
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1927656
防衛向け3Dプリンティングの世界市場(2026年~2036年)Global Defense 3D Printing Market 2026-2036 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| 防衛向け3Dプリンティングの世界市場(2026年~2036年) |
|
出版日: 2026年02月02日
発行: Aviation & Defense Market Reports (A&D)
ページ情報: 英文 150+ Pages
納期: 3営業日
|
概要
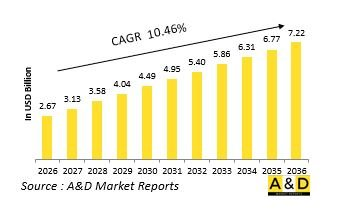
世界の防衛向け3Dプリンティングの市場規模は、2026年に推定26億7,000万米ドルであり、2036年までに72億2,000万米ドルに達すると予測され、2026年~2036年の予測期間にCAGRで10.46%の成長が見込まれています。
世界の防衛向け3Dプリンティングへのイントロダクション
世界の防衛向け3Dプリンティングは、軍用コンポーネントの設計・製造・維持管理の方法を変革する製造手法として台頭しています。従来の生産方式とは異なり、積層造形技術は部品を層ごとに構築するため、従来技術では困難または非現実的であった複雑な形状の実現を可能にします。防衛部門では、この技術が迅速なプロトタイピング、カスタマイズ部品の生産、作戦環境下での需要に応じた製造を支えています。防衛機関は、準備態勢の向上と長大なサプライチェーンへの依存度低減を図る戦略的ツールとして、3Dプリンティングをますます重視しています。この技術は設計の反復を迅速化し、開発サイクルを短縮しながらコンポーネントの試験と改良を可能にします。また、強度を損なうことなくプラットフォーム性能を向上させる軽量構造の生産も支援します。航空、陸上、海上の各領域において、3Dプリンティング技術は予備部品や作戦上重要なコンポーネントの現地製造を可能にすることで、装備の維持管理に寄与します。その普及の拡大は、スピード、適応性、運用上のレジリエンスといった現代の防衛要件に沿った、柔軟で応答性の高い製造モデルへの移行を反映しています。
世界の防衛向け3Dプリンティングにおける技術の影響
技術の進歩により、防衛用途における3Dプリンティングの適用範囲と信頼性が拡大しています。金属積層造形の進歩により、構造や荷重支持に適した高強度コンポーネントの製造が可能となりました。印刷精度の向上により寸法精度と表面品質が向上し、厳しい防衛仕様を満たしています。材料科学の革新により、過酷な運用環境向けに設計された特殊合金や複合材料が導入されました。統合デジタル設計ツールにより、モデリングから生産へのシームレスな移行が可能となり、迅速な修正もサポートしています。工程内モニタリングなどの品質保証技術は、一貫性を向上させ欠陥リスクを低減します。分散型製造における機密設計データを保護するセキュアなデジタルワークフローも確立されました。これらの発達により、3Dプリンティングはプロトタイピングツールから、実戦展開を支える生産技術へと進化を遂げました。現在では、性能向上、材料廃棄物の削減、防衛プラットフォーム全体における変化する作戦要件への迅速な対応を実現する役割を担っています。
世界の防衛向け3Dプリンティングの主な促進要因
防衛における3Dプリンティングの採用は、運用上の柔軟性、サプライチェーンのレジリエンス、コスト効率化の目標によって推進されています。軍事組織は、装備のダウンタイムを最小化するため、交換部品への迅速なアクセスを求めています。現場または近隣での製造は、中央集権的なサプライヤーや長距離の兵站経路への依存を軽減します。プラットフォーム近代化プログラムは、軽量化と最適化された設計を支える先進的な製造手法の活用を促進します。予算効率化の目標は、工具要件と材料廃棄を削減する技術の推進につながります。少量の複雑な部品を生産する能力は、防衛調達パターンとよく合致します。労働力のスキル開発とデジタルトランスフォーメーションの取り組みは、積層造形技術の防衛エコシステムへの統合をさらに支援します。これらの促進要因は、防衛製造における敏捷性、持続可能性、対応力への戦略的な注力を反映しています。
当レポートでは、世界の防衛向け3Dプリンティング市場について調査分析し、市場に影響を与える技術、今後10年間の予測、各地域の動向などの情報を提供しています。
目次
防衛向け3Dプリンティング市場レポートの定義
防衛向け3Dプリンティング市場のセグメンテーション
用途別
地域別
コンポーネント別
今後10年間の防衛向け3Dプリンティング市場の分析
防衛向け3Dプリンティング市場の技術
世界の防衛向け3Dプリンティング市場の予測
地域の防衛向け3Dプリンティング市場の動向と予測
北米
促進要因、抑制要因、課題
PEST
市場予測とシナリオ分析
主要企業
サプライヤーのTierの状況
企業ベンチマーク
欧州
中東
アジア太平洋
南米
防衛向け3Dプリンティング市場の国の分析
米国
防衛プログラム
最新ニュース
特許
この市場における現在の技術成熟度
市場予測とシナリオ分析
カナダ
イタリア
フランス
ドイツ
オランダ
ベルギー
スペイン
スウェーデン
ギリシャ
オーストラリア
南アフリカ
インド
中国
ロシア
韓国
日本
マレーシア
シンガポール
ブラジル


