|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1789844
常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎市場- 世界および地域別 - 分析と予測(2025年~2035年)Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market - A Global and Regional Analysis: Analysis and Forecast, 2025-2035 |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
|
|||||||
| 常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎市場- 世界および地域別 - 分析と予測(2025年~2035年) |
|
出版日: 2025年08月14日
発行: BIS Research
ページ情報: 英文 100 Pages
納期: 1~5営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎は、腎臓における多数の液体を含んだ嚢胞の進行性開発を特徴とする遺伝性疾患です。
これらの嚢胞は時間とともに増大し、腎臓の肥大、腎機能の低下、最終的には末期腎不全(ESRD)に至ります。常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎は、最も一般的な遺伝性腎疾患の一つであり、世界で約500~1,000人に1人が罹患しています。この疾患は主にPKD1およびPKD2遺伝子の変異によって引き起こされ、正常な腎細胞の成長と機能を障害します。症状は成人期から始まることが多く、高血圧、脇腹痛、尿路感染症、腎結石などがみられます。常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎は患者のQOLに大きな影響を及ぼし、腎機能障害が進行性であること、進行すると透析や腎移植が必要となることから、医療負担が大きくなります。
常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎市場は、疾患の病態生理学的理解の進歩、常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎の標的療法の出現、診断率の上昇を燃料として力強い成長を遂げています。歴史的に常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎の管理は、血圧コントロールと症状緩和に焦点を当てた支持療法が中心でした。しかし、大塚製薬によるトルバプタン(ジナルク)の承認は、バソプレシンV2受容体に拮抗することにより嚢胞の成長と腎機能低下を遅らせる初の疾患修飾療法として画期的な出来事でした。
常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎の有病率の上昇は、市場を牽引する主な要因の一つです。常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎は、世界で約400万人から600万人が罹患しており、有病率は500人から1,000人に1人と推定されています。高解像度の画像診断技術(MRIや超音波検査)や遺伝子検査などの診断ツールに対する意識の高まりや進歩により、より早期かつ正確な診断が可能となっています。例えば米国では、国立糖尿病・消化器・腎臓病研究所(NIDDK)の報告によると、早期発見が一般的になりつつあり、患者は病気の進行を遅らせることができるタイムリーな介入を受けることができます。常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎の世界の診断数の増加は、薬物治療を必要とする患者層を拡大し、ひいては医薬品市場の成長を牽引しています。
さらに、2018年にトルバプタン(大塚製薬がJynarqueとして販売)がFDAから承認されたことは、常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎の最初の疾患修飾療法として重要なマイルストーンとなっています。トルバプタンはバソプレシンV2受容体を遮断することで嚢胞の成長を遅らせ、腎機能を維持します。「TEMPO3:4」試験などの臨床試験では、トルバプタンを投与した患者において腎容積の増大が30%抑制され、腎機能の低下が緩徐であることが実証され、常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎管理における画期的な治療薬として位置づけられました。この成功は研究開発投資の増加を促し、複数の製薬企業が有効性と安全性プロファイルを改善する次世代薬剤を模索しています。
また、世界の高齢化に伴い、常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎のような慢性疾患を抱える患者数は増加しています。常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎患者は、40~50歳代で高血圧、心血管合併症、腎不全を発症することが多いです。世界銀行は、2050年までに65歳以上の世界人口が15億人に達し、慢性疾患管理の需要が高まると予測しています。この人口動向は、腎機能と関連する併存疾患の両方に対処する包括的な治療オプションの必要性を拡大し、常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎市場の成長に拍車をかけています。
しかし、高額な治療費と限られた治療オプションが常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎市場の成長を阻害する要因となっています。例えば、米国ではトルバプタン療法にかかる年間費用が5万米ドルを超えることもあり、患者やヘルスケアシステムにとって経済的な障壁となっています。特に償還や保険適用が制限されている中低所得国では、この高価格がアクセスを制限しています。
さらに、現在、常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎に特化して承認されている疾患修飾薬はトルバプタンだけであり、ほとんどの患者はACE阻害薬やARBによる血圧管理などの支持療法に頼っています。有効な薬物療法が乏しいことは、重大なアンメット・メディカル・ニーズを浮き彫りにしています。このギャップは、シロリムスのようなmTOR阻害剤、ソマトスタチン類似体、より効果的に疾患の進行に対処することを目的とした新たな遺伝子治療薬など、現在進行中の新規候補の臨床試験を後押ししています。
