
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1636209
北米の自治体固形廃棄物管理-市場シェア分析、産業動向と統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)North America Municipal Solid Waste Management - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 北米の自治体固形廃棄物管理-市場シェア分析、産業動向と統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年01月05日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 150 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
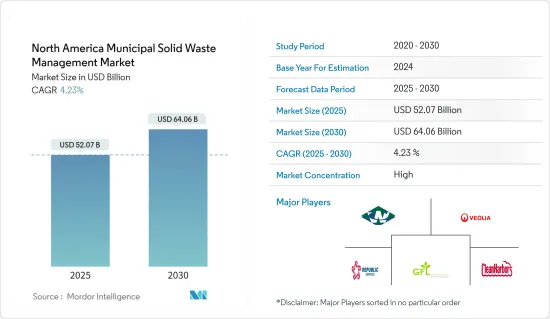
北米の自治体固形廃棄物管理市場規模は2025年に520億7,000万米ドルと推定・予測され、予測期間中(2025~2030年)のCAGRは4.23%で、2030年には640億6,000万米ドルに達すると予測されます。
北米の自治体固形廃棄物(MSW)管理市場は、環境サービス産業において極めて重要です。この市場には、住宅、商業施設、工業施設から出る固形廃棄物の収集、輸送、処理、リサイクル、処分が含まれます。北米、特に米国とカナダは、MSW管理市場に大きく貢献しています。廃棄物発生量の増加と先進的な廃棄物管理手法の採用を考えると、市場は今後数年で安定した成長を遂げると考えられます。
米国における自治体固形廃棄物(MSW)の管理は、概して満足のいくものです。民間団体が主にMSWの輸送と処分を行い、十分な資金を確保しています。米国では年間約2億5,800万トンのMSWが排出されています。このうち約53%は埋立地に運ばれ、この数字は安定しています。現在、MSWの34.6%はリサイクルされ、12.8%はエネルギー生成のために焼却されています。
米国資源保存回収法(RCRA)のような、連邦、州、地方レベルでの厳しい環境規制が、適切な廃棄物管理の重要性を強調しています。自治体化と人口増加は廃棄物発生量の増加に直結しており、スケーラブルな廃棄物管理ソリューションが必要とされています。
国民の意識と政府の取り組みが、リサイクル、廃棄物削減、廃棄物エネルギー化の推進を後押ししています。自動選別やIoTベースの廃棄物収集などの技術革新は、廃棄物管理プロセスの効率を高めています。また、経済開発と所得水準の上昇に伴い、消費量とそれに続く廃棄物発生量も増加し、先進的廃棄物管理サービスへの需要がさらに高まっています。
北米の自治体廃棄物管理市場の動向
自治体固形廃棄物成長の主要原動力は食品廃棄物の増加
毎年、アメリカ人は何10億ポンドもの食品廃棄物を生み出し、環境と経済に大きな影響を与えています。平均すると、米国人は年間400ポンド(181kg)以上の食品を廃棄しており、これは米国全体の食料供給の30~40%に相当します。この憂慮すべき傾向には、食品サプライチェーンにおける持続不可能なプラクティス、小売業者や消費者が設定する厳しい美的基準、しばしば無知な消費者行動など、いくつかの要因があります。
温室効果ガスの排出量の増加、水資源の浪費、経済の大幅な後退など、この廃棄物の影響は広範囲に及びます。しかし、余剰食品をフードバンクや教会などの団体に寄付するなどの取り組みが、食品廃棄と闘い、国内の食糧不安に対処しています。また、家庭での堆肥化も重要な戦略として浮上しており、食品を埋立地から転換し、温室効果ガスの排出を抑制しています。
米国の食品廃棄の規模は驚異的で、米国人は年間1,080億ポンド(約490億kg)という途方もない量を浪費しており、その量は着実に増加しています。この廃棄物は、持続不可能な食品生産と輸送方法、果物や野菜に対する完璧に近い美観へのこだわり、無数の消費習慣に寄与しています。このような食品廃棄の横行がもたらす結果は悲惨で、二酸化炭素やメタンの大量排出、水資源の汚染と枯渇、多大な経済的損失につながります。しかし、余剰食品を再分配し、家庭での堆肥化を促進することで、米国は年間の食品廃棄量を大幅に削減することができます。
米国における食品廃棄物は、埋立地の主要廃棄物という不名誉な地位にあり、全自治体固形廃棄物の24.1%を占めています。アメリカ人は野菜と果物の46%、魚介類の35%、肉の21%、乳製品の17%を廃棄しています。米国では年間、食料供給の30%から40%が廃棄されています。
米国における食品廃棄の規模は憂慮すべきもので、環境と経済に大きな影響を及ぼします。食品の再分配や家庭での堆肥化などの取り組みを通じてこの問題に対処することで、その影響を大幅に緩和し、持続可能性を促進し、食糧不安を軽減することができます。
自治体人口の拡大が米国の自治体固形廃棄物管理市場の成長を促す
米国の自治体固形廃棄物管理市場は、可処分所得の上昇に伴う自治体人口の増加によって牽引されており、この動向は市場の成長に大きな影響を与えると考えられています。
米国全体では、ほとんどのゴミは埋立処分か焼却処分されています。焼却はゴミの量を90%、重量を75%削減します。しかし、焼却と埋め立ての両方が、環境への著しい脅威となっています。そのため、多くの州の施策立案者は、サステイナブル廃棄物管理を提唱するようになっており、特にリサイクルに力を入れています。リサイクルプロセスでは、分別された廃棄物が様々な有用な材料に再加工されます。
米国の自治体廃棄物管理市場は、著しい改善を見せています。環境に優しい廃棄物処理の促進を目的とした厳しい規制が、市場を強化しています。各地域は現在、リサイクルと堆肥化AD産業への投資を強化しています。
COVID-19の大流行は、米国の廃棄物管理会社に課題を提起しました。特に閉鎖中の廃棄物処理の物流上の複雑さを考えると、労働力の継続性と業務効率を維持するための支援が必要でした。
プラスチックの使用を抑制する規制は、特に包装や新聞、コップ、ティッシュペーパーなどの非耐久性商品における紙と板紙の消費に影響を与えました。一方、牛乳パック、袋、段ボール箱のような製品は包装・容器に該当し、リサイクル可能性が高いため、需要の急増と応用範囲の拡大につながっています。
米国環境保護庁によると、紙と板紙のリサイクル率は約65%で、全材料の中で最も高いです。さらに、これらの材料を焼却しても環境への影響は最小限であるため、廃棄物処理への選好をさらに高めています。
米国西部、南中部、南大西洋、北東部、太平洋の各州は、合計で米国の自治体廃棄物管理市場シェアの65%以上を占めています。この市場は、高度廃棄物処理技術への注目の高まりにより、大幅な成長を遂げようとしています。
自治体化、可処分所得の増加、環境に優しい規制が、米国の顕著な自治体廃棄物管理市場の成長に拍車をかけています。同市場は、サステイナブル廃棄物管理プラクティスの重視に支えられ、リサイクルと堆肥化に対する投資の高まりを目の当たりにしており、これが同市場の成長軌道を加速させることになります。
北米の自治体固形廃棄物管理産業概要
北米の自治体固形廃棄物管理市場は、一握りの重要な参入企業が大きな影響力を持つ、顕著な集中を示しています。この市場の主要企業は、Waste Connection、Veolia、GFL Environmental、Republic Services、Clean Harborsなどがあります。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の成果
- 調査の前提
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場力学
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- 環境問題に対する意識の高まり
- 急速な自治体化と人口増加
- 市場抑制要因
- 高い初期投資と運用コスト
- 市場機会
- 先進的廃棄物管理技術の採用
- バリューチェーン/サプライチェーン分析
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 買い手/消費者の交渉力
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係の強さ
- PESTLE分析
- 市場における技術革新に関する洞察
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 廃棄物タイプ別
- 紙・段ボール
- 電子廃棄物
- プラスチック廃棄物
- 金属廃棄物
- ガラスくず
- その他の廃棄物
- 発生源別
- 住宅廃棄物
- 商業
- 建設廃棄物
- その他
- 廃棄方法別
- 埋立
- 焼却
- リサイクル
- その他の処分方法
- 国別
- 米国
- カナダ
- メキシコ
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中の概要
- 企業プロファイル
- Waste Management
- Republic Services
- Waste Connections
- Casella Waste Systems
- Advanced Disposal Services
- Clean Harbors
- GFL Environmental
- Veolia
- Covanta Holding Corporation
- Stericycle
- Rumpke Waste & Recycling
- EDCO Disposal Corporation
第7章 今後の動向
The North America Municipal Solid Waste Management Market size is estimated at USD 52.07 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 64.06 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.23% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

The North American municipal solid waste (MSW) management market is pivotal in the environmental services industry. It encompasses the collection, transportation, processing, recycling, and disposal of solid waste from residential, commercial, and industrial sources. North America, particularly the United States and Canada, significantly contributes to the MSW management market. Given the rising waste generation and the adoption of advanced waste management practices, the market is poised for steady growth in the coming years.
Managing municipal solid waste (MSW) in the United States is generally satisfactory. Private entities predominantly handle the transportation and disposal of MSW, ensuring adequate funding. Annually, Americans produce around 258 million tons of MSW. Of this, roughly 53% finds its way to landfills, a figure that has stabilized. Presently, 34.6% of MSW is recycled, while 12.8% is incinerated for energy generation.
Stringent environmental regulations at the federal, state, and local levels, such as the US Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), underscore the importance of proper waste management. Urbanization and population growth are directly linked to increased waste generation, necessitating scalable waste management solutions.
Public awareness and government initiatives drive the push for recycling, waste reduction, and waste-to-energy practices. Technological innovations, like automated sorting and IoT-based waste collection, are enhancing the efficiency of waste management processes. Also, as economic development and income levels rise, so does consumption and subsequent waste generation, further bolstering the demand for advanced waste management services.
North America Municipal Solid Waste Management Market Trends
The Primary Driver of Growth in Municipal Solid Waste is the Increasing Generation of Food Waste
Every year, Americans generate billions of pounds of food waste, significantly impacting the environment and the economy. On average, an American discards over 400 lbs (181 kg) of food annually, equating to a staggering 30%-40% of the entire US food supply. Several factors contribute to this alarming trend, including unsustainable practices in the food supply chain, stringent aesthetic standards set by retailers and consumers, and often uninformed consumer behavior.
The repercussions of this waste are far-reaching, encompassing heightened greenhouse gas emissions, squandered water resources, and substantial economic setbacks. However, initiatives like redirecting surplus food to entities such as food banks and churches combat food waste and address food insecurity in the nation. Also, household composting emerges as a pivotal strategy, diverting food from landfills and curbing greenhouse gas emissions.
The US food waste scale is staggering, with Americans squandering a colossal 108 billion lbs (49 billion kg) annually, steadily climbing. This waste contributes to unsustainable food production and transportation practices, the insistence on near-perfect aesthetics for fruits and vegetables, and a myriad of consumer habits. The consequences of this rampant food waste are dire, leading to significant carbon dioxide and methane emissions, contamination and depletion of water resources, and substantial economic losses. However, the nation can significantly reduce its annual food waste output by redistributing excess food and encouraging household composting.
Food waste in the United States holds the dubious distinction of being the primary material in landfills, constituting a substantial 24.1% of all municipal solid waste. Americans discard 46% of fruits and vegetables, 35% of seafood, 21% of meat, and 17% of dairy products. The United States discards 30% to 40% of its food supply annually.
The scale of food waste in the United States is alarming, with significant environmental and economic repercussions. Addressing this issue through initiatives like food redistribution and household composting can substantially mitigate its impact, promoting sustainability and reducing food insecurity.
An Expanding Urban Population is Driving Growth in the US Municipal Solid Waste Management Market
The US municipal solid waste management market is driven by a growing urban population with rising disposable incomes, a trend poised to impact market growth significantly.
Across the United States, most trash is either landfilled or incinerated. Incineration reduces waste volume and weight by 90% and 75%, respectively. However, both incineration and landfilling pose notable environmental threats. Consequently, policymakers in many states increasingly advocate for sustainable waste management, strongly focusing on recycling. In the recycling process, segregated waste is reprocessed into various useful materials.
The US municipal waste management market has seen marked improvements. Stringent regulatory mandates aimed at promoting eco-friendly waste disposal have bolstered the market. Regions are now ramping up investments in recycling and composting AD industries.
The COVID-19 pandemic raised challenges for waste management companies in the United States. They needed help maintaining workforce continuity and operational efficiency, especially given the logistical complexities of waste disposal during lockdowns.
Regulations that discourage plastic use have impacted the consumption of paper and paperboard, especially in packaging and non-durable goods like newspapers, cups, and tissue paper. On the other hand, products like milk cartons, bags, and corrugated boxes fall under packaging and containers and are highly recyclable, leading to a surge in demand and application scope.
According to the US Environmental Protection Agency, the recycling rate for paper and paperboard stood at nearly 65%, the highest among all materials. Moreover, incinerating these materials has minimal environmental impact, further fueling their preference for waste management.
The West, South Central, South Atlantic, Northeast, and Pacific States collectively hold over 65% of the US municipal waste management market share. This market is poised for substantial growth, driven by a heightened focus on advanced waste treatment technologies.
Urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and eco-friendly regulations fuel notable US municipal solid waste management market growth. The market is witnessing heightened investments in recycling and composting, underpinned by a robust emphasis on sustainable waste management practices, all set to amplify its growth trajectory.
North America Municipal Solid Waste Management Industry Overview
In North America, the municipal solid waste management market exhibits a notable concentration, with a handful of critical players holding significant sway. Some key players in this market are Waste Connection, Veolia, GFL Environmental, Republic Services, and Clean Harbors.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Deliverables
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
- 1.3 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Heightened Public Awareness of Environmental Concerns
- 4.2.2 Rapid Urbanization and Growing Population
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Initial Investment and Operational Costs
- 4.4 Market Opportunities
- 4.4.1 Adoption of Advanced Waste Management Technologies
- 4.5 Value Chain / Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.6 Porter's Five Force Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.7 PESTLE Analysis
- 4.8 Insights on technology Innovation in the Market
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Waste Type
- 5.1.1 Paper and Cardboard
- 5.1.2 E-waste
- 5.1.3 Plastic Waste
- 5.1.4 Metal Waste
- 5.1.5 Glass Waste
- 5.1.6 Other Waste Types
- 5.2 By Source
- 5.2.1 Residential
- 5.2.2 Commercial
- 5.2.3 Construction
- 5.2.4 Other Sources
- 5.3 By Disposal Methods
- 5.3.1 Landfill
- 5.3.2 Incineration
- 5.3.3 Recycling
- 5.3.4 Other Disposal Methods
- 5.4 By Country
- 5.4.1 United States
- 5.4.2 Canada
- 5.4.3 Mexico
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concetration Overview
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Waste Management
- 6.2.2 Republic Services
- 6.2.3 Waste Connections
- 6.2.4 Casella Waste Systems
- 6.2.5 Advanced Disposal Services
- 6.2.6 Clean Harbors
- 6.2.7 GFL Environmental
- 6.2.8 Veolia
- 6.2.9 Covanta Holding Corporation
- 6.2.10 Stericycle
- 6.2.11 Rumpke Waste & Recycling
- 6.2.12 EDCO Disposal Corporation


