|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1568196
産業用OTサイバーセキュリティ産業の分析 (2024~2030年)Industrials OT Cybersecurity Industry Analysis 2024-2030 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| 産業用OTサイバーセキュリティ産業の分析 (2024~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2024年08月31日
発行: Westlands Advisory Ltd
ページ情報: 英文
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
概要
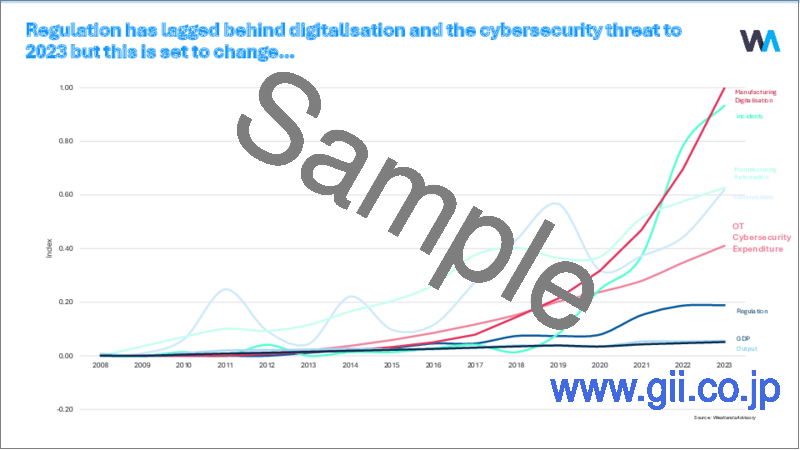
OTサイバーセキュリティへの支出は近年大幅に増加しており、2023年には推定84億米ドルに達します。米国が最大の市場であり、予測期間中もその傾向は続きます。
サイバーセキュリティ投資の増加は、製造業でのデジタル変革の進行や攻撃対象の拡大と強く相関しています。産業運営に影響を与えるサイバーインシデントの増加や現在の地政学的情勢、数多くの脆弱性が、資産所有者に資産保護・監視への投資を促しています。この動向は2031年まで強まると見込まれ、サイバーセキュリティへの投資につながると予想されますが、その増加率は、デジタル変革やサイバーインシデントの件数ほどではない見通しです。
最大の支出分野は、主要産業や大手多国籍企業におけるOTサイバーセキュリティ・プログラムの加速です。エッジでのデータ処理の増加やクラウドサービスの利用には、引き続きCISOの注意が必要となります。長期的には、オンプレミス、エッジ、クラウドの運用に関係なく、セキュリティリーダーが運用の回復力に焦点を当てることで、OTとIIoTは徐々に区別がつかなくなると思われます。
しかし、重要産業や大規模な多国籍企業だけでなく、世界の産業基盤の大部分を占める中小企業のサイバーセキュリティ成熟度に関しても、大きな課題が残されています。これらの組織は、規制や現地法律への準拠が一層求められる一方で、OTサイバーセキュリティ・プログラムを管理するのに必要なリソースや人材を有していません。
最大の支出分野は、依然としてネットワーク保護とセグメンテーションです。このため、NGFWベンダーは大きく成長し、OT環境向けに開発された新製品への投資もこれに対応しています。OTネットワークの脅威検知と脆弱性管理への支出は、2016年から2023年にかけて急速に拡大しましたが、現在は成熟し始めています。ベンダー各社は、複数の使用事例に対応するソリューションを顧客に提供するプラットフォーム・アプローチに移行しつつあります。マネージド・セキュリティサービスは高成長の要件であり、レベル2およびレベル3のSOCアナリストに対する顧客のニーズに対応しています。
2031年までには、大手メーカーは資産に特化し、自動化され、ゼロトラストの原則に基づいて構築されるようになると思われます。これはグリーンフィールド工場で標準化される一方、ブラウンフィールド工場では、OTサイバーセキュリティのコンセプトが成熟し、予算が確保できるようになり、メンテナンスウィンドウで更新が可能になるにつれて、徐々にこれらのモデルに移行します。
産業用OTサイバーセキュリティの定義
1980年代に開発されたPurdueモデルは、セキュリティ・信頼性・管理性の向上を目的に産業用ネットワークシステムを編成・分割するための標準的アプローチとして、現在も広く使用されており、またOTサイバーセキュリティの使用事例を説明するために、分析全体を通して使用されています。
- レベル0:物理プロセス。物理的データの取得とプロセス制御 (温度センサー、圧力計、制御バルブなど)。
- レベル1:コントローラLAN。プロセス制御 (PLC・RTU) を直接担当するハードウェアやソフトウェアを含みます。これは主に、物理プロセスのリアルタイム制御・監視や、制御ロジックの実行、およびレベル0デバイスからのデータ収集です。
- レベル2:ローカルHMI LAN。レベル1デバイスやリアルタイムモニタリング、データロギング、基本的アラーム機能を監督および調整する、監督・制御・データ収集システム。オペレーターがシステムを操作してプロセスを管理・監督する場所。
- レベル3:生産プロセスを企業目標に適合させるようなコントロールセンターまたはオペレーション管理 (製造実行システム (MES)、バッチ制御、生産スケジューリングを含む)。
- レベル3.5:プラントDMZは、当初のモデルにはなかった追加レイヤであり、IT (企業) レベルとOTレベルの間のセキュリティ管理を記述するために使用されます。典型的なコンポーネントには、ファイアウォール、IT・OT間のセキュリティポリシーの実施、および受信トラフィックの監視・制御、IDS/IPS、他のサーバからのリソースを求めるクライアントからの要求の仲介を行うプロキシサーバ、トラフィックの送信のみを許可するデータダイオード、リモートアクセスサーバなどがあります。
OTに対するサイバーセキュリティの脅威は、ユーザーエラー以外にも、主に管理不十分な認証情報、DMZを通過するマルウェア、またはUSBポート経由で挿入されるマルウェアによるシステムへの不正アクセスに由来します。ビジネスにとってのリスクとは、脅威・脆弱性・資産の重要性といった、複数の要因の集合です。
目次
エグゼクティブサマリー
サイバーセキュリティ投資の促進要因
- 投資の促進要因の概要
- 経済概要
- デジタルトランスフォーメーションの概要
- 規制の概要
- 主要な規制動向の概要
- 攻撃の対象領域
- 脅威
- リスクの認識
- 動向と経済指標 (2008~2023年)
- 動向と経済指標 (2024~2031年)
産業用OTのアーキテクチャとサイバーセキュリティ制御
- リファレンスアーキテクチャ
- Purdueモデル
- OTシステムのリスク
- サイバーセキュリティの技術的・管理的な制御
- 管理な制御
- OTサイバーセキュリティのリファレンスアーキテクチャ
- 産業用制御システムのセキュリティ制御
IIoTサイバーセキュリティ
- サマリー
- 動向と市場支出の予測
- IIoTセキュリティのリファレンスアーキテクチャ
- エコシステム
OTサイバーセキュリティ業界の成熟度
- サマリー
- 人材とプロセス
- リーダーシップ
- 人材と文化の成熟度
- プロセスの成熟度
- 技術の成熟度
- 産業用OTサイバーセキュリティの成熟度
- 業界の構成:零細企業、中小企業、大企業
- 業界別の成熟度
技術のライフサイクルと利用事例
- サマリー
- ネットワーク保護の動向
- OTネットワーク保護
- OTネットワーク保護 (続き)
- 産業用ネットワーク
- 検出・脅威検出の動向
- 検出・脅威検出ソリューション
- 検出・脅威検出ソリューション (続き)
- 資産脆弱性・リスク管理の動向
- 資産脆弱性・リスク管理ソリューション
- エンドポイント保護の動向
- エンドポイント保護ソリューション
- セキュアリモートアクセス管理の動向
- セキュアリモートアクセス管理ソリューション
- セキュリティ運用の動向
- セキュリティ運用ソリューション
- その他の技術ソリューション
- 高度な脅威防止・保護
- プロフェッショナルセキュリティサービスの定義
- プロフェッショナルセキュリティサービスの動向
- マネージドセキュリティサービスの定義
- マネージドセキュリティサービスの動向
- 技術の成熟ライフサイクル
- 技術市場の規模と予測
エコシステム
- サマリー
- 技術ベンダー
- サービスベンダー
市場支出と見通し
- 北米市場の予測:産業セグメント別 (2023~2031年)
- 北米の支出・CAGR:産業セグメント別 (2023年)
- 北米市場の予測:国別 (2023~2031年)
- アジア太平洋市場の予測:産業セグメント別 (2023~2031年)
- アジア太平洋の支出・CAGR:産業セグメント別 (2023年)
- アジア太平洋市場の予測:国別 (2023~2031年)
- 欧州市場の予測:産業セグメント別 (2023~2031年)
- 欧州の支出・CAGR:産業セグメント別 (2023年)
- 欧州市場の予測:国別 (2023~2031年)
- 中東市場の予測:産業セグメント別 (2023~2031年)
- 中東の支出・CAGR:産業セグメント別 (2023年)
- 中東市場の予測:国別 (2023~2031年)
- アフリカ市場の予測:産業セグメント別 (2023~2031年)
- アフリカの支出・CAGR:産業セグメント別 (2023年)
- アフリカ市場の予測:国別 (2023~2031年)
- ラテンアメリカ市場の予測:産業セグメント別 (2023~2031年)
- ラテンアメリカの支出・CAGR:産業セグメント別 (2023年)
- ラテンアメリカ市場の予測:国別 (2023~2031年)
- 中央アジア市場の予測:産業セグメント別 (2023~2031年)
- 中央アジアの支出・CAGR:産業セグメント別 (2023年)
- 中央アジア市場の予測:国別 (2023~2031年)
産業別の市場動向
- 食品・飲料向け市場の動向と予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 自動車向け市場の動向と予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 医薬品向け市場の動向と予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 製造業の動向
- 繊維・皮革向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 木材製品向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 紙製品向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- ゴム・プラスチック向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- その他の非鉄金属向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 機械向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 電気機器製造向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- その他の輸送機械向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- その他のディスクリート産業向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- コンピュータ・電子機器向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 半導体製造業向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 鉄道向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 港湾・海運向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 航空輸送向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 発電向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 送配電向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 水道事業向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 石油・ガス向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 製油所向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 化学向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 鉱業向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 基礎金属向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
- 金属加工向け市場の予測:地域別 (2023~2031年)
Overview
OT cybersecurity expenditure has increased significantly in recent years reaching an estimated $8.4B in 2023. The United States is the largest market and will remain so over the forecast period.
Increased cybersecurity investment is strongly correlated with the ongoing digital transformation of manufacturing industries and the increasing attack surface. The growing number of cyber incidents impacting industrial operations, current geopolitics, and the large number of vulnerabilities, has encouraged asset owners to invest in asset protection and monitoring. Trends are expected to strengthen to 2031 leading to additional cybersecurity investment though the rate of increase is likely to lag behind digital transformation and the number of cyber incidents.
The largest area of expenditure is on accelerating OT cybersecurity programs in critical industries and large multinational businesses. Growing data processing at the edge, and use of cloud services, will continue to demand the attention of the CISO. In the longer-term OT and IIoT will slowly become indistinguishable as security leaders focus on resilience of operations irrespective of on-prem, edge or cloud operations.
However, beyond critical industries and large multinationals, a significant challenge remains regarding the cybersecurity maturity of the large base of SME/Bs which comprise a large percentage of the global industrial base. Increasingly these organisations will be required to comply with regulations and local laws whilst having neither the resources or talent required to manage OT cybersecurity programs.
The largest area of expenditure remains network protection and segmentation. This has resulted in significant growth for NGFW vendors and corresponding investments in new products developed for OT environments. Expenditure on OT network threat detection and vulnerability management has grown rapidly over the period from 2016-2023 but is now beginning to mature. Vendors are shifting to a platform approach, offering customers solutions to multiple use-cases. Managed Security Services is a high growth requirement and addresses the customer need for Level 2 and 3 SOC analysts.
By 2031 leading manufacturers will be asset focussed, automated, and built on zero trust principles. This will become standardised in greenfield plants whilst brownfield operations will slowly migrate towards these models as OT cybersecurity concepts mature, budgets become available, and maintenance windows allow upgrades.
Industrial OT Cybersecurity Definitions
The Purdue Model, developed in the 1980's, is still widely used as a standardised approach to organising and segmenting industrial network systems to improve security, reliability and manageability and is used throughout the analysis to describe OT cybersecurity use cases.
- Level 0 – Physical Process. Physical data acquisition and process control, such as temperature sensors, pressure gauges, and control valves.
- Level 1 – Controller LAN. Includes the hardware and software directly responsible for the control of the processes (PLCs and RTUs). This is principally the real-time control and monitoring of physical processes, execution of control logic, and data acquisition from Level 0 devices.
- Level 2 – Local HMI LAN. Supervisory control and data acquisition systems that oversee and coordinate Level 1 devices, real-time monitoring, data logging, and basic alarming functions. This is where operators interact with the system to manage and supervise processes.
- Level 3 – Control Centre or Operations Management which includes Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), batch-control and production scheduling, ensuring that production processes align with enterprise goals.
- Level 3.5 – Plant DMZ is an additional layer that was not part of the original model and is used to describe the security controls between the IT (Enterprise) and OT levels. Typical components includes firewalls and enforce security policy between IT and OT and to monitor and control incoming traffic, IDS/IPS, proxy servers that act as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from other servers, data diodes to only allow traffic out, and remote access servers
The cybersecurity threat to OT, beyond user error, is primarily from unauthorised access to systems due to poorly managed credentials, malware passing through the DMZ or inserted via USB ports. The risk to the business is the sum or several factors – the threat, the vulnerabilities, and the criticality of the asset.
Table of Contents
Executive Summary
- Executive Summary (1)
- Executive Summary (2)
Cybersecurity Investment Drivers
- Summary of Investment Drivers
- Economics Summary
- Digital Transformation Summary
- Regulatory Summary
- Summary of Major Regulatory Developments
- Attack Surface
- Threats
- Perceptions of Risk
- Trends and economic indicators (2008-2023)
- Trends and economic indicators (2024-2031)
Industrial OT Architectures and Cybersecurity Controls
- Reference Architecture
- Purdue Model
- OT System Risk
- Technical & Administrative Cybersecurity Controls
- Administrative Controls
- OT Cybersecurity Reference Architecture
- Industrial Control System Security Controls
IIoT Cybersecurity
- Summary
- Trends and Market Expenditure Forecast
- IIoT Security Reference Architecture
- Ecosystem
OT Cybersecurity Industry Maturity
- Summary
- People and Process
- Leadership
- People & Culture Maturity
- Process Maturity
- Technology Maturity
- Industrial OT Cybersecurity Maturity
- Industry mix by Micro, Small, Medium and Large Business
- Maturity by industry
Technology Lifecycle & Use Cases
- Summary
- Network Protection Trends
- OT Network Protection
- OT Network Protection Contd.
- Industrial Networking
- Discovery & Threat Detection Trends
- Discovery & Threat Detection Solutions
- Discovery & Threat Detection Solutions Contd.
- Asset Vulnerability & Risk Management Trends
- Asset Vulnerability & Risk Management Solutions
- Endpoint Protection Trends
- Endpoint Protection Solutions
- Secure Remote Access Management Trends
- Secure Remote Access Management Solutions
- Security Operations Trends
- Security Operations Solutions
- Other Technology Solutions
- Advanced Threat Prevention & Protection
- Professional Security Services Definition
- Professional Security Services Trends
- Managed Security Services Definition
- Managed Security Services Trends
- Technology Maturity Lifecycle
- Technology Market Size and Forecast
Ecosystem
- Summary
- Technology Vendors
- Service Vendors
Market Expenditure & Outlook
- North America Market Forecast by Industry Segment 2023-2031
- North America Expenditure 2023 and CAGR by Industry Segment
- North America Market Forecast by Country 2023-2031
- APAC Market Forecast by Industry Segment 2023-2031
- APAC Expenditure 2023 and CAGR by Industry Segment
- APAC Market Forecast by Country 2023-2031
- Europe Market Forecast by Industry Segment 2023-2031
- Europe Expenditure 2023 and CAGR by Industry Segment
- Europe Market Forecast by Country 2023-2031
- Middle East Market Forecast by Industry Segment 2023-2031
- Middle East Expenditure 2023 and CAGR by Industry Segment
- Middle East Market Forecast by Country 2023-2031
- Africa Market Forecast by Industry Segment 2023-2031
- Africa Expenditure 2023 and CAGR by Industry Segment
- Africa Market Forecast by Country 2023-2031
- Latin America Market Forecast by Industry Segment 2023-2031
- Latin America Expenditure 2023 and CAGR by Industry Segment
- Latin America Market Forecast by Country 2023-2031
- Central Asia Market Forecast by Industry Segment 2023-2031
- Central Asia Expenditure 2023 and CAGR by Industry Segment
- Central Asia Market Forecast by Country 2023-2031
Vertical Market Trends
- Food & Beverage Trends & Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Automotive Trends & Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Pharmaceutical Trends & Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Manufacturing Trends
- Textile & Leather Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Wood Product Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Paper Product Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Rubber & Plastics Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Other Non-Metallic Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Machinery Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Electrical Manufacturing Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Other Transport Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Other Discrete Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Computing & Electronics Trends & Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Semiconductor Manufacturing Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Rail Trends Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Ports & Maritime Trends & Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Air Transportation Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Power Generation Trends & Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Transmission & Distribution Trends & Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Water Utilities Trends & Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Oil & Gas Trends & Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Refineries Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Chemical Trends & Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Mining Trends & Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Basic Metals Trends & Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031
- Fabricated Metals Market Forecasts by Region 2023-2031