
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1684102
ドイツの肥料:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Germany Fertilizer - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| ドイツの肥料:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 287 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
概要
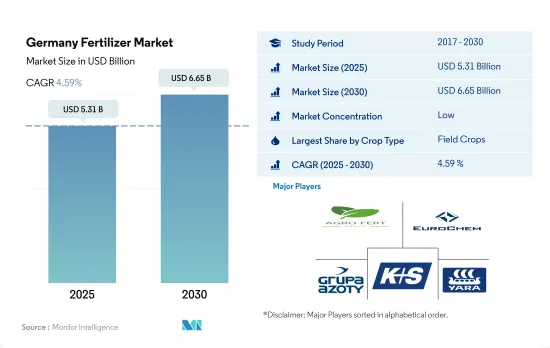
ドイツの肥料市場規模は2025年に53億1,000万米ドルと推定・予測され、2030年には66億5,000万米ドルに達し、予測期間(2025-2030年)のCAGRは4.59%で成長すると予測されています。
集約的な農法が肥料消費を増加させている
- ドイツは欧州地域で第4位の農業国であり、国土の57%以上を農業が占めています。1ヘクタール平均61ヘクタールの小規模農家が27万6,000軒近くあります。土壌の種類が多様なため、農家は栄養不足に対処し、作物の成長と品質を最適化するために、肥料の使用量を調整しています。
- 近年、ドイツでは肥料の使用量が顕著に増加しています。2022年の肥料使用量は前年比2.9%増となったが、これは同国の気候条件が大きく影響しています。農家は干ばつや熱波に苦しみ、食糧安全保障を守るために肥料や作物保護製品に大きく依存しました。
- 2022年には、畑作物が56.4%を占め、肥料消費の大半を占めました。これは主に、耕作面積の拡大、集約的な農法、継続的な耕作による栄養不足に対処する必要性によるものです。小麦、大麦、菜種、大豆が主要作物としてリードしています。ドイツは栽培面積の拡大を通じて国内のマメ科作物の生産に重点を置いており、2023年から2030年までのCAGRは3.7%と予測され、畑作物市場を牽引するものと思われます。
- 芝および観賞用作物分野はドイツで2番目に大きな市場シェアを占めており、2022年には35.9%に達します。これらの作物は、さまざまな用途で需要が高まっています。これに伴い、農家は作物の成長と品質を確実にするために作物栄養への依存度を高めています。このような需要の高まりは、今後数年間で市場を牽引するものと思われます。
ドイツの肥料市場動向
干ばつと熱波が畑作物の栽培に影響
- 2022年には、畑作物がドイツの栽培面積の78.2%を占めました。この優位性は、食料安全保障を保証し、農業部門にとって経済的に重要な作物としての役割を果たすという二重の意義に起因しています。調査期間中、畑作物の栽培面積は大幅に減少しました。2017年には、畑作物の総栽培面積は735万ヘクタールであったが、2022年には161万ヘクタール減少し、574万ヘクタールとなりました。このように畑作物の作付面積が顕著に減少したのは、近年の干ばつと猛暑の悪影響により収量が大幅に減少したためです。その結果、農家はこうした厳しい気候条件に対応して栽培面積を減らすことを選択しました。小麦、菜種、トウモロコシ、大豆が主な栽培作物です。
- 小麦は最も広範囲で栽培されている作物として主導権を握っており、この地域の第2位の生産者です。2022年には、小麦の耕作面積は全耕作地の49.8%を占めました。この優位性は、国内市場でも国際市場でも小麦の需要が高まっていることが主な原因です。小麦の耕作面積は、2017年と比較して約7%激減しました。2022年には298万ヘクタールとなったが、これは主に夏小麦の収穫面積が45%減少し、冬小麦の収穫面積が1.4%減少したことによるもので、乾燥した暑い気候条件によるものです。
- マメ科作物の栽培面積は2022年に46.3%増加したが、これは主に国内生産への依存によるものです。
窒素は畑作物が消費する主要養分です。
- 2022年、ドイツの畑作物の平均養分施用量は1ヘクタール当たり177.2kgでした。特に、トウモロコシ、コメ、小麦、ソルガム、大豆、菜種、綿花は主要な畑作作物であり、これらの作物は生育を支えるために高い養分レベルを要求します。集約的な農法と、小麦などの主要作物の継続的な栽培から生じる養分不足は、養分施用の増加を必要とします。このような状況では、土壌の肥沃度を維持するために、より多くの養分投入が必要となります。
- 窒素は、すべての主要養分の中で、畑作物が消費する主要養分として際立っています。窒素の平均養分施用量は、1ヘクタール当たり274.7kgです。同国の土壌は、高いpHレベル、砂質土壌の組成、繰り返し起こる干ばつによる持続的な乾燥状態のため、窒素欠乏に見舞われています。これらの要因が相まって、同国の農業では窒素養分の需要が増加しています。カリは2番目に消費量の多い一次養分であり、1ヘクタール当たりの平均養分施用量は142.9kg、リンの消費量は114.1kgです。
- 同国は、域内でも有数の菜種生産国です。菜種の平均養分施用量は最も多く、1ヘクタール当たり290.5キログラムに達します。菜種は窒素に大きく依存しています。重要な栄養素である窒素の平均施用量は、1ヘクタール当たり393.7キログラムです。この作物は養分利用効率が低いため、窒素施肥に大きく依存しており、これによってタンパク質含量が高まる。
ドイツ肥料産業概要
ドイツの肥料市場は細分化されており、上位5社で32.74%を占めています。この市場の主要企業は以下の通りです。 AGROFERT, EuroChem Group, Grupa Azoty S.A.(Compo Expert), K+S Aktiengesellschaft and Yara International ASA(sorted alphabetically).
