
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1641922
コネクテッド農業-市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Connected Agriculture - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| コネクテッド農業-市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年01月05日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 120 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
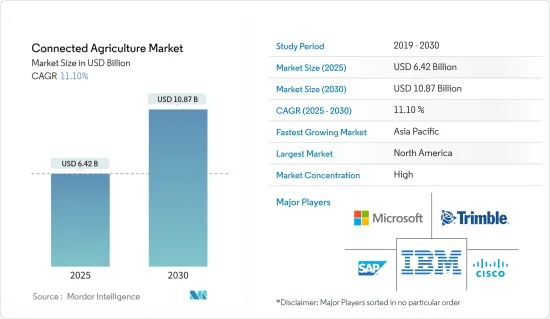
コネクテッド農業市場規模は2025年に64億2,000万米ドルと推定され、予測期間中(2025~2030年)のCAGRは11.1%で、2030年には108億7,000万米ドルに達すると予測されます。
水、肥料、種子などの資源を最小限に抑えながら作物の収量を最適化する先進的農業技術が求められていることが、コネクテッド農業市場の成長を促す主要要因となっています。農業従事者や企業は、さまざまな連結農業技術を実践することで、少ない資源を使用しながら農作業時間をより効率的に管理できるようになります。
主要ハイライト
- 農業における水管理は、コストを削減し環境の安定に貢献しながら農業の収量を増やすために不可欠です。農業関係者は水不足を懸念し、農業用水管理の強化に取り組んでいます。モノのインターネット(IoT)、モバイル用途、ビッグデータ分析、意思決定支援システムを組み込んだ連動型農業の水管理ソリューションは、人口増加のために環境に優しく最適な農業生産物の生産を支援しています。
- コネクテッド農業は、農業従事者が従来の農法に伴う経費や労力を削減しながら、作物栽培を最大限に行うことを可能にします。コネクテッド農業は、農業従事者が最適な播種密度をより正確に評価し、肥料を推定し、作物の収量を予測するために、適切な組み合わせで時間と資源を専門的に投入できるようにすることで、生産量を向上させています。農業従事者は現在、携帯電話やその他の連携機器の使用など、最新の農業の進歩に依存しています。低消費電力広域通信(LPWA)、Zigbee、WiFi、新しい無線センサ技術などの洗練された接続技術は、農業従事者が物資の購入、在庫管理、タイムリーな作付けや収穫など、さまざまな農業作業の計画と実行を支援します。
- データ収集は精密農業の最初の段階であり、したがって最も研究が進んでいます。これは主に土壌肥沃度(圃場、多角形、ゾーンから1サンプル)の決定によって達成されます。ゾーンは航空写真や衛星写真を使って作成され、収量マップや同じ作物を何年にもわたって撮影した写真に基づいています。最終的に収量を高めるために行われます。1ヘクタールの多角形グリッドは、最もよく使われる土壌検査法です。このグリッド寸法は、圃場のばらつきとその中で何が起こっているかを理解するのに十分です。最後に、土壌スキャンに基づいて、正確な施肥と石灰散布のためのタスクマップが作成されます。
- コネクテッドファームの技術については理解が不足しており、設置には法外な費用がかかります。これらは、予想される時間枠における技術の制約です。世界中の農業従事者の大半は小規模農業従事者であり、このような高価な機器を購入する余裕はないです。この技術には、有能で知識の豊富な農業従事者、多額の初期投資、効果的な農具が必要であり、農業従事者はこの技術による情報収集に消極的です。コストが高いため、大規模で工業化された農場にしか適していないです。
- COVID-19の大流行により、人工知能(AI)の活用が注目されるようになりました。人工知能や機械学習モデルによってデータがリアルタイムで利用され、いつ種を蒔くべきか、どの作物を選ぶべきか、収量を上げるにはどのハイブリッド種を選ぶべきか、いった洞察に満ちた知識を得ることができます。精密農業はしばしば人工知能システムとして知られ、収穫の全体的な品質と精度の向上に役立っています。AI技術は、農場における害虫、植物病、栄養不足の検出を助ける。人工知能(AI)センサは、どの除草剤を使用するかを決定する前に雑草を識別し、標的を定めることができます。
コネクテッド農業市場動向
用途別では、スマート灌漑が大幅な成長を遂げると分析されます。
- スマート灌漑用途は、予測期間中に大きな成長を確認すると分析されています。スマート灌漑におけるコネクテッド農業の応用は、水管理の課題に対するソリューションの不可欠な部分であるスマート水管理の利用の拡大によってさらに増幅されます。水管理におけるスマートシステムの潜在的用途は広大で、水質、水量、効率的な灌漑のためのソリューションが含まれます。
- さらに、国連報告によれば、水不足は2025年までに人類の20%近くに直接影響を及ぼし、地球上の他の住民にも間接的に影響を及ぼす可能性があります。IoT、ビッグデータ、AI技術の組み合わせによるスマート水システムは、こうした予測を阻止し、水資源の不用意な使用がすでに引き起こした損害を元に戻すのに役立つ可能性があります。
- さらに、スマート灌漑は、世界の食糧安全保障の支援や水資源の保護など、社会の重大な課題に対する解決策を記載しています。灌漑の先端技術に関する意識の高まりや、大規模農業従事者における農場へのリアルタイムデータアクセスは、スマート灌漑の展望におけるコネクテッド農業ソリューションとサービスの応用の一部です。このような開発は、このセグメントの成長をさらに促進します。
- IEAによると、2040年までに取水が必要となる水の総量は4兆3,500億立方メートルになると予測されています。ここ数十年の水消費量の増加は、人口増加の2倍を上回っています。このような莫大な水の消費と取水は、スマート灌漑におけるコネクテッド農業ソリューションとサービス用途の機会を生み出すと考えられます。
アジア太平洋が最も高い成長を遂げる
- アジア太平洋は、市場ベンダーの数の多さ、新時代の農業技術新興企業の出現、農業における先端技術の利用拡大により、予測期間中にコネクテッド農業市場が大きく成長すると分析されています。さらに、同地域ではスマート農業を支援するさまざまな政府の取り組みがあり、今後数年間で市場ベンダーに成長機会をもたらすと分析されています。
