
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1636191
インドのEPCM(設計・調達・建設管理):市場シェア分析、産業動向と統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)India Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| インドのEPCM(設計・調達・建設管理):市場シェア分析、産業動向と統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年01月05日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 150 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
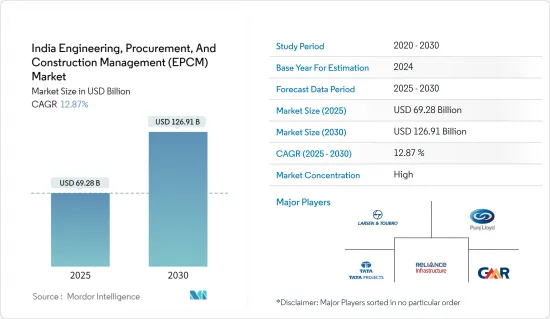
インドのEPCM(設計・調達・建設管理)市場規模は2025年に692億8,000万米ドルと推定され、予測期間(2025-2030年)のCAGRは12.87%で、2030年には1,269億1,000万米ドルに達すると予測されます。
主なハイライト
- インドの設計・調達・建設(EPC)市場は、国のインフラ整備において極めて重要な位置を占めています。この市場には、多様な産業にわたる動向、課題、機会が存在します。インドのEPC市場は堅調に成長しており、野心的なインフラ設計図と産業の進歩がその原動力となっています。政府の後押しと民間投資に支えられ、市場のCAGRは今後も勢いを維持する見通しです。注目すべき投資は、道路建設のためのBharatmalaプロジェクト、鉄道網の近代化、スマートシティミッションのような構想に注がれています。さらに、太陽光発電や風力発電などの再生可能エネルギー・プロジェクトが急増しています。
- また、火力発電所、水力発電所、原子力発電所の開発・拡張や、トランスミッションの強化も進んでいます。スマート・シティ・ミッション、AMRUT、Bharatmalaなどの主要なイニシアチブは、インドのインフラ成長へのコミットメントを強調しています。さらに、急速な工業化と都市化により、インフラ整備への需要が高まっています。最後に、FDI政策の自由化が国際的なEPCプレーヤーを引き寄せており、彼らは最先端の建設技術やプロジェクト管理ツールも取り入れています。
インドのEPCM(設計・調達・建設管理)市場動向
インフラ開発がEPCサービスの需要を牽引
インド政府は野心的なインフラ計画に着手しており、特にスマートシティミッション、高速道路のBharatmala Pariyojana、港湾のSagarmalaプロジェクトなどが挙げられます。スマート・シティ・ミッションは、中核インフラを強化し、生活の質を高め、クリーンで持続可能な環境を育成し、「スマート」ソリューションを導入することによって、都市を向上させることを目的としています。持続可能で包括的な成長を重視する同ミッションは、コンパクトな地域に重点を置き、他都市の指針となる再現可能なモデルの構築を目指しています。このイニシアチブは、単に個々の都市を変革するだけでなく、よりスマートな都心部を目指す全国的な動きを触媒するものです。
こうした取り組みは、インドのインフラ開発へのコミットメントを強調するものであり、EPCMサービスにとって大きなチャンスとなります。都市化が急速に進む中、地下鉄から空港、スマートシティプロジェクトに至るまで、都市インフラのアップグレードが急務となっています。同時に、製造業を強化することを目的とした「メイク・イン・インディア」キャンペーンが新工場や産業施設の建設に拍車をかけ、EPCMサービスの需要をさらに押し上げています。
メイク・イン・インディア」イニシアティブの世界の立ち上げは、インドが製造業に再び注力することを示すものでした。このイニシアチブの主な目標は、インドを世界の製造業の最有力候補として位置づけることです。発足以来、インド政府は製造、設計、技術革新、新興企業を強化するために数多くの改革を先導してきました。世界的に経済情勢が低迷する中、インドは7.5%の成長率を誇る最も成長著しい経済国として頭角を現し、その成長率は加速し続けています。Make in India」、「Digital India」、「100 Smart Cities」、「Skill India」などのイニシアチブは、この成長を推進する上で極めて重要な役割を果たしています。
「メイク・イン・インディア」は特に、インドを世界・サプライ・チェーンに組み込むことを目標としており、インド企業が世界な舞台で活躍する必要性を強調しています。インドは経済を大幅に自由化し、国防、鉄道、建設、保険、年金基金、医療機器などの分野を外国直接投資(FDI)に開放しました。この動きは、インドを世界で最も開放的な経済のひとつに位置づけた。ビジネス環境をさらに強化するため、インド政府はビジネスのしやすさを改善することを優先しています。規制を簡素化し、ビジネスがしやすい環境を整えることに重点を置いています。テクノロジーを活用し、政府は14のサービスをeBizポータルに統合し、様々な政府機関からのクリアランスを合理化しています。メイク・イン・インディア "の効果はすでに現れています。
