|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1688514
より環境に優しいネットワークへ - 通信事業者はトラフィック効率を強化:2023年の通信事業者のエネルギー消費量は2022年比で1ペタバイトあたり15.4%減少、排出量と再生可能エネルギーの導入は依然低水準にとどまるGreener Networks - Telcos Power Up Traffic Efficiency: Telcos Consumed 15.4% Less Energy in 2023 per Petabyte of Traffic Carried than 2022, Emissions and Renewables Adoption Remain Dismal |
||||||
|
|||||||
| より環境に優しいネットワークへ - 通信事業者はトラフィック効率を強化:2023年の通信事業者のエネルギー消費量は2022年比で1ペタバイトあたり15.4%減少、排出量と再生可能エネルギーの導入は依然低水準にとどまる |
|
出版日: 2025年03月25日
発行: MTN Consulting, LLC
ページ情報: 英文 8 Pages
納期: 即納可能
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
2023年後半、MTNコンサルティングは、通信事業者ネットワークにおけるトラフィックの増加とエネルギー消費の関係についてのはじめのレビューを発表しました。同レビューには16の通信事業者のデータが含まれ、2020-22年のデータに焦点を当てていました。今回の更新版では、対象通信事業者を30社に拡大し、2年間(2019年・2023年)のデータを追加しました。当社の分析は、現在2019-23年の時間枠を扱っています。
ビジュアル
本分析に含まれる30社の通信事業者グループは、収益ベースで世界市場の約55%を占めています。2023年、通信事業者は収益100万米ドルあたり平均2.06ペタバイトのトラフィックを伝送し、2019年の100万米ドルあたり1.00ペタバイトの2倍以上となりました。このようなことが可能なのは、通信事業者がより安価にトラフィックを伝送することを目的とした絶え間ない改善を行っているからです。エネルギーはコストの大きな部分を占めています。では、ネットワークは、単位消費エネルギーあたりのトラフィック輸送において、より効率的になっているのでしょうか?
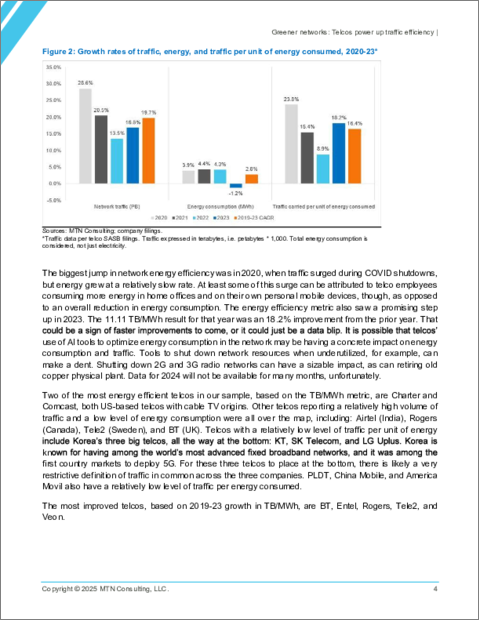
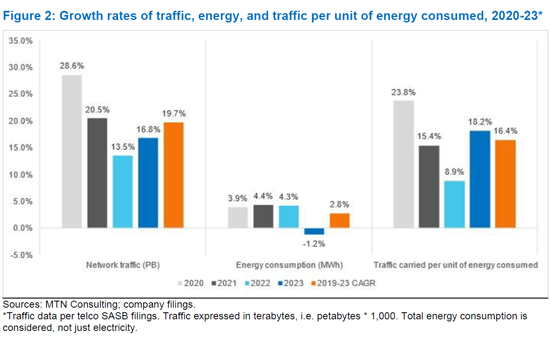
2019年から2023年の期間において、通信事業者30社はネットワークトラフィックをCAGR 19.7%で増加させ、総エネルギー消費量はCAGR 2.8%で増加しました。その結果、2023年の通信事業者のエネルギー消費量は平均90.0MWh/PBとなり、2019年の165.5MWh/PBから減少しました。これは、ペタバイトあたりのMWhの年平均改善率がCAGR 14.1%であることを意味します。つまり、通信事業者が前年と同じトラフィック負荷を伝送するために必要なエネルギーは、平均して年間14.1%少なくなっています。この改善は、ネットワークのエネルギー効率を長期的に改善するという、通信事業者とそのベンダーの目標に沿ったものです。2019年以降、MWh/PBの指標が最も改善したのは、BT、Entel、Rogers、Tele2、Veonです。
対象範囲
掲載組織
|
|
目次
- サマリー
- 通信ネットワークのエネルギー効率:年間14%向上
- データセット:概要
- 収益とトラフィックの難問:依然として続く
- 消費エネルギー単位あたりのトラフィック
- ベンダーは改善を継続する上で中心的な役割を担っている
- 総論
- 付録
List of Tables and Figures
- Table 1: Summary metrics for the "Group of 30" telcos
- Figure 1: Petabytes of traffic on network per US$M in revenue, 2019-23*
- Figure 2: Growth rates of traffic, energy, and traffic per unit of energy consumed, 2020-23*
- Figure 3: Terabytes of traffic per MWh of energy consumed*
In late 2023, MTN Consulting published an initial review of the relationship between traffic growth and energy consumption in telco networks. That review included data for 16 telcos, and focused on 2020-22 data. This updated analysis extends coverage to 30 telcos, and adds two years (2019 and 2023) of data. Our analysis now addresses the 2019-23 timeframe.
VISUALS

The group of 30 telcos included in this analysis represent about 55% of the global market, based on revenues. Our data verify the well-known revenue-traffic conundrum, where traffic rises faster than revenues: in 2023, the average telco carried 2.06 Petabytes of traffic per US$1M in revenue, over double the 1.00 Petabytes per $M carried in 2019. This is possible because telcos make constant improvements aimed at carrying traffic more cheaply. Energy is a big part of the cost story. So, are networks getting more efficient in their carriage of traffic per unit of energy consumed? In the 2019-23 timeframe, our group of 30 telcos increased network traffic at an average annual rate (CAGR) of 19.7%, while their total energy consumption grew at a CAGR of 2.8%. As a result, in 2023 the average telco consumed 90.0 MWh of energy per Petabyte of traffic, down from 165.5 MWh/PB in 2019. That works out to an annual average (CAGR) improvement in MWh per Petabyte of 14.1%. Meaning, on average, telcos need 14.1% less energy per year to carry the same traffic load as the prior year. This improvement is in line with the stated goal of both telcos and their vendors: to improve the network's energy efficiency over time. The biggest improvements in the MWh/Petabyte metric since 2019 are BT, Entel, Rogers, Tele2, and Veon. The worst result came from Saudi Telecom (STC), which used 104 MWh/PB in 2023, from 90 in 2019. The poorest result in 2023 alone was reported by Vodafone, which improved (lowered) its MWh/PB ratio by just 3.8% YoY.
For climate change watchers, an important metric is greenhouse gas emissions (GHG), as measured in CO2 equivalent metric tons. We don't address emissions in this report, but we did in a December 2024 report. That report found that telco emissions in 2023 were about the same level (per unit of revenue) as in 2019, and that renewables accounted for only about 20% of energy used in 2023. Both findings were disappointing. So, this current report's conclusion is a welcome bit of good news.
Telco sustainability reports emphasize the importance of adopting energy efficient technologies and network designs. Vendors consider the energy efficiency of their solutions a crucial differentiator. As telcos attempt to lower energy costs and reduce their carbon footprints, vendors have an opportunity to support further improvements.
Coverage
Organizations mentioned:
|
|
Table of Contents
- Summary
- Telco network energy efficiency rising 14% per year
- Overview of the dataset
- The revenue-traffic conundrum persists
- Traffic carried per unit of energy consumed
- Vendors have a central role in sustaining improvements
- Conclusion
- Appendix