常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎市場の主要企業は、競争優位性を獲得し、成長機会を活用するために、いくつかの戦略的イニシアチブを採用しています。大塚製薬のような主要企業は、トルバプタンのような既存の治療薬よりも有効性と安全性を向上させた次世代治療薬のポートフォリオを拡大するため、研究開発に多額の投資を行っています。例えば、大塚製薬は、患者のアドヒアランスと忍容性を向上させるための併用療法や新規製剤を検討しながら、トルバプタンの臨床応用を強化し続けています。
さらに、常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎の技術革新と臨床試験の成功を加速するため、企業はバイオテクノロジー企業、学術機関、診断企業との戦略的提携や協力関係を結んでおり、市場の成長を促しています。
当レポートでは、世界の常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎市場について調査し、市場の概要とともに、地域別の動向、および市場に参入する企業のプロファイルなどを提供しています。
目次
エグゼクティブサマリー
第1章 世界の常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎市場:業界展望
- 市場概要
- 常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎の疫学的解析
- 規制状況
- 主な動向
- 臨床試験分析
- 市場力学
- 影響分析
- 市場促進要因
- 市場抑制
- 市場機会
第2章 世界の常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎市場(地域別、100万米ドル、2023年~2035年)
- 北米
- 欧州
- アジア太平洋
第3章 世界の常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎市場:競合情勢と企業プロファイル
- 競合情勢
- 主要戦略と開発
- 企業プロファイル
- Otsuka Pharmaceutical
- Reata Pharmaceuticals
- Janssen Pharmaceuticals (Johnson & Johnson)
- Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated
- PKD
- Centessa Pharmaceuticals
- Novartis AG (Regulus Therapeutics)
- XORTX Therapeutics Inc.
第4章 調査手法
List of Figures
- Figure: Global Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market, Market Overview
- Figure: Global Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market, Epidemiological Analysis
- Figure: Global Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market Key Trends, Impact Analysis, 2023-2035
- Figure: Global Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market, Competitive Landscape, January 2022-April 2025
List of Tables
- Table: Global Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market, Regulatory Scenario
- Table: Global Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
Global Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market, Analysis and Forecast: 2025-2035
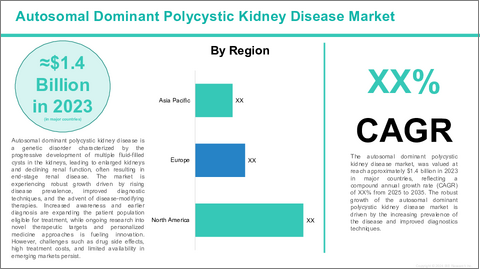
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disorder characterized by the progressive development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. These cysts enlarge over time, leading to kidney enlargement, loss of renal function, and eventually end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease is one of the most common inherited kidney disorders, affecting approximately 1 in 500 to 1,000 individuals globally. The disease is caused primarily by mutations in the PKD1 and PKD2 genes, which disrupt normal kidney cell growth and function. Symptoms often begin in adulthood and include hypertension, flank pain, urinary tract infections, and kidney stones. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease significantly impacts patient quality of life and imposes a substantial healthcare burden due to the progressive nature of renal impairment and the need for dialysis or kidney transplantation in advanced stages.
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease market is witnessing robust growth fueled by advancements in understanding the disease pathophysiology, the emergence of targeted therapies for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, and increasing diagnosis rates. Historically, management of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease was largely supportive, focusing on blood pressure control and symptom relief. However, the approval of tolvaptan (Jynarque) by Otsuka Pharmaceuticals marked a breakthrough as the first disease-modifying therapy that slows cyst growth and renal function decline by antagonizing vasopressin V2 receptors.
The rising prevalence of the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease is one of the major factors driving the market. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease affects approximately 4 to 6 million people worldwide, with prevalence estimates ranging from 1 in 500 to 1,000 individuals. Increasing awareness and advancements in diagnostic tools such as high-resolution imaging techniques (MRI and ultrasound) and genetic testing-have enabled earlier and more accurate diagnosis. For instance, in the U.S., the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) reports that earlier detection is becoming more common, allowing patients to receive timely interventions that can delay disease progression. The global rise in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease diagnosis is expanding the patient pool requiring pharmacological treatment, which in turn is driving growth in the drug market.
Moreover, the approval of tolvaptan (marketed as Jynarque by Otsuka Pharmaceuticals) in 2018 by the FDA marked a significant milestone as the first disease-modifying therapy for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Tolvaptan works by blocking vasopressin V2 receptors to slow cyst growth and preserve kidney function. Clinical trials such as the TEMPO 3:4 study demonstrated a 30% reduction in kidney volume growth and a slower decline in kidney function among treated patients, positioning tolvaptan as a breakthrough in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease management. This success has encouraged increased R&D investments, with several pharmaceutical companies exploring next-generation agents to improve efficacy and safety profiles.
In addition, as global populations age, the number of patients with chronic conditions like autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease is increasing. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease patients frequently develop hypertension, cardiovascular complications, and renal failure in their 40s and 50s. The World Bank estimates that the global population aged 65 and above will reach 1.5 billion by 2050, intensifying demand for chronic disease management. This demographic trend expands the need for comprehensive treatment options addressing both kidney function and associated comorbidities, thereby fueling growth in the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease market.
However, the high treatment cost and limited treatment options are some of the factors hindering the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease market growth. For instance, the annual cost of tolvaptan therapy can exceed $50,000 in the U.S., creating substantial affordability barriers for patients and healthcare systems. This high price limits access, particularly in low- and middle-income countries where reimbursement and insurance coverage are limited.
Moreover, currently, tolvaptan is the only approved disease-modifying drug specifically for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, with most patients relying on supportive care such as blood pressure management using ACE inhibitors or ARBs. The scarcity of effective pharmacotherapies underscores a significant unmet medical need. This gap drives ongoing clinical trials for new candidates, including mTOR inhibitors like sirolimus, somatostatin analogs, and emerging gene therapies aimed at addressing disease progression more effectively.
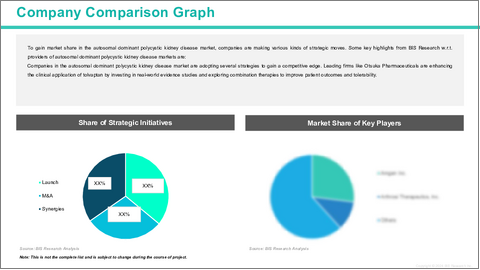
Key players in the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease market are adopting several strategic initiatives to gain a competitive edge and capitalize on growing opportunities. Leading companies such as Otsuka Pharmaceuticals are investing heavily in research and development to expand their portfolios with next-generation therapies that offer improved efficacy and safety over existing treatments, such as tolvaptan. For instance, Otsuka continues to enhance tolvaptan's clinical applications while exploring combination therapies and novel formulations to improve patient adherence and tolerability.
Additionally, companies are forming strategic collaborations and partnerships with biotech firms, academic institutions, and diagnostic companies to accelerate innovation and clinical trial success for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, thereby impelling the market growth.