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主な調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 主要作物の作付面積
- 畑作物
- 園芸作物
- 平均養分施用率
- 微量栄養素
- 畑作物
- 園芸作物
- 一次栄養素
- 畑作物
- 園芸作物
- 二次多量栄養素
- 畑作物
- 園芸作物
- 微量栄養素
- 灌漑農地
- 規制の枠組み
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- タイプ
- 複合型
- ストレート
- 微量栄養素
- ホウ素
- 銅
- 鉄
- マンガン
- モリブデン
- 亜鉛
- その他
- 窒素
- 尿素
- その他
- リン酸
- DAP
- MAP
- SSP
- TSP
- ポタシック
- MoP
- SoP
- 二次栄養素
- カルシウム
- マグネシウム
- 硫黄
- 形態
- 従来型
- 特殊
- CRF
- 液体肥料
- SRF
- 水溶性
- 施肥方法
- 施肥
- 葉面散布
- 土壌
- 作物タイプ
- 畑作物
- 園芸作物
- 芝・観賞用
第6章 競合情勢
- 主要な戦略動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- AGLUKON Spezialduenger GmbH & Co.
- AGROFERT
- EuroChem Group
- Grupa Azoty S.A.(Compo Expert)
- ICL Group Ltd
- K+S Aktiengesellschaft
- Nouryon
- PhosAgro Group of Companies
- Sociedad Quimica y Minera de Chile SA
- Yara International ASA
第7章 CEOへの主な戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界のバリューチェーン分析
- 市場力学(DROs)
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表一覧
- 主要洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
目次
Product Code: 50002250
The Germany Fertilizer Market size is estimated at 5.31 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 6.65 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 4.59% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Intensive agricultural practices are increasing fertilizer consumption
- Germany ranks as the fourth largest agricultural nation in the European region, with agriculture occupying over 57% of its land. The country boasts nearly 276,000 small farms, averaging 61 hectares each. Given the diverse soil types, farmers tailor their fertilizer usage to address nutrient deficiencies and optimize crop growth and quality.
- In recent years, Germany has seen a notable surge in fertilizer utilization. In 2022, fertilizer usage rose by 2.9% compared to the previous year, largely influenced by the country's climatic conditions. Farmers struggled with droughts and heatwaves and relied heavily on fertilizers and crop protection products to safeguard food security.
- In 2022, field crops dominated fertilizer consumption, accounting for 56.4%. This is primarily due to their expansive cultivation areas, intensive agricultural practices, and the need to address nutrient deficiencies resulting from continuous cultivation. Wheat, barley, rapeseed, and soybean take the lead as major crops. Germany's emphasis on domestic legume production, achieved through expanding cultivation areas, is set to drive the field crops market with a projected CAGR of 3.7% from 2023 to 2030.
- The turf and ornamental crop segment claims the second-largest market share in Germany, standing at 35.9% in 2022. These crops are witnessing heightened demand across various applications. Farmers, in response, are increasingly relying on crop nutrition to ensure robust growth and quality. This rising demand is poised to propel the market in the coming years.
Germany Fertilizer Market Trends
Droughts and heat waves impacted the cultivation of field crops
- In 2022, field crops dominated Germany's cultivation area, accounting for 78.2%. This prominence can be attributed to their dual significance in guaranteeing food security and serving as economically vital crops for the agricultural sector. A substantial decline in the cultivation area of field crops was observed during the study period. In 2017, the total cultivation area dedicated to field crops accounted for 7.35 million hectares, but by 2022, it had reduced by 1.61 million hectares and reached 5.74 million hectares. This noteworthy reduction in the country's field crop acreage can be attributed to the adverse impacts of recent droughts and persistent heat waves, which led to significant yield losses. Consequently, farmers opted to reduce their cultivation areas in response to these challenging climatic conditions. Wheat, rapeseed, corn, and soybean are major cultivating crops.
- Wheat takes the lead as the most extensively cultivated crop and is the region's second-largest producer. In 2022, the wheat cultivation area comprised a substantial 49.8% of the total cultivated land. This predominance can be majorly attributed to the escalating demand for wheat both within the domestic market and on the international market. The wheat cultivation area reduced drastically by approximately 7% compared to the year 2017. In 2022, it accounted for 2.98 million hectares, which is majorly due to a reduction in summer wheat harvesting area, down by 45%, and winter wheat harvesting area by 1.4%, due to dry and hot climatic conditions.
- The legume crop cultivation area increased in 2022 by 46.3%, which was majorly due to the country's dependence on domestic production.
Nitrogen is the main primary nutrient consumed by the field crops
- In the year 2022, the average nutrient application rate of field crops stood at 177.2 kg per hectare in Germany. Notably, corn, rice, wheat, sorghum, soybean, rapeseed, and cotton represent the primary field crops cultivated, and they demand higher nutrient levels to support their growth. The nutrient deficiency arising from intensive agricultural practices and the continuous cultivation of major crops, such as wheat, necessitates an increased application of nutrients. This situation calls for higher nutrient input to maintain soil fertility.
- Nitrogen stands out as the predominant nutrient consumed by field crops among all the primary nutrients. The average nutrient application rate for nitrogen is a substantial 274.7 kg per hectare. The country's soils experience nitrogen deficiency due to its high pH levels, sandy soil composition, and persistent dry conditions resulting from recurrent droughts. These factors collectively drive an increased demand for nitrogen nutrients in the country's agricultural practices. Potash is the second most consumed primary nutrient, with an average nutrient application rate of 142.9 kg per hectare, and phosphorus consumption accounts for 114.1 kg per hectare.
- The country holds a prominent position as a leading producer of oil rapeseed within the region. The rapeseed crop exhibits the highest average nutrient application rate, reaching 290.5 kilograms per hectare. The oil rapeseed crop relies heavily on nitrogen. It is notable that the average nutrient application rate for this crucial nutrient stands at 393.7 kilograms per hectare. This crop heavily depends on nitrogen fertilization due to its lower nutrient use efficiency, and while this enhances protein content.
Germany Fertilizer Industry Overview
The Germany Fertilizer Market is fragmented, with the top five companies occupying 32.74%. The major players in this market are AGROFERT, EuroChem Group, Grupa Azoty S.A. (Compo Expert), K+S Aktiengesellschaft and Yara International ASA (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Acreage Of Major Crop Types
- 4.1.1 Field Crops
- 4.1.2 Horticultural Crops
- 4.2 Average Nutrient Application Rates
- 4.2.1 Micronutrients
- 4.2.1.1 Field Crops
- 4.2.1.2 Horticultural Crops
- 4.2.2 Primary Nutrients
- 4.2.2.1 Field Crops
- 4.2.2.2 Horticultural Crops
- 4.2.3 Secondary Macronutrients
- 4.2.3.1 Field Crops
- 4.2.3.2 Horticultural Crops
- 4.2.1 Micronutrients
- 4.3 Agricultural Land Equipped For Irrigation
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD and Volume, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Type
- 5.1.1 Complex
- 5.1.2 Straight
- 5.1.2.1 Micronutrients
- 5.1.2.1.1 Boron
- 5.1.2.1.2 Copper
- 5.1.2.1.3 Iron
- 5.1.2.1.4 Manganese
- 5.1.2.1.5 Molybdenum
- 5.1.2.1.6 Zinc
- 5.1.2.1.7 Others
- 5.1.2.2 Nitrogenous
- 5.1.2.2.1 Urea
- 5.1.2.2.2 Others
- 5.1.2.3 Phosphatic
- 5.1.2.3.1 DAP
- 5.1.2.3.2 MAP
- 5.1.2.3.3 SSP
- 5.1.2.3.4 TSP
- 5.1.2.4 Potassic
- 5.1.2.4.1 MoP
- 5.1.2.4.2 SoP
- 5.1.2.5 Secondary Macronutrients
- 5.1.2.5.1 Calcium
- 5.1.2.5.2 Magnesium
- 5.1.2.5.3 Sulfur
- 5.2 Form
- 5.2.1 Conventional
- 5.2.2 Speciality
- 5.2.2.1 CRF
- 5.2.2.2 Liquid Fertilizer
- 5.2.2.3 SRF
- 5.2.2.4 Water Soluble
- 5.3 Application Mode
- 5.3.1 Fertigation
- 5.3.2 Foliar
- 5.3.3 Soil
- 5.4 Crop Type
- 5.4.1 Field Crops
- 5.4.2 Horticultural Crops
- 5.4.3 Turf & Ornamental
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 AGLUKON Spezialduenger GmbH & Co.
- 6.4.2 AGROFERT
- 6.4.3 EuroChem Group
- 6.4.4 Grupa Azoty S.A. (Compo Expert)
- 6.4.5 ICL Group Ltd
- 6.4.6 K+S Aktiengesellschaft
- 6.4.7 Nouryon
- 6.4.8 PhosAgro Group of Companies
- 6.4.9 Sociedad Quimica y Minera de Chile SA
- 6.4.10 Yara International ASA
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR FERTILIZER CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms


