
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1651059
北米の郵便サービス:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025~2030年)North America Postal Services - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 北米の郵便サービス:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年02月03日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 120 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
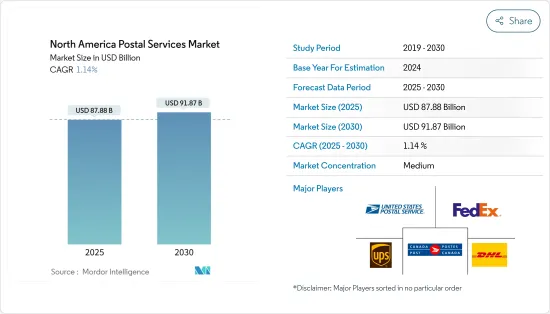
北米の郵便サービスの市場規模は2025年に878億8,000万米ドルと推定され、予測期間(2025-2030年)のCAGRは1.14%で、2030年には918億7,000万米ドルに達すると予測されます。
主なハイライト
- 北米では、デジタル通信の台頭により従来の郵便物の量が減少しています。同時に、eコマースの隆盛が宅配便やラストワンマイル・ロジスティクスの需要拡大に拍車をかけています。こうした相互関連的な動向は郵便業界に変革をもたらし、郵便事業者にサービスの拡大と業務の近代化を促しています。米国郵便公社(USPS)は米国の正式な郵便事業体です。USPSのエクスプレス・メールと直接競合するフェデックスとUPSは、緊急の手紙や小包の全国配達サービスを提供しています。
- 米国郵便公社は、その独占力を活用し、他の宅配業者が緊急でない手紙を配達することを制限し、住宅や事業所の米国の郵便受けに発送することを禁止しています。少数の例外を除き、USPSは、私設書簡配達人に罰金と投獄の可能性を課す私設速達法令に支えられ、書簡配達の法的独占を維持しています。カナダでは、カナダポストが支配的な地位を占めており、小包と従来の郵便物の大半を扱っています。政府が運営するこのサービスは多くのカナダ人の信頼を得ており、小包の3通に2通を発送しています。
- 2023年、米国の小包収入は7年ぶりに減少し、2022年の1,984億米ドルから1,979億米ドルに減少しました。この減少は、小包の総輸送量が2022年の215億個から2023年の217億個へと0.5%のわずかな増加を見せたにもかかわらず生じたものです。毎年恒例の米国宅配便出荷指数によると、4つの主要輸送業者(米国郵便公社、アマゾン・ロジスティクス、UPS、フェデックス)のうち、アマゾン・ロジスティクスだけが前年比15.7%増と大幅な伸びを記録しました。さらに、アマゾン・ロジスティクスは小包取扱量でフェデックスとUPSを上回り、市場リーダーのUSPSに急接近しています。情報筋によると、小規模な運送会社を含む「その他」のカテゴリーは、売上高と取扱量の両方で大幅に増加し、2023年の市場シェアは28.5%増加し、約3%(約6億個の小包)に達しました。情報筋によると、2023年の小包取扱量はUSPSが66億個(前年比約1%減)でトップ、次いでアマゾン・ロジスティクスが59億個(同15.7%増)、UPSが46億個(同10.3%減)、フェデックスが39億個(同6.1%減)となっています。
- 近年、北米の郵便サービス業界はデジタル化の進展による混乱の状況に直面しています。コミュニケーションのオンライン化が進むにつれ、従来の郵便配達事業は衰退の一途をたどっています。同時に、業界は拡大するeコマース小包市場における熾烈な競争に直面しています。その結果、郵便・メーリング事業体は、国営の独占企業から、多様なポートフォリオを持つ営利企業へと進化しつつあります。
北米の郵便サービス市場の動向
米国が市場で明確な優位性を示す
パンデミックの後、米国のeコマースは空前の成長を遂げ、他の多くの国々の動向を反映するようになった。人口3億3,200万人の米国は、インドと中国に次いで世界で3番目に人口の多い国です。特筆すべきは、アメリカのインターネット・ユーザーの80%近くがオンライン・ショッピングを利用していることです。このeコマースの急増は、郵便事業にとって大きなチャンスです。消費者が新興のeコマース・プラットフォームや従来の実店舗のオンライン化をますます利用するようになるにつれ、効率的な配達・集荷チャネルへの需要が高まっています。確立された全国ネットワークとラストワンマイルデリバリーの専門知識を活用することで、郵便事業はこの進化する状況において価値あるパートナーとしての地位を確立しつつあります。2024年第2四半期までに、米国のeコマース売上高は2,916億4,000万米ドルに達し、小売売上高全体の15.9%を占める。今年上半期、米国のeコマース売上高は5,794億5,000万米ドルに急増し、年末には1兆2,200億米ドルに達するとの予測もあります。eコマースの継続的な成長は、デジタル経済を支える郵便サービスの重要な役割を浮き彫りにしています。
書状量は減少傾向
米国郵政公社(USPS)は米国の正式な郵便当局です。2006年の約2,130億通をピークに、USPSの郵便物量は毎年一貫して減少しています。2023年には、配達数はわずか1,161億5,000万通にまで激減しています。この減少は主に、伝統的な郵便物、マーケティング資料、定期刊行物の数量減少によるものです。これとは対照的に、小包配送の収入は急増しています。この変革の主なきっかけはテクノロジーです。多くのアメリカ人がEメールを利用するようになり、従来の郵便物に対する需要が減少しています。さらに、米国のオンライン小売売上は過去10年間で倍増し、小包配送の需要が高まっています。カナダの正式な郵便サービスであるカナダポストも、この動向を反映しています。
北米の郵便サービス業界の概要
業界は現在、細分化されています。大企業は広範なインフラとサービスの多様性で優位に立っています。小規模企業は専門化することで競争しています。政府所有の郵便局は通常、郵便配達を独占しているが、民間の荷物配達会社との激しい競争に直面しています。競合する事業体は、互いの強みを生かすために提携を結ぶ。例えば、大手速達業者のフェデラル・エクスプレス(FedEx)とユナイテッド・パーセル・サービス(UPS)は、特定の住宅配達を米国郵政公社(USPS)に委託し、USPSは航空輸送をFedExとUPSに委託しています。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリスト・サポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場力学と洞察
- 現在の市場シナリオ
- 市場促進要因
- 電子商取引の増加
- 当日・翌日配送の拡大
- 市場抑制要因
- 人件費の上昇
- サイバーセキュリティとメールセキュリティ
- 市場機会
- 自動化と技術の向上
- バリューチェーン/サプライチェーン分析
- 業界の魅力- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 買い手/消費者の交渉力
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係の強さ
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- タイプ別
- 速達郵便サービス
- 定型郵便サービス
- 品目別
- レター
- 小包
- 宛先別
- 国内
- 国際
- 地域別
- 米国
- カナダ
- メキシコ
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度の概要
- 企業プロファイル
- USPS
- Canada Post Corporation
- UPS
- DHL
- FedEX
- Purolator
- Correos de Mexico
- Estafeta
- GLS
- APC Postal Logistics
- Santa Lucia Post
- Grenada Postal Corporation
- Paquetexpress
第7章 市場の将来
第8章 付録
- マクロ経済指標
- 輸送・保管のGDP寄与度
The North America Postal Services Market size is estimated at USD 87.88 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 91.87 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 1.14% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- In North America, the rise of digital communication has diminished the volume of traditional mail. At the same time, the flourishing e-commerce sector has spurred greater demand for parcel delivery and last-mile logistics. These interconnected trends are transforming the industry, prompting postal operators to expand their services and modernize their operations. The United States Postal Service (USPS) is the official postal entity in the USA. FedEx and UPS, in direct competition with USPS's Express Mail, provide nationwide delivery services for urgent letters and packages.
- Leveraging its monopoly, USPS restricts other U.S. couriers from delivering non-urgent letters and prohibits them from shipping to U.S. mailboxes at residential and business locations. With few exceptions, USPS maintains a legal monopoly on letter delivery, backed by the Private Express Statutes, which impose fines and potential imprisonment on private letter carriers. In Canada, Canada Post is the dominant player, overseeing the majority of both package and traditional mail shipments. This government-run service enjoys the trust of many Canadians, managing the shipment of two out of every three parcels.
- In 2023, US parcel revenue saw its first dip in seven years, falling from USD198.4bn in 2022 to USD197.9bn. This decline came despite a modest 0.5% uptick in total parcel volume, which rose from 21.5 billion in 2022 to 21.7 billion in 2023. The annual US Parcel Shipping Index reveals that among the four primary carriers (USPS, Amazon Logistics, UPS, and FedEx), only Amazon Logistics registered a significant year-over-year (YoY) volume surge of 15.7%. Moreover, Amazon Logistics has surpassed both FedEx and UPS in parcel volumes and is rapidly approaching the market leader, USPS. Sources indicate that the 'others' category, which includes smaller carriers, saw a substantial uptick in both revenue and volume, enhancing their market share by 28.5% in 2023, bringing it to nearly 3%, or about 0.6 billion parcels. According to the sources, in 2023, USPS led in parcel volume with 6.6 billion parcels (a nearly 1% YoY decline), followed by Amazon Logistics at 5.9 billion parcels (a 15.7% increase), UPS with 4.6 billion parcels (a 10.3% decrease), and FedEx at 3.9 billion parcels (down 6.1%).
- In recent years, North America's postal service industry has faced disruptions from the digital landscape. As communication increasingly migrates online, the traditional mail delivery business is witnessing a decline. Concurrently, the industry is grappling with fierce competition in the expanding e-commerce parcel market. As a result, postal and mailing entities are evolving from state-owned monopolies to commercial firms with diversified portfolios.
North America Postal Services Market Trends
United States exhibits a clear dominance in the market
In the wake of the pandemic, e-commerce in the United States has experienced unprecedented growth, mirroring trends seen in many other countries. With a population of 332 million, the U.S. ranks as the world's third most populous nation, trailing only India and China. Notably, nearly 80% of American internet users engage in online shopping. This surge in e-commerce presents a significant opportunity for postal services. As consumers increasingly turn to both emerging e-commerce platforms and traditional brick-and-mortar stores transitioning online, the demand for efficient delivery and collection channels has intensified. Leveraging their established national networks and expertise in last-mile delivery, postal services are positioning themselves as valuable partners in this evolving landscape. By Q2 2024, e-commerce sales in the U.S. reached USD 291.64 billion, constituting 15.9% of the nation's total retail sales. In the first half of the year, U.S. e-commerce sales soared to USD 579.45 billion, with projections suggesting a climb to USD 1.22 trillion by year's end. The continued growth of e-commerce underscores the critical role of postal services in supporting the digital economy.
Letter Volume is on Decline
The U.S. Postal Service (USPS) stands as the official postal authority in the United States. After peaking at approximately 213 billion units in 2006, USPS has witnessed a consistent annual decline in mail volume. By 2023, deliveries had plummeted to a mere 116.15 billion units. This decline is primarily due to reduced volumes in traditional mail, marketing materials, and periodicals. In contrast, revenue from package shipping has surged. Technology is the primary catalyst for this transformation. An increasing number of Americans are turning to email, leading to a reduced appetite for traditional mail. Additionally, U.S. online retail sales have doubled in the last decade, heightening the demand for package deliveries. Canada Post, Canada's official postal service, mirrors this trend.
North America Postal Services Industry Overview
The industry is currently fragmented. Large companies have advantages in widespread infrastructure and diversity of services. Small companies compete by specializing. Government-owned postal agencies typically have a monopoly on mail delivery but face heavy competition from private package delivery companies. The competing entities form partnerships to capitalize on each other's strengths. For instance, major express delivery companies Federal Express (FedEx) and United Parcel Service (UPS) contract certain residential deliveries to the US Postal Service (USPS), while the USPS contracts air transportation out to FedEx and UPS.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS AND DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rise In Ecommerce
- 4.2.2 Expansion of Same Day and Next- Day Delivery
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Rising Labor Costs
- 4.3.2 Cybersecurity and Mail Security
- 4.4 Market Opportunities
- 4.4.1 Increased Automation and Technology
- 4.5 Value Chain / Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.6 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Express Postal Services
- 5.1.2 Standard Postal Services
- 5.2 By Item
- 5.2.1 Letter
- 5.2.2 Parcel
- 5.3 By Destination
- 5.3.1 Domestic
- 5.3.2 International
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 US
- 5.4.2 Canada
- 5.4.3 Mexico
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 USPS
- 6.2.2 Canada Post Corporation
- 6.2.3 UPS
- 6.2.4 DHL
- 6.2.5 FedEX
- 6.2.6 Purolator
- 6.2.7 Correos de Mexico
- 6.2.8 Estafeta
- 6.2.9 GLS
- 6.2.10 APC Postal Logistics
- 6.2.11 Santa Lucia Post
- 6.2.12 Grenada Postal Corporation
- 6.2.13 Paquetexpress*
7 FUTURE OF THE MARKET
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Macroeconomic Indicators
- 8.2 Contribution of Transportation and Storage to GDP


