|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1604918
二次電池用バインダー技術の開発状況と見通し(~2035年)<2025> Development Status and Outlook of Binder Technology for Secondary Batteries (~2035) |
||||||
|
|||||||
| 二次電池用バインダー技術の開発状況と見通し(~2035年) |
|
出版日: 2024年11月25日
発行: SNE Research
ページ情報: 英文 321 Pages
納期: お問合せ
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
LIBの特性は電極によって大きく左右され、優れた電池性能を実現するためには電極構造の最適化が最優先課題です。現在実用化されているLIBのみならず、研究部門においても正極活物質、負極活物質の研究、見直しが盛んに行われています。電極反応に関与しない不活性なバインダーは、低い重量比(5wt%以下)で電極の健全性を維持し、電気化学プロセスを支えており、活物質、導電剤とともに電極の性能を発揮させる上で重要な位置を占めていますが、その重要性に比べて注目度は低いです。
バインダーは電極のごく小さな部分を占めますが、電極の全体的な性能を決定する上で重要な役割を果たしています。正極と負極の両方に含まれる活物質や導電剤が集電体にしっかりと接着するのを助けるとともに、耐久性を向上させます。バインダーは、(1)電解液中で電気化学的に安定であること、(2)柔軟性と不溶性を有すること、(3)特に正極用バインダーの場合、酸化に対する耐食性を有することが必要です。
したがって、活物質と導電剤を集電体に効果的に接続し、体積膨張に対応し、充放電サイクル中に安定した電極構造を確保するためには、高い接着強度と弾性を持つ機能性バインダーが必要となります。近年の研究では、バインダーのスクリーニングと設計に関する深い知見により、単に機械的安定化に用いる構造的支持体としての役割から、電気化学的な利点も提供する多機能バインダーの開発へと焦点が移りつつあります。
近年、シリコン系負極材料の採用が進むにつれて、バインダーがリチウム化反応に大きく影響し、電極容量とサイクル安定性の向上に寄与することが研究で明らかになっています。このため、次世代バインダーの開発が積極的に進められています。従来、正極用バインダーにはフッ素樹脂系のPVDF(ポリフッ化ビニリデン)が、負極用バインダーにはSBR(スチレンブタジエンゴム)やCMC(カルボキシメチルセルロース)が主に使用されてきました。しかし、シリコン系負極は体積膨張が大きいため、これらの従来のバインダーはシリコン系材料には適しません。
近年では、正極用PTFE(ポリテトラフルオロエチレン)バインダーが注目され、負極にはPAA(ポリアクリル酸)やPI(ポリイミド)などの水系バインダーが使用されるようになってきています。これらの水系バインダーは、電解質として水系溶媒を利用するシリコン系負極に特に適しています。従来のバインダーと比べて、PAAやPIは引っ張り強度が高く、接着力が強いため、シリコン系負極の体積膨張に強いです。さらに、これらのバインダーは活物質を包み込み、安定したSEI(固体電解質界面)層の形成に役立ち、電極の安定性とサイクル性能を向上させます。
次世代の正極用バインダーであるPTFE(ポリテトラフルオロエチレン)は、乾式電極プロセス向けのバインダーです。疎水性が高く、耐薬品性・耐熱性に優れた材料として、乾式電極プロセスや固体電池への応用が予測されています。
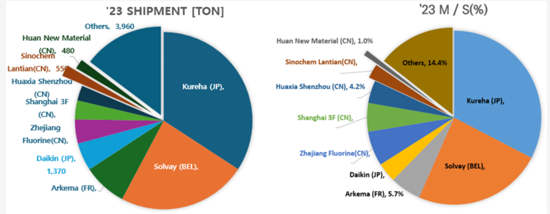
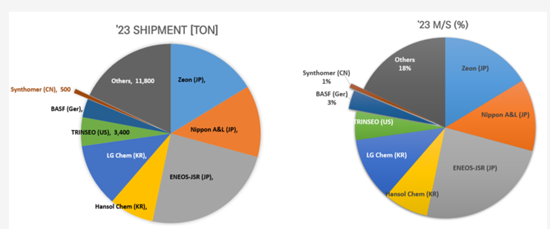
PVDFバインダーはKureha(日本)、Solvay(ベルギー)、Arkema(フランス)、SBRバインダーはZeon(日本)が生産しており、国外サプライヤーへの依存度が高い高コスト材料です。
正極用バインダーはChemtros(韓国)が現地生産に成功しており、負極用バインダーもHansol Chemical(韓国)が国内生産を実現し、Samsung SDIとSK Onに供給しています。さらに、LG ChemとKumho Petrochemicalが負極用バインダー供給市場に参入しています。
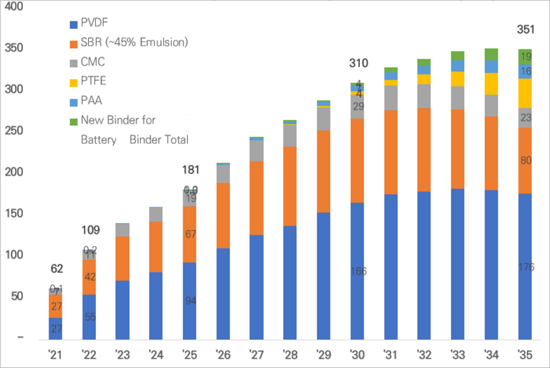
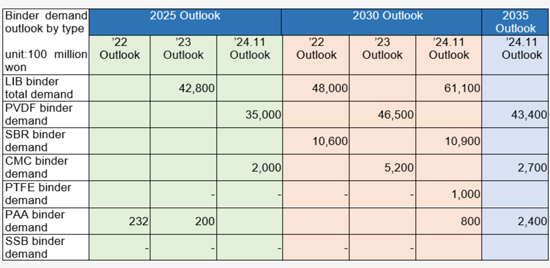
SNE Researchの2024年11月時点の世界のリチウムイオンバッテリー用バインダーの需要予測によると、市場は2025年の181.2トンから2030年に311.4トンに達する見込みです。金額ベースでは、2025年の4兆4,000億ウォンから2030年までに 6兆1,100億ウォンに達する見込みです。
当レポートでは、二次電池用バインダー市場について調査分析し、リチウムイオン電池市場の見通しに基づいて、バインダーの需要と市場動向を予測しています。
PVDFバインダーメーカーの出荷量と市場シェア(M/S)
SBRバインダーメーカーの出荷量と市場シェア(M/S)
世界のLIB用バインダー(正極+負極)需要の予測(キロトン)
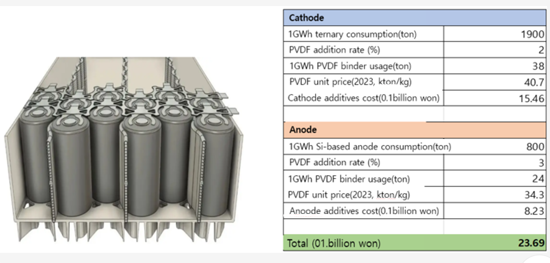
Tesla 4680電池のバインダーコスト分析
- 正極:NCM811、負極:シリコン系
- 1GWh電池のPVDF正極用バインダー要件とコスト:約38トン
- 1GWh電池のPAA負極用バインダー要件とコスト:約24トン
目次
第1章 バインダーの概要
- イントロダクション
- 定義、役割、要件
- カテゴリとタイプ
- 動作メカニズム
- バインダーの破損メカニズム
- バインダー開発に向けた先進の戦略
- バインダー特性評価技法
第2章 バインダーのタイプと研究開発活動
- 正極用バインダー
- 負極用バインダー
- 次世代電池用バインダー(1)
- 乾式プロセス向け4680用バインダー
- 次世代電池用バインダー(2)
第3章 バインダー市場
- バインダー市場の全体的な見通し(その他の研究者による見通し)
- 世界のLIB向けPVDF市場の見通し
- 世界の電池市場の需要見通し
- 世界のLIB用バインダー需要見通し
- LIB用バインダーの価格の見通し
- LIB用バインダーの市場規模の見通し
- 世界の正極用バインダー需要の見通し:主要電池企業別
- 世界の負極用バインダー需要の見通し:主要電池企業別
- シリコン系負極用バインダー市場の見通し
- シリコン系負極用PAAバインダー市場の見通し
- 世界のLFPバインダー需要の見通し(CAGR 12%)
- Tesla向け4680電池のバインダーコスト分析
- LIB用バインダーメーカーの出荷量とM/S
- PVDFバインダーメーカーの出荷量とM/S
- SBRバインダーメーカーの出荷量とM/S
- CMCバインダーメーカーの出荷量とM/S
第4章 バインダーメーカーの状況
- Arkema Group
- BASF SE
- Solvay
- Kureha Corp.
- ZEON Corp.
- JSR Corp.
- Fujian Blue Ocean Co. Ltd (BLUE OCEAN & BLACK STONE)
- Dupont (CMC)
- Ashland Inc.
- MTI Corp.
- TRINSEO
- Xinxiang Jinbang Power Technology Co., Ltd.
- Chongqing Lihong Fine Chemical (CMC Binder Manufacturers)
- Chemtros
- Hansol Chemical
- Kumho Petrochemical
- Daikin Industry
- Nanografi Nano Technology
- Nippon Paper Group
- APV Engineered Coatings LLC
- Sichuan Indigo Materials Science & Technology (INDIGO)
- Guangzhou Songbai Chemical Co (Songbai)
- Nippon A&L Inc.
- Daicel Miraizu Ltd.
- Sinochem Group Co.
- Ube Corp.
- AOT Battery Equipment Technology
- Shanghai Huayi 3F New Materials
- GL Chem
第5章 付録(参考)(水系正極用バインダーのコストの分析など)
第6章 参考文献
The characteristics of LIBs are largely determined by the electrodes, and optimizing the electrode structure is the top priority in order to achieve excellent battery performance. While the active materials of the cathode and anode are being studied and reviewed with much interest not only in currently commercialized LIBs but also in the research field, the inactive binder that does not participate in the electrode reaction maintains the integrity of the electrode with a low weight ratio (less than or equal to 5 wt%) and supports the electrochemical process, and occupies an important position in terms of implementing the performance of the electrode along with the active material and the conductive agent, but it is receiving less attention compared to its importance.
The binder occupies a very small portion of the electrode but plays a crucial role in determining the overall performance of the electrode. It helps active materials and conductive agents in both the cathode and anode adhere firmly to the current collector while enhancing durability. A binder must be (1) electrochemically stable in the electrolyte, (2) possess flexibility and insolubility, and (3) specifically for cathode binders, provide corrosion resistance against oxidation.
Therefore, a functional binder with high bonding strength and elasticity is required to effectively connect the active material and conductive agent to the current collector, accommodate volume expansion, and ensure a stable electrode structure during charge and discharge cycles. Recently, with deeper insights into binder screening and design, research has been shifting its focus from merely serving as a structural support for mechanical stabilization to developing multifunctional binders that also provide electrochemical advantages.
Recently, with the increasing adoption of silicon anode materials, research has shown that binders significantly influence the lithiation reaction, contributing to improved electrode capacity and cycle stability. This has led to active advancements in next-generation binder development. Traditionally, fluoropolymer-based PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) has been primarily used as a binder for cathodes, while SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) and CMC (Carboxymethyl Cellulose) have been used for anodes. However, due to the significant volume expansion of silicon anodes, these conventional binders are unsuitable for use with silicon-based materials.
Recently, PTFE (PolyTetraFluoroEthylene) binders have been gaining attention for cathodes, while water-based binders such as PAA (PolyAcrylic Acid) and PI (PolyImide) are increasingly used for anodes. These water-based binders are particularly suitable for silicon anodes, which utilize water-based solvents as electrolytes. Compared to conventional binders, PAA and PI offer higher tensile strength and stronger adhesion, making them more resistant to the volume expansion of silicon anodes. Additionally, these binders encapsulate the active material, helping to form a stable SEI (Solid Electrolyte Interphase) layer, which enhances electrode stability and cycle performance.
The next-generation cathode binder, PTFE (PolyTetraFluoroEthylene), is a binder for dry electrode processes. As a highly hydrophobic material with excellent chemical and thermal resistance, it is expected to gain attention for use in dry electrode processes and solid-state batteries.
PVDF binders are produced by Kureha (Japan), Solvay (Belgium), and Arkema (France), while SBR binders are manufactured by Zeon (Japan), making them high-cost materials with a high reliance on foreign suppliers.
For cathode binders, Chemtros (South Korea) has successfully localized production, while for anode binders, Hansol Chemical (South Korea) has also achieved domestic production and is supplying to Samsung SDI and SK On. Additionally, LG Chem and Kumho Petrochemical are entering the anode binder supply market.
According to SNE Research's global demand forecast for lithium-ion battery binders as of November 2024, the market is expected to grow from 181.2 kton in 2025 to 311.4 kton in 2030. In terms of value, it is projected to increase from KRW 4.4 trillion in 2025 to KRW 6.11 trillion in 2030.
The 2024 edition of the report has been enhanced with a particular focus on solid-state batteries and sodium-ion batteries, which have recently become hot topics. It includes thermal and dispersion properties of binders for these next-generation batteries and provides additional insights into the operational mechanisms and failure mechanisms of binders to improve understanding. Additionally, the report presents a chronological compilation of research on binder design, synthesis, and application in lithium-ion battery electrodes, covering all relevant literature published to date. For those seeking deeper technical details, references to the original papers have been included, allowing for further exploration of the subject.
Based on our lithium-ion battery market outlook, we have projected the demand and market trends for binders. In the appendix, we have included market size estimates and forecasts from external research institutions to help readers gain a comprehensive understanding of the overall market scale. For key binders such as PVDF, SBR, and CMC, the report includes detailed market data from 2021, 2022, and 2023, along with forecasts for 2024, providing a clear view of demand trends over time.
Finally, by compiling the most recent status and key products of binder manufacturers in 2024, this report aims to provide comprehensive insights for researchers and industry professionals. It is expected to contribute significantly to improving battery performance, including energy density, fast-charging capability, and long-term cycle life.
Strong Points of This Report :
- 1. Comprehensive overview and detailed technical content on binders
- 2. Key design and synthesis considerations derived from binder development case studies
- 3. Analysis of binder development trends and case studies for next-generation batteries, including Li-S batteries, solid-state batteries, and sodium-ion batteries (SIBs), in addition to LIBs
- 4. Binder market outlook based on SNE Research's battery forecasts, along with data on the binder market for LFP batteries
- 5. Detailed information on the latest developments and product status of major binder manufacturers
[PVDF Binder Manufacturers' Shipment Volume and Market Share (M/S)]

[SBR Binder Manufacturers' Shipment Volume and Market Share (M/S)]

Global LIB Binder(Cathode + Anode) Demand Forecast (kTon)


[Tesla 4680 Battery Binder Cost Analysis]
- Cathode: NCM811, Anode: Si-based
- PVDF cathode binder requirement and cost for 1 GWh battery: around 38 tons
- PAA anode binder requirement and cost for 1 GWh battery: around 24 tons

Table of Contents
1. Binder Overview
- 1.1. Introduction
- 1.2. Definition, Role, and Requirements
- 1.2.1. Role and Features
- 1.2.1.1. Mechanical Properties
- 1.2.1.1.1. Improvement of Adhesion and Mechanical Strength
- 1.2.1.1.2. Control of Volume Change
- 1.2.1.2. Mitigation of Interface Performance Degradation
- 1.2.1.3. Electrical Properties
- 1.2.1.3.1. Improvement of Electrical Conductivity
- 1.2.1.3.2. Improvement of Ion Conductivity
- 1.2.1.4. Thermal Properties
- 1.2.1.4.1. Improvement of Thermal Stability and Wide Temperature Operation Range
- 1.2.1.5. Dispersion Properties
- 1.2.1.5.1. Improvement of Electrode Homogeneity
- 1.2.1.1. Mechanical Properties
- 1.2.2. Requirements
- 1.2.1. Role and Features
- 1.3. Categories and Types
- 1.3.1. Types
- 1.4. Operation Mechanism
- 1.5. Binder Failure Mechanisms
- 1.6. Advanced Strategies for Binder Development
- 1.6.1. Improvement of Mechanical Bonding Strength
- 1.6.2. Improvement of Chemical Bonding Strength
- 1.6.3. Design of Multifunctional Integrated Binders
- 1.7. Binder Characterization Techniques
- 1.7.1. Evaluation of Binder Distribution and Composition in Cathode
2. Types of Binders and R&D Practices
- 2.1. Binder for Cathodes
- 2.1.1. Non-Aqueous Binders
- 2.1.2. Industry Status of PVDF Cathode Binders
- 2.1.3. Industry Status of (CMC+SBR) Anode Binders
- 2.1.4. Water-based Binders
- 2.1.5. Other Binders
- 2.1.5.1. Conductive Polymer
- 2.1.5.1.1. Polyacrylonitrile(PAN)
- 2.1.5.1. Conductive Polymer
- 2.2. Binders for Anodes
- 2.2.1. Insertable Anode Binder
- 2.2.1.1. Binders for Graphite Electrodes
- 2.2.1.2. Anode Binder for LTO
- 2.2.2. Alloy Anode Binders
- 2.2.2.1. Linear Polymer Binders
- 2.2.2.2. Crosslinked Polymer Binders
- 2.2.2.3. Branched and Extra-Large Polymer Binders
- 2.2.2.4. Conductive Polymer Binders
- 2.2.1. Insertable Anode Binder
- 2.3. Binder for Next-Generation Batteries (1)
- 2.3.1. Binders for Lithium-Sulfur (Li-S) Batteries
- 2.3.2 (4680)Binders for Dry Process
- 2.3.3. Binders for Sodium-Ion Batteries (SIB)
- 2.3.3.1. Development of Binders for SIB
- 2.3.3.2. Conventional Binders
- 2.3.3.2.1. PVDF
- 2.3.3.2.2. PAA
- 2.3.3.2.3. SA(Sodium Alginate)
- 2.3.3.2.4. CMC
- 2.3.3.3. New Binders
- 2.3.3.3.1. Conductive Binders
- 2.3.3.3.2. Cross-linking Binders
- 2.3.3.3.3. Self-healing Binders
- 2.3.3. Binders for Sodium-Ion Batteries (SIB)
- 2.4. Binder for Next-Generation Batteries (2)
- 2.4.1. Binders for Solid Electrolytes
- 2.4.1.1. Overview of All-Solid-State Batteries
- 2.4.1.2. Sulfide-based All-Solid-State Battery Technology
- 2.4.1.3. Manufacturing of All-Solid-State Cells and the Purpose of Binders
- 2.4.1.4. Binder Technology for Cathodes
- 2.4.1.4.1. Binder Technology for Wet Processes
- 2.4.1.4.2. Binder Technology for Dry Processes
- 2.4.1.5. Binder Technology for Electrolyte Layers
- 2.4.1.6. Binder Technology for Anodes
- 2.4.1.6.1. Binder Technology for Graphite-Based Anodes
- 2.4.1.6.2. Next Generation Binder Technology for Anodes
- 2.4.1. Binders for Solid Electrolytes
3. Binder Market
- 3.1. Overall Outlook for the Binders Market(Outlook by Other Researchers)
- 3.2. PVDF Market Outlook for Global LIBs
- 3.2.1. Global Battery Market Demand Outlook
- 3.2.1.1. Global LIB Demand Outlook by Form Factor (GWh, %)
- 3.2.1.2. Global LIB Cathode Material Demand Outlook (GWh, k ton)
- 3.2.1.3. Global LIB Anode Material Demand Outlook (k ton)
- 3.2.2. Global LIB Binder Demand Outlook
- 3.2.3. LIB Binder Price Outlook
- 3.2.4. LIB Binder Market Size Outlook
- 3.2.5. Global Cathode Binder Demand Outlook by Major Battery Companies
- 3.2.6. Global Anode Binder Demand Outlook by Major Battery Companies
- 3.2.7. Market Outlook for Binders for Silicon-based Anodes
- 3.2.8. PAA Binders for Silicon Anode Market Outlook
- 3.2.9. Global LFP Binder Demand Outlook (k ton)(CAGR 12%)
- 3.2.10. Binder cost analysis for 4680 batteries for Tesla
- 3.2.11. Shipments and M/S of LIB Binder Manufacturers
- 3.2.12. Shipments and M/S of PVDF Binder Manufacturers
- 3.2.13. Shipments and M/S of SBR Binder Manufacturers
- 3.2.14. Shipments and M/S of CMC Binder Manufacturers
- 3.2.1. Global Battery Market Demand Outlook
4. Binder Manufacturer Status
- Arkema Group
- BASF SE
- Solvay
- Kureha Corp.
- ZEON Corp.
- JSR Corp.
- Fujian Blue Ocean Co. Ltd (BLUE OCEAN & BLACK STONE)
- Dupont (CMC)
- Ashland Inc.
- MTI Corp.
- TRINSEO
- Xinxiang Jinbang Power Technology Co., Ltd.
- Chongqing Lihong Fine Chemical (CMC Binder Manufacturers)
- Chemtros
- Hansol Chemical
- Kumho Petrochemical
- Daikin Industry
- Nanografi Nano Technology
- Nippon Paper Group
- APV Engineered Coatings LLC
- Sichuan Indigo Materials Science & Technology (INDIGO)
- Guangzhou Songbai Chemical Co (Songbai)
- Nippon A&L Inc.
- Daicel Miraizu Ltd.
- Sinochem Group Co.
- Ube Corp.
- AOT Battery Equipment Technology
- Shanghai Huayi 3F New Materials
- GL Chem






