
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1735760
水中スウォーム戦の世界市場(2025年~2035年)Global Underwater Swarm Warfare Market 2025-2035 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| 水中スウォーム戦の世界市場(2025年~2035年) |
|
出版日: 2025年05月29日
発行: Aviation & Defense Market Reports (A&D)
ページ情報: 英文 150+ Pages
納期: 3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
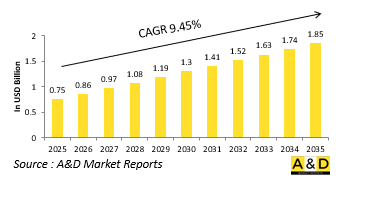
世界の水中スウォーム戦の市場規模は、2025年に推定7億5,000万米ドルであり、2035年までに18億5,000万米ドルに達すると予測され、予測期間の2025年~2035年にCAGRで9.45%の成長が見込まれます。
水中スウォーム戦市場における技術の影響
自律システム、通信プロトコル、水中推進の進歩により、水中スウォーム戦能力の開発が大幅に加速しています。この進化の中心はAIの利用であり、水中ドローンが人間の直接的な制御なしに共同作業を行うことを可能にしています。これらのシステムは分散型の意思決定モデルを使用しており、各ユニットがセンサーデータを処理し、動的なシナリオに集団で対応することを可能にしています。水中での通信には独特の課題がありますが、音響信号と光データ転送における近年の技術革新により、スウォームのメンバー間のリアルタイム協調が改良されました。センサーの小型化とエネルギー効率の向上により、小さな車両が長く作動し、複雑な水中地形を航行できるようになっています。機械学習アルゴリズムは、経路計画、脅威の特定、適応的な作戦遂行を洗練させるのに役立ち、監視、地域制圧、または協調攻撃の役割において、スウォームをより効果的にします。スウォームシステムは、ソナーマッピング、ペイロードデリバリー、電子戦などのタスクに合わせたペイロードを搭載できるモジュール性という利点もあります。冗長性も技術的な強みであり、1つのユニットが故障したり無力化されたりしても、その他のユニットがシームレスに適応して作戦の継続性を維持します。これらの技術革新により、海中戦は硬直化した集中型の作戦から、柔軟でインテリジェントな作戦へと移行しつつあります。その結果、脅威や機会にリアルタイムで適応できるレジリエントな水中ネットワークが構築され、海軍の水面下での作戦が根本的に変わることになります。
水中スウォーム戦市場の主な促進要因
水中スウォーム戦の勢いは、戦略的、作戦的、技術的な要請の収束によって促進されています。主な促進要因の1つは、敵対者がステルスプラットフォーム、無人システム、型破りな戦術を採用することが増えている水中環境の複雑化です。スウォームベースのアプローチは、広大な海洋空間にわたって持続的かつ分散的な監視と迅速な対応能力を提供することで、効果的な対抗策を提供します。さらに、従来の有人潜水艇や水上艇の高いコストと脆弱性から、特にリスクの高い作戦や資源集約的な作戦では、スウォームが魅力的な補完手段や代替手段となります。特に争いの絶えない海域において、海中での優位性を維持したいという戦略的欲求が、海軍を柔軟に多数展開できるスケーラブルなソリューションの追求へと駆り立てています。運用面では、スウォームは人員のリスクを増大させることなく状況認識と戦力投射を強化するため、偵察、機雷対策、電子撹乱の作戦に理想的です。開発面では、AUVやオープンソースのナビゲーションシステムが手頃な価格で入手できるようになったことで、より多くの国がスウォーム技術を探求できるようになっています。リアルタイムインテリジェンスやネットワーク化された戦争、適応的な作戦遂行の重視により、その魅力はさらに強調されます。結果として、戦略的抑止力、作戦の汎用性、技術的実現可能性の組み合わせにより、水中スウォームは将来の海上防衛方針における重要な構成要素となっています。
地域の水中スウォーム戦市場の動向
水中スウォーム戦に対する地域のアプローチは、さまざまな戦略的関心、技術的能力、海洋における優先順位を反映しています。アジア太平洋では、緊張の高まりと領土紛争が自律型水中技術への投資の急増を促しています。広大な海岸線を持ち、積極的な海洋権益を主張する国々は、水中監視や侵入対策を強化するため、スウォーム能力を模索しています。
当レポートでは、世界の水中スウォーム戦市場について調査分析し、成長促進要因、今後10年間の見通し、各地域の動向などの情報を提供しています。
目次
水中スウォーム戦市場レポートの定義
水中スウォーム戦市場のセグメンテーション
地域別
動作方式別
推進別
今後10年間の水中スウォーム戦市場の分析
水中スウォーム戦市場の技術
世界の水中スウォーム戦市場の予測
地域の水中スウォーム戦市場の動向と予測
北米
促進要因、抑制要因、課題
PEST
市場予測とシナリオ分析
主要企業
サプライヤーのTierの情勢
企業ベンチマーク
欧州
中東
アジア太平洋
南米
水中スウォーム戦市場の分析:国別
米国
防衛プログラム
最新ニュース
特許
この市場における現在の技術成熟度
市場予測とシナリオ分析
カナダ
イタリア
フランス
ドイツ
オランダ
ベルギー
スペイン
スウェーデン
ギリシャ
オーストラリア
南アフリカ
インド
中国
ロシア
韓国
日本
マレーシア
シンガポール
ブラジル
水中スウォーム戦市場の機会マトリクス
水中スウォーム戦市場レポートに関する専門家の意見
結論
Aviation and Defense Market Reportsについて
List of Tables
- Table 1: 10 Year Market Outlook, 2025-2035
- Table 2: Drivers, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 3: Restraints, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 4: Challenges, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 5: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 6: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 7: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 8: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 9: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 10: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 11: Drivers, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 12: Restraints, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 13: Challenges, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 14: Drivers, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 15: Restraints, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 16: Challenges, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 17: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 18: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Mode of Operation, 2025-2035
- Table 19: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Propulsion, 2025-2035
- Table 20: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 21: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Mode of Operation, 2025-2035
- Table 22: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Propulsion, 2025-2035
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Global Underwater Swarm Warfare Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 2: Global Underwater Swarm Warfare Market Forecast, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 3: Global Underwater Swarm Warfare Market Forecast, By Mode of Operation, 2025-2035
- Figure 4: Global Underwater Swarm Warfare Market Forecast, By Propulsion, 2025-2035
- Figure 5: North America, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 6: Europe, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 7: Middle East, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 8: APAC, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 9: South America, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 10: United States, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 11: United States, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 12: Canada, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 13: Canada, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 14: Italy, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 15: Italy, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 16: France, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 17: France, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 18: Germany, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 19: Germany, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 20: Netherlands, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 21: Netherlands, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 22: Belgium, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 23: Belgium, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 24: Spain, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 25: Spain, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 26: Sweden, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 27: Sweden, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 28: Brazil, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 29: Brazil, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 30: Australia, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 31: Australia, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 32: India, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 33: India, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 34: China, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 35: China, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 36: Saudi Arabia, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 37: Saudi Arabia, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 38: South Korea, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 39: South Korea, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 40: Japan, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 41: Japan, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 42: Malaysia, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 43: Malaysia, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 44: Singapore, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 45: Singapore, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 46: United Kingdom, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 47: United Kingdom, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 48: Opportunity Analysis, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, By Region (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 49: Opportunity Analysis, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, By Region (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 50: Opportunity Analysis, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, By Mode of Operation (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 51: Opportunity Analysis, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, By Mode of Operation (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 52: Opportunity Analysis, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, By Propulsion (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 53: Opportunity Analysis, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, By Propulsion (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 54: Scenario Analysis, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Cumulative Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 55: Scenario Analysis, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Global Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 56: Scenario 1, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 57: Scenario 1, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 58: Scenario 1, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, By Mode of Operation, 2025-2035
- Figure 59: Scenario 1, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, By Propulsion, 2025-2035
- Figure 60: Scenario 2, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 61: Scenario 2, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 62: Scenario 2, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, By Mode of Operation, 2025-2035
- Figure 63: Scenario 2, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, By Propulsion, 2025-2035
- Figure 64: Company Benchmark, Underwater Swarm Warfare Market, 2025-2035
The Global Underwater Swarm Warfare market is estimated at USD 0.75 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 1.85 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 9.45% over the forecast period 2025-2035.

Introduction to Underwater Swarm Warfare Market:
Underwater swarm warfare is emerging as a transformative concept in naval defense, characterized by the coordinated use of multiple autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) to achieve strategic and tactical objectives. These swarms operate as decentralized, intelligent networks capable of executing complex missions with minimal human oversight. Unlike traditional underwater systems that rely on singular, high-value assets, swarm-based strategies emphasize redundancy, adaptability, and coverage. This paradigm enables navies to conduct reconnaissance, surveillance, mine detection, and offensive operations simultaneously across large maritime areas. The core advantage lies in the swarm's collective behavior, where individual units share information in real-time to respond dynamically to threats, obstacles, or environmental changes. As maritime zones grow increasingly contested and adversaries adopt stealthier undersea tactics, the need for persistent and reactive underwater presence becomes critical. Swarm warfare introduces a new layer of deterrence by overwhelming enemy defenses, complicating targeting decisions, and enhancing domain awareness. Global interest in this capability is rising, with militaries investing in research and prototyping to harness its full potential. As the underwater domain becomes a theater of greater strategic competition, swarm warfare is set to play a pivotal role in shaping future naval engagements, offering a blend of autonomy, scalability, and resilience that traditional systems cannot match.
Technology Impact in Underwater Swarm Warfare Market:
Advances in autonomous systems, communication protocols, and underwater propulsion have significantly accelerated the development of underwater swarm warfare capabilities. Central to this evolution is the application of artificial intelligence, enabling underwater drones to operate collaboratively without direct human control. These systems use decentralized decision-making models, allowing each unit to process sensor data and respond collectively to dynamic scenarios. Communication underwater presents unique challenges, and recent innovations in acoustic signaling and optical data transfer have improved real-time coordination among swarm members. Sensor miniaturization and improved energy efficiency allow for smaller vehicles that can operate longer and navigate complex underwater terrains. Machine learning algorithms help refine path planning, threat identification, and adaptive mission execution, making swarms more effective in surveillance, area denial, or coordinated attack roles. Swarm systems also benefit from modularity, with payloads tailored for tasks like sonar mapping, payload delivery, or electronic warfare. Redundancy is another technological strength-if one unit fails or is neutralized, others seamlessly adapt to maintain mission continuity. Collectively, these innovations are shifting undersea warfare from rigid, centralized operations to flexible, intelligent engagements. The result is a resilient underwater network capable of adjusting in real-time to threats and opportunities, fundamentally changing how naval forces operate beneath the surface.
Key Drivers in Underwater Swarm Warfare Market:
The momentum behind underwater swarm warfare is being driven by a convergence of strategic, operational, and technological imperatives. One of the primary motivators is the growing complexity of undersea environments, where adversaries increasingly employ stealthy platforms, unmanned systems, and unconventional tactics. Swarm-based approaches provide an effective counter by offering persistent, distributed surveillance and rapid response capabilities across broad ocean spaces. Additionally, the high cost and vulnerability of traditional manned submarines and surface ships make swarms an attractive supplement or alternative, especially for high-risk or resource-intensive missions. The strategic desire to maintain undersea dominance, particularly in contested maritime zones, is pushing navies to seek scalable solutions that can be deployed flexibly and in large numbers. Operationally, swarms enhance situational awareness and force projection without escalating risk to personnel, making them ideal for reconnaissance, mine countermeasures, and electronic disruption tasks. From a development standpoint, the increasing affordability of autonomous underwater vehicles and open-source navigation systems is enabling more countries to explore swarm technologies. The emphasis on real-time intelligence, networked warfare, and adaptive mission execution further underscores the appeal. Ultimately, the combination of strategic deterrence, operational versatility, and technological feasibility positions underwater swarms as a key component in future naval defense doctrines.
Regional Trends in Underwater Swarm Warfare Market:
Regional approaches to underwater swarm warfare reflect a range of strategic interests, technological capacities, and maritime priorities. In the Asia-Pacific, rising tensions and territorial disputes have prompted a surge in investment in autonomous underwater technologies. Countries with large coastlines and active maritime claims are exploring swarm capabilities to enhance underwater surveillance and counter-intrusion measures. North American defense initiatives, particularly those led by the United States, are focusing on integrating swarms into broader multi-domain strategies, emphasizing interoperability and long-range mission capabilities. These efforts include experimentation with autonomous swarms as force multipliers in complex undersea environments. In Europe, collaborative defense projects are developing scalable swarm systems tailored for littoral defense, port protection, and anti-submarine operations, with a strong emphasis on interoperability among NATO allies. Middle Eastern navies are increasingly interested in undersea swarms for coastal monitoring and infrastructure protection, particularly around chokepoints and strategic waterways. In Latin America and Africa, while adoption is in earlier stages, interest is growing in using underwater swarms for anti-smuggling, illegal fishing deterrence, and maritime resource protection. Across all regions, there is a growing recognition that underwater swarm warfare offers a low-risk, high-impact method of securing maritime interests, especially as near-peer competition and asymmetric threats continue to evolve in the underwater domain.
Key Underwater Swarm Warfare Program:
German Company Deploys Underwater Spy Drone Swarm That Can Operate Stealthily for 3 Months, Marking a Major Maritime Breakthrough. Amid rising concerns over underwater security, an innovative German firm has introduced the SG-1 Fathom-an advanced autonomous underwater glider designed to patrol the ocean's depths for up to three months at a time. This cutting-edge technology is set to transform maritime surveillance and reshape the landscape of underwater threat detection.
Table of Contents
Underwater Swarm Warfare Market Report Definition
Underwater Swarm Warfare Market Segmentation
By Region
By Mode Of Operation
By Propulsion
Underwater Swarm Warfare Market Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year underwater swarm warfare market analysis would give a detailed overview of underwater swarm warfare market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Underwater Swarm Warfare Market
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Underwater Swarm Warfare Market Forecast
The 10-year underwater swarm warfare market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Underwater Swarm Warfare Market Trends & Forecast
The regional underwater swarm warfare market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Underwater Swarm Warfare Market
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Underwater Swarm Warfare Market
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Underwater Swarm Warfare Market Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.