Table of Contents
Executive Summary
Scope and Definition
Market/Product Definition
Key Questions Answered
Analysis and Forecast Note
1. Global Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market: Industry Outlook
- 1.1 Market Overview
- 1.2 Epidemiological Analysis of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
- 1.3 Regulatory Landscape
- 1.4 Key Trends
- 1.5 Clinical Trial Analysis
- 1.6 Market Dynamics
- 1.6.1 Impact Analysis
- 1.6.2 Market Drivers
- 1.6.3 Market Restraint
- 1.6.4 Market Opportunities
2. Global Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market, by Region, $Million, 2023-2035
- 2.1 North America
- 2.1.1 Market Dynamics
- 2.1.2 Market Sizing and Forecast
- 2.1.2.1 North America Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market, by Country
- 2.1.2.1.1 U.S.
- 2.1.2.1 North America Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market, by Country
- 2.2 Europe
- 2.2.1 Market Dynamics
- 2.2.2 Market Sizing and Forecast
- 2.2.2.1 Europe Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market, by Country
- 2.2.2.1.1 Germany
- 2.2.2.1.2 U.K.
- 2.2.2.1.3 France
- 2.2.2.1.4 Italy
- 2.2.2.1.5 Spain
- 2.2.2.1 Europe Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market, by Country
- 2.3 Asia-Pacific
- 2.3.1 Market Dynamics
- 2.3.2 Market Sizing and Forecast
- 2.3.2.1 Asia-Pacific Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market, by Country
- 2.3.2.1.1 Japan
- 2.3.2.1 Asia-Pacific Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market, by Country
3. Global Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market: Competitive Landscape and Company Profiles
- 3.1 Competitive Landscape
- 3.1.1 Key Strategies and Developments
- 3.1.1.1 Funding Activities
- 3.1.1.2 Mergers and Acquisitions
- 3.1.1.3 Regulatory Approvals
- 3.1.1.4 Partnerships, Collaborations and Business Expansions
- 3.1.1 Key Strategies and Developments
- 3.2 Company Profiles
- 3.2.1 Otsuka Pharmaceutical
- 3.2.1.1 Overview
- 3.2.1.2 Product Portfolio
- 3.2.1.3 Target Customers
- 3.2.1.4 Key Personnel
- 3.2.1.5 Analyst View
- 3.2.2 Reata Pharmaceuticals
- 3.2.2.1 Overview
- 3.2.2.2 Product Portfolio
- 3.2.2.3 Target Customers
- 3.2.2.4 Key Personnel
- 3.2.2.5 Analyst View
- 3.2.3 Janssen Pharmaceuticals (Johnson & Johnson)
- 3.2.3.1 Overview
- 3.2.3.2 Product Portfolio
- 3.2.3.3 Target Customers
- 3.2.3.4 Key Personnel
- 3.2.3.5 Analyst View
- 3.2.4 Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated
- 3.2.4.1 Overview
- 3.2.4.2 Product Portfolio
- 3.2.4.3 Target Customers
- 3.2.4.4 Key Personnel
- 3.2.4.5 Analyst View
- 3.2.5 PKD
- 3.2.5.1 Overview
- 3.2.5.2 Product Portfolio
- 3.2.5.3 Target Customers
- 3.2.5.4 Key Personnel
- 3.2.5.5 Analyst View
- 3.2.6 Centessa Pharmaceuticals
- 3.2.6.1 Overview
- 3.2.6.2 Product Portfolio
- 3.2.6.3 Target Customers
- 3.2.6.4 Key Personnel
- 3.2.6.5 Analyst View
- 3.2.7 Novartis AG (Regulus Therapeutics)
- 3.2.7.1 Overview
- 3.2.7.2 Product Portfolio
- 3.2.7.3 Target Customers
- 3.2.7.4 Key Personnel
- 3.2.7.5 Analyst View
- 3.2.8 XORTX Therapeutics Inc.
- 3.2.8.1 Overview
- 3.2.8.2 Product Portfolio
- 3.2.8.3 Target Customers
- 3.2.8.4 Key Personnel
- 3.2.8.5 Analyst View
- 3.2.1 Otsuka Pharmaceutical