
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1687714
インドのコンバインハーベスター:市場シェア分析、産業動向と統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)India Combine Harvester - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| インドのコンバインハーベスター:市場シェア分析、産業動向と統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 80 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
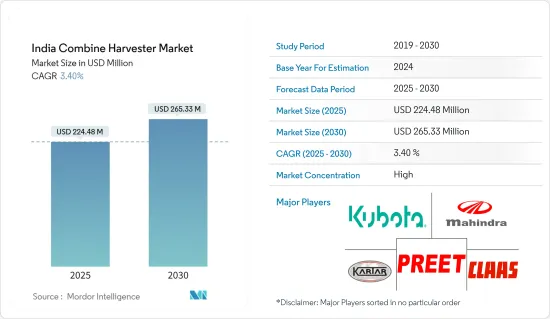
インドのコンバインハーベスター市場規模は2025年に2億2,448万米ドルと予測され、予測期間(2025年~2030年)のCAGRは3.4%で、2030年には2億6,533万米ドルに達すると予測されます。
主なハイライト
- インド農業研究評議会(ICAR)によると、インドでは主要穀物、豆類、油糧種子、雑穀、換金作物(米と小麦を除く)の収穫・脱穀作業は32%近く機械化されています。特に、コメと小麦の収穫・脱穀作業の機械化率は60%を超えています。この動向は、収穫と脱穀を合理化するコンバインの採用が拡大していることを強調しており、市場の拡大を後押ししています。
- さらに、調査期間中、様々な作物の栽培面積が増加しています。例えば、FAOSTAT統計によると、インド全土の粗粒穀物の栽培総面積は、2019年の9,510万ヘクタールから2022年には9,960万ヘクタールに増加しています。これはコンバインにとって大きな可能性のように思えます。
- 調査期間を通じて、Preet 987、Mahindra Arjun 605、Kartar 4000、Dasmesh 9100 Self Combine Harvester、New Holland TC5.30、Kubota HARVESTING DC-68G-HKといった著名ブランドが同国で大きな存在感を示しています。インドでこれらのコンバインが採用されるようになったのは、農作業の労働力不足が顕著になったためです。
- インド政府は、機械を含むさまざまな農業投入物に補助金を支給しています。2022年には、村落開発を目的としたアッサム州政府の制度であるCMSGUY(Chief Minister's Samagra Gramya Unnayan Yojana)の下、アッサム州チラン郡の農家生産者企業(FPC)2社にコンバインが90%という驚くべき補助率で支給されました。補助金によってコンバインハーベスター機械をより利用しやすくするこうした取り組みは、コンバインハーベスター機械の採用を拡大し、市場成長をさらに促進する構えです。
インドのコンバインハーベスター市場動向
高い農業労働コスト
農業は人口の大部分にとって主要な生計手段です。インド経済調査2022年~23年によると、農業部門はインドの労働人口の45.76%近くを雇用しています。インドで見られる都市化動向の上昇は、人口拡大の結果です。世界銀行のデータによると、2020年から2023年にかけて都市化の度合いは34.9%から36.4%に上昇しました。その結果、農村部の世帯が近隣の都市に移住し、国内の農業労働力が不足することになりました。例えば、世界銀行のデータによれば、農業に従事する労働人口は2020年から2022年にかけて44.3%から42.9%に減少しました。
同様に、農業労働力の不足は賃金も上昇させ、農家の生産コスト全体を上昇させました。インド政府の統計によると、2022年の全インドレベルでの女性の畑(農業)労働者の年間平均日当は328.51インドルピー(4米ドル)と報告されており、前年比8.32%増を記録しています。同様に、男性の現場(農業)労働の場合、全インドレベルでの日当は2022年に394.52インドルピー(USD 4.8)と報告されており、前年比8.55%の上昇を記録しています。このため、農家での雇用が抑制され、コンバインの導入が進んでいます。
同国の農業は手作業に大きく依存しており、農業従事者の減少は収穫などの農作業を行う上で大きな課題となっています。この問題の解決策として、これらの農作業を効果的かつ効率的に行うための先進的な収穫機械の使用がますます普及しています。
インドにおける穀物栽培の増加が自走式コンバインハーベスターの需要を促進
インドでは、穀物が食卓において極めて重要な役割を果たしており、同国はこれらの主食の主要な生産国および消費国として位置づけられています。穀物の消費量が増加するにつれ、栽培面積を拡大する必要性が高まっています。この傾向は、穀物や穀類の収穫面積が増加傾向にあることからも明らかです。例えば、FAOSTATによると、穀物の収穫面積は2019年の9,510万ヘクタールから2022年には9,960万ヘクタールに増加します。コンバイン、特に自走式コンバインが主に穀物に利用されていることを考えると、このような栽培の増加は直接的にそのような機器の需要を押し上げ、市場の成長を促進します。
堅牢なエンジンを搭載した自走式コンバインは、畑での作業に優れ、効率的な収穫と生産性の向上を保証します。この生産性の向上は、このセグメントの拡大にとって重要なドライバーです。自走式コンバインは、インド北部、西部、中部で主に米、小麦、その他の季節作物に使用されています。さらに、特にパンジャブ州やハリヤナ州のような主要な稲作・小麦作地域では、大規模農家によるこれらの収穫機の有利な慣行雇用が、他の農家における採用の急増につながっています。
穀物作物専用地域の拡大に対応するため、メーカーは穀物作物用に特化したコンバイン製品を展開しています。その一例が、マヒンドラ・アンド・マヒンドラ社の子会社であるスワラージ事業部で、同社は2021年10月に自走式コンバイン「Gen2 8100 EX」を発表しました。このモデルは、水田農家の生産性と性能を向上させ、広大な面積で最適な穀物収量を確保することを目的としています。
インドのコンバインハーベスター産業概要
