
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1858534
大陸間弾道ミサイルの世界市場:2025年~2035年Global Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market 2025-2035 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| 大陸間弾道ミサイルの世界市場:2025年~2035年 |
|
出版日: 2025年11月01日
発行: Aviation & Defense Market Reports (A&D)
ページ情報: 英文 150+ Pages
納期: 3営業日
|
概要
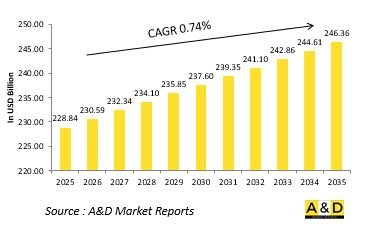
世界の大陸間弾道ミサイルの市場規模は、2025年に2,288億4,000万米ドルと推定され、2035年までに2,463億6,000万米ドルに成長すると予測されており、予測期間の2025年~2035年の年間平均成長率(CAGR)は0.74%と見込まれています。
大陸間弾道ミサイル市場のイントロダクション
大陸間弾道ミサイル(ICBM)市場は、戦略的抑止力の中核であり、世界の安全保障アーキテクチャと大国間の軍事バランスを支えています。ICBMは、通常弾頭または核弾頭を搭載できる長距離運搬システムであり、侵略が行われた場合に確実な報復と抑止力を確保するように設計されています。その速度、到達距離、精度は、国家防衛戦略や核三極体制の重要な要素となっています。この市場の特徴は、新興のミサイル防衛システムに対する信頼性、精度、生存性の向上を目指した、進行中の近代化努力にあります。各国が信頼性の高い抑止態勢の維持に重点を置く中、先進的な推進、誘導、再突入体技術への投資が加速しています。移動発射プラットフォームと強化サイロの開発は、戦略的即応性をさらに強化します。全体として、ICBM市場は依然として世界防衛戦略の要であり、戦力投射と抑止力の安定のバランスを保っています。
大陸間弾道ミサイル市場における技術の影響
技術の進歩は大陸間弾道ミサイルの能力と有効性を大きく形成してきました。推進システム、特に固体燃料技術の改良により、発射準備の迅速化と運用寿命の延長が可能になっています。慣性航法、衛星による補正、AIによる軌道最適化などを統合した誘導・航法システムの強化により、目標精度が大幅に向上しました。複数の独立目標再突入機(MIRV)を含む再突入機技術の発展により、単一のミサイルで複数の目標を同時に攻撃できるようになっています。高度なミサイル防衛システムを克服するために、ステルス・コーティング、デコイ、操縦可能な弾頭が導入されています。デジタル指揮統制の統合は、戦略ユニットと国防ネットワーク間の安全かつ迅速な通信を保証します。さらに、近代化プログラムでは、電子的干渉から保護するために、サイバーに強いアーキテクチャを組み込むことが増えています。これらの技術革新の総体として、ICBMはより正確で生存性が高く、戦略的に柔軟な抑止システムへと変貌を遂げつつあります。
大陸間弾道ミサイル市場の主要な促進要因
ICBM市場を牽引する主な要因は、進化する安全保障上の脅威、戦略的抑止力のニーズ、近代化の必要性に起因します。地政学的緊張の高まりと核抑止力の再重視により、主要国はミサイル兵装を強化・拡大するようになっています。第二次攻撃能力を維持し、同等の戦略的資産を持つ敵対国に対して信頼できる抑止力を確保する必要性が、絶え間ない技術進歩の原動力となっています。信頼性を高め、最新のミサイル防衛ネットワークに対抗するために、老朽化したミサイルシステムをアップグレードすることも主要な推進力となっています。防衛組織はまた、生存性と運用の柔軟性を高めるため、移動式や隠蔽式の発射プラットフォームを優先しています。発射システムにおけるデジタル技術と自動化の統合は、即応性を高め、人的ミスを減らします。これらの要因を総合すると、ICBMは戦略的防衛態勢と抑止の枠組みの不可欠な構成要素としての役割を強化しつつあります。
大陸間弾道ミサイル市場の地域動向:
ICBM市場の地域開拓は、それぞれ異なる戦略的野心と防衛理念を反映しています。北米では、近代化計画は精度の向上、安全な通信、既存のミサイルシステムの延命に重点を置いています。欧州の防衛戦略は依然として同盟に基づく抑止の枠組みと密接に結びついており、より広範な戦略的防衛ネットワークとの統合に重点を置いています。アジア太平洋では、地域の大国が戦略的自主性を強化し、ライバル国に対抗するためにICBM能力を開発またはアップグレードする動きが活発化しています。中東では、長距離ミサイル技術への関心が高まっているが、地政学的および規制上の制約から、開発は依然として限定的です。他の地域の新興防衛産業は、潜在的な協力関係や技術移転の機会を求めて、その進展を注視しています。すべての地域において、ICBM計画は技術力と戦略的独立性を象徴し続け、国防とグローバル・パワー・ダイナミックスを強化しています。
主要な防衛大陸間弾道ミサイル計画:
米国の核三原則の陸上部門は現在、モンタナ州、ノースダコタ州、ワイオミング州、ネブラスカ州、コロラド州にまたがる地下サイロに配備された400基のミニットマンIII大陸間弾道ミサイル(ICBM)で構成され、マームストローム空軍基地、マイノ空軍基地、ウォーレン空軍基地から運用されています。各ミサイルは、W87またはW78の核弾頭を1つずつ搭載しているが、理論的には2つまたは3つの核弾頭を搭載することができます。
米国空軍は、少なくとも2030年までミニットマンIIIの運用寿命を延ばし、数十年にわたる70億米ドルの近代化努力を終了しました。アップグレードの後、空軍はリニューアルされたミサイルを"外殻を除けば本質的に新しいシステム"と説明しました。
目次
大陸間弾道ミサイル市場- 目次
大陸間弾道ミサイル市場レポートの定義
大陸間弾道ミサイル市場セグメンテーション
地域別
推進力別
範囲別
今後10年間の大陸間弾道ミサイル市場分析
この章では、10年間の大陸間弾道ミサイル市場の分析により、大陸間弾道ミサイル市場の成長、変化する動向、技術採用の概要、および全体的な市場の魅力の詳細な概要が提供されます。
大陸間弾道ミサイル市場の市場技術
このセグメントでは、この市場に影響を与えると予想される上位10の技術と、これらの技術が市場全体に与える可能性のある影響について説明します。
世界の大陸間弾道ミサイル市場予測
この市場の10年間の大陸間弾道ミサイル市場予測は、上記のセグメント全体で詳細にカバーされています。
地域別大陸間弾道ミサイル市場の動向と予測
このセグメントでは、地域ごとの大陸間弾道ミサイル市場の動向、促進要因、制約要因、課題、そして政治、経済、社会、技術といった側面を網羅しています。また、地域別の市場予測とシナリオ分析も詳細に取り上げています。地域分析の最後には、主要企業のプロファイリング、サプライヤーの情勢、企業ベンチマークが含まれています。現在の市場規模は、通常のシナリオに基づいて推定されています。
北米
促進要因、抑制要因、課題
PEST
市場予測とシナリオ分析
主要企業
サプライヤー階層の情勢
企業ベンチマーク
欧州
中東
アジア太平洋
南米
大陸間弾道ミサイル市場の国別分析
この章では、この市場における主要な防衛プログラムを取り上げ、この市場で申請された最新のニュースや特許についても解説します。また、国レベルの10年間の市場予測とシナリオ分析についても解説します。
米国
防衛プログラム
最新ニュース
特許
この市場における現在の技術成熟度
市場予測とシナリオ分析
カナダ
イタリア
フランス
ドイツ
オランダ
ベルギー
スペイン
スウェーデン
ギリシャ
オーストラリア
南アフリカ
インド
中国
ロシア
韓国
日本
マレーシア
シンガポール
ブラジル
大陸間弾道ミサイル市場の機会マトリックス
機会マトリックスは、読者がこの市場における機会の高いセグメントを理解するのに役立ちます。
大陸間弾道ミサイル市場レポートに関する専門家の意見
この市場の分析の可能性について、当社の専門家の意見をお届けします。


