptor modulator, given as an oral once-daily tablet. While the cause of SLE is not fully known, T and B-lymphocytes are considered the key immune cells playing a role in the development of SLE. T and B-lymphocytes have a cell surface receptor called S1P1. These receptors enable T and B-lymphocytes to detect the signaling molecule S1P - sphingosine 1 phosphate - which is responsible for lymphocyte trafficking from the lymph nodes to the circulation. By binding to S1P1 receptors, a receptor modulator can trigger the internalization of those receptors. This effectively blinds T and B lymphocytes to the S1P gradient, thereby holding them in the lymph nodes and reducing autoreactive T and B cells in the circulation and, consequently, also in the tissues. In December 2017, the US FDA designated the investigation of cenerimod for the treatment of SLE as a fast-track development program. Currently it is in Phase III of its clinical development.
Litifilimab: Biogen
Litifilimab is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) targeting BDCA2 and is being investigated for the potential treatment of SLE and cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE). BDCA2 is a receptor that is predominantly expressed on a subset of human immune cells called Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells (pDCs). The binding of litifilimab to BDCA2 has been shown to reduce the production of pro-inflammatory molecules by pDCs, including type-I interferon (IFN-I) as well as other cytokines and chemokines. Currently it is in Phase III of its clinical development.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Market Outlook
Key players, such as Novartis/MorphoSys, Idorsia Pharmaceuticals/Viatris, RemeGen, Biogen, and others are evaluating their lead candidates in different stages of clinical development, respectively. They aim to investigate their products for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus.
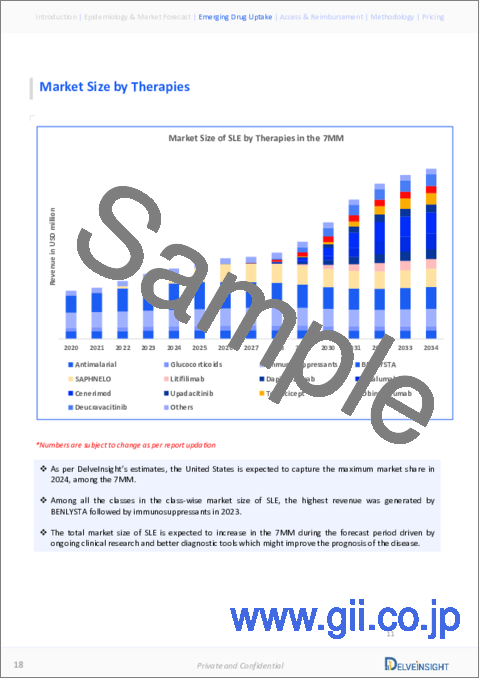
- The market size of systemic lupus erythematosus in the seven major markets was around USD 3,200 million in 2023.
- The United States accounts for the largest market size (around USD 2,600 million) of systemic lupus erythematosus, in comparison to EU4 (Germany, Spain, Italy, France), the United Kingdom, and Japan.
- Among EU4 and the UK, Spain had the highest market size followed by the UK.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Drugs Uptake
This section focuses on the uptake rate of potential drugs expected to be launched in the market during 2024-2034, which depends on the competitive landscape, safety, and efficacy data along with order of entry. It is important to understand that the key players evaluating their novel therapies in the pivotal and confirmatory trials should remain vigilant when selecting appropriate comparators to stand the greatest chance of a positive opinion from regulatory bodies, leading to approval, smooth launch, and rapid uptake.
Further detailed analysis of emerging therapies drug uptake in the report...
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Activities
The report provides insights into different therapeutic candidates in Phase III and Phase II stages. It also analyzes key players involved in developing targeted therapeutics.
Pipeline Development Activities
The report covers information on collaborations, acquisitions and mergers, licensing, and patent details for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus emerging therapies.
KOL Views
To keep up with the real-world scenario in current and emerging market trends, we take opinions from Key Industry leaders working in the domain through primary research to fill the data gaps and validate our secondary research. Industry Experts were contacted for insights on the evolving treatment landscape, patient reliance on conventional therapies, patient therapy switching acceptability, and drug uptake along with challenges related to accessibility.
DelveInsight's analysts connected with 10+ KOLs to gather insights; however, interviews were conducted with 5+ KOLs in the 7MM. Their opinion helps understand and validate current and emerging treatment patterns of systemic lupus erythematosus. This will support the clients in potential upcoming novel treatments by identifying the overall scenario of the market and the unmet needs.
Qualitative Analysis
We perform Qualitative and market Intelligence analysis using various approaches, such as SWOT analysis and Conjoint Analysis. In the SWOT analysis, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in terms of gaps in disease diagnosis, patient awareness, physician acceptability, competitive landscape, cost-effectiveness, and geographical accessibility of therapies are provided.
