|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1690950
LEO衛星:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)LEO Satellite - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| LEO衛星:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 204 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
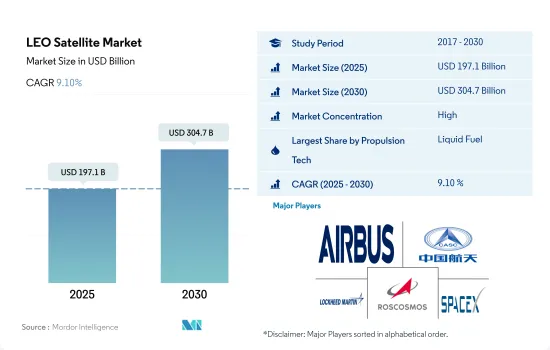
LEO衛星の市場規模は2025年に1,971億米ドルと予測され、2030年には3,047億米ドルに達すると予測され、予測期間(2025-2030年)のCAGRは9.10%で成長します。
市場シェアの大半を占める液体燃料推進システム
- 地球低軌道(LEO)衛星は、通信、地球観測、ナビゲーション、リモートセンシングなど、さまざまな産業に不可欠なものとなっています。推進システムは、これらの衛星の性能、効率、運用能力を決定する重要な役割を果たしています。
- 液体推進システムはLEO衛星市場で広く使用されており、高い推力と比推力能力を提供しています。これらのシステムは通常、ヒドラジンなどの液体燃料と四酸化窒素などの酸化剤を組み合わせて使用します。液体推進は、正確な軌道操作、静止遷移軌道(GTO)投入、ミッションの柔軟性を可能にします。複雑な軌道調整、特定の軌道へのペイロード輸送、衛星の退役を必要とするLEO衛星ミッションは、液体推進システムに依存しています。
- 電気推進は、その燃料効率とミッション寿命の延長により、LEO衛星市場で大きな支持を得ています。イオンやホール効果スラスタを含む電気推進システムは、電界を利用してイオンを加速し、推力を発生させる。電気推進は、SpaceX社のStarlinkやOneWebなどの企業が実証しているように、大規模なLEO衛星コンステレーションの展開を可能にします。これらのシステムは、正確なステーションキープマニューバや、長期間にわたる軌道調整を必要とするアプリケーションに特に適しています。
- コールドガス・スラスターやウォームガス・スラスターを含むガスベースの推進システムは、LEO衛星市場で広く使用されています。これらのシステムは、窒素やキセノンなどの圧縮ガスを利用して推力を発生させる。急速な軌道変更や頻繁な再ポジショニングを必要とするLEO衛星ミッションでは、その高い推力能力からガスベースの推進システムに頼ることが多いです。
北米が2029年の市場シェア85.4%で市場需要を牽引
- 世界のLEO衛星市場は、高速インターネット、通信サービス、さまざまな業界にわたるデータ転送の需要増に牽引され、今後数年間で大きく成長すると予想されます。同市場は、北米、欧州、アジア太平洋の市場シェアと収益創出に関して分析することができます。2017-2022年の間に、4100以上の衛星が製造され、このセグメントの様々なオペレータによってLEOに打ち上げられました。
- 北米は、The Boeing Company、Lockheed Martin、Northrop Grummanなど複数の主要市場企業の存在により、世界のLEO衛星市場を独占すると予想されています。また、米国政府は先進的な衛星技術の開発に多額の投資を行っており、これが北米市場の成長を促進すると期待されています。2017-2022年の間に、この地域はLEOに製造・打ち上げられた衛星全体の72%を占めています。
- LEO衛星市場は、欧州における高速インターネットや通信サービスの需要増加により、大きく成長すると予想されています。欧州宇宙機関(ESA)は高度な衛星技術の開発に多額の投資を行っており、これが市場の成長を促進すると期待されています。2017-2022年の間に、この地域は製造されLEOに打ち上げられた衛星全体の12%を占めています。
- アジア太平洋は、中国、インド、日本などの国々で衛星ベースの通信サービスの需要が増加しているため、LEO衛星市場で大きな成長が見込まれています。2017-2022年の間、アジア太平洋はLEOに製造・打ち上げられた衛星全体の9%を占めています。
世界のLEO衛星市場動向
燃料効率と運用効率の向上傾向が市場にプラスの影響を与える見込み
- 衛星ミッションの成功は、飛行前の質量特性の測定精度と、質量特性を厳しい制限内に収めるための衛星の適切なバラストに大きく依存します。質量特性を適切に制御できないと、打上げ後に衛星が転倒したり、正しい方向に向かおうとしてスラスターの能力をすぐに使い果たしてしまったりする可能性があります。太陽電池パネルは、衛星が地球を周回する間、太陽の方向を向き続けなければならないです。
- 低軌道衛星は、地球上空160kmから2000kmの軌道を周回し、1周するのに約1時間半かかり、地球表面の一部しかカバーしないです。衛星の質量は打ち上げに大きな影響を与えます。衛星が重ければ重いほど、宇宙に打ち上げるのに必要な燃料とエネルギーが増えるからです。衛星を打ち上げるには、時速約2万8,000kmという超高速まで加速し、地球の周回軌道に乗せる必要があります。この速度を達成するのに必要なエネルギー量は、衛星の質量に比例します。
- その結果、衛星が重ければ重いほど、宇宙に打ち上げるにはより大きなロケットとより多くの燃料が必要になります。その結果、打ち上げコストが上昇し、使用できるロケットの種類も制限されることになります。質量によって大きく分類されるのは、1,000kgを超える大型衛星です。2017年から2022年の間に、65以上の大型衛星がLEO軌道で打ち上げられました。中型衛星は質量が500kgと1000kgの衛星で、250機以上の中型衛星が打ち上げられました。打ち上げ質量が500kg未満の衛星は小型衛星です。LEO軌道には4000機以上の小型衛星があります。
地球観測、画像処理、接続サービスへの需要の高まりは、LEO衛星カテゴリーの研究開発費を急増させると予想されます。
- 地球低軌道(LEO)は、比較的地表に近い軌道です。LEOは通常高度1000km以下であるが、地球上空160kmまで上昇することもあります。LEO衛星は、通信、軍事偵察、その他の画像アプリケーションに広く使用されています。通信衛星は、LEOまでの信号ランタイムが短いという利点があります。この伝搬遅延の減少により、待ち時間が短縮されます。宇宙に送られる衛星のほとんどは、LEOコンステレーションに属しています。主要なLEO衛星コンステレーションの1つは、衛星通信プロバイダーのイリジウムが所有しています。アマゾンが所有するカイパー・システムズのような企業は、宇宙からのブロードバンド接続を提供するためにワンウェブのスターリンクのような企業と競争したいと考えているため、世界的にLEO軌道での競争企業間の敵対関係は高いです。連邦通信委員会の承認後、同社は2023年に最初の衛星を打ち上げる予定です。
- アジア太平洋地域における宇宙関連活動の増加を考慮し、衛星メーカーは衛星製造能力を強化しています。強力な宇宙インフラを持つ著名なアジア太平洋諸国は、中国、インド、日本、韓国です。中国国家宇宙局は、国家民間宇宙インフラ施設の強化を含む、2021~2025年の宇宙探査優先事項を発表しました。この計画の一環として、中国政府は衛星インターネット用の1万3,000衛星コンステレーションを開発するため、中国衛星ネットワークグループを設立しました。全体として、LEO衛星に対する研究開発費の動向は、技術革新の必要性と政府資金に後押しされて増加傾向にあります。この投資は、LEO衛星の性能と能力を向上させる新技術の開発につながると期待されています。
LEO衛星産業の概要
LEO衛星市場はかなり統合されており、上位5社で95.84%を占めています。この市場の主要企業は以下の通りです。Airbus SE, China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation(CASC), Lockheed Martin Corporation, ROSCOSMOS and Space Exploration Technologies Corp.(sorted alphabetically).
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主な調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 衛星の質量
- 宇宙開発への支出
- 規制の枠組み
- 世界
- オーストラリア
- ブラジル
- カナダ
- 中国
- フランス
- ドイツ
- インド
- イラン
- 日本
- ニュージーランド
- ロシア
- シンガポール
- 韓国
- アラブ首長国連邦
- 英国
- 米国
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 用途
- 通信
- 地球観測
- ナビゲーション
- 宇宙観測
- その他
- 衛星質量
- 10-100kg
- 100-500kg
- 500-1000kg
- 10kg未満
- 1000kg以上
- エンドユーザー
- 商業
- 軍事・政府
- その他
- 推進技術
- 電気式
- ガス
- 液体燃料
- 地域
- アジア太平洋
- 欧州
- 北米
- 世界のその他の地域
第6章 競合情勢
- 主要な戦略動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル.
- Airbus SE
- Astrocast
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation(CASC)
- German Orbital Systems
- GomSpaceApS
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Nano Avionics
- Planet Labs Inc.
- ROSCOSMOS
- Space Exploration Technologies Corp.
- SpaceQuest Ltd
- Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd.
第7章 CEOへの主な戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界のバリューチェーン分析
- 市場力学(DROs)
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表一覧
- 主要洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
The LEO Satellite Market size is estimated at 197.1 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 304.7 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 9.10% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Liquid fuel propulsion system occupies majority of the market share
- Low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites have become integral to various industries, including telecommunications, Earth observation, navigation, and remote sensing. The propulsion system plays a crucial role in determining the performance, efficiency, and operational capabilities of these satellites.
- Liquid propulsion systems have been widely used in the LEO satellite market, offering high thrust and specific impulse capabilities. These systems typically use liquid fuels, such as hydrazine, combined with oxidizers like nitrogen tetroxide. Liquid propulsion enables precise orbital maneuvers, geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) insertion, and mission flexibility. LEO satellite missions requiring complex orbital adjustments, payload delivery to specific orbits, and satellite decommissioning rely on liquid propulsion systems.
- Electric propulsion has gained significant traction in the LEO satellite market due to its fuel efficiency and extended mission lifetimes. Electric propulsion systems, including ions and Hall-effect thrusters, utilize electric fields to accelerate ions and generate thrust. Electric propulsion enables the deployment of large-scale LEO satellite constellations, as demonstrated by companies like SpaceX's Starlink and OneWeb. These systems are particularly suitable for applications that require precise station-keeping maneuvers and orbital adjustments over extended periods.
- Gas-based propulsion systems, including cold gas and warm gas thrusters, are extensively used in the LEO satellite market. These systems utilize compressed gases, such as nitrogen or xenon, to generate thrust. LEO satellite missions that require rapid orbital changes or frequent repositioning often rely on gas-based propulsion systems due to their higher thrust capabilities.
North America is driving the market demand with a market share of 85.4% in 2029
- The global LEO satellite market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by increasing demand for high-speed internet, communication services, and data transfer across different industries. The market can be analyzed with respect to North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific as to market share and revenue generation. During 2017-2022, more than 4100 satellites were manufactured and launched by various operators in this segment into LEO.
- North America is expected to dominate the global LEO satellite market due to the presence of several leading market players, such as The Boeing Company, Lockheed Martin, and Northrop Grumman. The US government has also been investing heavily in the development of advanced satellite technology, which is expected to drive the growth of the market in North America. During 2017-2022, the region accounted for 72% of the total satellites manufactured and launched into LEO.
- The LEO satellite market is expected to grow significantly due to the increasing demand for high-speed internet and communication services in Europe. The European Space Agency (ESA) has been investing heavily in the development of advanced satellite technology, which is expected to drive the growth of the market. During 2017-2022, the region accounted for 12% of the total satellites manufactured and launched into LEO.
- Asia-Pacific is expected to witness significant growth in the LEO satellite market due to the increasing demand for satellite-based communication services in countries such as China, India, and Japan. During 2017-2022, Asia-Pacific accounted for 9% of the total satellites manufactured and launched into LEO.
Global LEO Satellite Market Trends
The trend for better fuel and operational efficiency is expected to positively impact the market
- The success of a satellite mission is highly dependent on the accuracy of measuring its mass properties before the flight and the proper ballasting of the satellite to bring the mass properties within tight limits. Failure to properly control mass properties can result in the satellite tumbling end over end after launch or quickly using up its thruster capacity in an attempt to point in the correct direction. Solar panels must continue to point toward the sun as the satellite orbits the Earth.
- Low earth orbit satellites orbit from 160 to 2000 km above the Earth, take approximately 1.5 hours for a full orbit, and only cover a portion of the Earth's surface. The mass of a satellite has a significant impact on the launch of the satellite. This is because the heavier the satellite, the more fuel and energy are required to launch it into space. Launching a satellite involves accelerating it to a very high speed, typically around 28,000 km per hour, to place it in orbit around the Earth. The amount of energy required to achieve this speed is proportional to the mass of the satellite.
- As a result, a heavier satellite requires a larger rocket and more fuel to launch it into space. This, in turn, increases the cost of the launch and can also limit the types of launch vehicles that can be used. The major classification types according to mass are large satellites that are more than 1,000 kg. During 2017-2022, 65+ large satellites were launched in the LEO orbit. A medium-sized satellite has a mass of 500 and 1000 kg, and 250+ medium-sized satellites were launched. Satellites with a launch mass of less than 500 kg are small satellites. There are 4000+ small satellites in the LEO orbit.
Growing demand for earth observation, imaging, and connectivity services is expected to surge the research and development expenditure in LEO satellites category
- Low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit relatively closer to the surface of the Earth. LEO is usually below 1000 km altitude but can be as high as 160 km above Earth. LEO satellites are widely used for communications, military reconnaissance, and other imaging applications. Communications satellites have the advantage of short signal runtimes to LEO. This reduction in propagation delay results in lower latency. Most satellites sent into space are in the LEO constellation. One of the major LEO satellite constellations is owned by satellite communications provider Iridium. The competitive rivalry in the LEO orbit globally is high as companies such as Amazon-owned Kuiper Systems want to compete with companies like OneWeb's Starlink to provide broadband connectivity from space. After Federal Communications Commission approval, the company plans to launch its first satellite to be launched in 2023.
- Considering the increase in space-related activities in the Asia-Pacific region, satellite manufacturers are enhancing their satellite production capabilities. The prominent Asia-Pacific countries with robust space infrastructure are China, India, Japan, and South Korea. China National Space Administration announced space exploration priorities for 2021-2025, including enhancing national civil space infrastructure facilities. As a part of this plan, the Chinese government established China Satellite Network Group Co. Ltd to develop a 13,000-satellite constellation for satellite internet. Overall, the trend in R&D expenditure on LEO satellites is an increase, driven by the need for innovation and government funding. This investment is expected to lead to the development of new technologies that will improve the performance and capabilities of LEO satellites.
LEO Satellite Industry Overview
The LEO Satellite Market is fairly consolidated, with the top five companies occupying 95.84%. The major players in this market are Airbus SE, China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), Lockheed Martin Corporation, ROSCOSMOS and Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Satellite Mass
- 4.2 Spending On Space Programs
- 4.3 Regulatory Framework
- 4.3.1 Global
- 4.3.2 Australia
- 4.3.3 Brazil
- 4.3.4 Canada
- 4.3.5 China
- 4.3.6 France
- 4.3.7 Germany
- 4.3.8 India
- 4.3.9 Iran
- 4.3.10 Japan
- 4.3.11 New Zealand
- 4.3.12 Russia
- 4.3.13 Singapore
- 4.3.14 South Korea
- 4.3.15 United Arab Emirates
- 4.3.16 United Kingdom
- 4.3.17 United States
- 4.4 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Application
- 5.1.1 Communication
- 5.1.2 Earth Observation
- 5.1.3 Navigation
- 5.1.4 Space Observation
- 5.1.5 Others
- 5.2 Satellite Mass
- 5.2.1 10-100kg
- 5.2.2 100-500kg
- 5.2.3 500-1000kg
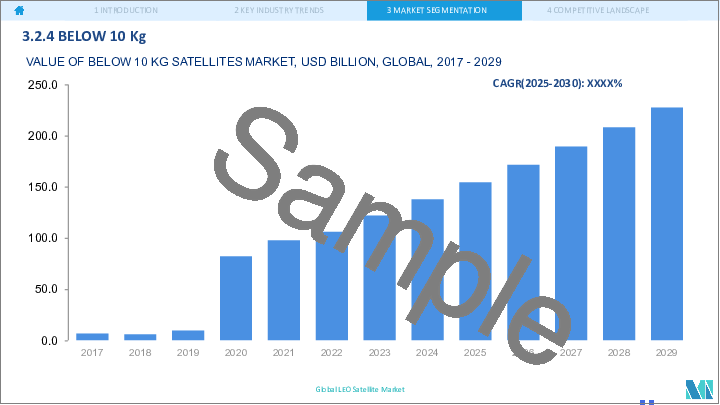
- 5.2.4 Below 10 Kg
- 5.2.5 above 1000kg
- 5.3 End User
- 5.3.1 Commercial
- 5.3.2 Military & Government
- 5.3.3 Other
- 5.4 Propulsion Tech
- 5.4.1 Electric
- 5.4.2 Gas based
- 5.4.3 Liquid Fuel
- 5.5 Region
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.3 North America
- 5.5.4 Rest of World
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 Airbus SE
- 6.4.2 Astrocast
- 6.4.3 China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC)
- 6.4.4 German Orbital Systems
- 6.4.5 GomSpaceApS
- 6.4.6 Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 6.4.7 Nano Avionics
- 6.4.8 Planet Labs Inc.
- 6.4.9 ROSCOSMOS
- 6.4.10 Space Exploration Technologies Corp.
- 6.4.11 SpaceQuest Ltd
- 6.4.12 Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd.
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SATELLITE CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms