|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1753876
凝固因子欠乏症市場 - 世界および地域別分析:欠乏症タイプ別、製品タイプ別、エンドユーザー別、地域別 - 分析と予測(2025年~2035年)Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market - A Global and Regional Analysis: Focus on Deficiency Type, Product Type, End-User, and Region - Analysis and Forecast, 2025-2035 |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
|
|||||||
| 凝固因子欠乏症市場 - 世界および地域別分析:欠乏症タイプ別、製品タイプ別、エンドユーザー別、地域別 - 分析と予測(2025年~2035年) |
|
出版日: 2025年06月23日
発行: BIS Research
ページ情報: 英文 110 Pages
納期: 1~5営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
凝固因子欠乏症は、正常な血液凝固に必要なタンパク質(凝固因子)の1つ以上が欠損しているか、正常に機能していない血液凝固障害です。
その結果、血液が効果的に凝固塊を形成できなくなり、出血過多になったり、けがや手術後の出血が止まりにくくなったりします。最も一般的な凝固因子欠乏症には、血友病A(血液凝固第VIII因子の欠乏)、血友病B(血液凝固第IX因子の欠乏)、およびフォン・ヴィレブランド病(フォン・ヴィレブランド因子の欠乏または機能障害)があります。凝固因子欠乏症は遺伝する可能性があり、血友病AおよびBのような疾患はX連鎖性劣性遺伝であるため、男性に多くみられます。しかし、肝疾患や特定の自己免疫疾患など、血液凝固能に影響を及ぼす疾患が原因で後天的に発症する因子欠乏症もあります。これらの因子欠乏症では、出血エピソードを予防または制御し、病状を効果的に管理するために、凝固因子濃縮製剤や遺伝子治療による継続的な治療が必要となることが多いです。
凝固因子欠乏症市場の主な促進要因のひとつは、治療法の進歩、特に長時間作用型の遺伝子組換え凝固因子や遺伝子治療の開発です。これらの技術革新は、一般的に凝固因子の頻繁な注入を必要とする従来の治療法に比べて大きな改善をもたらします。例えば、長時間作用型の遺伝子組換え凝固因子は、定期的な点滴の必要性を減らし、患者にとってより便利な治療法となり、QOLを向上させます。さらに、血友病Aや血友病Bのような疾患の根底にある遺伝的欠陥に対処することで、治癒の可能性を提供することを目的とした遺伝子治療は、画期的な解決策として支持を集めています。遺伝子治療が臨床試験で良好な結果を示し続けていることから、長期的あるいは治癒的な効果が期待され、凝固因子欠乏症治療に対する需要をさらに押し上げています。これらの進歩は、患者により効果的で個別化された、負担の少ない治療選択肢を提供するため、市場の成長拡大に寄与しています。
凝固因子欠乏症市場の成長にもかかわらず、いくつかの課題が依然としてその潜在能力を十分に発揮することを妨げています。特に遺伝子治療や長時間作用型遺伝子組換え凝固因子製剤のような高度な治療法では、治療費が高額になることが大きな課題です。これらの治療法は有望ではあるが、多額の初期費用がかかるため、多くの患者、特に中低所得国の患者にとってはアクセスの障壁となりうる。高額な治療費は、患者個人の経済的な負担を制限するだけでなく、ヘルスケアシステムにも負担をかけ、政府や保険会社がこれらの最先端治療へのアクセスを広く提供することを困難にしています。その結果、患者の治療負担は依然として大きく、救命治療へのアクセスは不平等なままであり、革新的な治療法が利用可能であるにもかかわらず、市場の成長可能性は制限されています。