インドのコンバイン市場は統合されています。Claas India、Preet Group、Kubota Corporation、Mahindra &Mahindra Ltd、Kartar Agro Industries Private Limitedが主要市場企業です。各社は製品の品質と販売促進で競争し、戦略的な取り組みに重点を置いて圧倒的な市場シェアを占めています。また、研究開発活動を強化しながら市場シェアを拡大するため、他社との提携や買収を進め、新製品の開発に多額の投資を行っています。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場力学
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- 作物生産強化の必要性
- 政府支援の増加
- 農業機械化の需要
- 市場抑制要因
- コンバインハーベスターの高コスト
- 小規模で断片的な土地保有
- 業界の魅力- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 買い手の交渉力
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係の強さ
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- タイプ
- 自走式コンバインハーベスター
- トラック式コンバインハーベスター
- トラクター式コンバインハーベスター
第6章 競合情勢
- 最も採用されている戦略
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業プロファイル
- PREET Group
- John Deere India Pvt. Ltd
- CLAAS India
- Tractors and Farm Equipment(TAFE)Ltd
- Mahindra Tractors
- Kubota Agricultural Machinery India Pvt. Ltd
- Dasmesh Group
- Balkar Combines
- Kartar Agro Industries Pvt. Ltd
- Sonalika Group
第7章 市場機会と今後の動向
The India Combine Harvester Market size is estimated at USD 224.48 million in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 265.33 million by 2030, at a CAGR of 3.4% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), in India, harvesting and threshing operations for major cereals, pulses, oil seeds, millets, and cash crops (excluding rice and wheat) are nearly 32% mechanized. Notably, mechanization levels for harvesting and threshing in rice and wheat exceed 60%. This trend emphasizes the growing adoption of combine harvesters, which streamlines harvesting and threshing, bolstering market expansion.
- Additionally, the area under cultivation of various crops has been rising during the study period. For instance, according to the FAOSTAT Statistics, the total area for cultivating coarse cereals across India increased from 95.1 million hectares in 2019 to 99.6 million hectares in 2022. This seems like a great potential for combine harvesters.
- Throughout the study period, prominent brands such as Preet 987, Mahindra Arjun 605, Kartar 4000, Dasmesh 9100 Self Combine Harvester, New Holland TC5.30, and Kubota HARVESTING DC-68G-HK have established a significant presence in the country. The rising adoption of these combines in India can be largely attributed to a notable shortage of farm labor.
- The Indian government extends subsidies on various agricultural inputs, including machinery. In 2022, under the Chief Minister's Samagra Gramya Unnayan Yojana (CMSGUY) - a scheme by the Assam Government aimed at village development - two farmer-producer companies (FPCs) in Assam's Chirang District were granted combined harvester machinery at a remarkable 90% subsidized rate. Such initiatives, making combined harvester machinery more accessible through subsidies, are poised to amplify their adoption and further fuel market growth.
