|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1687807
インドネシアのCEP(クーリエ・エクスプレス・パーセル):市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Indonesia Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| インドネシアのCEP(クーリエ・エクスプレス・パーセル):市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 378 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
概要
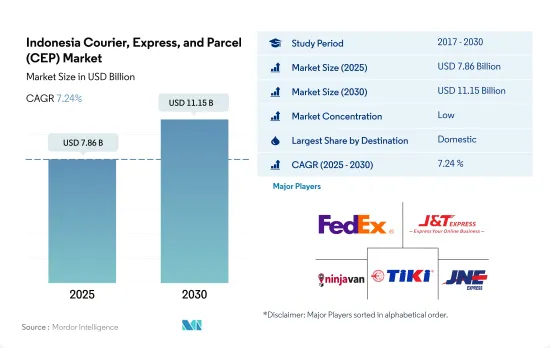
インドネシアのCEP(クーリエ・エクスプレス・パーセル)市場規模は2025年に78億6,000万米ドルと推定され、2030年には111億5,000万米ドルに達すると予測され、予測期間(2025-2030年)のCAGRは7.24%で成長すると予測されます。
国内および国境を越えた需要の急増が市場機会の迅速な拡大を促進
- 2024年10月、DHL Expressは香港とインドネシアのジャカルタを結ぶ新たな直行便路線を開設し、航空ネットワークを強化しました。同路線専用のB737-800型貨物機は週4便運航し、現地時間午前8時にジャカルタに到着します。この取り組みにより、インドネシアの企業や個人向けのアジア太平洋域内配送のスピードと信頼性が大幅に向上します。積載量20トンのB737-800型貨物機は、中国本土、香港、日本、韓国、台湾、フィリピン、ベトナムからのeコマースや大型貨物を、香港の中央アジア・ハブを経由して輸送します。
- 活況を呈するeコマースに牽引され、インドネシアの国内CEP部門は目覚ましい成長を遂げています。インドネシアのeコマース市場は、2022年の433億米ドルから2023年には452億8,000万米ドルに急増しました。動向によれば、この上昇傾向は今後も続き、2024年には512億4,000万米ドルに達する見込みです。2023年から2027年までの予測CAGRは10.41%で、市場価値は2027年までに673億米ドルに達する勢いです。eコマースのユーザーベースも拡大しており、基本推定では2027年までに2億4,470万人に達します。2023年に70.8%を記録したユーザー普及率は、2027年には85.5%まで上昇する見込みです。
インドネシアのCEP(クーリエ・エクスプレス・パーセル)市場動向
輸送・保管セクターは、インフラプロジェクトの増加によりGDP貢献の増加が見込まれる
- 2024年5月、日本政府はインドネシアのジャカルタにおける高速鉄道建設に約1,407億円(9億米ドル)の融資を実行しました。総延長84.1kmに及ぶこの東西鉄道プロジェクトは、2026年から2031年までの2期に分けて実施されます。この鉄道路線には、列車と信号システムの両方に日本の先進技術が導入されます。これらの構想は、輸送・貯蔵部門からのGDP貢献を強化する態勢を整えています。
- 輸送は、国のインフラ拡大努力の最前線にあります。この分野では、現在進行中および今後予定されているイニシアチブの総額の29%が道路プロジェクトに、22%が鉄道プロジェクトに、23%が港湾インフラに割り当てられています。これらのプロジェクトは、連結性を強化し、経済成長を後押しするために極めて重要です。インドネシアで重要な事業は、135kmに及ぶロクスマウェ~ランサ有料道路です。この野心的なプロジェクトは2024年初頭に開始され、交通渋滞の緩和と移動時間の短縮を目標に、2027年後半までに完成する予定です。この有料道路は、物流を最適化し、輸送・貯蔵部門のGDPへの寄与を高めるのに役立つと思われます。
インドネシアは2022年、原油価格の高騰と補助金圧力の中で財政課題に直面したが、税率は2024年まで据え置かれました。
- 2024年11月、インドネシアは燃料補助金制度を改革しました。新大統領は、2023年に政府支出の約16%を占めていた補助金の削減を目指しています。LPGの補助金は据え置かれるが、政府は燃料と電力の補助金の調整を決定中です。インドネシアのエネルギー補助金はインフレを抑えるのに役立っているが、世界の原油価格の変動にさらされています。政府は、これらの補助金を貧困家庭への現金給付で置き換えることを計画しており、より的を絞った支援によって約129億9,000万米ドルの節約を目指しています。
- 2024年6月の時点で、インドネシア・エネルギー鉱物資源省(ESDM)は、グリーン水素産業の成長を促進するため、グリーン水素開発業者に対するインセンティブと減税を提供するための規制を起草していました。ESDMは、2060年までに年間990万トンの水素を生産し、産業(3.9 Mtpa)、輸送(1.1 Mtpa)、電力(4.6 Mtpa)、家庭用ガスネットワーク(0.28 Mtpa)のニーズを満たすことを目標としています。これらの分野は輸出商品にもなりうる。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリスト・サポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主な調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 人口動態
- 経済活動別GDP分布
- 経済活動別GDP成長率
- インフレ率
- 経済パフォーマンスとプロファイル
- eコマース産業の動向
- 製造業の動向
- 運輸・倉庫業のGDP
- 輸出動向
- 輸入動向
- 燃料価格
- 物流実績
- インフラ
- 規制の枠組み
- インドネシア
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 仕向地
- 国内
- 国際
- 配達スピード
- エクスプレス
- 非エクスプレス
- モデル
- 企業間(B2B)
- 企業対消費者(B2C)
- 消費者間(C2C)
- 出荷重量
- 重量貨物
- 軽量貨物
- 中量貨物
- 輸送形態
- 航空便
- 道路
- その他
- エンドユーザー
- eコマース
- 金融サービス(BFSI)
- ヘルスケア
- 製造業
- 第一次産業
- 卸売・小売業(オフライン)
- その他
第6章 競合情勢
- 主要な戦略動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- DHL Group
- FedEx
- Grab Holdings Limited
- J&T Express
- Lion Parcel(a part of Lion Group)
- Ninja Van(including Ninja Express)
- PT Citra Van Titipan Kilat(TIKI)
- PT Garuda Indonesia(Persero)TBK
- PT Globalindo Dua Satu Express(21 Express)
- PT ID Express Logistik Indonesia
- PT Jalur Nugraha Ekakurir(JNE Express)
- PT Kereta Api Indonesia(including KAI Logistik)
- PT Pandu Siwi Group(Pandu Logistics)
- PT Pos Indonesia(Persero)
- PT Repex Wahana(RPX)
- PT Satria Antaran Prima TBK(SAPX Express)
- PT SiCepat Express Indonesia
- PT Synergy First Logistics
- PT Yapindo Transportama(PCP Express)
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc.(UPS)
第7章 CEOへの主な戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界のバリューチェーン分析
- 市場力学(DROs)
- 技術の進歩
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表リスト
- 主要洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
目次
Product Code: 66260
The Indonesia Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market size is estimated at 7.86 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 11.15 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 7.24% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Surging domestic and cross-border demand fuels swift expansion in market opportunities
- In October 2024, DHL Express launched a new direct flight route connecting Hong Kong to Jakarta, Indonesia, enhancing its aviation network. The B737-800 freighter, dedicated to this route, operates four times weekly, landing in Jakarta at 8:00 am local time. This initiative is set to significantly enhance the speed and reliability of intra-Asia Pacific deliveries for businesses and individuals in Indonesia. With a capacity of 20 tons, the B737-800 freighter carries e-commerce and larger shipments from Mainland China, Hong Kong, Japan, Korea, Taiwan, the Philippines, and Vietnam, all routed through Hong Kong's Central Asia Hub.
- Driven by a booming e-commerce landscape, Indonesia's domestic CEP segment has witnessed remarkable growth. The e-commerce market in Indonesia surged from USD 43.3 billion in 2022 to USD 45.28 billion in 2023. Projections indicate this upward trend will persist, with the market poised to reach USD 51.24 billion by 2024. With a forecasted CAGR of 10.41% from 2023 to 2027, the market value is on track to hit USD 67.30 billion by 2027. The e-commerce user base is also expanding, with estimates suggesting a reach of 244.7 million users by 2027. User penetration, recorded at 70.8% in 2023, is expected to rise to 85.5% by 2027.
Indonesia Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market Trends
The transportation and storage sector expected to witness boost in GDP contributions, fueled by rising infrastructure projects
- In May 2024, the Japanese government extended a loan of approximately JPY140.7 billion (USD 900 million) for the construction of a high-speed rail line in Jakarta, Indonesia. Spanning 84.1 km, the East-West rail project will be executed in two phases, commencing in 2026 and concluding by 2031. The rail line will incorporate advanced Japanese technology for both trains and signaling systems. These initiatives are poised to enhance the GDP contribution from the transport and storage sector.
- Transportation is at the forefront of the nation's infrastructure expansion efforts. In this domain, ongoing and upcoming initiatives allocate 29% of their overall value to road projects, 22% to rail, and 23% to port infrastructure. These projects are crucial for enhancing connectivity and boosting economic growth. A significant undertaking in Indonesia is the Lhokseumawe to Langsa Toll Road, spanning 135 km. Commencing in early 2024, this ambitious project is slated for completion by late 2027, with the goal of alleviating traffic congestion and shortening travel times. This toll road will be instrumental in optimizing logistics and boosting the transport and storage sector's contribution to GDP.
Indonesia faced fiscal challenges amid surging crude oil prices and subsidy pressures in 2022, however the rates remained unchanged till 2024
- In November 2024, Indonesia reformed its fuel subsidy system. The new president is targeting a reduction in subsidies, which constituted roughly 16% of government spending in 2023. While the subsidy for LPG will stay the same, the government is still determining adjustments for fuel and electricity subsidies. Indonesia's energy subsidies help keep inflation low but expose the nation to global oil price swings. The government plans to replace these subsidies with cash transfers for needy families, aiming to save about USD 12.99 billion through more targeted support.
- As of June 2024, the Indonesian Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources (ESDM) was drafting regulations to provide incentives and tax relief for green hydrogen developers to boost the industry's growth. ESDM aimed to produce 9.9 million tons of hydrogen per year by 2060 to meet the needs of industry (3.9 Mtpa), transportation (1.1 Mtpa), electricity (4.6 Mtpa), and household gas networks (0.28 Mtpa). These sectors could also become export commodities.
Indonesia Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Industry Overview
The Indonesia Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market is fragmented, with the major five players in this market being FedEx, J&T Express, Ninja Van (including Ninja Express), PT Citra Van Titipan Kilat (TIKI) and PT Jalur Nugraha Ekakurir (JNE Express) (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Demographics
- 4.2 GDP Distribution By Economic Activity
- 4.3 GDP Growth By Economic Activity
- 4.4 Inflation
- 4.5 Economic Performance And Profile
- 4.5.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.5.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.6 Transport And Storage Sector GDP
- 4.7 Export Trends
- 4.8 Import Trends
- 4.9 Fuel Price
- 4.10 Logistics Performance
- 4.11 Infrastructure
- 4.12 Regulatory Framework
- 4.12.1 Indonesia
- 4.13 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes Market Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Destination
- 5.1.1 Domestic
- 5.1.2 International
- 5.2 Speed Of Delivery
- 5.2.1 Express
- 5.2.2 Non-Express
- 5.3 Model
- 5.3.1 Business-to-Business (B2B)
- 5.3.2 Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- 5.3.3 Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
- 5.4 Shipment Weight
- 5.4.1 Heavy Weight Shipments
- 5.4.2 Light Weight Shipments
- 5.4.3 Medium Weight Shipments
- 5.5 Mode Of Transport
- 5.5.1 Air
- 5.5.2 Road
- 5.5.3 Others
- 5.6 End User Industry
- 5.6.1 E-Commerce
- 5.6.2 Financial Services (BFSI)
- 5.6.3 Healthcare
- 5.6.4 Manufacturing
- 5.6.5 Primary Industry
- 5.6.6 Wholesale and Retail Trade (Offline)
- 5.6.7 Others
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 DHL Group
- 6.4.2 FedEx
- 6.4.3 Grab Holdings Limited
- 6.4.4 J&T Express
- 6.4.5 Lion Parcel (a part of Lion Group)
- 6.4.6 Ninja Van (including Ninja Express)
- 6.4.7 PT Citra Van Titipan Kilat (TIKI)
- 6.4.8 PT Garuda Indonesia (Persero) TBK
- 6.4.9 PT Globalindo Dua Satu Express (21 Express)
- 6.4.10 PT ID Express Logistik Indonesia
- 6.4.11 PT Jalur Nugraha Ekakurir (JNE Express)
- 6.4.12 PT Kereta Api Indonesia (including KAI Logistik)
- 6.4.13 PT Pandu Siwi Group (Pandu Logistics)
- 6.4.14 PT Pos Indonesia (Persero)
- 6.4.15 PT Repex Wahana (RPX)
- 6.4.16 PT Satria Antaran Prima TBK (SAPX Express)
- 6.4.17 PT SiCepat Express Indonesia
- 6.4.18 PT Synergy First Logistics
- 6.4.19 PT Yapindo Transportama (PCP Express)
- 6.4.20 United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR CEP CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.1.5 Technological Advancements
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms