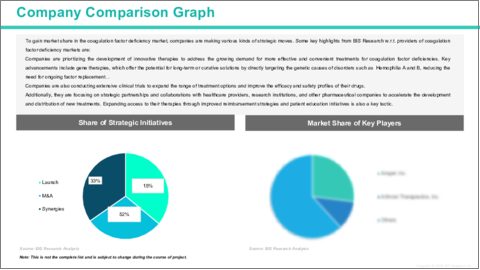
世界の凝固因子欠乏症市場は競争が激しく、複数の主要企業が技術革新と市場成長を牽引しています。Hoffmann-La Roche LtdやNovo Nordisk A/Sなどの主要企業が最先端を走っており、血友病Aや血友病Bに対する長時間作用型遺伝子組換え凝固因子や遺伝子治療などの先進的な治療法を開発しています。幅広いポートフォリオで知られるPfizer Inc.はこの分野での製品提供を拡大し続けており、Grifols, S.A.は凝固障害に対する血漿由来治療薬で躍進しています。さらに、Alnylam PharmaceuticalsやSangamo Therapeuticsなどの企業は、より効果的で個別化された治療を提供するために、遺伝子サイレンシングや遺伝子編集技術などの新しいアプローチを模索しています。これらの業界リーダーは、革新的な治療法や戦略的提携を通じて患者の転帰を改善する努力を続け、凝固因子欠乏症市場における競合優位性を高めています。
市場セグメンテーション
セグメンテーション1:欠乏症タイプ別
- 血友病A
- 血友病B
- フォンウィルブランド病
- 第XI因子および第XIII因子欠乏症
- その他の欠乏症
セグメンテーション2:製品タイプ別
- 遺伝子組み換え凝固因子
- 血漿由来凝固因子
- その他
セグメンテーション3:エンドユーザー別
- 病院
- 専門クリニック
- その他
セグメンテーション4:地域別
- 北米
- 欧州
- アジア太平洋
世界の凝固因子欠乏症市場は、診断と治療の展望を再構築しつつあるいくつかの重要な新興動向に見舞われています。このアプローチは、これらの凝固異常症の原因となる遺伝的欠陥に直接対処し、凝固因子濃縮製剤による生涯にわたる治療の必要性を低減することから、支持を集めています。さらに、市場では長時間作用型の遺伝子組換え凝固因子の開発が進んでおり、輸液の頻度を減らすことで患者の利便性を向上させています。もう一つの新たなトレンドは個別化医療の進展で、治療動向を個々の遺伝子プロファイルに合わせて調整し、患者により効果的で的確な治療を提供するものです。このような技術革新により、凝固因子欠乏症市場は、より効率的で患者中心のソリューションへと移行しつつあり、出血性疾患のQOLと長期管理の両方が改善されることが期待されています。
当レポートでは、世界の凝固因子欠乏症市場について調査し、市場の概要とともに、欠乏症タイプ別、製品タイプ別、エンドユーザー別、地域別の動向、および市場に参入する企業のプロファイルなどを提供しています。
目次
エグゼクティブサマリー
第1章 世界の凝固因子欠乏症市場:業界展望
- イントロダクション
- 市場動向
- 規制の枠組み
- 疫学分析
- 臨床試験分析
- 市場力学
- 影響分析
- 市場の促進要因
- 市場の課題
- 市場の機会
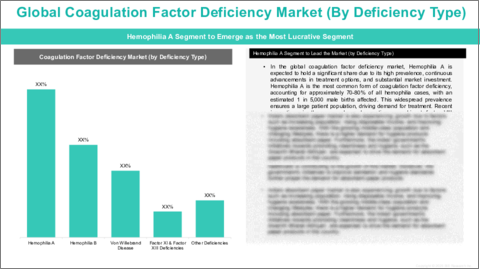
第2章 世界の凝固因子欠乏症市場(欠乏症タイプ別)、2023年~2035年
- 血友病A
- 血友病B
- フォン・ヴィレブランド病
- 第XI因子欠乏症
- 第XIII因子欠乏症
- その他
第3章 世界の凝固因子欠乏症市場(製品タイプ別)、2023年~2035年
- 血漿由来凝固因子
- 組換え凝固因子
- その他
第4章 世界の凝固因子欠乏症市場(エンドユーザー別)、2023年~2035年
- 病院
- 専門クリニック
- その他
第5章 世界の凝固因子欠乏症市場(地域別)、2023年~2035年
- 北米
- 欧州
- アジア太平洋
第6章 世界の凝固因子欠乏症市場:競合情勢と企業プロファイル
- 主要戦略と開発
- 合併と買収
- 相乗効果のある活動
- 事業拡大と資金調達
- 製品の発売と承認
- その他の活動
- 企業プロファイル
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- Sanofi S.A.
- Grifols, S.A.
