
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1693486
インドのイネ種子:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)India Rice Seed - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| インドのイネ種子:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 182 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
概要
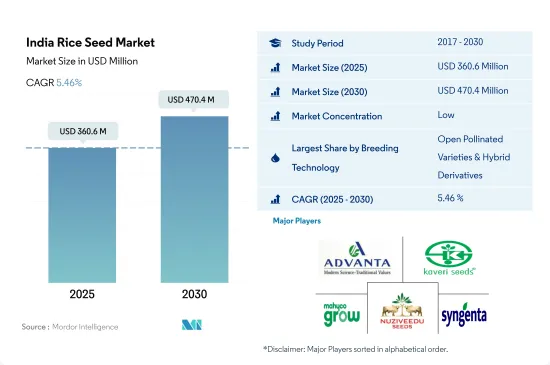
インドのイネ種子市場規模は2025年に3億6,060万米ドルと推定され、2030年には4億7,040万米ドルに達すると予測され、予測期間中(2025-2030年)のCAGRは5.46%で成長する見込みです。
高い開発コストとハイブリッドの入手不可能性が、開放受粉種子品種の需要を促進しています。
- インドでは、農家は稲作に関して、ハイブリッドよりも開放受粉品種やハイブリッド派生品種を主に好みます。このような嗜好は、稲作は大部分が自家受粉であり、ハイブリッド開発に伴う高コストが普及を制限しているという事実に起因しています。
- 2022年、同国のコメ栽培面積は4,600万haで、高収量と製品品質のために市販種子の使用が増加しているため、2017年から7%増加しました。
- 2022年にはハイブリッドが16.5%を占めるのに対し、OPVは83.5%を占める。ハイブリッド種子がOPV種子に比べてシェアが低いのは、ハイブリッド種子の開発にはより高いコストがかかること、インド市場ではハイブリッド種子が入手できないことから、生産者がより大量の露地受粉種子品種を播種することを好むためです。
- さらに、民間部門は、コメを含む大量生産・低収益作物の種子生産のための研究開発を行っていないです。インドでは、イネ種子を含む穀物分野では、公的部門である種子公社が引き続き支配的であると予想されます。現在、国内では15の州立種子公社と2つの国立種子公社が活動しています。
- しかし、ハイブリッド種子分野は、一人当たりの耕地利用可能面積が減少していることから生産性が高く、さまざまな病気や雑草に対する耐性があるため、予測期間中にCAGR 5.7%を記録すると予測されます。これらの要因は、米生産者が作物の損失を減らすことによって高い利益を得るのに役立っています。
- 同国では市販のハイブリッド種子が入手できず、OPVを大量に播種することが好まれるため、予測期間中、同国の開放受粉種子品種分野が牽引すると予想されます。
インドのイネ種子市場動向
稲作を促進する国や州レベルのさまざまな制度と需要の増加がインドの稲作を促進
- インドは世界最大の米の生産国および消費国のひとつであり、2022年現在、全体の米栽培面積は約4,630万ヘクタールです。インドの米栽培面積は、同年のアジア太平洋地域の米栽培面積の約32.7%を占めています。インドでは、広く様々な標高と気候条件の下で米が栽培されています。インドの稲作は北緯8度から350度、海抜3000メートルまで広がっています。インドの稲作は、北緯8度から350度、海抜3000メートルの高地まで広がっています。
- インドでは、ウッタル・プラデシュ州、オディシャ州、チャティスガル州、ビハール州、パンジャブ州が稲作面積の上位を占めています。これらの州を合わせると、2022年のインドの稲作面積の約41.6%を占めています。さらに、国家食糧安全保障ミッション(NFSM)のような国や州レベルのさまざまな制度が、全国的に米栽培を積極的に推進しています。これらの制度は、予測期間中、同国の米栽培を促進すると予想されます。
- 国内の米の総栽培面積は、2017年から2022年の間に約5.2%増加しました。これはさらに約10.0%増加し、予測期間終了時には5,160万ヘクタールに達すると予測されます。この増加は主に、国内需要の増大とインド産米の輸出ポテンシャルによるものです。例えば、インドは2022年に2,200万トンの米を輸出し、その価値は約96億米ドルでした。
- 国内市場と国際市場の両方で米の需要が伸びていることと、米栽培を促進する政府の制度が、予測期間中にインドの米栽培を促進すると予想される主な要因です。
耐病性、異なる地域や気候条件への幅広い適応性など、改良された形質を持つイネ種子への高い需要
- インドでは、米は最大の栽培面積を占める主要作物です。緑の革命以来、インドでは数多くの品種が導入されてきました。現在、この作物は生物学的ストレスや、Tryporyza incertulasやGundhi bugsのような様々な害虫の影響を受けるため、従来の雑種は高度な形質を持つ雑種に置き換えられつつあります。そのため、企業はハイブリッド種子や除草剤耐性のトランスジェニック種子を生産者に提供し、生産性の向上と高収益を目指しています。主要な生物学的制約である稲の病害は、深刻度にもよるが、収量を20~100%減少させる可能性があります。いもち病、褐斑病、細菌性病害、鞘枯病、タングロウィルス病などの主要病害は大きな被害をもたらし、偽スムット、穀粒変色、早苗病、狭褐斑病、鞘腐病などの新たな小病害も重大な問題として浮上しています。生育条件や品種感受性を含む様々な要因により、1~100%の損失が発生する可能性があります。
- イネで利用可能な主な形質は、耐病性、異なる地域や気候条件への幅広い適応性、宿水条件や水分ストレスへの耐性、干ばつ耐性であり、栽培に使用される広範なパニクルを持つ効果的で多数の蘖を生み出します。耐病性品種は、特にBLB(細菌性葉枯病)の収量を増加させるために大きな需要があります。現在のところ、圃場条件下で最大50%の収量低下を引き起こすこの病原菌に対して有効な薬剤はないです。
- 農家が持続可能な農業を目指すようになり、改良された形質を持つ稲種子の需要が増加しています。従って、改良型形質を持つ種子の市場は予測期間中、プラスの傾向を示すと予想されます。
インドのイネ種子産業概要
インドのイネ種子市場は断片化されており、上位5社で36.82%を占めています。この市場の主要企業は以下の通り。 Advanta Seeds-UPL, Kaveri Seeds, Maharashtra Hybrid Seeds Co.(Mahyco), Nuziveedu Seeds Ltd and Syngenta Group(アルファベット順)
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主な調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 栽培面積
- 最も人気のある形質
- 育種技術
- 規制の枠組み
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 育種技術
- ハイブリッド
- 非遺伝子組み換え雑種
- 開放受粉品種とハイブリッド派生品種
- ハイブリッド
- 州
- アンドラ・プラデシュ州
- アッサム州
- ビハール州
- チャティスガル州
- オディシャ州
- パンジャブ州
- タミルナドゥ州
- テランガナ州
- ウッタル・プラデシュ州
- 西ベンガル州
- その他の州
第6章 競合情勢
- 主要な戦略動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- Advanta Seeds-UPL
- Bayer AG
- Corteva Agriscience
- DCM Shriram Ltd(Bioseed)
- Kaveri Seeds
- Maharashtra Hybrid Seeds Co.(Mahyco)
- Nuziveedu Seeds Ltd
- Rasi Seeds Private Limited
- Syngenta Group
- VNR Seeds
第7章 CEOへの主な戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界のバリューチェーン分析
- 世界市場規模とDRO
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表リスト
- 主要洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
目次
Product Code: 92549
The India Rice Seed Market size is estimated at 360.6 million USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 470.4 million USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 5.46% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Higher development cost and non-availability of the hybrids are driving the demand for open-pollinated seed varieties
- In India, farmers predominantly favor open-pollinated varieties and hybrid derivatives over hybrids when it comes to rice cultivation. This preference stems from the fact that rice crops are largely self-pollinated, and the high costs associated with hybrid development have limited their widespread adoption.
- In 2022, the area under the cultivation of rice in the country was 46 million ha, an increase of 7% from 2017 due to the increasing usage of commercial seeds for high yield and product quality.
- Hybrids accounted for 16.5%, whereas OPVs accounted for 83.5% in 2022. Hybrids had a lower share than OPVs because the growers prefer to sow larger quantities of open-pollinated seed varieties as the development of hybrid seed involves higher cost and non-availability of hybrid rice seeds in the Indian market.
- Furthermore, the private sector is not performing research and development for the seed production of high-volume and low-margin crops, including rice. The public sector seed corporations are expected to remain dominant in cereals, including the rice seed segment in the country. At present, 15 state seed corporations and two national seed corporations are operating in the country.
- However, the hybrid seed segment is projected to register a CAGR of 5.7% during the forecast period due to higher productivity from the decreasing per capita availability of arable land and resistance to different diseases as well as weeds. These factors help the rice growers to earn high profits by reducing crop loss.
- The non-availability of commercial hybrid seeds in the country and preference for sowing large quantities of OPVs are expected to drive the open-pollinated seed varieties segment in the country during the forecast period.
India Rice Seed Market Trends
Various national and state-level schemes promoting rice cultivation and growing demand are driving rice cultivation in India
- India is one of the largest producers and consumers of rice globally, with an overall rice cultivation area of about 46.3 million hectares as of 2022. Indian rice cultivation area accounted for about 32.7% of the Asia-Pacific rice cultivation area in the same year. In India, rice is grown under widely varying altitudes and climate conditions. Rice cultivation in India extends from 8 to 350N latitude and from sea level as high as 3000 meters. The khraif season is a major rice-growing season in the country.
- In India, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, Chattisgarh, Bihar, and Punjab are the top states in terms of total area under rice cultivation. Collectively, these states accounted for about 41.6% of the Indian rice cultivation area in 2022. Moreover, various national and state-level schemes, such as the National Food Security Mission (NFSM), actively promote rice cultivation nationwide. These schemes are anticipated to drive rice cultivation in the country during the forecast period.
- The total rice cultivation area in the country increased by about 5.2% between 2017 and 2022. This is further anticipated to increase by about 10.0% and reach 51.6 million hectares by the end of the forecast period. This increase is mainly attributed to the growing domestic demand and the export potential of rice from India. For instance, India exported 22 million metric tons of rice in 2022, worth about USD 9.6 billion.
- The growing demand for rice in both domestic and international markets and the government schemes promoting rice cultivation are the major factors anticipated to drive rice cultivation in India during the forecast period.
High demand for rice seeds with improved traits such as disease resistance, wider adaptability to different regions and climatic conditions
- In India, rice is a major crop occupying the largest area for cultivation in the country. Since the Green Revolution, a number of varieties of rice have been introduced in the country. Currently, conventional hybrids are being replaced with hybrids with advanced traits as the crop is affected by biotic stresses and different pests such as Tryporyza incertulas and Gundhi bugs. Therefore, companies are offering hybrid seeds and herbicide-tolerant transgenic seeds to growers to increase productivity and earn high profits. A major biotic constraint to rice diseases can reduce yields by 20-100%, depending on severity. Major diseases such as blast, brown spot, bacterial blight, sheath blight, and tungro viral disease cause significant damage, and new minor diseases such as false smut, grain discoloration, early seedling blight, narrow brown spot, and sheath rot have also emerged as significant problems. Various factors, including growing conditions and varietal susceptibility, can lead to losses of 1-100%.
- Major traits available in rice are disease resistance, wider adaptability to different regions and climatic conditions, tolerance to water lodging conditions, moisture stress, and drought tolerance, producing an effective and high number of tillers with extensive panicles used in cultivation. Disease-tolerant varieties are in huge demand, especially BLB (bacterial leaf blight), to increase yields. Currently, there are no effective chemicals against this pathogen, which causes up to 50% yield losses in field conditions.
- The demand for rice seeds with improved traits is increasing as farmers are turning toward sustainable agriculture. Thus, the market for seeds with improved traits is anticipated to show a positive trend during the forecast period.
India Rice Seed Industry Overview
The India Rice Seed Market is fragmented, with the top five companies occupying 36.82%. The major players in this market are Advanta Seeds - UPL, Kaveri Seeds, Maharashtra Hybrid Seeds Co. (Mahyco), Nuziveedu Seeds Ltd and Syngenta Group (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Area Under Cultivation
- 4.2 Most Popular Traits
- 4.3 Breeding Techniques
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Breeding Technology
- 5.1.1 Hybrids
- 5.1.1.1 Non-Transgenic Hybrids
- 5.1.2 Open Pollinated Varieties & Hybrid Derivatives
- 5.1.1 Hybrids
- 5.2 State
- 5.2.1 Andhra Pradesh
- 5.2.2 Assam
- 5.2.3 Bihar
- 5.2.4 Chhattisgarh
- 5.2.5 Odisha
- 5.2.6 Punjab
- 5.2.7 Tamil Nadu
- 5.2.8 Telangana
- 5.2.9 Uttar Pradesh
- 5.2.10 West Bengal
- 5.2.11 Other States
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 Advanta Seeds - UPL
- 6.4.2 Bayer AG
- 6.4.3 Corteva Agriscience
- 6.4.4 DCM Shriram Ltd (Bioseed)
- 6.4.5 Kaveri Seeds
- 6.4.6 Maharashtra Hybrid Seeds Co. (Mahyco)
- 6.4.7 Nuziveedu Seeds Ltd
- 6.4.8 Rasi Seeds Private Limited
- 6.4.9 Syngenta Group
- 6.4.10 VNR Seeds
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SEEDS CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Global Market Size and DROs
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms


