|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1805544
臍帯血・組織バンクの世界市場:業界レポート-市場規模、セグメンテーション、予測(2025年)Global Cord Blood & Tissue Banking Industry Report - Market Size, Segmentation, & Forecasts, 2025 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| 臍帯血・組織バンクの世界市場:業界レポート-市場規模、セグメンテーション、予測(2025年) |
|
出版日: 2025年11月30日
発行: BioInformant
ページ情報: 英文 327 Pages
納期: 即納可能
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
エグゼクティブサマリー
臍帯血由来の造血幹細胞を用いた最初の移植が成功したのは1988年10月のことです。それ以来、臍帯血研究の分野では大きな進歩がなされてきました。現在までに、世界中で4万件以上の臍帯血移植(UCBT)が行われ、血液疾患、代謝疾患、免疫疾患、腫瘍性疾患、神経疾患など、幅広い疾患の治療が行われています。
臍帯血保存は1990年代初めに商業サービスとして始まったが、臍帯組織保存が商業的に導入されたのは2008年になってからです。このサービスを最初に提供したのは台湾のHealthBanks Biotechで、2009年には香港のHealthBabyとCryolifeがこれに続きました。米国では、2010年7月にCord Blood Registry(CBR)が臍帯組織保管サービスを開始しました。現在では、米国のほぼすべての臍帯血バンクと、世界のバンクの約3分の1が臍帯組織保管サービスを提供しています。
胎盤バンキングについては、LifebankUSAが2006年に胎盤血保存、2011年に胎盤組織保存の提供を開始しました。Americord Registryは2017年9月、米国で2番目に胎盤組織バンクを提供しました。国際的にも、多くの臍帯血バンクが胎盤血や組織の保存サービスを提供しています。歯髄幹細胞バンクであるDentCellは、ラテンアメリカ最大の臍帯血バンクコンソリデーターであるCryoholdcoによって管理されています。さらに、脂肪由来幹細胞の保管を開始したバンクもいくつかあります。
臍帯血業界は近年、前例のないレベルのM&Aを経験し、特に欧州、ラテンアメリカ、米国において、大幅な市場統合が進んでいます。2000年代初頭の業界の急成長を考えると、この統合は注目に値します。米国、欧州、アジア、ラテンアメリカで、大きな統合が起こっています。
- PBKM FamiCordは、最大の競合であるVita34との合併や、Cryo-Save AGの2019年の破産に伴う資産の取得を含め、欧州市場の大半を獲得しました。
- CooperSurgicalは米国内で生殖医療、新生児幹細胞、遺伝子サービスを統合し、少なくとも110万個を管理しています。
- Cryoholdcoはラテンアメリカ全土に幹細胞バンクの資産を蓄積しており、メキシコに4つ、コロンビアに2つ、ブラジルに2つ、ペルーに1つ、合計30万ユニットと推定されます。
- Sanpower Groupは、Global Cord Blood Corporationをはじめ、東南アジア全域で120万ユニット以上の資産を所有し、アジア市場を独占しています。
- 急成長する人口14億人のインドは、世界の人口78億人の約36%を占め、その規模は中国に匹敵します。LifeCell Internationalは、32万個以上の臍帯血を保管するインド有数の幹細胞バンクです。
このような統合により、多くの臍帯血バンクが新たな幹細胞保管方法を模索し、不妊治療や生殖医療、遺伝子検査、細胞治療への応用など、サービスの拡大に拍車をかけています。臍帯血、臍帯組織、胎盤血、羊水が持つ治療の可能性が、これらの生体材料の保管サービスの普及を促しました。
多くの臍帯血バンクは現在、以下のようなサービスを提供するまでに拡大していています。
- 生殖および生殖補助医療サービス
- 出生前および出生後の遺伝子検査
- 細胞治療製品開発
民間部門が統合される一方で、特に米国の多くの公的(非営利)臍帯血バンクは、財政的に苦境に立たされています。これらのバンクは、処理、検査、保管、ライセンシング技術に年間100万米ドルから600万米ドルを費やしています。臍帯血の販売による収入は比較的少なく、政府からの補助金、寄付金、助成金によって補われていることが多いです。
臍帯血・臍帯組織市場は、いくつかのセグメントで構成されています。
- 1.保存(凍結保存)市場:このセグメントは、長期保存契約から大きな収益を生み出しています。大手投資会社は最近、臍帯血バンク会社の株式を取得してこの市場に参入しています。
- 2.移植医療:白血病や鎌状赤血球症などの疾患の治療に臍帯血を使用する市場は堅調です。これまでに4万件以上の臍帯血移植が行われ、米国FDAは臍帯血の造血幹細胞(造血幹細胞)を用いた治療として80以上の疾患を承認しています。
- 3.再生医療:再生医療を目的とした臍帯血と組織の調査は、ますます盛んになっています。2000年代半ばからの研究では、神経疾患の治療に臍帯血が役立つ可能性が示されています。例えば、臨床試験では、脳性麻痺や自閉症などの疾患の治療において、最小限の操作で臍帯血の安全性と有効性が実証されています。現在Catalentが所有するRheinCell Therapeuticsは、細胞治療用の臍帯血由来iPSCの製造に関するGMP認証を取得しています。
- 4.調査供給製品:細胞、組織、試薬、キットなど、臍帯血や組織由来の研究用製品の市場が拡大しています。Lonza、STEMCELL Technologies、AllCellsなどの大手市場企業がこの分野に大きく貢献しています。
当レポートでは、以下に関する洞察を提供する:
- 公的および私的バンクに保管されている世界の臍帯血ユニット数
- 臍帯血細胞を用いた造血幹細胞移植の件数
- 再生医療臨床試験における臍帯血の利用
- 2005年以降の造血幹細胞移植における臍帯血利用の動向
- 公的臍帯血バンクの財務安定性に影響を及ぼす新たな技術
- 臍帯血に由来するコンパニオン製品の将来の機会
- 臍帯血バンクの進化する状況
- 臍帯血バンク別サービスの拡大と拡張
- 公的および私的臍帯血バンクの経済モデルとコスト分析
- 民間バンクにおける処理と保存の価格設定
- 臍帯血処理技術の比較分析とその利点
- 臍帯血と組織に関する臨床試験と特許の数と種類
- さまざまな臍帯血登録からの移植データ
当レポートはまた、以下のような重要な質問にも答えています。
- 公的臍帯血バンクの財務安定性向上のための戦略
- 臍帯血から開発されたコンパニオン製品
- 臍帯血の処理および保存に関連する費用と収益
- 各地域における臍帯血ユニットの価格と収益の比較
- 臍帯血バンクの認定制度と処理技術
- 臍帯血と組織由来細胞の利用率と研究重点分野
この包括的なレポートは、臍帯血・組織バンク市場の詳細な分析を提供し、過去のデータと2032年までの将来予測を含みます。保管、処理技術、市場リーダー、最近のM&A活動、市場規模指標、予測などを網羅しています。
目次
第1章 報告書の概要
第2章 臍帯血と臍帯血バンク:概要
- 臍帯血サンプルの組成
- 臍帯血バンク
- 臍帯血を保管している親の割合(国別、上位10カ国)
- 臍帯血移植のユニークな利点
第3章 臍帯血バンクの認定
- 血液・生物療法振興協会(AABB)
- 細胞療法認定財団(FACT)
- FDA登録臍帯血バンク
- 臍帯血のFDA生物学的製剤申請
- 臍帯血の治験薬(IND)
- ヒューマンティッシュオーソリティ(HTA)
- 医薬品法(TGA)
第4章 臍帯血、臍帯組織、胎盤の特許情勢
- 臍帯血幹細胞に関する特許
- 臍帯組織の特許
- 胎盤組織に関する特許
- 臍帯血増殖に関する特許
第5章 臍帯血調査出版物
- 臍帯血(UCB)に関する論文数
- PubMed.govに掲載された臍帯組織に関する論文数
- 胎盤組織に関する論文数
- 臍帯血増殖法に関する論文発表
第6章 臨床試験データ
- 臍帯血ユニット(CBU)を使用した臨床試験
- 臍帯組織を用いた臨床試験
- 臨床試験における胎盤組織幹細胞
- 臍帯血を用いた臨床試験
第7章 臍帯血処理技術
- 臍帯血幹細胞の分離プロセス
- 臍帯血処理技術の性能比較
- 処理技術別好中球生着までの日数
- 臍帯血処理で使用される抗凝固剤
- 臍帯血の凍結保存
- 臍帯組織のバイオプロセス
- 臍帯血増殖技術
第8章 世界中で入手可能な臍帯血ユニット:概要
- 世界中で利用可能な臍帯血ドナーとCBUの数
- 地域別に入手可能なCBU
- 米国登録機関に登録された臍帯血ユニット(CBU)
- 欧州でCBUが利用可能
- アジア太平洋地域でCBUが利用可能
- 世界中の非血縁臍帯血ドナーとCBUのHLAタイピング
- WMDAの検索&マッチングサービス
第9章 UBC移植の適応
- 臍帯血幹細胞の利点
- UCB移植が対応可能な悪性腫瘍
- CBU移植の非悪性腫瘍適応
- 再生医療におけるUCBの応用
第10章 臍帯血:移植医療
- 世界におけるPB、BM、CB移植の比較
- 地域別臍帯血幹細胞移植
- アジア
- 北米
- 欧州
- オセアニア
- 南米
- UCB移植の費用
- 造血幹細胞移植後1年間の合併症
第11章 再生医療における臍帯血幹細胞
- 自閉症
- 脳性麻痺
- アルツハイマー病
- 糖尿病
- 心臓病
- 多発性硬化症
- 脳卒中
第12章 市場分析
- 臍帯血バンキングサービス市場
- 臍帯組織バンキングサービスの世界市場
- 臍帯血産業の歴史的収益分析
- 臍帯血バンキングにおける地域別収益変動
- 臍帯血バンキングの収益に影響を与えるイノベーション
- 臍帯血産業の促進要因
第13章 臍帯血バンクと関連団体のプロファイル
- AllCells
- AlphaCord
- Americord Registry, Inc.
- Angiocrine Bioscience
- Anja Health Personalized Cord Blood Banking
- Anthony Nolan
- Baylx, Inc.
- NMDPSM
- Biocell Center
- BioEden
- Bloodworks Northwest
- California Umbilical Cord Collection Program
- Carolinas Cord Blood Bank (CCBB)
- Celaid Therapeutics
- Celebration Stem Cell Centre (CSCC)
- Cell Care
- Cellenkos, Inc.
- Cells4Life Group LLP
- CellSave Arabia
- Celularity, Inc.
- Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR)
- CHOC Blood Bank
- Cleveland Cord Blood Center
- ClinImmune Cell and Gene Therapy
- Cord Blood Bank of Arkansas (CBBA)
- Cord Blood Center Group
- Cord Blood Registry (CBR)
- Cord for Life
- CordLife Group, Ltd
- CordVida
- Crioestaminal
- Cryo-Cell International, Inc.
- CryoCyte, LLC
- CryoHoldco LATAM
- Cryopoint
- Cryoviva Biotech Pvt., Ltd.
- DKMS gGMBH
- Duke University School of Medicine
- European Society for Blood and Bone Marrow Transplantation (EBMT)
- Ever Supreme Bio Technology, Co., Ltd
- ExCellThera
- FamiCord Group
- Fate Therapeutics, Inc
- Future Health
- Gamida Cell
- GeneCell
- Global Cord Blood Corporation (GCBC)
- Glycostem Therapeutics
- Hawaii Cord Blood Bank
- HealthBaby
- HealthBanksUSA
- HEMAFUND
- Hemogenyx Pharmaceuticals
- IMMUNIQUE
- Insception LifeBank
- JP McCarthy Cord Stem Cell Bank
- Kangstem Biotech, Co., Ltd.
- LifebankUSA
- LifeCell International Pvt. Ltd.
- Life Line Stem Cell
- LifeSouth Cord Blood Bank
- Magenta Therapeutics
- Maze Cord Blood
- Medipost, Co., Ltd
- MD Anderson Cord Blood Bank
- Mesoblast, Ltd
- MiracleCord, Inc.
- Mononuclear Therapeutics, Ltd
- New England Cord Blood Bank, Inc.
- New York Blood Center
- OrganaBio
- PacifiCord
- PacifiCord
- ReeLabs Pvt. Ltd.
- Restem, LLC
- San Diego Cord Blood Bank
- Saneron CCEL Therapeutics, Inc
- SmartCells
- SSM Cardinal Glennon Children's Medical Center
- Stembanc, Inc
- Stem Cell Cryobank, Inc.
- StemCyte, Inc
- Throne Biotechnologies, Inc
- Transcell Biolife
- Upstate Cord Blood Bank
- ViaCord
- Versity, Inc.
- Vita 34 AG
- Vitalant Clinical Services
- World Marrow Donor Association (WMDA)
- Worldwide Network for Blood & Marrow Transplantation (WBMT)
付録
- 付録1:臍帯血バンキングの進歩
- 付録1.1:市場の成長と傾向
- 付録1.2:自動化と凍結保存の進歩
- 付録1.3:分離方法の進歩
- 付録1.4:CBUの用途拡大
- 付録1.5:UCB銀行における人工知能(AI)の可能性
図表索引
表の索引
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
The first successful transplant using cord blood-derived hematopoietic stem cells was conducted in October 1988. Since then, significant advancements have been made in the field of umbilical cord blood research. To date, over 40,000 umbilical cord blood transplants (UCBTs) have been performed globally, treating a wide range of conditions including hematologic, metabolic, immunologic, neoplastic, and neurologic disorders.
Cord blood storage began as a commercial service in the early 1990s, but it was not until 2008 that cord tissue storage was introduced commercially. The first company to offer this service was Taiwan's HealthBanks Biotech Company Ltd., followed by HealthBaby and Cryolife in Hong Kong in 2009. In the U.S., Cord Blood Registry (CBR) started offering cord tissue storage in July 2010. Today, nearly all U.S. cord blood banks and approximately one-third of global banks offer cord tissue storage services.
For placental banking, LifebankUSA began offering placental blood storage in 2006 and placental tissue storage in 2011. Americord Registry followed in September 2017 as the second U.S. bank to offer placental tissue banking. Internationally, a number of cord blood banks also provide placental blood and tissue storage services. Some have expanded into storing other stem cell types, such as dental pulp stem cells, with DentCell, a dental pulp stem cell bank, being controlled by Cryoholdco, the largest cord blood banking consolidator in Latin America. Additionally, a few banks have started storing adipose-derived stem cells.
The cord blood industry has experienced unprecedented levels of mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in recent years, leading to significant market consolidation, particularly in Europe, Latin America, and the U.S. The market is now predominantly controlled by a handful of large cord blood banking operators. This consolidation is notable given the rapid growth of the industry in the early 2000s. Significant consolidation has occurred in the U.S., Europe, Asia, and Latin America:
- PBKM FamiCord has acquired most of the European market, including merging with it largest competitor Vita34 and acquiring assets following Cryo-Save AG's 2019 bankruptcy.
- CooperSurgical has consolidated reproductive, newborn stem cell, and genetic services within the U.S., managing at least 1.1 million units.
- Cryoholdco has amassed stem cell banking assets across Latin America, including four in Mexico, two in Colombia, two in Brazil, and one in Peru, totaling an estimated 300,000 units.
- Sanpower Group dominates the Asian market through its ownership of Global Cord Blood Corporation and other assets across Southeast Asia, controlling over 1.2 million units.
- India, with its burgeoning population of 1.4 billion, rivals China in size, making up approximately 36% of the world's 7.8 billion people. LifeCell International is the leading stem cell bank in India, storing over 320,000 units.
This consolidation has spurred many cord blood banks to explore new stem cell storage options and expand their services to include fertility and reproductive services, genetic testing, and cell therapy applications. The therapeutic potential of cord blood, cord tissue, placental blood, and amniotic fluid has driven the proliferation of storage services for these biomaterials.
Many cord blood banks have now expanded their offerings to include:
- Reproductive and assisted fertility services
- Pre- and post-natal genetic testing
- Cell therapy product development
While the private sector consolidates, many public (nonprofit) cord blood banks, particularly in the U.S., are struggling financially. These banks spend between $1 million and $6 million annually on processing, testing, storage, and licensing technologies. Revenue from cord blood sales is relatively low, often supplemented by government subsidies, donations, and grants.
The umbilical cord blood and tissue market is composed of several segments:
- 1. Storage (Cryopreservation) Market: This segment generates significant revenue from long-term storage contracts. Major investment firms have recently entered this market by acquiring stakes in cord blood banking companies.
- 2. Transplantation Medicine: There is a robust market for using cord blood in treating diseases such as leukemia and sickle cell disease. Over 40,000 UCB transplants have been performed, and the U.S. FDA has approved over 80 medical conditions for treatment using hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) from cord blood.
- 3. Regenerative Medicine: Research into cord blood and tissue for regenerative medicine is growing. Studies from the mid-2000s have shown the potential of cord blood for treating neurological disorders. For instance, clinical trials have demonstrated the safety and effectiveness of minimally manipulated cord blood in treating conditions like cerebral palsy and autism. RheinCell Therapeutics, now owned by Catalent, has achieved GMP certification for manufacturing cord blood-derived iPSCs for cell therapy.
- 4. Research Supply Products: There is a growing market for research products derived from cord blood and tissue, including cells, tissues, reagents, and kits. Leading market players like Lonza, STEMCELL Technologies, and AllCells are major contributors to this sector.
This report provides insights into the following:
- The number of cord blood units stored globally, in both public and private banks.
- The number of hematopoietic stem cell transplants performed using cord blood cells.
- Utilization of cord blood in regenerative medicine clinical trials.
- Trends in cord blood use for HSCTs since 2005.
- Emerging technologies impacting the financial stability of public cord blood banks.
- Future opportunities for companion products derived from cord blood.
- The evolving landscape of cord blood banking.
- Expansion and extension of services by cord blood banks.
- Economic models and cost analyses for public and private cord blood banks.
- Pricing for processing and storage in private banks.
- Comparative analysis of cord blood processing technologies and their merits.
- Number and types of clinical trials and patents related to cord blood and tissue.
- Transplantation data from different cord blood registries.
The report also answers key questions such as:
- Strategies for improving the financial stability of public cord blood banks.
- Companion products developed from cord blood.
- Costs and revenues associated with processing and storing cord blood.
- Comparative pricing and revenue for cord blood units in different regions.
- Accreditation systems and processing technologies for cord blood banks.
- Utilization rates and research focus areas for cord blood and tissue-derived cells.
This comprehensive report provides a detailed analysis of the cord blood and tissue banking market, including historical data and future projections through 2032. It covers storage, processing technologies, market leaders, and recent M&A activity, market size metrics, forecasts, and so much more.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. REPORT OVERVIEW
- 1.1. Statement of the Report
- 1.2. Executive Summary
- 1.3. Introduction
2. CORD BLOOD & CORD BLOOD BANKS: AN OVERVIEW
- 2.1. Composition of a Cord Blood Sample
- 2.2. Cord Blood Banks
- 2.2.1. Public Cord Blood Banks
- 2.2.1.1. WMDA Registry on Global Cord Blood Units
- 2.2.1.2. Public Cord Blood Banks in the U.S.
- 2.2.1.3. Public Cord Blood Banks in Major European Countries
- 2.2.1.4. Economic Model of Public Cord Blood Banks
- 2.2.1.5. Cost Analysis for Public Cord Blood Banks
- 2.2.1.6. Relationship between Cost and Release Rates
- 2.2.2. Private Cord Blood Banks
- 2.2.2.1. Private Cord Blood Banks in the U.S.
- 2.2.2.2. World's Top Ten Private Cord Blood Banks by Size of Inventory
- 2.2.2.3. Processing and Storage Charges in Private Cord Blood Banks, U.S.
- 2.2.2.4. Processing & Storage Charges in Private Banks in Europe
- 2.2.2.5. Processing and Storage Fee Charged by LifeCell (India)
- 2.2.2.6. Processing & Storage Fees Charged by Global Cord Blood Corp. (China)
- 2.2.2.7. Cost Analysis for Private Cord Blood Banks
- 2.2.2.8. Revenue Generation by Private Cord Blood Banks
- 2.2.2.9. Status and Noteworthy Features of Some U.S. Private Cord Blood Banks
- 2.2.2.10. Public vs. Private Cord Blood Banks
- 2.2.3. Hybrid Cord Blood Banks
- 2.2.3.1. Proportion of Public, Private and Hybrid Cord Blood Banks
- 2.2.4. Community Cord Blood Banks
- 2.2.1. Public Cord Blood Banks
- 2.3. Percent Share of Parents Storing Cord Blood by Country (Top 10)
- 2.4. The Unique Benefits of Cord Blood Transplant
3. CORD BLOOD BANK ACCREDITATIONS
- 3.1. Association for the Advancement Blood and Biotherapies (AABB)
- 3.1.1. AABB Accreditation Phases and Expectations
- 3.2. Foundation for the Accreditation of Cellular Therapy (FACT)
- 3.2.1. FACT Standards
- 3.2.3. FACT Accreditation Process
- 3.3. FDA-Registered Cord Blood Banks
- 3.4. FDA Biologics Application for Cord Blood
- 3.5. Investigation New Drug (IND) for Cord Blood
- 3.6. Human Tissue Authority (HTA)
- 3.7. Therapeutic Goods Act (TGA)
4. PATENT LANDSCAPE OF CORD BLOOD, CORD TISSUE & PLACENTA
- 4.1. Patents on Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells
- 4.1.1. Legal Status of Cord Blood Stem Cell Patents
- 4.1.2. Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cell Patent Applications by Year
- 4.1.3. Cord Blood Stem Cell Patent Applications by Jurisdiction
- 4.1.4. Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cell Patent Applicants
- 4.1.5. Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cell Inventors
- 4.1.6. Owners of Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cell Patents
- 4.2. Patents of Umbilical Cord Tissue
- 4.2.1. Legal Status of Cord Tissue Patents
- 4.2.2. Umbilical Cord Tissue Patent Applications by Year
- 4.2.3. Umbilical Cord Tissue Patent Applications by Jurisdiction
- 4.2.4. Umbilical Cord Tissue Patent Applicants
- 4.2.5. Inventors of Umbilical Cord Tissue Patents
- 4.2.6. Owners of Umbilical Cord Tissue Patents
- 4.3. Patents on Placental Tissue
- 4.3.1. Placental Tissue Patent Applicants
- 4.3.2. Placental Tissue Patent Applications by Year
- 4.3.3. Placental Tissue Patents by Jurisdiction
- 4.3.4. Inventors of Placental Tissue Patents
- 4.3.5. Owners of Placental Tissue Patents
- 4.3.6. Legal Status of Placental Tissue Patents
- 4.4. Patents on Cord Blood Expansion
- 4.4.1. Number of Cord Blood Expansion Patent Applications by Year
- 4.4.2. Cord Blood Expansion Patent Applications by Jurisdiction
- 4.4.3. Legal Status of Cord Blood Expansion Patents
- 4.4.4. Inventors of Cord Blood Expansion Patents
- 4.4.5. Owners of Cord Blood Expansion Patents
5. UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD RESEARCH PUBLICATIONS
- 5.1. Number of Papers Published on Umbilical Cord Blood (UCB)
- 5.2. Number of Papers Published in PubMed.gov on Umbilical Cord Tissue
- 5.3. Number of Papers Published on Placental Tissue
- 5.4. Published Papers on Cord Blood Expansion Methods
6. CLINICAL TRIAL DATA
- 6.1. Clinical Trials Using Umbilical Cord Blood Units (CBUs)
- 6.1.1. Number of Umbilical Cord Blood Clinical Trials by Study Type
- 6.1.2. Number of Cord Blood Clinical Trials by Phase of Study
- 6.1.3. Number of Cord Blood Clinical Trials by Funder Type
- 6.1.4. Diseases Addressed by Ongoing Cord Blood Clinical Trials
- 6.1.5. Companies Participating in Cord Blood Clinical Trials, April 18, 2025
- 6.2. Clinical Trials using Umbilical Cord Tissue
- 6.2.1. Umbilical Cord Tissue Clinical Trials by Phase of Study
- 6.2.2. Umbilical Cord Tissue Clinical Trials by Funder Type
- 6.2.3. Umbilical Cord Tissue Clinical Trials Sponsored by Companies
- 6.3. Placental Tissue Stem Cells in Clinical Trials
- 6.3.1. Placental Tissue Stem Cells in Clinical Trials by Phase of Study
- 6.4. Clinical Trials using Expanded Cord Blood
- 6.4.1. Major Participants in Expanded Cord Blood Clinical Trials
7. CORD BLOOD PROCESSING TECHNOLOGIES
- 7.1. The Process of Separation of Cord Blood Stem Cells
- 7.1.1. Plasma Depletion (MaxCell Process)
- 7.1.2. Density Gradient
- 7.1.3. Hetastarch (HES)
- 7.1.4. PrepaCyte-CB
- 7.1.5. SEPAX
- 7.1.6. AutoXpress (AXP)
- 7.1.7. TotiCyte
- 7.1.8. MacoPress Smart
- 7.2. Performance Comparison of Cord Blood Processing Technologies
- 7.3. Days to Neutrophil Engraftment by Processing Technology
- 7.4. Anticoagulants used in Cord Blood Processing
- 7.5. Cryopreservation of Umbilical Cord Blood
- 7.6. Bioprocessing of Umbilical Cord Tissue
- 7.7. Cord Blood Expansion Technologies
- 7.7.1. Umbilical Cord Blood Expansion Strategies
- 7.7.1.1. Aryl Hydrocarbon Antagonists
- 7.7.1.2. Pyrimidoindole Derivatives
- 7.7.1.3. Nicotinamide
- 7.7.1.4. Notch Ligands
- 7.7.1.5. Copper Chelator
- 7.7.1.6. Valproic acid
- 7.7.1. Umbilical Cord Blood Expansion Strategies
8. CORD BLOOD UNITS AVAILABLE WORLDWIDE: AN OVERVIEW
- 8.1. Number of Cord Blood Donors & CBUs Available Worldwide
- 8.2. CBUs Available by Geography
- 8.3. Cord Blood Units (CBUs) Registered in U.S. Registries
- 8.3.1. Cord Blood Units (CBUs) in the U.S. by Race and Ethnicity as of 2024
- 8.4. CBUs Available in Europe
- 8.5. CBUs Available in Asia/Pacific
- 8.6. HLA Typing of Unrelated Cord Blood Donors and CBUs Worldwide
- 8.6.1. Unrelated BM, PB and CB HSCs Shipped Worldwide
- 8.6.2. Global Exchange of Cord Blood Units (CBUs)
- 8.7. WMDA's Search & Match Service
- 8.7.1. Number of Searches made in WMDA Registry for CBUs by Year
- 8.7.2. Yield of Search Results from WMDA Registry, 2017-2023
9. INDICATIONS FOR UBC TRANSPLANTATION
- 9.1. Advantages of Cord Blood Stem Cells
- 9.1.1. Hematopoietic Properties of Cord Blood Stem Cells
- 9.1.2. Immune Properties of Cord Blood Stem Cells
- 9.1.3. Impact of HLA Mismatch in UCB Transplant Recipients
- 9.2. Malignant Indications Addressable by UCB Transplantation
- 9.3. Non-Malignant Indications for CBU Transplantation
- 9.4. Application of UCB in Regenerative Medicine
10. CORD BLOOD: A TRANSPLANT MEDICINE
- 10.1. Worldwide PB, BM & CB Transplants Compared
- 10.2. Cord Blood Stem Cells Transplantation by Geography
- 10.2.1. CBU Transplantations in Asia
- 10.2.2. UCB Transplants in North America
- 10.2.3. UCB Transplants in Europe
- 10.2.4. UCB Transplants in Oceania
- 10.2.5. CBU Transplants in South America
- 10.3. Cost of UCB Transplantation
- 10.3.1. Complications through 1-Year Post HSCT
11. CORD BLOOD STEM CELLS IN REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
- 11.1. Autism
- 11.2. Cerebral palsy
- 11.3. Alzheimer's Disease
- 11.4. Diabetes
- 11.5. Heart Diseases
- 11.6. Multiple Sclerosis
- 11.7. Stroke
12. MARKET ANALYSIS
- 12.1. Umbilical Cord Blood Banking Services Market
- 12.1.1. Umbilical Cord Blood (UCB) Banking Market Share by Geography, 2024
- 12.1.2. Public vs. Private Cord Blood Banking Service Market
- 12.1.3. Global Market Share for Cord Blood & Cord Tissue Banking Services
- 12.1.4. Market Share of CB for Transplantation & Regenerative Medicine
- 12.1.5. Percent Share of Cord Blood & Cord Tissue Market by Indication
- 12.2. Global Market for Umbilical Cord Tissue Banking Service
- 12.3. Historical Revenue Analysis of the Cord Blood Industry
- 12.4. Geographical Revenue Variations in Cord Blood Banking
- 12.5. Innovations Impacting Cord Blood Banking Revenue
- 12.6. Growth Drivers for the Cord Blood Industry
13. PROFILES OF SELECT CORD BLOOD BANKS & RELATED ORGANIZATIONS
- 13.1. AllCells
- 13.1.1. Research Use Only (RUO) Products
- 13.1.1.1. Mobilized Leukopak
- 13.1.1.2. Leukopak
- 13.1.1.3. Bone Marrow
- 13.1.1.4. Cord Blood
- 13.1.1.5. Whole Blood
- 13.1.2. GMP Products
- 13.1.2.1. Clinical Grade Mobilized Leukopak
- 13.1.2.2. Clinical Grade Leukopak
- 13.1.2.3. Clinical Grade Bone Marrow
- 13.1.3. Isolated Cell Products
- 13.1.3.1. CD34+ HSPCs
- 13.1.3.2. T Cells
- 13.1.3.3. NK Cells
- 13.1.3.4. Monocytes
- 13.1.3.5. B Cells
- 13.1.3.6. PBMCs (MNCs)
- 13.1.1. Research Use Only (RUO) Products
- 13.2. AlphaCord
- 13.2.1. Prices
- 13.3. Americord Registry, Inc.
- 13.4. Angiocrine Bioscience
- 13.4.1. Proprietary E-CEL Platform
- 13.5. Anja Health Personalized Cord Blood Banking
- 13.5.1. Anja's Mannual Processing of Cord Blood
- 13.6. Anthony Nolan
- 13.6.1. Products & Services
- 13.6.1.1. Cell Isolation & Purification
- 13.6.1.2. Cell Culture & Expansion
- 13.6.1. Products & Services
- 13.7. Baylx, Inc.
- 13.7.1. Core Technology
- 13.7.2. Product Piupeline
- 13.8. NMDPSM
- 13.8.1. NMDP Network
- 13.9. Biocell Center
- 13.10. BioEden
- 13.10.1. Dental Pulp Cells
- 13.10.2. Differences between Dental Pulp Cells and Cord Blood Cells
- 13.11. BioIntegrate, LLC
- 13.11.1. GeneXSTEM Injectables
- 13.12. Bloodworks Northwest
- 13.12.1. Products & Services
- 13.13. California Umbilical Cord Collection Program
- 13.13.1. Participating Locations
- 13.14. Carolinas Cord Blood Bank (CCBB)
- 13.15. Celaid Therapeutics
- 13.15.1. In Vitro Expansion Technology
- 13.15.2. Business Model
- 13.16. Celebration Stem Cell Centre (CSCC)
- 13.16.1. Products
- 13.17. Cell Care
- 13.18. Cellenkos, Inc.
- 13.18.1. Technology
- 13.18.2. Cellenkos' Pipeline
- 13.19. Cells4Life Group LLP
- 13.19.1. Cellsplus
- 13.19.2. TotiCyte Processing Technology
- 13.19.3. Cord Blood Releases from Cells4Life
- 13.20. CellSave Arabia
- 13.20.1. Cord Blood Stem Cell Banking Services
- 13.20.2. Stem Cell Banking Price
- 13.21. Celularity, Inc.
- 13.22. Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR)
- 13.23. CHOC Blood Bank
- 13.24. Cleveland Cord Blood Center
- 13.24.1. Research on Diabetic Retinopathy
- 13.24.2. Research on Type I Diabetes
- 13.24.3. Research on Parkinson's disease
- 13.24.4. Research on Wound Healing
- 13.25. ClinImmune Cell and Gene Therapy
- 13.25.1. FDA Licensed Cord Blood
- 13.25.2. Gene Therapy
- 13.25.3. Cellular Therapies
- 13.26. Cord Blood Bank of Arkansas (CBBA)
- 13.27. Cord Blood Center Group
- 13.28. Cord Blood Registry (CBR)
- 13.28.1. Business Experience
- 13.28.2. Licensing & Accreditation
- 13.28.3. Pricing
- 13.29. Cord for Life
- 13.29.1. Technology: PremierMax
- 13.30. CordLife Group, Ltd.
- 13.30.1. Accreditations & Certifications
- 13.30.2. Services
- 13.30.3. Cordlife Group's Network
- 13.30.4. Cordlife's Market
- 13.31. CordVida
- 13.32. Crioestaminal
- 13.32.1. Cord Blood Transplantation in Portugal
- 13.33. Cryo-Cell International, Inc.
- 13.33.1. Processing Technology
- 13.33.2. Recovery of Viable CFU by PrepaCyte-CB
- 13.33.3. Cryo-Cell International's Revenue Generation
- 13.33.4. Cryo-Cell International's Pricing
- 13.34. CryoCyte, LLC
- 13.35. CryoHoldco LATAM
- 13.36. Cryopoint
- 13.37. Cryoviva Biotech Pvt., Ltd.
- 13.38. DKMS gGMBH
- 13.38.1. Cord Blood Units
- 13.38.2. Services
- 13.38.3. DKMS' Donor Typing Profile & Active Donors
- 13.39. Duke University School of Medicine
- 13.39.1. Ducord (HPC Cord Blood)
- 13.40. European Society for Blood and Bone Marrow Transplantation (EBMT)
- 13.40.1. EBMT Transplant Activity
- 13.41. Ever Supreme Bio Technology, Co., Ltd.
- 13.41.1. Allogeneic UMSC01
- 13.41.2. New Research
- 13.42. ExCellThera
- 13.42.1. ECT-001 Cell Therapy
- 13.43. FamiCord Group
- 13.44. Fate Therapeutics, Inc.
- 13.44.1. FT1050 - Stem Cell Modulator
- 13.45. Future Health
- 13.45.1. Locations of Laboratories
- 13.45.2. Business Experience
- 13.45.3. Collection Kit
- 13.45.4. Transportation Container
- 13.45.5. Processing Method
- 13.45.6. Components Stored
- 13.45.7. Storage Methods
- 13.45.8. Licensing & Accreditation
- 13.45.9. Prices
- 13.45.10. Additional Services
- 13.46. Gamida Cell
- 13.46.1. OMIDUBICELL
- 13.47. GeneCell
- 13.48. Global Cord Blood Corporation (GCBC)
- 13.48.1. GCBC's Revenue Generation
- 13.49. Glycostem Therapeutics
- 13.49.1. Science and Technology
- 13.49.2. oNKord
- 13.49.3. viveNK
- 13.49.4. uNiK Production Process
- 13.50. Hawaii Cord Blood Bank
- 13.51. HealthBaby
- 13.51.1. Service Plans
- 13.51.2. 18-Year Cord Blood (HSCs) Storage Plan
- 13.51.3. 18-Year CordBasic Umbilical Cord Lining Storage Plan
- 13.51.4. CellOptima CordPlus Umbilical Cord Lining Storage
- 13.52. HealthBanksUSA
- 13.52.1. BioArchive Cryogenic Storage System
- 13.52.2. AXP Cord Blood Processing
- 13.53. HEMAFUND
- 13.54. Hemogenyx Pharmaceuticals
- 13.54.1. Technology
- 13.55. IMMUNIQUE
- 13.56. Insception LifeBank
- 13.56.1. Cord Blood Releases from Insception LifeBank
- 13.56.2. Cord Blood Cells Released for Regenerative Medicine from Insception
- 13.57. JP McCarthy Cord Stem Cell Bank
- 13.58. Kangstem Biotech, Co., Ltd.
- 13.58.1. GD11 Brand
- 13.58.2. Core Technology
- 13.59. LifebankUSA
- 13.60. LifeCell International Pvt. Ltd.
- 13.61. Life Line Stem Cell
- 13.62. LifeSouth Cord Blood Bank
- 13.62.1. Accreditation & Hospital Partners
- 13.63. Magenta Therapeutics
- 13.63.1. Magenta's Cord Blood-Based Clinical Trial
- 13.64. Maze Cord Blood
- 13.65. Medipost, Co., Ltd.
- 13.65.1. Medipost's Product & Products in Development
- 13.65.1.1. CARTISTEM
- 13.65.1.2. PNEUMOSTEM
- 13.65.1.3. SMUP-IA-01
- 13.65.1. Medipost's Product & Products in Development
- 13.66. MD Anderson Cord Blood Bank
- 13.67. Mesoblast, Ltd.
- 13.67.1. Mesoblast's UCB-Based Clinical Trial
- 13.68. MiracleCord, Inc.
- 13.68.1. AXP II Automated Processing
- 13.68.2. StemCare Collection Kit
- 13.68.3. Cost of Cord Blood Banking
- 13.69. Mononuclear Therapeutics, Ltd.
- 13.69.1. MonoTx Cord Blood Bank
- 13.69.2. MonoTx's Pipeline
- 13.69.3. Products
- 13.69.3.1. Human Cord Blood Mononuclear Cells (MNCs)
- 13.69.3.2. Exosome Rich Plasma (ERP)
- 13.69.3.3. Activated Human Cord Blood Platelet-Depleted-Plasma (aPDP)
- 13.70. New England Cord Blood Bank, Inc.
- 13.70.1. Cord Blood Processing
- 13.70.2. Cord Blood & Tissue Storage
- 13.71. New York Blood Center
- 13.71.1. Blood Products & Services
- 13.71.2. Cell Therapies
- 13.71.3. Cord Blood
- 13.72. OrganaBio
- 13.72.1. OrganaBio's Proprietary Supply Chains
- 13.72.2. Perenatal Tissues
- 13.73. PacifiCord
- 13.73.1. FDA-Approved Sterile Collection Bags
- 13.73.2. AXP Processing System
- 13.73.3. BioArchive System
- 13.74. Plasticell Ltd.
- 13.74.1. CombiCult Technology
- 13.74.2. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Expansion
- 13.75. ReeLabs Pvt. Ltd.
- 13.76. Restem, LLC
- 13.76.1. Clinical Trial for COVID-19
- 13.76.2. Clinical Trial for Muscular Dystrophy
- 13.76.3. Clinical Trial for Idiopathic Inflammatory Myositis (IIM)
- 13.76.4. Clinical Trial for Heart Failure
- 13.77. San Diego Cord Blood Bank
- 13.78. Saneron CCEL Therapeutics, Inc.
- 13.78.1. U-CORD-CELL Program
- 13.78.2. SERT-CELL Program
- 13.79. SmartCells
- 13.80. SSM Cardinal Glennon Children's Medical Center
- 13.80.1. ALLOCORD
- 13.81. Stembanc, Inc.
- 13.81.1. Popular Packages from Stembanc
- 13.82. Stem Cell Cryobank, Inc.
- 13.83. StemCyte, Inc.
- 13.83.1. Services
- 13.83.2. Add On Services
- 13.83.3. StemCyte in Clinical Trials
- 13.83.4. StemCyte's Plans & Pricing
- 13.84. Throne Biotechnologies, Inc.
- 13.84.1. Effects of CB-SCs in Diabetics
- 13.84.2. Effects of CB-SCs on Alopecia Areata
- 13.85. Transcell Biolife
- 13.85.1. ScellCare
- 13.85.2. ToothScell
- 13.86. Upstate Cord Blood Bank
- 13.87. ViaCord
- 13.87.1. ViaCord's Complete Services
- 13.87.2. Cord Blood + Tissue Banking
- 13.87.3. Newborn Digestive Health
- 13.87.4. Newborn DNA Guardian
- 13.88. Versity, Inc.
- 13.89. Vita 34 AG (Recently Merged with Famicord)
- 13.89.1. Revenue Generation by Vita 34 AG
- 13.90. Vitalant Clinical Services
- 13.90.1. Hospital Services
- 13.90.2. Laboratory Services
- 13.90.3. Research
- 13.91. World Marrow Donor Association (WMDA)
- 13.91.1. WMDA Search & Match Service
- 13.92. Worldwide Network for Blood & Marrow Transplantation (WBMT)
APPENDIX
- APPENDIX 1: Advancements in Umbilical Cord Blood Banking
- Appendix 1.1: Market Growth and Trnds
- Appendix 1.2: Advances in Automation and Cryopreservation
- Appendix 1.3: Advances in Isolation Methods
- Appendix 1.4: Expanding Applications of CBUs
- Appendix 1.5: Potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in UCB Banking
INDEX OF FIGURES
- FIGURE 2.1: Schematic Cross-Sectional View of Umbilical Cord
- FIGURE 2.2: Percent Utilization of HSCs by Type in Pediatric Patients
- FIGURE 2.3: Composition of a Cord Blood Sample
- FIGURE 2.4: World's Top Ten Private Cord Blood Banks by Inventory Size
- FIGURE 2.5: Revenue Generation in Three Major Private Cord Blood Banks, 2017-2024
- FIGURE 2.6: Proportion of Public, Private and Hybrid Cord Blood Banks
- FIGURE 2.7: Percent Share of Parents Storing Cord Blood in Top Ten Countries
- FIGURE 4.1: Legal Status of Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cell Patents
- FIGURE 4.2: Number of Applications for Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells, 2000-2024
- FIGURE 4.3: Legal Status of Cord Tissue Patents
- FIGURE 4.4: Umbilical Cord Tissue Patent Applications, 2000-2024
- FIGURE 4.5: Placental Tissue
- FIGURE 4.6: Placental Tissue Patent Applications by Year
- FIGURE 4.7: Cord Blood Expansion Patent Applications by Year
- FIGURE 5.1: Number of Papers on Umbilical Cord Blood in PubMed.gov, 2000-2024
- FIGURE 5.2: Number of Papers Published in PubMed.gov on Cord Tissue, 2000-2024
- FIGURE 5.3: Number of Published Papers on Placental Tissue, 2000-2024
- FIGURE 5.4: Published Papers on Cord Blood Expansion in PubMed.gov
- FIGURE 6.1: Percent Share of UCB Clinical Trials by Study Type, April 18, 2025
- FIGURE 6.2: Percent Share of Cord Blood Clinical Trials by Phase of Study, April 18, 2025
- FIGURE 6.3: Percent Share of Cord Blood Clinical Trials by Funder Type, April 18, 2025
- FIGURE 6.4: Percent Share of Studies Addressing Various Diseases, April 18, 2025
- FIGURE 6.5: Umbilical Cord Tissue Clinical Trials by Phase of Study, April 19, 2025
- FIGURE 6.6: Umbilical Cord Tissue Clinical Trials, April 19, 2025
- FIGURE 6.7: Placental Stem Cells in Clinical Trials by Phase of Study, April 19, 2025
- FIGURE 7.1: The Buffy Coat of Cord Blood after Centrifugation
- FIGURE 7.2: Cord Blood Sample Bag after Plasma Depletion
- FIGURE 7.4: PrepaCyte-CB System
- FIGURE 7.5: SEPAX
- FIGURE 7.6: AutoXpress
- FIGURE 7.7: TotiCyte Processing Steps
- FIGURE 7.9: Percent Viable Stem Cells in the Processed Cord Blood by Technology
- FIGURE 7.10: Days to Neutrophil Engraftment by Technology
- FIGURE 7.11: Stem Cell (CD34+) and Nucleated White Cell Count with CPD and Heparin
- FIGURE 7.12: A Comparative Analysis with Three Different Cryoprotectants
- FIGURE 8.1: Number of CB Donors and CBUs available Worldwide, 1997-2024
- FIGURE 8.2: Cord Blood Units (CBUs) Registered in the U.S. Registries by Year, 2001-2024
- FIGURE 8.3: HLA Typing of Unrelated Cord Blood Donors and CBUs Worldwide
- FIGURE 8.4: HSCs of BM, PB and CB Shipped Worldwide, 1997-2023
- FIGURE 8.5: Global Exchange of CBUs, 2023
- FIGURE 8.6: Number of Searches made in WMDA Registry for CBUs, 2017-2023
- FIGURE 8.7: Yield of Search Results from WMDA Registry, 2017-2023
- FIGURE 9.1: Percent Utilization of PB, BM and CB Worldwide, 1997-2023
- FIGURE 10.1: Worldwide PB, BM & CB Transplants Compared
- FIGURE 10.2: CBU Transplantations in Asia, 1999-2003
- FIGURE 10.3: UCB Transplants in North America
- FIGURE 10.4: CUB Transplants in Europe
- FIGURE 10.5: UCB Transplants in Oceania
- FIGURE 12.1: Global Cord Blood Banking Service Market, 2024-2032
- FIGURE 12.2: Percent Share of Cord Blood Service Market by Geography, 2024
- FIGURE 12.3: Public vs. Private Cord Blood Banking Service Market
- FIGURE 12.4: Global Market Share for Cord Blood & Cord Tissue Banking Services, 2024
- FIGURE 12.5: Market Share of CB for Transplantation & Regenerative Medicine
- FIGURE 12.6: Percent Share of Cord Blood & Cord Tissue Market by Indication
- FIGURE 13.1: Funders for CIBMTR in 2023
- FIGURE 13.2: Sales Revenues and Gross Profits for CordLife, 2014-2023
- FIGURE 13.3: Cryo-Cell International's Revenue Generation, 2017-2023
- FIGURE 13.4: GCBC's Revenue Generation, 2015-2022
- FIGURE 13.5: Revenue Generation by Vita 34 AG, 2014-2021
- FIGURE App.1.1: Proportion of Clinical Conditions Investigated using UCB-MSCs
INDEX OF TABLES
- TABLE 2.1: General Features of Public Cord Blood Banks
- TABLE 2.2: Number of CBUs in WMDA Registry
- TABLE 2.3: Public Cord Blood Banks in the U.S.
- TABLE 2.4: Public Cord Blood Banks in European Countries
- TABLE 2.5: International Prices of Cord Blood Unit (CBU)
- TABLE 2.6: Prices of CBUs in NMDP Banks in the U.S.
- TABLE 2.7: General Features of Private Cord Blood Banks
- TABLE 2.8: Leading Private Cord Blood Banks in the U.S.
- TABLE 2.9: World's Top Ten Private Cord Blood Banks by Inventory Size
- TABLE 2.10: Processing and Storage Charges in CBR (U.S.)
- TABLE 2.11: Processing and Storage Fee Charged by Vita34 (Europe)
- TABLE 2.12: Processing and Storage Fees Charged by LifeCell (India)
- TABLE 2.13: Processing & Storage Fees Charged by Global Cord Blood Corp. (China)
- TABLE 2.14: Revenue Generation by Three Major Private Cord Blood Banks, 2017-2024
- TABLE 2.15: Examples of Hybrid Cord Blood Banks
- TABLE 2.16: Percent Share of Parents Storing Cord Blood in Top Ten Countries
- TABLE 3.1: AABB Accredited Cord Blood Banks
- TABLE 3.2: Select FACT-Accredited Cord Blood Banks
- TABLE 4.1: Legal Status of Umbilical Cord Stem Cell Patents
- TABLE 4.2: Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cell Patent Applications by Year
- TABLE 4.3: Umbilical Cord Blood Patent Applications by Jurisdiction
- TABLE 4.4: Applicants of Umbilical Cord Patents
- TABLE 4.5: Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cell Patent Inventors
- TABLE 4.6: Owners of Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cell Patents
- TABLE 4.7: Legal Status of Cord Tissue Patents
- TABLE 4.8: Number of Umbilical Cord Tissue Patent Applications, 2000-2024
- TABLE 4.9: Umbilical Cord Tissue Patent Applications by Jurisdiction
- TABLE 4.10: Umbilical Cord Tissue Patent Applicants
- TABLE 4.11: Umbilical Cord Tissue Patent Inventors
- TABLE 4.12: Owners of Umbilical Cord Tissue Patents
- TABLE 4.13: Placental Tissue Patent Applicants
- TABLE 4.14: Placental Tissue Patent Applications by Year
- TABLE 4.15: Placental Tissue Patent Jurisdictions
- TABLE 4.16: Inventors of Placental Tissue Patents
- TABLE 4.17: Owners of Placental Tissue Patents
- TABLE 4.18: Legal Status of Placental Tissue Patents
- TABLE 4.19: Cord Blood Expansion Patent Applications by Year
- TABLE 4.20: Cord Blood Expansion Patent Applications by Jurisdiction
- TABLE 4.21: Legal Status of Cord Blood Expansion Patents
- TABLE 4.22: Inventors of Cord Blood Expansion Patents
- TABLE 4.23: Owners of the Cord Blood Expansion Patents
- TABLE 6.1: Total Number of Clinical Trials (CBU, CT, PT and Expanded CBU), Apr. 2025
- TABLE 6.2: Number of Umbilical Cord Blood Clinical Trials by Study Type, April 18, 2025
- TABLE 6.3: Number of Cord Blood Clinical Trials by Phase of Study, April 18, 2025
- TABLE 6.4: Number of Cord Blood Clinical Trials by Funder Type, April 18, 2025
- TABLE 6.5: Select Companies Sponsoring Cord Blood Clinical Trials
- TABLE 6.6: Umbilical Cord Tissue Clinical Trials by Phase of Study, April 19, 2025
- TABLE 6.7: Umbilical Cord Tissue Clinical Trials by Funder Type, April 19, 2025
- TABLE 6.8: Select Companies Sponsoring Cord Tissue Clinical Trials, April 19, 2025
- TABLE 6.9: Placental Tissue Stem Cells in Clinical Trials by Phase of Study, April 19, 2025
- TABLE 6.10: Major Clinical Trials Using Expanded Umbilical Cord Blood Cells
- TABLE 7.1: Umbilical Cord Blood Expansion Strategies
- TABLE 8.1: Umbilical Cord Blood Units Registered with WMDA, April 22, 2025
- TABLE 8.2: Number of CB Donors and CBUs available Worldwide, 1997-2024
- TABLE 8.3: Number of Cord Blood Donors and CBUs available by Geography, 2023
- TABLE 8.4: Available CBUs in the U.S. by Race & Ethnicity, September 30, 2024
- TABLE 8.5: CBUs Available in Europe as of April 23, 2025
- TABLE 8.6: CBUs Available in Asia/Pacific as of April 23, 2025
- TABLE 8.7: HSCs of BM, PB and CB Shipped Worldwide, 1997-2023
- TABLE 8.8: Number of Searches made in WMDA Registry for CBUs, 2017-2023
- TABLE 8.9: Yield of Search Results from WMDA Registry, 2017-2023
- TABLE 9.1: Malignant Indications Addressed by UCB Transplantation
- TABLE 9.2: Non-Malignant Indications for CUB Transplantation
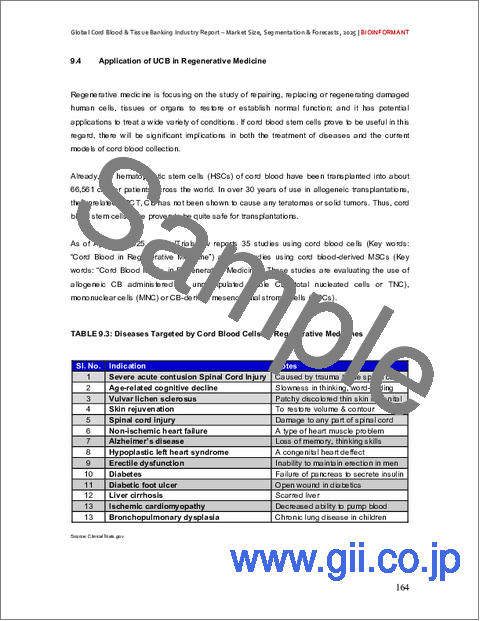
- TABLE 9.3: Diseases Targeted by Cord Blood Cells as Regenerative Medicines
- TABLE 10.1: Worldwide PB, BM & CB Transplants Compared
- TABLE 10.2: CBU Transplantations by Geography, 1999-2023
- TABLE 10.3: Comparison of Median Cost during Admit for CB, PB and BM HSCTs
- TABLE 10.4: Complications through 1-Year Post HSCT
- TABLE 11.1: UCB & UCBT in Clinical Trials on Autism
- TABLE 11.2: A Sample List of Clinical Trials for Cerebral Palsy using CBUs
- TABLE 11.3: A Sample List of Clinical Studies for Alzheimer's Disease using CBUs
- TABLE 11.4: A Sample List of Clinical Studies for Diabetes using CBUs
- TABLE 11.5: A Small List of Clinical Studies for Heart Diseases using CBUs
- TABLE 11.6: A Short List of Clinical Studies for Multiple Sclerosis using CBUs
- TABLE 12.1: Global Cord Blood Banking Service Market, 2024-2032
- TABLE 12.2: Global Market for Cord Tissue Banking Service, 2024-2032
- TABLE 13.1: Angiocrine's R&D Pipeline
- TABLE 13.2: Baylx's hUC-MSC-Derived Product Pipeline
- TABLE 13.3: NMDP Network of Cord Blood Banks
- TABLE 13.4: Cell Care's Pricing for Cord Blood Processing and Storage
- TABLE 13.5: Cellenkos' Product Pipeline
- TABLE 13.6: Cord Blood Releases from Cells4Life
- TABLE 13.7: Celularity's Active Clinical Pipeline
- TABLE 13.8: Recovery of Viable CFU by PrepaCyte-CB
- TABLE 13.9: Cryo-Cell International's Revenue Generation, 2017-2023
- TABLE 13.10: Cryo-Cell International's Pricing
- TABLE 13.11: CryoCyte's Option Plans & Pricing
- TABLE 13.12: DKMS' Donor Typing Profile & Active Donors
- TABLE 13.13: EBMT Transplant Activity, 2023
- TABLE 13.14: Cord Blood Banking Cost in GeneCell
- TABLE 13.15: GCBC's Revenue Generation, 2015-2022
- TABLE 13.16: Glycostem's Product Pipeline
- TABLE 13.17: Insception LifeBank's Pricing
- TABLE 13.18: Cord Blood Releases from Insception LifeBank for Transplantation
- TABLE 13.19: Cord Blood Cells Released for Regenerative Medicine from Insception
- TABLE 13.20: Kangstem's Sponsor Initiated Clinical Trials
- TABLE 13.21: LifeCell International's Pricing
- TABLE 13.22: Maze Cord Blood: Banking Cost
- TABLE 13.23: MiracleCord's Cord Blood Banking Cost
- TABLE 13.24: MonoTx's Product Pipeline