- Novo Holdings A/S
- Pfizer Inc.
- Alnylam Pharmaceuticals
- Sangamo Therapeutics
- Centessa Pharmaceuticals
- Staidson Biopharma Inc.
- Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical
- OPKO Health, Inc.
- Novo Nordisk
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited
- Biogen Inc
- Octapharma AG
第7章 調査手法
List of Figures
- Figure: Global Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market (by Region), $Billion, 2024 and 2035
- Figure: Global Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market Key Trends, Analysis
List of Tables
- Table: Global Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
- Table: Global Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market (by Region), $Billion, 2024-2035
- Table: Global Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market (by Deficiency Type), $Billion, 2024-2035
- Table: Global Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market (by Product Type), $Billion, 2024-2035
- Table: Global Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market (by End-User), $Billion, 2024-2035
Global Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market, Analysis and Forecast: 2025-2035
Coagulation factor deficiency is a blood clotting disorder where one or more of the proteins (clotting factors) necessary for normal blood coagulation are either missing or not functioning properly. This results in the blood's inability to form clots effectively, leading to excessive bleeding or difficulty stopping bleeding after injury or surgery. The most common coagulation factor deficiencies include Hemophilia A (deficiency of Factor VIII), Hemophilia B (deficiency of Factor IX), and Von Willebrand Disease (deficiency or dysfunction of Von Willebrand factor). Coagulation factor deficiencies can be inherited, with conditions such as Hemophilia A and B being X-linked recessive, meaning they are more commonly seen in males. However, some factor deficiencies can also be acquired due to conditions that affect the blood's clotting ability, such as liver disease or certain autoimmune disorders. These deficiencies often require ongoing treatment with clotting factor concentrates or gene therapy to prevent or control bleeding episodes and manage the condition effectively.
One of the key drivers of the coagulation factor deficiency market is the advancement in treatment options, particularly the development of long-acting recombinant clotting factors and gene therapies. These innovations offer significant improvements over traditional treatments, which typically require frequent infusions of clotting factors. Long-acting recombinant clotting factors, for example, reduce the need for regular infusions, making treatment more convenient for patients and improving their quality of life. Additionally, gene therapy, which aims to provide a potential cure by addressing the genetic defects underlying conditions such as Hemophilia A and Hemophilia B, is gaining traction as a groundbreaking solution. As gene therapy continues to show positive results in clinical trials, it promises long-term or even curative benefits, further driving demand for coagulation factor deficiency treatments. These advancements are contributing to increased market growth as they offer patients more effective, personalized, and less burdensome treatment options.
Despite the growth of the coagulation factor deficiency market, several challenges continue to impede its full potential. One major challenge is the high cost of treatment, particularly for advanced therapies such as gene therapy and long-acting recombinant clotting factors. These therapies, while promising, come with significant upfront costs, which can be a barrier to access for many patients, especially in low- and middle-income countries. The high cost not only limits affordability for individual patients but also places a strain on healthcare systems, making it difficult for governments and insurers to provide widespread access to these cutting-edge treatments. As a result, the treatment burden on patients remains substantial, and access to life-saving therapies remains unequal, limiting the market's growth potential despite the availability of innovative treatments.
The global coagulation factor deficiency market is highly competitive, with several key players driving innovation and market growth. Leading companies such as Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd and Novo Nordisk A/S are at the forefront, developing advanced therapies such as long-acting recombinant clotting factors and gene therapies for Hemophilia A and Hemophilia B. Pfizer Inc., known for its broad portfolio, continues to expand its offerings in this space, while Grifols, S.A. is making strides with its plasma-derived therapies for coagulation disorders. Additionally, companies such as Alnylam Pharmaceuticals and Sangamo Therapeutics are exploring novel approaches, including gene silencing and gene editing techniques, to provide more effective and personalized treatments. These industry leaders are continually working to improve patient outcomes through innovative therapies and strategic collaborations, enhancing their competitive edge in the coagulation factor deficiency market.
Market Segmentation:
Segmentation 1: by Deficiency Type
- Hemophilia A
- Hemophilia B
- Von Willebrand Disease
- Factor XI & Factor XIII Deficiencies
- Other Deficiencies
Segmentation 2: by Product Type
- Recombinant Coagulation Factors
- Plasma-derived Coagulation Factors
- Others
Segmentation 3: by End-User
- Hospitals
- Specialty Clinics
- Others
Segmentation 4: by Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
The global coagulation factor deficiency market is experiencing several key emerging trends that are reshaping the landscape of diagnosis and treatment. One prominent trend is the increasing use of gene therapy, which holds the potential to provide long-term or curative solutions for conditions such as Hemophilia A and Hemophilia B. This approach is gaining traction as it directly addresses the genetic defects responsible for these coagulation disorders, reducing the need for lifelong treatments with clotting factor concentrates. Additionally, the market is seeing a rise in the development of long-acting recombinant clotting factors, which improve patient convenience by reducing the frequency of infusions. Another emerging trend is the advancement of personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to individual genetic profiles, offering more effective and precise care for patients. With these innovations, the coagulation factor deficiency market is moving toward more efficient, patient-centric solutions that promise to improve both the quality of life and the long-term management of bleeding disorders.
Table of Contents
Executive Summary
Scope and Definition
Market/Product Definition
Inclusion and Exclusion
Key Questions Answered
Analysis and Forecast Note
1. Global Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market: Industry Outlook
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 Market Trends
- 1.3 Regulatory Framework
- 1.4 Epidemiology Analysis
- 1.5 Clinical Trial Analysis
- 1.6 Market Dynamics
- 1.6.1 Impact Analysis
- 1.6.2 Market Drivers
- 1.6.3 Market Challenges
- 1.6.4 Market Opportunities
2. Global Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market (Deficiency Type), ($Billion), 2023-2035
- 2.1 Hemophilia A
- 2.2 Hemophilia B
- 2.3 Von Willebrand Disease
- 2.4 Factor XI Deficiency
- 2.5 Factor XIII Deficiency
- 2.6 Others
3. Global Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market (Product Type), ($Billion), 2023-2035
- 3.1 Plasma-derived Coagulation Factors
- 3.2 Recombinant Coagulation Factors
- 3.3 Other
4. Global Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market (End-User), ($Billion), 2023-2035
- 4.1 Hospitals
- 4.2 Specialty Clinics
- 4.3 Others
5. Global Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market (Region), ($Billion), 2023-2035
- 5.1 North America
- 5.1.1 Key Findings
- 5.1.2 Market Dynamics
- 5.1.3 Market Sizing and Forecast
- 5.1.3.1 North America Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market, by Country
- 5.1.3.1.1 U.S.
- 5.1.3.1 North America Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market, by Country
- 5.2 Europe
- 5.2.1 Key Findings
- 5.2.2 Market Dynamics
- 5.2.3 Market Sizing and Forecast
- 5.2.3.1 Europe Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market, by Country
- 5.2.3.1.1 Germany
- 5.2.3.1.2 U.K.
- 5.2.3.1.3 France
- 5.2.3.1.4 Italy
- 5.2.3.1 Europe Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market, by Country
- 5.3 Asia Pacific
- 5.3.1 Key Findings
- 5.3.2 Market Dynamics
- 5.3.3 Market Sizing and Forecast
- 5.3.3.1 Asia Pacific Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market, by Country
- 5.3.3.1.1 China
- 5.3.3.1.2 Japan
- 5.3.3.1 Asia Pacific Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market, by Country
6. Global Coagulation Factor Deficiency Market: Competitive Landscape and Company Profiles
- 6.1 Key Strategies and Development
- 6.1.1 Mergers and Acquisitions
- 6.1.2 Synergistic Activities
- 6.1.3 Business Expansions and Funding
- 6.1.4 Product Launches and Approvals
- 6.1.5 Other Activities
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- 6.2.1.1 Overview
- 6.2.1.2 Top Products / Product Portfolio
- 6.2.1.3 Top Competitors
- 6.2.1.4 Target Customers/End-Users
- 6.2.1.5 Key Personnel
- 6.2.1.6 Analyst View
- 6.2.2 Sanofi S.A.
- 6.2.2.1 Overview
- 6.2.2.2 Top Products / Product Portfolio
- 6.2.2.3 Top Competitors
- 6.2.2.4 Target Customers/End-Users
- 6.2.2.5 Key Personnel
- 6.2.2.6 Analyst View
- 6.2.3 Grifols, S.A.
- 6.2.3.1 Overview
- 6.2.3.2 Top Products / Product Portfolio
- 6.2.3.3 Top Competitors
- 6.2.3.4 Target Customers/End-Users
- 6.2.3.5 Key Personnel
- 6.2.3.6 Analyst View
- 6.2.4 Novo Holdings A/S
- 6.2.4.1 Overview
- 6.2.4.2 Top Products / Product Portfolio
- 6.2.4.3 Top Competitors
- 6.2.4.4 Target Customers/End-Users
- 6.2.4.5 Key Personnel
- 6.2.4.6 Analyst View
- 6.2.5 Pfizer Inc.
- 6.2.5.1 Overview
- 6.2.5.2 Top Products / Product Portfolio
- 6.2.5.3 Top Competitors
- 6.2.5.4 Target Customers/End-Users
- 6.2.5.5 Key Personnel
- 6.2.5.6 Analyst View
- 6.2.6 Alnylam Pharmaceuticals
- 6.2.6.1 Overview
- 6.2.6.2 Top Products / Product Portfolio
- 6.2.6.3 Top Competitors
- 6.2.6.4 Target Customers/End-Users
- 6.2.6.5 Key Personnel
- 6.2.6.6 Analyst View
- 6.2.7 Sangamo Therapeutics
- 6.2.7.1 Overview
- 6.2.7.2 Top Products / Product Portfolio
- 6.2.7.3 Top Competitors
- 6.2.7.4 Target Customers/End-Users
- 6.2.7.5 Key Personnel
- 6.2.7.6 Analyst View
- 6.2.8 Centessa Pharmaceuticals
- 6.2.8.1 Overview
- 6.2.8.2 Top Products / Product Portfolio
- 6.2.8.3 Top Competitors
- 6.2.8.4 Target Customers/End-Users
- 6.2.8.5 Key Personnel
- 6.2.8.6 Analyst View
- 6.2.9 Staidson Biopharma Inc.
- 6.2.9.1 Overview
- 6.2.9.2 Top Products / Product Portfolio
- 6.2.9.3 Top Competitors
- 6.2.9.4 Target Customers/End-Users
- 6.2.9.5 Key Personnel
- 6.2.9.6 Analyst View
- 6.2.10 Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical
- 6.2.10.1 Overview
- 6.2.10.2 Top Products / Product Portfolio
- 6.2.10.3 Top Competitors
- 6.2.10.4 Target Customers/End-Users
- 6.2.10.5 Key Personnel
- 6.2.10.6 Analyst View
- 6.2.11 OPKO Health, Inc.
- 6.2.11.1 Overview
- 6.2.11.2 Top Products / Product Portfolio
- 6.2.11.3 Top Competitors
- 6.2.11.4 Target Customers/End-Users
- 6.2.11.5 Key Personnel
- 6.2.11.6 Analyst View
- 6.2.12 Novo Nordisk
- 6.2.12.1 Overview
- 6.2.12.2 Top Products / Product Portfolio
- 6.2.12.3 Top Competitors
- 6.2.12.4 Target Customers/End-Users
- 6.2.12.5 Key Personnel
- 6.2.12.6 Analyst View
- 6.2.13 Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited
- 6.2.13.1 Overview
- 6.2.13.2 Top Products / Product Portfolio
- 6.2.13.3 Top Competitors
- 6.2.13.4 Target Customers/End-Users
- 6.2.13.5 Key Personnel
- 6.2.13.6 Analyst View
- 6.2.14 Biogen Inc
- 6.2.14.1 Overview
- 6.2.14.2 Top Products / Product Portfolio
- 6.2.14.3 Top Competitors
- 6.2.14.4 Target Customers/End-Users
- 6.2.14.5 Key Personnel
- 6.2.14.6 Analyst View
- 6.2.15 Octapharma AG
- 6.2.15.1 Overview
- 6.2.15.2 Top Products / Product Portfolio
- 6.2.15.3 Top Competitors
- 6.2.15.4 Target Customers/End-Users
- 6.2.15.5 Key Personnel
- 6.2.15.6 Analyst View
- 6.2.1 F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd