
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1692550
インドの種子:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)India Seed - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| インドの種子:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 490 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
概要
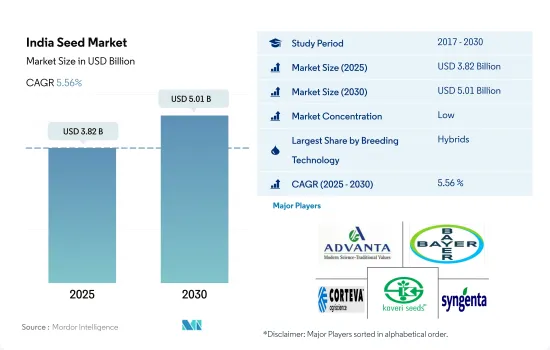
インドの種子市場規模は2025年に38億2,000万米ドルと推定され、2030年には50億1,000万米ドルに達し、予測期間中(2025-2030年)のCAGRは5.56%で成長すると予測されています。
高収量への関心の高まりでハイブリッド種子が同国の種子市場を独占
- インドでは、ハイブリッドが露地受粉品種を圧倒し、2022年には23億米ドルを占めました。農家は、損失と生産コストを削減するハイブリッド種子の害虫抵抗性を考慮し、より多くのハイブリッド種子を採用・使用しています。
- 一人当たりの耕地利用可能面積が2016年の0.12ヘクタールから2020年には0.11ヘクタールに減少することは、インドの商業用種子産業の促進要因と考えられています。
- 2022年には、トランスジェニック綿ハイブリッド、シングルクロスコーンハイブリッド、オイルリッチ油糧種子ハイブリッド、ハイブリッド野菜の採用により、同国でハイブリッド種子の使用量が増加しました。このようなハイブリッド種子需要の増加は、商業用種子市場を押し上げました。この動向は、農家が従来の種子供給源から、より良い収量が約束されるパッケージ化された種子に重点を移すことを促しています。
- 2022年のインドにおける商業種子の栽培面積では、ハイブリッド種子が80.6%を占めるのに対し、OPV種子は19.4%です。そのため、同国ではハイブリッド種の利用が拡大するにつれて、種子市場も拡大すると推定されます。
- 主な育種技術には、自然の変種に基づく植物の選択、交配、分子ツールを使用した特定の遺伝子またはマーカープロファイルの選択が含まれます。これらの技術の主な目的は、収量、品質、害虫抵抗性の面で、変種の中からより優れた植物タイプを選択することです。
- ハイブリッドや改良型OPVの採用後のシナリオは、収量の向上、高価格の確保、手頃な価格での種子の入手など、多くの利点をもたらしています。これらの要因は、予測期間におけるインド種子市場の成長を促進すると思われます。
インドの種子市場動向
インドでは連作作物の中でも米の栽培が盛んであるが、その主な理由は栽培に適した条件と安定した市場需要にあります。
- インドは地理的に多様であり、様々な気候と異なる土壌タイプを持っています。この多様性により、年間を通じて様々な連作作物を栽培することができます。その結果、2022年の連作作物栽培面積は1億7,920万に達し、2017年から2022年の間に2.7%増加しました。この成長は、改良された種子品種や機械化機器などの近代的農業技術の導入と関連しており、農家が連作作物を栽培することをより現実的なものにしています。
- 2022年のインドの連作作物作付面積のうち、米が25.8%と大きなシェアを占めています。これは、インドの多様な農業気候帯が稲作に好条件を提供しているためです。さらに、米市場の安定性とその安定した需要が相まって、多くのインドの農家にとって魅力的な選択肢となっています。その結果、コメの作付面積は2030年には5,160万haに達すると推定されます。
- インドでは小麦の作付面積が2番目に多く、2022年にはインド全体の連作作物栽培面積の17.0%を占める。これは、小麦がインドの多くの人々の主食であり、インド政府が最低支持価格(MSP)や調達プログラムなどの政策を通じて小麦栽培を支援しているためです。
- 2022年には、ウッタル・プラデシュ州とマディヤ・プラデシュ州がインドの穀物・穀類の主要耕作地を占め、そのシェアは17.2%(1,710万ha)と10.6%(1,050万ha)でした。これは、両州がインド最大の面積を有し、穀物・穀物栽培に適した肥沃な土壌を有しているためです。有利な政府政策と国内市場における連作作物への安定した需要が、同国の作付面積を牽引していると推定されます。
様々な病気に対する感受性と高品質の農作物に対する需要が、病気に対する耐性、幅広い適応性、品質特性を持つキャベツとタマネギ品種の使用を促進しています。
- キャベツは国内で広く栽培されています。高付加価値製品に対する需要は、国内市場でも国際市場でも高まっています。国内で入手可能な人気の高い形質は、頭重、葉色、幅広い季節への適応性(キャベツは寒さに特有であるため)、早熟性、葉面病に対する耐病性です。頭の大きさと頭の重さは、1ヘクタールあたりの収量生産性を高めるのに役立つため、大きな需要がある主要形質です。シンジェンタAGやバイエルAGなどの企業は、悪天候下でも高品質で栽培できるよう、これらの形質を持つ種子を提供しています。
- タマネギは、インドで栽培されている主要な野菜作物のひとつです。世界的に、インドのタマネギは辛味で有名です。耐病性、貯蔵期間の長さ(長期貯蔵や長距離輸送中の腐敗ロスの回避に役立つ)、大きさの均一性、タマネギの色(赤、黄、白)、害虫(特にアザミウマ)に対する耐性、早生品種などの主な形質が、国内でのタマネギ栽培を促進しています。Bayer AG、BASF SE、Bejo Zaden BVといった大手種苗会社は、高収量、魅力的な色、冬期適応性に重点を置いた品種を開発しています。紫斑病やべと病に対する耐病性を持つ品種は、収量が20%~60%低下するため、広く栽培されています。例えば、2021年にBejoとDe Groot en Slotは、イノベーターと名付けられた種子から初のダウニー抵抗性エシャロットを発売しました。
- 高い耐病性を持つ高品質の作物、保存期間の延長、品質属性形質を持つ製品イノベーションが、予測期間中にこれらの種子の需要を増加させる一助となっています。
インドの種子産業の概要
インドの種子市場は細分化されており、上位5社で28.95%を占めています。同市場の主要企業は以下の通り。 Advanta Seeds-UPL, Bayer AG, Corteva Agriscience, Kaveri Seeds and Syngenta Group(sorted alphabetically).
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主な調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 耕作面積
- 耕作作物
- 野菜
- 最も一般的な作物
- キャベツ・タマネギ
- 米・トウモロコシ
- トマト・チリ
- 小麦・綿花
- 育種技術
- 畑作物・野菜
- 規制の枠組み
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 育種技術
- ハイブリッド
- 非トランスジェニック・ハイブリッド
- 遺伝子組み換え雑種
- 昆虫抵抗性ハイブリッド
- 開放受粉品種とハイブリッド派生品種
- ハイブリッド
- 栽培メカニズム
- 露地栽培
- 保護栽培
- 作物タイプ
- 畑作物
- 繊維作物
- 綿花
- その他の繊維作物
- 飼料作物
- アルファルファ
- 飼料用トウモロコシ
- 飼料用ソルガム
- その他の飼料作物
- 穀物
- トウモロコシ
- 米
- ソルガム
- 小麦
- その他の穀物
- 油糧種子
- キャノーラ、菜種、マスタード
- 大豆
- ひまわり
- その他油糧種子
- 豆類
- 野菜
- アブラナ
- キャベツ
- ニンジン
- カリフラワー&ブロッコリー
- その他のアブラナ
- ウリ科
- キュウリ・ガーキン
- かぼちゃ・カボチャ
- その他ウリ科
- 根菜・球根
- ニンニク
- タマネギ
- ジャガイモ
- その他の根菜類
- ナス科
- 唐辛子
- ナス科
- トマト
- その他ナス科
- 分類されていない野菜
- アスパラガス
- レタス
- オクラ
- エンドウ豆
- ほうれん草
- その他分類されていない野菜
- 畑作物
- 州
- ビハール州
- グジャラート州
- ハリヤーナー州
- カルナータカ州
- マディヤ・プラデシュ州
- マハラシュトラ州
- ラジャスタン州
- テランガナ州
- ウッタル・プラデシュ州
- 西ベンガル州
- その他の州
第6章 競合情勢
- 主要な戦略動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- Advanta Seeds-UPL
- BASF SE
- Bayer AG
- Corteva Agriscience
- East-West Seed
- Groupe Limagrain
- Kaveri Seeds
- Nuziveedu Seeds Ltd
- Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel BV
- Syngenta Group
第7章 CEOへの主な戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界のバリューチェーン分析
- 世界市場規模とDRO
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表リスト
- 主要洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
目次
Product Code: 92367
The India Seed Market size is estimated at 3.82 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 5.01 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 5.56% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Hybrids dominate the seed market in the country with the increase in the concerns for higher yield
- In India, hybrids dominated over open-pollinated varieties, accounting for USD 2.3 billion in 2022. Farmers are adopting and using more hybrid seeds, considering the pest-resistant properties of these seeds that reduce the losses and cost of production.
- The per capita availability of arable land decreasing to 0.11 ha in 2020 from 0.12 ha in 2016 is considered a driver for India's commercial seed industry.
- In 2022, hybrid seed usage increased in the country by adopting transgenic cotton hybrids, single-cross corn hybrids, oil-rich oilseed hybrids, and hybrid vegetables. This increased demand for hybrid seeds has boosted the market for commercial seeds. This trend has encouraged farmers to shift their focus from conventional seed sources to packaged seeds that promise better yields.
- In commercial seed cultivation acreage in 2022, hybrids alone accounted for 80.6% of the area, whereas OPVs accounted for 19.4% in India. Therefore, the seed market is estimated to increase as hybrid usage grows in the country.
- The major breeding techniques include selecting plants based on natural variants, hybridizing, and choosing specific genes or marker profiles using molecular tools. The main objective of these techniques is the selection of better plant types among variants in terms of yield, quality, and pest resistance.
- The scenario post-adoption of hybrids and improved OPVs has resulted in many advantages, such as yield improvement, ensuring higher prices, and availability of seeds at an affordable price. These factors will drive the growth of the Indian seed market in the forecast period.
India Seed Market Trends
Rice is highly cultivated in India among row crops, primarily because of the favorable conditions for its cultivation and the consistent market demand
- India is geographically diverse, with various climates and different soil types. This diversity allows for cultivating various row crops throughout the year. As a result, the area under row crops reached 179.2 million in 2022, which increased by 2.7% between 2017 and 2022. This growth is associated with the introduction of modern agricultural technologies, including improved seed varieties and mechanized equipment, making it more feasible for farmers to cultivate row crops.
- Rice accounted for the major share of 25.8% of the Indian row crop acreage in 2022. This is because the country's diverse agro-climatic zones provide favorable conditions for rice cultivation. Additionally, the stability of the rice market, combined with its consistent demand, makes it an attractive option for many Indian farmers. As a result, the acreage for rice is estimated to reach 51.6 million ha in 2030.
- Wheat accounted for the second largest acreage in India, with a share of 17.0% of the overall country's row crop cultivation area in 2022. This is because wheat is a staple food for many Indian populations, and The Indian government supports wheat cultivation through policies such as minimum support prices (MSPs) and procurement programs, which in turn drive the cultivation of wheat.
- In 2022, Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh accounted for India's major cultivation land for grains and cereals, with a share of 17.2% (17.1 million ha) and 10.6% (10.5 million ha). This is because both states have the largest geographical area in India and have fertile soils, which are highly suitable for cereal and grain cultivation. The favorable government policies and stable demand for row crops in the domestic market are estimated to drive the acreage in the country.
Susceptibility to various diseases and demands for high-quality crop produce are driving the usage of cabbage and onion varieties with resistance to diseases, wider adaptability, and quality attributes
- Cabbage is widely cultivated in the country. The demand for high-value products is growing both in domestic and international markets. Popular traits available in the country are head weight, foliage color, adaptability to wide seasons (as cabbage is cold-specific), early maturity, and disease tolerance to foliar diseases. The size of heads and head weight are the major traits that have a significant demand, as they help increase yield productivity per hectare. Companies such as Syngenta AG and Bayer AG provide seeds with these traits to grow with high quality in adverse weather conditions.
- Onion is one of the major vegetable crops cultivated in the country. Globally, Indian onions are famous for pungency. Major traits such as disease tolerance, long shelf-life (helps in avoiding decay losses during long storage and long-distance transports), uniform size, the color of the onions (red, yellow, and white), tolerance to pest attacks, especially thrips, and early maturing varieties are promoting onion cultivation in the country. The major seed companies, such as Bayer AG, BASF SE, and Bejo Zaden BV, are developing varieties focusing on high yields, attractive colors, and winter adaptability traits. Varieties with disease resistance to purple blotch and downy mildew are widely cultivated, as they cause yield loss of 20%-60%. For instance, in 2021, Bejo and De Groot en Slot launched the first Downy-resistant shallot from seed named Innovator.
- High-quality crops with high disease resistance, increased shelf life, and product innovations with quality attribute traits are helping to increase the demand for these seeds during the forecast period.
India Seed Industry Overview
The India Seed Market is fragmented, with the top five companies occupying 28.95%. The major players in this market are Advanta Seeds - UPL, Bayer AG, Corteva Agriscience, Kaveri Seeds and Syngenta Group (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Area Under Cultivation
- 4.1.1 Row Crops
- 4.1.2 Vegetables
- 4.2 Most Popular Traits
- 4.2.1 Cabbage & Onion
- 4.2.2 Rice & Corn
- 4.2.3 Tomato & Chilli
- 4.2.4 Wheat & Cotton
- 4.3 Breeding Techniques
- 4.3.1 Row Crops & Vegetables
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Breeding Technology
- 5.1.1 Hybrids
- 5.1.1.1 Non-Transgenic Hybrids
- 5.1.1.2 Transgenic Hybrids
- 5.1.1.2.1 Insect Resistant Hybrids
- 5.1.2 Open Pollinated Varieties & Hybrid Derivatives
- 5.1.1 Hybrids
- 5.2 Cultivation Mechanism
- 5.2.1 Open Field
- 5.2.2 Protected Cultivation
- 5.3 Crop Type
- 5.3.1 Row Crops
- 5.3.1.1 Fiber Crops
- 5.3.1.1.1 Cotton
- 5.3.1.1.2 Other Fiber Crops
- 5.3.1.2 Forage Crops
- 5.3.1.2.1 Alfalfa
- 5.3.1.2.2 Forage Corn
- 5.3.1.2.3 Forage Sorghum
- 5.3.1.2.4 Other Forage Crops
- 5.3.1.3 Grains & Cereals
- 5.3.1.3.1 Corn
- 5.3.1.3.2 Rice
- 5.3.1.3.3 Sorghum
- 5.3.1.3.4 Wheat
- 5.3.1.3.5 Other Grains & Cereals
- 5.3.1.4 Oilseeds
- 5.3.1.4.1 Canola, Rapeseed & Mustard
- 5.3.1.4.2 Soybean
- 5.3.1.4.3 Sunflower
- 5.3.1.4.4 Other Oilseeds
- 5.3.1.5 Pulses
- 5.3.2 Vegetables
- 5.3.2.1 Brassicas
- 5.3.2.1.1 Cabbage
- 5.3.2.1.2 Carrot
- 5.3.2.1.3 Cauliflower & Broccoli
- 5.3.2.1.4 Other Brassicas
- 5.3.2.2 Cucurbits
- 5.3.2.2.1 Cucumber & Gherkin
- 5.3.2.2.2 Pumpkin & Squash
- 5.3.2.2.3 Other Cucurbits
- 5.3.2.3 Roots & Bulbs
- 5.3.2.3.1 Garlic
- 5.3.2.3.2 Onion
- 5.3.2.3.3 Potato
- 5.3.2.3.4 Other Roots & Bulbs
- 5.3.2.4 Solanaceae
- 5.3.2.4.1 Chilli
- 5.3.2.4.2 Eggplant
- 5.3.2.4.3 Tomato
- 5.3.2.4.4 Other Solanaceae
- 5.3.2.5 Unclassified Vegetables
- 5.3.2.5.1 Asparagus
- 5.3.2.5.2 Lettuce
- 5.3.2.5.3 Okra
- 5.3.2.5.4 Peas
- 5.3.2.5.5 Spinach
- 5.3.2.5.6 Other Unclassified Vegetables
- 5.3.1 Row Crops
- 5.4 State
- 5.4.1 Bihar
- 5.4.2 Gujarat
- 5.4.3 Haryana
- 5.4.4 Karnataka
- 5.4.5 Madhya Pradesh
- 5.4.6 Maharashtra
- 5.4.7 Rajasthan
- 5.4.8 Telangana
- 5.4.9 Uttar Pradesh
- 5.4.10 West Bengal
- 5.4.11 Other States
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 Advanta Seeds - UPL
- 6.4.2 BASF SE
- 6.4.3 Bayer AG
- 6.4.4 Corteva Agriscience
- 6.4.5 East-West Seed
- 6.4.6 Groupe Limagrain
- 6.4.7 Kaveri Seeds
- 6.4.8 Nuziveedu Seeds Ltd
- 6.4.9 Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel BV
- 6.4.10 Syngenta Group
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SEEDS CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Global Market Size and DROs
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms


