|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1720934
インドの量子通信の進展:International Quantum Communication Conclave 2025からの考察:政府・学界・産業界が結集し、QKD・PQC・フォトニックチップにおける国産技術でインドの量子の未来を切り拓くIndia's Quantum Communication Journey - Insights from the International Quantum Communication Conclave 2025: Government, Academia, and Industry Unite to Drive India's Quantum Future with Indigenous Innovations in QKD, PQC, and Photonic Chips |
||||||
|
|||||||
| インドの量子通信の進展:International Quantum Communication Conclave 2025からの考察:政府・学界・産業界が結集し、QKD・PQC・フォトニックチップにおける国産技術でインドの量子の未来を切り拓く |
|
出版日: 2025年05月07日
発行: MTN Consulting, LLC
ページ情報: 英文 10 Pages
納期: 即納可能
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
本レポートでは、International Quantum Communication Conclave 2025において発表された戦略的取り組み、技術革新、マイルストーンを概説し、それらがインドの将来に備えた量子ネットワークの構築をいかに推進しているかを示します。
ビジュアル
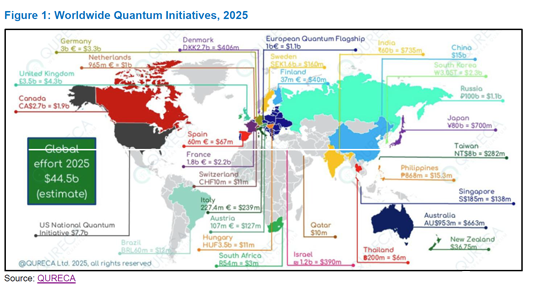
インドは、量子ベースの安全な通信に向けた世界の競争において、急速に重要なプレーヤーとして台頭しています。2025年のIQCC (International Quantum Communication Conclave) では、この分野におけるインドの成長する技術力が注目されました。量子通信 (QC) は、将来の安全なネットワークの中核を担う技術になると期待されています。従来の暗号方式とは異なり、量子通信は量子力学の法則を利用しており、従来型・量子型の両方のサイバー脅威に対して高い耐性を備えています。量子技術に対する世界の投資総額が445億ドルを超える中、インドは国産技術と国家規模の導入を武器に、リーダーシップを確立しようと戦略的に動いています。
インド政府は、量子通信をNQM (National Quantum Mission ) の中核的柱の一つと位置づけており、研究・商業化・導入を支える強固なエコシステムの構築を目指しています。インド工科大学マドラス校 (IIT Madras)、電気通信開発センター (C-DOT)、ラマン研究所 (RRI) などの機関が、基盤的なプロジェクトを主導しています。たとえば、IITマドラスは、チェンナイで都市圏量子アクセスネットワーク (MAQAN) の光ファイバーテストベッドを構築しました。また、C-DOTはニューデリーのサンチャール・バワンにおいて、量子鍵配送 (QKD) のライブ実験を実施し、重要なマイルストーンとなっています。さらに、IITデリーと国防研究開発機構 (DRDO) は、実験室環境で50kmの光ファイバーリンクを用いたエンタングルメント型QKDの実証に成功し、実地試験でも8kmのファイバー伝送に成功しました。また、ウッタル・プラデーシュ州のプラヤグラージとヴィンディヤチャル間 (100km) で都市間QKD通信試験も実施しています。これらの取り組みを基盤として、QUILA (Quantum Internet with Local Access) プログラムでは、地上・衛星のQKDにポスト量子暗号 (PQC) や量子メモリを統合し、2,000kmの量子バックボーンで主要都市を結ぶ国家量子インターネットの構築を目指しています。
インドで量子技術の商業化を担うエンジンとして台頭するCDOTは、COW (Coherent One Way) およびDPS (Differential Phase Shift) プロトコルに基づいた認証済みのQKDシステムを開発しています。CDOTはさらに、サイドチャネル攻撃を防ぐために測定器独立型QKD (MDI-QKD) の試作にも取り組んでいます。また、CDOTの多重化およびマルチコアファイバーQKDの技術革新により、高価なダークファイバー (未使用専用線) を使用せずに、120km超の安全な通信距離を実現しています。ここで 重要なのは、CDOTが単一光子検出器などの主要部品を国産化し、コストを90%削減するとともに、海外依存を大幅に低減している点です。
調査対象
言及された組織
|
|
目次
サマリー
イントロダクション
- 量子通信の重要性の理由
IQCC 2025の主なハイライト
- 国家の責務:NQM、CDOT、IIT Madrasの役割
- ファンデーションプロジェクト:MAQAN・QUILA
- CDOTによる独自のイノベーション
- 小型化と大規模化:チップスケールQKDに向けて
- 衛星ベースの量子通信:RRIとISROが先頭に立つ
- QNu Labs:研究開発から展開まで
- 耐量子暗号:統合の準備完了
- 世界な連携と学び:Toshiba・IBM・Ericsson
インドの量子エコシステムが重要な理由とは?
総論:量子通信におけるインドの決定的な飛躍
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Worldwide Quantum Initiatives, 2025
- Figure 2: Quantum Networks Deployment Projects across India
This brief outlines the strategic initiatives, innovations, and milestones showcased at the International Quantum Communication Conclave 2025 that are steering India's progress toward future-ready quantum networks.
VISUALS

India is fast emerging as a significant player in the global race toward secure, quantum-based communications. The International Quantum Communication Conclave (IQCC) 2025 spotlighted India's growing capabilities in this field, with quantum communications (QC) poised to become the backbone of future secure networks. Unlike traditional encryption, quantum communication leverages the laws of quantum mechanics, offering resilience against classical and quantum cyber threats. As global investments in quantum technologies exceed $44.5 billion, India is strategically positioning itself to lead with indigenous innovations and national-scale deployments.
The Indian government has made quantum communications a core pillar of its National Quantum Mission (NQM), aiming to create a robust ecosystem of research, commercialization, and deployment. Several institutions such as Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras, the Centre for Development of Telematics (CDOT), and the Raman Research Institute (RRI) are spearheading foundational projects. For example, IIT Madras has pioneered the Metro Area Quantum Access Network (MAQAN) metro fiber testbed in Chennai, while C-DOT's live Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) setup at Sanchar Bhawan, New Delhi marks an important milestone. Separately, IIT Delhi and the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) have jointly demonstrated entanglement-based QKD over 50 km of fiber link in lab conditions and 8 km of optical fiber in field trials, in addition to executing a 100 km inter-city QKD trial between Prayagraj and Vindhyachal in Uttar Pradesh. Building on these, the ambitious Quantum Internet with Local Access (QUILA) program aims to link major Indian cities through a 2,000 km quantum backbone, integrating terrestrial and satellite QKD with Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) and quantum memory, laying the foundation for a national quantum internet.
CDOT, emerging as the country's quantum commercialization engine, has developed certified QKD systems based on Coherent One Way (COW) and Differential Phase Shift (DPS) protocols. CDOT also is prototyping Measurement Device Independent (MDI) QKD for mitigating side-channel attacks. Its innovations in multiplexed and multi-core fiber QKD remove the need for costly dark fiber while extending secure communication ranges to 120+ km. Critically, CDOT has indigenized key components like single-photon detectors, cutting costs by 90% and reducing foreign dependency.
Another major leap forward is the shift toward chip-scale QKD. Miniaturizing bulky quantum components into photonic integrated circuits will allow for scalable, cost-effective deployment across telecom and cloud networks. India is investing heavily in this direction via the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY) and the Department of Science and Technology (DST), funding photonic chip R&D at institutions like Indian Institute of Science (IISc) and IITs. These chips will also form the building blocks for future 6G and AI infrastructure.
Satellite quantum communication is the next frontier. RRI, in collaboration with the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), is developing ground-to-satellite QKD systems with adaptive optics and precision tracking, offering a viable solution for long-distance, terrain-agnostic secure links. Their research in device-independent randomness and free-space optics enhances India's readiness for global-scale quantum communication networks.
Finally, industry players like QNu Labs are transitioning research into deployable systems by commercializing hybrid models that integrate QKD, PQC, and quantum random number generators. These efforts, aligned with NQM, mark India's emergence as a serious contender in the global quantum race - strategically, scientifically, and commercially.
Research Coverage
Organizations mentioned:
|
|
Table of Contents
Summary
Introduction
- Why does quantum communications matter?
IQCC 2025 key highlights
- National imperatives: the role of NQM, CDOT, and IIT Madras
- Foundational projects: MAQAN and QUILA
- Indigenous innovation by CDOT
- Miniaturization and scale: Toward chip-scale QKD
- Satellite-Based Quantum Communication: RRI and ISRO lead the charge
- QNu Labs: from R&D to deployment
- Post-Quantum Cryptography: Ready for Integration
- Global alignment and learnings: Toshiba, IBM, and Ericsson






