|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1644949
半導体ロジスティクス:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Semiconductor Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 半導体ロジスティクス:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年01月05日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 150 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
半導体ロジスティクス市場は予測期間中に7%を超えるCAGRで推移する見込みです。
主なハイライト
- スマートデバイスの需要増加、持続可能な生産方法の必要性、人材育成の重要性、APACの半導体市場シェアの伸びが半導体ロジスティクス産業を形成します。しかし、COVID-19によるサプライチェーンと労働力の混乱は、世界のチップ不足の危機を招き、米国と中国の間で続く貿易摩擦やロシアでの紛争によって悪化していました。技術進歩のペースは速まると思われます。5Gネットワークとモノのインターネットの構築は、コネクティビティと自動化のための基盤をすでに築いています。
- 市場の需要を満たす製造能力の不足は、半導体サプライチェーンの多くの側面に浸透している主要なテーマ動向です。半導体は、多くの再生可能エネルギー・アプリケーション、電気自動車、スマートフォンやその他のパーソナル・エレクトロニクス、データセンター、さらには防衛兵器に至るまで、必要不可欠な部品です。しかしその裏では、今日の半導体企業は多くの課題に直面しています。工場がフル稼働しても需要を満たすことができず、その結果、製品のリードタイムは6ヵ月以上となっています。現在進行中の半導体不足は、特に自動車OEMが自動車生産の遅れを余儀なくされるなど、定期的な見出しを飾っています。さらに、半導体企業は設計の複雑化、人材不足、パンデミック関連の問題に対処しており、これらはすべて、さまざまな市場のプレーヤーをつなぐ複雑で世界なサプライチェーンを混乱させています。
- 半導体業界は、この2年間の物流の課題を、抜本的な対策が必要だという警鐘と受け止めなければならないです。COVID-19が施行されたとき、多くの企業で売上が大幅に減少しました。自動車産業はバイヤーの80%を失い、その結果、半導体需要が激減しました。世界の半導体不足は2024年まで続くという予測もあります。2020年から2022年にかけて、このような不足が世界経済に5,000億米ドル以上の損害を与えたと推定されています。直接的な経済的影響よりも深刻なのは、こうした供給不足によって半導体のサプライチェーンが不十分であることが明らかになったことです。いくつかの明らかな欠陥が露呈しており、それらに対処するには、単に受注残を取り戻すだけでは不十分です。
- 半導体企業の将来は、抜本的な対策が必要であることを示すシグナルとして、物流の課題に対抗する方法を見つけるかどうかにかかっています。半導体の需要は増加の一途をたどっているため、より効率的にエンドユーザーに半導体を届けることができる企業が、今後数年間で最も恩恵を受けることになると思われます。半導体のバリューチェーンは異例なほど複雑で、材料や装置のサプライヤーの世界なネットワークに依存しています。そのため、効率的なサプライチェーン・マネジメントが非常に難しく、過剰在庫や日常的なボトルネックが発生します。その好例が貨物管理です。港の混雑からコンテナの不足に至るまで、貨物の問題はリードタイムの長期化や出荷遅延の長期化を招く。サプライチェーンに影響を与えるその他の要因には、湿度、衝撃、盗難などがあります。しかし、出荷の進捗に関する正確なデータやGPS追跡がなければ、リーダーはしばしば暗闇の中で業務を行うことになります。
半導体ロジスティクス市場の動向
半導体需要の増加が市場を牽引
2020年以降、世界のチップ不足が深刻化し、価格上昇が半導体業界の決定的な動向となっています。川上の材料メーカーや装置メーカーは供給不足に直面し、チップメーカーは製品ラインを拡大するために投資を増やすこともあり、川下の半導体企業は大きな利益を上げています。全体として、パネル駆動用IC、民生用MCU、メモリーチップなどの供給不足は緩和され始め、価格下落の始まりを告げています。しかし、一部のパワー半導体チップ、特に車載、産業制御、IoTなどの分野で使用されるチップは依然として品薄が続いています。
その最大の理由は、DRAMが市場の循環変動に伴い、一気に価格下落動向に入ったことです。世界最大のメモリー・チップ生産国である韓国では、チップ在庫が過去4年間で最大に増加しました。韓国統計庁が2022年6月に発表した統計によると、同国のチップ在庫は2021年同期比で53.4%増加し、2021年10月以降も着実に増加しています。スマートフォンやパソコン、コンシューマー向けアプリケーションの需要が落ち込むと、電子製品に使用されるメモリーチップの世界の需要も落ち込みます。サーバー需要は比較的強いもの、在庫水準が高いため、メモリーチップ価格は2022年後半も下落が続くと思われます。
コンシューマー市場の下落傾向はストレージ市場の循環的変化を加速させ、MCUチップも影響を受ける。携帯電話やパソコンに代表されるコンシューマーエレクトロニクスは近年減少傾向を示しており、2022年通年ではマイナス成長となる可能性が高いです。こうした動向を受け、今年4月には家電向け端末チップの受注キャンセルが最大30%に達する可能性があるとのニュースが流れ、商品準備に追われる端末メーカーやサプライチェーンに大きな在庫圧力がかかった。民生用電子端末の注文キャンセルは、今やチップメーカーにも徐々に波及しています。
先端技術と付加価値サービスの利用が市場を牽引
半導体のサプライチェーンやロジスティクスの可視性が低いため、重要な意思決定が不十分なまま行われています。トラック市場が断片化し、輸送コンテナのコストが急騰する中、リーダーは選択肢を確認し、さまざまな行動方針を比較できなければならないです。しかし、そのためには一元化された信頼できるリアルタイムデータが必要です。83%の企業が、パンデミック以前よりも輸送封鎖に関連するリスクを認識していると回答しているが、それでも適切な可視化を可能にする適切なテクノロジーを見つける必要があります。パンデミックは、単一の事象が半導体サプライチェーン全体に連鎖的な影響を及ぼし、いかに破壊的であり得るかを例証しています。このことは、サプライチェーンの柔軟性、つまり需要に合わせて材料の購入、生産レベル、輸送能力を調整する能力の重要性を浮き彫りにしています。しかし、このことを認識することは非常に難しいです。
半導体のサプライチェーンにおいて、単一のパートナーに過度に依存することは問題です。サプライチェーンの強靭性を確保するために、半導体企業は、材料サプライヤーであれ、製造拠点であれ、運送業者であれ、複数のパートナーへのアクセスを必要としています。一方、複数のパートナーにアクセスすることは、それほど簡単ではないです。特に、多くのブローカーが隠れたバイアスを抱えている場合はなおさらです。つまり、リーダーは、非常に複雑な複数の市場を自力でナビゲートするか、完全な公平性をもってプロバイダーと接続できるパートナーを見つけなければならないです。もうひとつの問題は信頼です。柔軟性を確保するためには、企業が規制を遵守するために信頼できる複数のプロバイダーを用意する必要があります。つまり、企業は広範なデューデリジェンスを実施するか、完全な透明性をもってこの責任を委任できるパートナーを見つけなければならないです。
半導体ロジスティクス業界の概要
半導体ロジスティクス市場は競争が激しく断片化されており、多数の地元企業、地域企業、少数の世界企業が市場に参入しています。主なプレーヤーは、DHL、日本通運、郵船ロジスティクス、DBシェンカー、Kuehne+Nagelなどです。半導体のサプライチェーンとロジスティクスを明確にするための適切かつ高度な技術の使用は、企業間に違いをもたらすと思われます。世界プレーヤーは、地域や地元のプレーヤーと比較して、サービスの利用可能性により、この市場で良好なシェアを保持しています。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリスト・サポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
- 分析方法
- 調査フェーズ
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場力学
- 現在の市場シナリオ
- 市場概要
- 市場力学
- 促進要因
- 抑制要因
- 機会
- バリューチェーン/サプライチェーン分析
- 業界の魅力度-ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 買い手/消費者の交渉力
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係の強さ
- COVID-19が市場に与える影響
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 機能別
- 輸送
- 道路
- 鉄道
- 水路・海路
- 航空
- 倉庫・流通
- 付加価値サービス(梱包、通関、貨物仲介、その他サービス)
- 輸送
- 仕向地別
- 国内
- 国際
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度の概要
- 企業プロファイル
- DHL
- Nippon Express
- Yusen Logistics
- DB Schenker
- Kuehne+Nagel
- Omni Logistics
- Dimerco
- CEVA Logistics
- HOYER Group
- MAERSK
- Dintec Shipping Express
第7章 市場の将来
第8章 付録
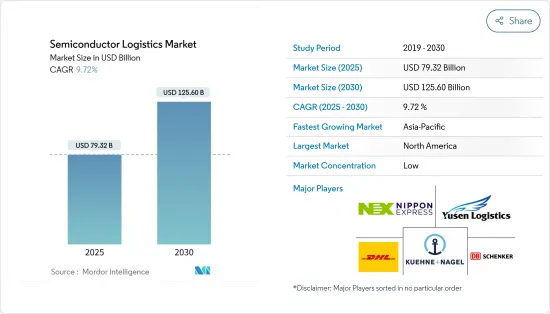
The Semiconductor Logistics Market is expected to register a CAGR of greater than 7% during the forecast period.

Key Highlights
- There has been an increasing demand for smart devices, the need for sustainable production methods, the importance of cultivating a talent pool, and growth in APAC's semiconductor market share will shape the semiconductor logistics industry. However, supply chain and labour disruptions caused by COVID-19 had resulted in a worldwide chip shortage crisis, which had been exacerbated by ongoing trade tensions between the US and China, as well as conflict in Russia. The pace of technological advancement will quicken. The construction of 5G networks and the Internet of Things has already laid the groundwork for connectivity and automation.
- Insufficient manufacturing capacity to meet market demand is a key thematic trend permeating many facets of the semiconductor supply chain. Semiconductors are essential components in many renewable energy applications, electric vehicles, smartphones and other personal electronics, data centres, and even defence weapons. However, behind the scenes, today's semiconductor companies are facing a slew of challenges. Even at full capacity, fabs have been unable to meet demand, resulting in product lead times of six months or longer. The ongoing semiconductor shortage is now making headlines regularly, especially when it forces automotive OEMs to delay vehicle production. Furthermore, semiconductor firms are dealing with increased design complexity, a talent shortage, and pandemic-related issues, all of which are disrupting the complex, global supply chain that connects players in different markets.
- The semiconductor industry must see the logistical challenges of the last two years as a wake-up call that drastic action is required. When COVID-19 went into effect, many businesses saw a significant drop in sales. The automotive industry lost 80% of its buyers, resulting in a sharp drop in semiconductor demand. Some predict a global semiconductor shortage that will last until 2024. Between 2020 and 2022, it was estimated that these shortages cost the global economy more than USD 500 billion. Worse than the immediate financial impact, these shortages have revealed that semiconductor supply chains are inadequate. Several obvious flaws have been exposed, and addressing them requires more than simply catching up on order backlogs.
- The future of semiconductor companies is dependent on finding a way to compete with logistical challenges as a signal that drastic action is required. Because the demand for semiconductors is only going to increase, those who can get them to end users more efficiently will be the ones to benefit the most in the coming years. The semiconductor value chain is unusually complex, relying on a global network of material and equipment suppliers. This makes efficient supply chain management extremely difficult, resulting in excess stock and routine bottlenecks. A good example is freight management. Freight issues, ranging from port congestion to container shortages, can result in longer lead times and longer shipment delays. Other factors influencing the supply chain include humidity, shock impact, and theft. But without precise data on the progress of shipments and GPS tracking, leaders are often left operating in the dark.
Semiconductor Logistics Market Trends
Increasing demand for semiconductor driving the market
Since 2020, the global chip shortage has worsened, with price increases being the semiconductor industry's defining trend. Upstream material and equipment manufacturers are facing supply shortages, chipmakers have increased investments to expand their product lines on occasion, and downstream semiconductor companies have made significant profits. Overall, the supply shortage of panel drive IC, consumer-grade MCU, memory chips, and other products have begun to ease, signalling the start of a price decrease. However, some power semiconductor chips, particularly those used in automotive, industrial control, IoT, and other fields, remain scarce.
The primary reason for this is that DRAM has quickly entered a downward price trend as the market undergoes cyclical changes. South Korea, the world's largest memory chip producer, has seen the largest increase in chip inventory in more than four years. According to statistics released by the South Korean statistics office in June 2022, the country's chip inventory increased by 53.4% over the same period in 2021 and has been steadily increasing since October 2021. As demand for smartphones, PCs, and consumer applications falls, global demand for memory chips used in electronic products falls. Despite relatively strong server demand, memory chip prices will continue to fall in the second half of 2022 as a result of high inventory levels.
The consumer market's downward trend has accelerated the cyclical changes in the storage market, and MCU chips are also affected. Consumer electronics, as represented by mobile phones and computers, have shown a downward trend in recent years, with likely negative growth in the entire year of 2022. According to this trend, news circulated in April of this year that terminal chips for consumer electronics could face up to 30% order cancellations, putting huge inventory pressure on the supply chain and terminal manufacturers who were busy preparing goods. Order cancellations from consumer electronic terminals have now gradually spread to chip manufacturers.
Increasing use of advanced technology and value-added services driving the market
Key decisions are made with insufficient insight as there is less visibility in the semiconductor supply chain and logistics. Leaders must be able to see their options and compare different courses of action as truck markets fragment and shipping container costs spiral. However, this requires centralized, dependable real-time data. While 83% of businesses say they are more aware of the risks associated with transportation blockades than they were before the pandemic, they still need to find the right technology to enable proper visibility. The pandemic exemplified how disruptive a single event can be, causing cascading effects across entire semiconductor supply chains. This highlights the critical importance of supply chain flexibility - the ability to adjust material purchases, production levels, and transportation capacity to meet demand. However, acknowledging this proves extremely tough.
Overreliance on single partners in semiconductor supply chains is a problem. To ensure the resilience of their supply chains, semiconductor companies require access to multiple partners, whether it's a material supplier, manufacturing base, or freight provider. Gaining access to multiple partners, on the other hand, is not so simple, especially when many brokers have hidden biases. This means that leaders must either navigate multiple highly complex markets on their own or find a partner who can connect them with providers with complete impartiality. Another issue is trust: flexibility necessitates companies having multiple providers they can trust to comply with regulations. This means they must either conduct extensive due diligence or find a partner to whom they can delegate this responsibility in complete transparency.
Semiconductor Logistics Industry Overview
The Semiconductor Logistics Market is highly competitive and fragmented with a large number of local, regional and a few global players penetrating the market. Major players are DHL, Nippon Express, Yusen Logistics, DB Schenker, Kuehne+Nagel, and many more. The use of proper and advanced technology to bring clarity in the semiconductor supply chain and logisitcs is going to bring a difference between the companies. Global players hold a good share in this market due to availibility of services compared to the regional and local players.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Method
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Market Overview
- 4.3 Market Dynamics
- 4.3.1 Drivers
- 4.3.2 Restraints
- 4.3.3 Opportunities
- 4.4 Value Chain / Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.5.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.6 Impact of the COVID-19 on the Market
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Function
- 5.1.1 Transportation
- 5.1.1.1 Roadways
- 5.1.1.2 Railways
- 5.1.1.3 Water and Seaways
- 5.1.1.4 Airways
- 5.1.2 Warehousing and Distribution
- 5.1.3 Value-added Services (Packaging, Customs Clearance, Freight Brokerage, and Other Services)
- 5.1.1 Transportation
- 5.2 By Destination
- 5.2.1 Domestic
- 5.2.2 International
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 DHL
- 6.2.2 Nippon Express
- 6.2.3 Yusen Logistics
- 6.2.4 DB Schenker
- 6.2.5 Kuehne+Nagel
- 6.2.6 Omni Logistics
- 6.2.7 Dimerco
- 6.2.8 CEVA Logistics
- 6.2.9 HOYER Group
- 6.2.10 MAERSK
- 6.2.11 Dintec Shipping Express*