Conjoint Analysis analyzes multiple approved and emerging therapies based on relevant attributes such as safety, efficacy, frequency of administration, route of administration, and order of entry. Scoring is given based on these parameters to analyze the effectiveness of therapy.
In efficacy, the trial's primary and secondary outcome measures are evaluated; for instance, in event-free survival, one of the most important primary outcome measures is event-free survival and overall survival.
Further, the therapies' safety is evaluated wherein the acceptability, tolerability, and adverse events are majorly observed, and it sets a clear understanding of the side effects posed by the drug in the trials. In addition, the scoring is also based on the probability of success, and the addressable patient pool for each therapy. According to these parameters, the final weightage score and the ranking of the emerging therapies are decided.
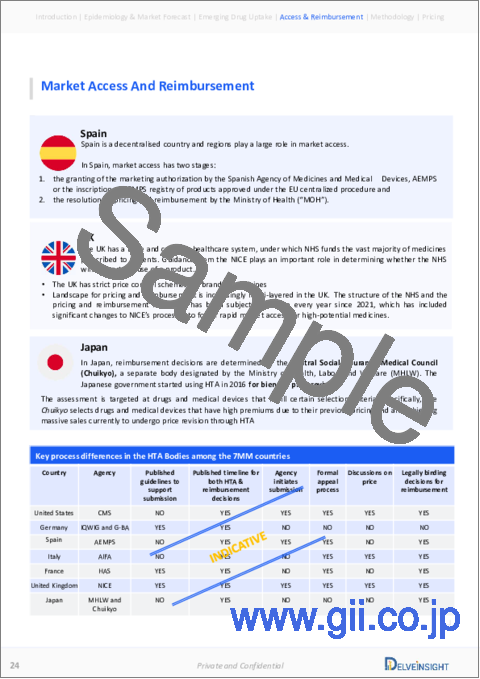
Market Access and Reimbursement
The treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus is mostly covered under the patients' insurance policy, either private or government. The companies like Genentech and AstraZeneca are also putting an effort in increasing the sales and market of their approved therapies by providing various kinds of financial assistance and reimbursement support to SLE patients. Moreover, as some of the emerging therapies are already approved for other indications, their respective companies provide some reimbursement or financial assistance to the patients. Therefore, it can be expected that once these therapies get approved for SLE, patients with SLE will also be able to avail these facilities and support without much delay or waiting time for the reimbursement to be approved by the government agencies.
The report further provides detailed insights on the country-wise accessibility and reimbursement scenarios, cost-effectiveness scenario of currently used therapies, programs making accessibility easier and out-of-pocket costs more affordable, insights on patients insured under federal or state government prescription drug programs, etc.
Scope of the Report:
- The report covers a segment of key events, an executive summary, descriptive overview of systemic lupus erythematosus, explaining its causes, signs and symptoms, pathogenesis, and currently available therapies.
- Comprehensive insight has been provided into the epidemiology segments and forecasts, the future growth potential of diagnosis rate, and disease progression along with country specific treatment guidelines.
- Additionally, an all-inclusive account of both the current and emerging therapies, along with the elaborative profiles of late-stage and prominent therapies, will have an impact on the current treatment landscape.
- A detailed review of the systemic lupus erythematosus market, historical and forecasted market size, market share by therapies, detailed assumptions, and rationale behind our approach is included in the report, covering the 7MM drug outreach.
- The report provides an edge while developing business strategies, by understanding trends, through SWOT analysis and expert insights/KOL views, patient journey, and treatment preferences that help in shaping and driving the 7MM systemic lupus erythematosus market.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Report Insights
- Patient Population
- Therapeutic Approaches
- Systemic lupus erythematosus Pipeline Analysis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus Market Size and Trends
- Existing and future Market Opportunity
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Report Key Strengths
- Ten Years Forecast
- 7MM Coverage
- Systemic lupus erythematosus Epidemiology Segmentation
- Inclusion of Country specific treatment guidelines
- KOL's feedback on approved and emerging therapies
- Key Cross Competition
- Conjoint analysis
- Drugs Uptake and Key Market Forecast Assumptions
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Report Assessment
- Current Treatment Practices
- Unmet Needs
- Pipeline Product Profiles
- Market Attractiveness
- Qualitative Analysis (SWOT and Conjoint Analysis)
FAQs:
- What is the growth rate of the 7MM systemic lupus erythematosus treatment market?
- What was the systemic lupus erythematosus total market size, the market size by therapies, market share (%) distribution in 2020, and what would it look like in 2034? What are the contributing factors/key catalysts for this growth?
- Is there any unexplored patient setting that can open the window for growth in the future?
- What are the pricing variations among different geographies for approved and off-label therapies?
- How would the market drivers, barriers, and future opportunities affect the market dynamics and subsequent analysis of the associated trends?
- What are the current and emerging options for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus?
- How many companies are developing therapies for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus?
- What are the recent novel therapies, targets, mechanisms of action, and technologies developed to overcome the limitations of existing therapies?
- Patient acceptability in terms of preferred treatment options as per real-world scenarios.
- What are the country-specific accessibility issues of expensive, recently approved therapies?
Reasons to buy:
- The report will help in developing business strategies by understanding the latest trends and changing treatment dynamics driving the systemic lupus erythematosus Market.
- Insights on patient burden/disease prevalence, evolution in diagnosis, and factors contributing to the change in the epidemiology of the disease during the forecast years
- Understand the existing market opportunities in varying geographies and the growth potential over the coming years.
- Distribution of historical and current patient share based on real-world prescription data along with reported sales of approved products in the US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the United Kingdom, and Japan.
- Identifying strong upcoming players in the market will help devise strategies to help get ahead of competitors.
- Detailed analysis and ranking of class-wise potential current and emerging therapies under the conjoint analysis section to provide visibility around leading classes.
- Highlights of access and reimbursement policies of approved therapies, barriers to accessibility of expensive off-label therapies, and patient assistance programs.
- To understand Key Opinion Leaders' perspectives around the accessibility, acceptability, and compliance-related challenges of existing treatment to overcome barriers in the future.
- Detailed insights on the unmet needs of the existing market so that the upcoming players can strengthen their development and launch strategy.
Table of Contents
1. Key Insights
2. Report Introduction
3. Executive Summary of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- 3.1. Key Events
4. Epidemiology and Market Forecast Methodology
5. SLE Market Overview at a Glance
- 5.1. Market Share by Therapies (%) in 2020 in the 7MM
- 5.2. Market Share by Therapies (%) in 2034 in the 7MM
6. Disease Background and Overview
- 6.1. Introduction
- 6.2. Causes and Risk Factors
- 6.3. Signs and Symptoms
- 6.4. Pathophysiology
- 6.5. Diagnosis
- 6.5.1. New Classification Criteria for SLE
- 6.5.2. Diagnostic Algorithm
- 6.5.3. Diagnostic Guidelines
- 6.5.3.1. EULAR Recommendations for the Management of SLE
- 6.5.3.2. The British Society for Rheumatology Guideline for the Management of SLE in Adults
- 6.5.3.3. European Evidence-based Recommendations for Diagnosis and Treatment of Childhood-onset SLE: The SHARE Initiative (2017)
- 6.6. Treatment
- 6.6.1. Treatment Algorithm
- 6.6.2. Treatment Guidelines
- 6.6.2.1. EULAR Recommendations for the Management of SLE
- 6.6.2.2. The British Society for Rheumatology guideline for the management of SLE in adults
- 6.6.2.3. European Evidence-based Recommendations for Diagnosis and Treatment of Childhood-onset SLE: The SHARE Initiative (2017)
7. Epidemiology and Patient Population
- 7.1. Key Findings
- 7.2. Assumptions and Rationale
- 7.2.1. The United States
- 7.2.2. EU4 and the UK
- 7.2.3. Japan
- 7.3. Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in the 7MM
- 7.4. The United States
- 7.4.1. Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in the United States
- 7.4.2. Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE by Gender in the United States
- 7.4.3. Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE by Age in the United States
- 7.4.4. Severity-Based Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in the United States
- 7.4.5. Total Treated Cases of SLE in the United States
- 7.5. EU4 and the UK
- 7.5.1. Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in EU4 and the UK
- 7.5.2. Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE by Gender in EU4 and the UK
- 7.5.3. Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE by Age in EU4 and the UK
- 7.5.4. Severity-Based Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in EU4 and the UK
- 7.5.5. Total Treated Cases of SLE in EU4 and the UK
- 7.6. Japan
- 7.6.1. Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in Japan
- 7.6.2. Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE by Gender in Japan
- 7.6.3. Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE by Age in Japan
- 7.6.4. Severity-Based Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of SLE in Japan
- 7.6.5. Total Treated Cases of SLE in Japan
- 7.7. Patient Journey
8. Marketed Therapies
- 8.1. Marketed Key Cross
- 8.2. BENLYSTA (belimumab): GlaxoSmithKline
- 8.2.1. Product Description
- 8.2.2. Regulatory Milestone
- 8.2.3. Other Developmental Activities
- 8.2.4. Clinical Development
- 8.2.4.1. Clinical Trial Information
- 8.2.5. Safety and Efficacy
- 8.3. SAPHNELO (anifrolumab): AstraZeneca
- 8.3.1. Product Description
- 8.3.2. Regulatory Milestone
- 8.3.3. Other Developmental Activities
- 8.3.4. Clinical Development
- 8.3.4.1. Clinical Trial Information
- 8.3.5. Safety and Efficacy
9. Emerging Therapies
- 9.1. Key Cross Competition
- 9.2. Litifilimab: Biogen
- 9.2.1. Other Developmental Activities
- 9.2.2. Clinical Development
- 9.2.2.1. Clinical Trial Information
- 9.2.3. Safety and Efficacy
- 9.2.4. Analyst Views
- 9.3. Ianalumab (VAY736): Novartis/MorphoSys
- 9.3.1. Drug Description
- 9.3.2. Other Developmental Activities
- 9.3.3. Clinical Development
- 9.3.3.1. Clinical Trials Information
- 9.3.4. Safety and Efficacy
- 9.3.5. Analyst Views
- 9.4. Cenerimod: Idorsia Pharmaceuticals/Viatris
- 9.4.1. Other Developmental Activities
- 9.4.2. Clinical Development
- 9.4.2.1. Clinical Trials Information
- 9.4.3. Safety and Efficacy
- 9.4.4. Analyst Views
- 9.5. Telitacicept (RC18): RemeGen
- 9.5.1. Drug Description
- 9.5.2. Other Developmental Activities
- 9.5.3. Clinical Development
- 9.5.3.1. Clinical Trials Information
- 9.5.4. Safety and Efficacy
- 9.5.5. Analyst Views
- 9.6. Dapirolizumab pegol: UCB Pharma/Biogen
- 9.6.1. Drug Description
- 9.6.2. Clinical Development
- 9.6.2.1. Clinical Trials Information
- 9.6.3. Safety and Efficacy
- 9.6.4. Analyst Views
- 9.7. GAZYVA (obinutuzumab): Genentech/Roche
- 9.7.1. Product Description
- 9.7.2. Clinical Development
- 9.7.2.1. Clinical Trials Information
- 9.7.3. Analyst Views
- 9.8. SOTYKTU (deucravacitinib): Bristol Myers Squibb
- 9.8.1. Clinical Development
- 9.8.1.1. Clinical Trials Information
- 9.8.2. Safety and Efficacy
- 9.8.3. Analyst Views
- 9.8.1. Clinical Development
- 9.9. RINVOQ (upadacitinib): AbbVie
- 9.9.1. Other Developmental Activities
- 9.9.2. Clinical Development
- 9.9.2.1. Clinical Trials Information
- 9.9.3. Safety and Efficacy
- 9.9.4. Analyst Views
10. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): The 7MM Analysis
- 10.1. Key Findings
- 10.2. Market Outlook
- 10.3. Conjoint Analysis
- 10.4. Key Market Forecast Assumptions
- 10.5. Total Market Size of SLE in the 7MM
- 10.6. The United States Market Size
- 10.6.1. Total Market Size of SLE in the United States
- 10.6.2. Market Size of SLE by Therapies in the United States
- 10.7. EU4 and the UK Market Size
- 10.7.1. Total Market Size of SLE in EU4 and the UK
- 10.7.2. Market Size of SLE by Therapies in EU4 and the UK
- 10.8. Japan
- 10.8.1. Total Market Size of SLE in Japan
- 10.8.2. Market Size of SLE by Therapies in Japan
11. Unmet Needs
12. SWOT Analysis
13. KOL Views
14. Market Access and Reimbursement
- 14.1. United States
- 14.1.1. Centre for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS)
- 14.2. EU4 and the UK
- 14.2.1. Germany
- 14.2.2. France
- 14.2.3. Italy
- 14.2.4. Spain
- 14.2.5. United Kingdom
- 14.3. Japan
- 14.3.1. MHLW
- 14.4. Market Access and Reimbursement
- 14.4.1. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE): UK
- 14.4.2. Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG): Germany
- 14.4.3. Haute Autorite de Sante (HAS): France
- 14.4.4. Spanish Agency of Medicines and Medical Products (AEMPS): Spain
- 14.4.5. Italian Medicines Agency (AIFA): Italy
- 14.4.6. Patient Access Program
- 14.4.7. Appendix
- 14.4.8. Bibliography
- 14.4.9. Report Methodology
- 14.4.10. DelveInsight Capabilities
- 14.4.11. Disclaimer
- 14.4.12. About DelveInsight