India Combine Harvester Market Trends
High Cost of Farm Labor
Agriculture is a major source of livelihood for a large group of the population. As per the Indian Economic Survey 2022 -23, the agriculture sector employs nearly 45.76% of the Indian workforce. The rise in urbanization trends observed in the country is a result of the expanding population. According to the World Bank data, the degree of urbanization increased from 34.9% to 36.4% from 2020 to 2023. This resulted in the migration of rural households to the nearby cities, leading to the scarcity of farm labor in the country. For instance, the workforce employed in agriculture dropped from 44.3% to 42.9% from 2020 to 2022, as per the World Bank data.
Likewise, the scarcity of farm labor also increased wage rates, which increased the overall production costs of the farmers. As per the Government of India statistics, the annual average daily wage rate for female field (Agriculture) labor, at all India levels, has reported at ₹ 328.51 (USD 4.0) in 2022, registering an increase of 8.32% over the previous year. Likewise, in the case of male field (agriculture) labor, the daily wage rate at all India levels was reported at ₹ 394.52 (USD 4.8) in 2022, registering an increase of 8.55 percent over the previous year. This resulted in a restrain in employing them in farms, favoring the adoption of combine harvesters by the farmers in the country.
The agricultural industry of the country heavily relies on manual labor, and the decreasing workforce in agriculture has led to major challenges in performing farming operations such as harvesting. As a solution to this problem, the usage of advanced harvesting machinery has become increasingly popular for performing these agricultural operations effectively and efficiently.
Rising Grain Cultivation in India Fuels Demand for Self-Propelled Combine Harvesters
In India, cereals play a pivotal role in the culinary landscape, positioning the nation as a leading producer and consumer of these staples. As the consumption of cereal crops rises, so does the need for expanded cultivation. This trend is evident, with harvested areas for cereals and grains on the upswing. For instance, according to FAOSTAT, the area harvested under cereals increased from 95.1 million hectares in 2019 to 99.6 million hectares in 2022. Given that combines, especially self-propelled ones, are predominantly utilized for cereals, this uptick in cultivation directly boosts the demand for such equipment, propelling the market growth.
Equipped with a robust engine, self-propelled combine harvesters excel in the fields, ensuring efficient harvesting and heightened productivity. This boost in productivity is a key driver for the segment's expansion. Predominantly, these harvesters find their application in Northern, Western, and Central India, catering mainly to rice, wheat, and other seasonal crops. Moreover, the lucrative custom hiring of these harvesters by large farmers, especially in major rice-wheat regions like Punjab and Haryana, has led to a surge in adoption among other farmers.
In response to the expanding areas dedicated to grain crops, manufacturers are rolling out specialized combine harvester products tailored for these crops. A case in point is Swaraj Division, a Mahindra and Mahindra Ltd subsidiary, which unveiled its Gen2 8100 EX self-propelled combine harvester in October 2021. This model aims to enhance productivity and performance for paddy farmers, ensuring optimal grain yield across extensive acreage.
India Combine Harvester Industry Overview
The Indian combined harvester market is consolidated. Claas India, Preet Group, Kubota Corporation, Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd, and Kartar Agro Industries Private Limited are the major market players. Companies compete based on product quality and promotion and focus on strategic initiatives to account for prominent market shares. They are also heavily investing in developing new products while collaborating with and acquiring other companies, which may increase their market shares while strengthening their R&D activities.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Need to Enhance Crop Production
- 4.2.2 Increase In Government Support
- 4.2.3 Demand for Farm Mechanization
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Cost of Combine Harvesters
- 4.3.2 Small and Fragmented Land Holdings
- 4.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Type
- 5.1.1 Self-propelled Combine Harvester
- 5.1.2 Track Combine Harvester
- 5.1.3 Tractor-powered Combine Harvester
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Most Adopted Strategies
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 PREET Group
- 6.3.2 John Deere India Pvt. Ltd
- 6.3.3 CLAAS India
- 6.3.4 Tractors and Farm Equipment (TAFE) Ltd
- 6.3.5 Mahindra Tractors
- 6.3.6 Kubota Agricultural Machinery India Pvt. Ltd
- 6.3.7 Dasmesh Group
- 6.3.8 Balkar Combines
- 6.3.9 Kartar Agro Industries Pvt. Ltd
- 6.3.10 Sonalika Group