- 日本の農業生産費は他国に比べて高く、これは肥料や農機具などの農業投入物のコストが高いためです。農林水産省によると、日本の主要農産物である米の栽培には、昨年生産された米60kgあたり平均9,180円の総投入コストがかかっています。そのうち13%が肥料費で、残りの32%が農業機械とその導入費です。その結果、肥料の浪費を減らしたり機械コストを下げたりするコネクテッド農業の進歩は、日本の農業従事者に多大な利益をもたらすと考えられます。
- さらに、フィリピンの農務省(DA)は、種の植え付け方法、肥料や農薬の散布方法、作物のモニタリング方法を変えるドローンの可能性を評価しています。さらに日本の農林水産省は、2022年までに日本全国の米、小麦、大豆の作付面積の約半分に農業用ドローンを導入する目標を掲げています。
- インドでは、マハラシュトラ州政府が2022年10月にドローンによる農薬散布をセンターが許可した後、まだ施策を策定していないです。センターが承認したドローン購入プログラムの補助金を承認する前に、州行政は明確化を待っています。ドローンは労働危機と闘い、農業の機械化を進める手段として推進されています。国際的な農薬会社シンジェンタは月曜日、同社の殺菌剤製剤2種が、散布規制を担当する中央農薬委員会からドローン散布のゴーサインを受けたと発表しました。
コネクテッド農業産業概要
コネクテッド農業市場は、複数の参入企業の存在により統合されています。市場の参入企業は、製品ポートフォリオを拡大し、地理的範囲を拡大し、主に市場での競合を維持するために、製品革新、合併、買収などの戦略を採用しています。
2023年1月、アストン大学は知識移転パートナーシップ(KTP)を通じて、エンジニアリング企業のSolargen Technologies(SGT)とナイロビ大学と協力し、太陽エネルギーと風力エネルギーを利用して土地に年間を通じて散水を行い、ケニアの作物生産を改善するスマート灌漑システムを開発しました。SGTは、エネルギー、水、灌漑のソリューションとサービスを提供するケニア最大のプロバイダーです。非政府組織、政府、人々と協力し、東部アフリカの農村部や紛争の影響を受けた地域のコミュニティに、カスタマイズ型エネルギー、水、食糧安全保障ソリューションを提供しています。
2022年11月、Trimble AgricultureとxFarm Technologiesは本日、新たな協業を発表しました。精密農業技術の世界的参入企業であるトリンブルは、技術企業xFarm Technologiesが開発したxFarmアプリとの統合により、より価値ある効率的なソリューションを農業従事者に提供できるようになりました。xFarm Technologiesは、そのデジタルプラットフォームを使用して、100カ国以上の170万ヘクタールに広がる12万の農場の作業をサポートし、簡素化しています。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場洞察
- 市場概要
- 産業の魅力-ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 買い手/消費者の交渉力
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 産業バリューチェーン分析
- 競争企業間の敵対関係の強さ
- COVID-19の市場への影響評価
第5章 市場力学
- 市場促進要因
- コネクテッド農業におけるBYOD(Bring Your Own Drone)の出現
- スマート水管理システムの需要急増
- 市場抑制要因
- コネクテッド農業に関する深い学習曲線
第6章 市場セグメンテーション
- コンポーネント別
- ソリューション
- ネットワーク管理
- 農業資産管理
- 監督管理
- サービス
- ソリューション
- 用途別
- スマート物流
- スマート灌漑
- 農業計画と管理
- 地域別
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- 欧州
- ドイツ
- 英国
- フランス
- その他の欧州
- アジア太平洋
- 中国
- 日本
- インド
- その他のアジア太平洋
- ラテンアメリカ
- 中東・アフリカ
- 北米
第7章 競合情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- IBM Corporation
- SAP SE
- Trimble Navigation Ltd
- Microsoft Corporation
- Vodafone Group PLC
- Accenture PLC
- SWIIM System
- Orange Business Services
- Link Labs LLC
第8章 投資分析
第9章 市場機会と今後の動向
The Connected Agriculture Market size is estimated at USD 6.42 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 10.87 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 11.1% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

The demand for advanced agricultural techniques to optimize crop yields while using the least amount of resources, such as water, fertilizer, and seeds, is the key factor driving the growth of the connected agriculture market. Farmers and businesses will be able to manage their time more effectively on the farm while using fewer resources by putting various linked agricultural technologies into practice.
Key Highlights
- Water management in agriculture is critical for increasing agricultural yields while decreasing costs and contributing to environmental stability. Agriculture officials are concerned about water scarcity and are working to enhance agricultural water management. Water management solutions in linked agriculture, which incorporate the Internet of Things (IoT), mobile applications, Big Data analytics, and decision support systems, are assisting in the production of environmentally friendly and optimum agricultural outputs for a growing population.
- Connected agriculture enables farmers to maximize crop cultivation while reducing expenses and effort associated with traditional agricultural methods. Connected agriculture boosts production by allowing farmers to expertly invest time and resources in the right combination to more precisely evaluate optimum sowing density, estimate fertilizers, and predict crop yields. Farmers currently rely on the most recent agricultural advancements, such as the usage of cell phones and other linked equipment. Sophisticated connected technologies such as low power wide area (LPWA), Zigbee, WiFi, and new wireless sensor technologies aid farmers in the planning and execution of various agricultural operations such as purchasing supplies, inventory control, timely planting and harvesting, and so on.
- Data collection is the first stage of precision agriculture and, thus, the most researched. This is accomplished mostly through the determination of soil fertility (one sample from the field, a polygon, or a zone). Zones are created using aerial or satellite imagery and are based on yield maps or photographs of the same crop over numerous years. It is done to boost yields eventually. A one-hectare polygon grid is the most often used soil testing method. This grid dimension is adequate for understanding the field's variability and what is going on in it. Finally, based on the soil scan, task maps are created for precise fertilizer and liming applications.
- There is a lack of understanding of connected farm technology, and installation is prohibitively expensive. These are the technology's constraints over the anticipated timeframe. The majority of farmers worldwide are small-scale farmers who cannot afford such costly equipment. This technique necessitates competent and knowledgeable farmers, large initial investments, and effective farming instruments, making farmers unwilling to gather information from it. Because of its high cost, it is only suitable for large and industrialized farms.
- The COVID-19 pandemic brought attention to using artificial intelligence (AI). Data is used in real-time by artificial intelligence and machine learning models to get insightful knowledge, such as when to plant seeds, which crops to choose, which hybrid seeds to select for higher yields, and other things. Precision agriculture, often known as artificial intelligence systems, is assisting in enhancing the overall quality and accuracy of harvests. AI technology aids in the detection of pests, plant diseases, and undernutrition in farms. Artificial intelligence (AI) sensors can identify and target weeds before deciding which herbicide to use.
Connected Agriculture Market Trends
By Application, Smart Irrigation is Analyzed to Witness Substantial Growth
- The smart irrigation application is analyzed to witness significant growth over the forecast period. The application of connected agriculture in smart irrigation is further amplified by the growing use of Smart water management, which is an integral part of the solution for water management challenges. The potential application of smart systems in water management is vast and includes solutions for water quality, water quantity, and efficient irrigation.
- Moeover, water scarcity may directly affect nearly 20% of the human population by 2025, UN reports state, and indirectly influence the rest of the planet's inhabitants. Smart water systems based on the combination of the IoT, big data, and AI technologies may help stop these predictions and undo the damage the imprudent usage of water resources has already caused.
- Further, Smart irrigation provides solutions to society's critical challenges, such as supporting global food security and protecting water resources. Rising awareness regarding advanced technologies in irrigation and real-time data access to farms among large-scale farmers are some of the applications of connected agriculture solutions and services in the smart irrigation landscape. Such developments further foster the growth of the segment.
- According to IEA, by 2040, it is predicted that the total amount of water that will need to be withdrawn will be 4,350 billion cubic meters. The increase in water consumption in recent decades has outpaced population growth by a factor of two. Such huge water consumption and withdrawal would create an opportunity for connected agriculture solutions and services application in smart irrigation.
Asia Pacific to Witness the Highest Growth
- The Asia Pacific region is analyzed to witness significant growth in the connected agriculture market over the forecast period, owing to presence of significant number of market vendors, emergence of new age agri-tech startups coupled with growing use of advanced technologies in farming. In addition, various government initiatives to support smart agriculture in the region is analyzed to create growth opportunities for market vendors in the coming years.
- Japan's agricultural production expenses are high in comparison to other countries, owing to the high cost of agricultural inputs such as fertilizers and agricultural gear. According to the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries, rice cultivation, Japan's principal agricultural commodity, costs, on average, JPY 9,180 in total input costs for every 60kg of rice produced last year. Fertilizer expenditures account for 13% of this total, with agricultural machinery and implementation accounting for the remaining 32%. As a result, advancements in connected agriculture that reduce fertilizer waste or lower machinery costs will tremendously benefit Japanese farmers.
- Further, the Department of Agriculture (DA) in the Philippines is evaluating the potential of drones to change the way seeds are planted, the way fertilizers and pesticides are applied, and the way crops are monitored. Moreover, the Ministry of Japan set a goal to introduce agricultural drones for about half of the land planted with rice, wheat, and soy across Japan by 2022.
- In India, the Maharashtra government has yet to develop a policy following the Center's clearance of the use of drones to spray pesticides in October 2022. Before approving subsidies under the Center-approved drone purchase program, the state administration is awaiting clarifications. Drones are being promoted as a way to combat the labor crisis and advance agricultural mechanization. International agrochemical company Syngenta said on Monday that two of its fungicide formulations had been given the go-ahead for drone spraying by the central pesticide board, the organization in charge of spraying regulations.
Connected Agriculture Industry Overview
The connected agriculture market is consolidated owing to the presence of multiple players. The players in the market are adopting strategies like product innovation, mergers, and acquisitions in order to expand their product portfolio and expand their geographic reach and primarily to stay competitive in the market.
In January 2023, through a Knowledge Transfer Partnership (KTP), Aston University collaborated with engineering firm Solargen Technologies (SGT) and the University of Nairobi to develop a smart irrigation system that uses solar and wind energy to provide year-round watering of land and improve crop production in Kenya. SGT is Kenya's largest provider of energy, water, and irrigation solutions and services. They collaborate with non-governmental organizations, governments, and people to provide customized energy, water, and food security solutions to communities in rural and conflict-affected areas of Eastern Africa.
In November 2022, Trimble Agriculture and xFarm Technologies today announced a new collaboration. Trimble, the global player in precision farming technology, can now provide farmers with more valuable and efficient solutions through integration with the xFarm app developed by tech company xFarm Technologies, which uses its digital platform to support and simplify the work of 120,000 farms spread across 1.7 million hectares in over 100 countries.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.2.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.2.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.2.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.3 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.3.1 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.4 Assessment of the Impact of COVID-19 on the Market
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Emergence of BYOD (Bring Your Own Drone) in Connected Agriculture
- 5.1.2 Upsurge in Demand for Smart Water Management Systems
- 5.2 Market Restraints
- 5.2.1 Steep Learning Curve Regarding Connected Agriculture
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Component
- 6.1.1 Solution
- 6.1.1.1 Network Management
- 6.1.1.2 Agriculture Asset Management
- 6.1.1.3 Supervisory Control
- 6.1.2 Service
- 6.1.1 Solution
- 6.2 By Application
- 6.2.1 Smart Logistics
- 6.2.2 Smart Irrigation
- 6.2.3 Farming Planning and Management
- 6.3 Geography
- 6.3.1 North America
- 6.3.1.1 United States
- 6.3.1.2 Canada
- 6.3.2 Europe
- 6.3.2.1 Germany
- 6.3.2.2 United Kingdom
- 6.3.2.3 France
- 6.3.2.4 Rest of Europe
- 6.3.3 Asia-Pacific
- 6.3.3.1 China
- 6.3.3.2 Japan
- 6.3.3.3 India
- 6.3.3.4 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 6.3.4 Latin America
- 6.3.5 Middle-East and Africa
- 6.3.1 North America
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 Cisco Systems Inc.
- 7.1.2 IBM Corporation
- 7.1.3 SAP SE
- 7.1.4 Trimble Navigation Ltd
- 7.1.5 Microsoft Corporation
- 7.1.6 Vodafone Group PLC
- 7.1.7 Accenture PLC
- 7.1.8 SWIIM System
- 7.1.9 Orange Business Services
- 7.1.10 Link Labs LLC