全体として、インドは経済指標の上昇、外国投資の増加、製造業の拡大など、"Make in India "イニシアティブの具体的な成果を目の当たりにしています。Smart Cities Mission、Bharatmala Pariyojana、Sagarmala Project、Make in Indiaの協調的な取り組みにより、インドのインフラは再構築されつつあります。この野心的なアジェンダは都市と産業の能力を強化し、エンジニアリング、調達、建設管理サービスに大きな道を開いています。インドの世界・サプライチェーンへの統合が深まり、ビジネス環境の改善に向けた取り組みが進む中、インドは製造業とインフラの極めて重要な拠点として台頭し、持続的な経済成長と開発の舞台を整えようとしています。
インドのエネルギー・公益事業部門、投資とイニシアチブの増加により需要が急増
インドはいまだ信頼性の低い送電網に悩まされており、国民のかなりの部分が接続されておらず、毎日停電に直面しています。インドの電力部門は、その多様なエネルギー源で世界的に際立っています。石炭、天然ガス、石油、原子力といった伝統的なエネルギー源に加え、風力、太陽光、水力、都市ごみ、バイオマスといった新しいエネルギー源も利用しています。クリーン・エネルギーへの移行を推進するインド政府は、業界の大幅な改革を先導しています。これには、インフラの刷新や、風力や太陽光発電をはじめとするグリーンエネルギーへの投資も含まれます。
民間投資の重要な役割を認識しているインド政府は、このセクターを強化するためにいくつかのインセンティブ制度を展開しています。野心的な目標を掲げるインドは、10年後までに二酸化炭素排出量を45%削減し、2030年までに電力の50%を自然エネルギーで賄い、最終的には2070年までにカーボンニュートラルを達成することを目指しています。これらの目標とインドの堅調で安定した経済成長は、エネルギー企業にとって有利な展望をもたらします。
インドの2030年ビジョンには、5億kWのクリーンエネルギー容量が盛り込まれており、そのうち太陽光発電は2億8,000万kWに達します。2023年2月現在、インドの総発電容量は412.21GWで、そのうち約100GWがクリーンエネルギーによるものです。特筆すべきは、インドがアジアで中国に次いで2番目に高い風力発電容量を誇っていることです。また、世界で5番目に急成長している太陽エネルギー市場であり、最もコスト効率の高い太陽光発電の生産国でもあります。
世界的に見ても、再生可能エネルギー発電においてインドは第4位です。政府は、イノベーションを促進し、エネルギー部門を拡大するために、今後5年間で420億米ドルの予算を計上しています。世界銀行の「2019年ビジネスのしやすさ(Ease of Doing Business-Getting Electricity)」調査において、インドは89.4という素晴らしいスコアを獲得しています。このスコアは、送電網への接続のしやすさ、供給の信頼性、料金の透明性、電力価格などを評価したものです。ちなみに、デンマークは90.2と若干高いスコアを獲得しています。
今後、インドは洋上風力発電の野心的な計画を打ち出し、2022年までに5GW、2030年までに30GWのプロジェクト設立を目指しています。Grid Connected Solar Rooftop Program」は、2022年までに屋上太陽光発電(RTS)プロジェクトで40GWの容量を達成することを目標としています。主な焦点は、新エネルギーや再生可能エネルギーの導入を強化するための研究開発・実証(RD&D)です。新・再生可能エネルギー省(MNRE)は、エネルギー技術、材料、現地生産能力を向上させるための研究開発を積極的に推進しています。
全体として、インドの電力セクターは大きな変革期を迎えており、エネルギーミックスは多様化し、クリーンエネルギーへの注目が顕著になっています。この転換は、大幅なインフラ強化に拍車をかけ、多額の投資を引き寄せています。二酸化炭素排出量を削減し、再生可能エネルギー容量を増強し、最終的にはカーボンニュートラルを達成するという明確な目標を持つインドは、エネルギー企業にとって魅力的な有望株として浮上しています。政府の積極的な措置は、イノベーションを育成し、セクターの成長を促進する寛大な資金提供や支援政策など、この魅力をさらに高めています。インドがエネルギーの展望を強化し、より多くの自然エネルギーを採用するにつれて、持続可能なエネルギーにおける世界のフロントランナーとしての地位を固めつつあります。これは、国民にとってより信頼できる電力供給を約束するものであり、世界の環境目標に対するインドのコミットメントを強調するものです。
インドのEPCM(設計・調達・建設管理)産業概要
インドのEPCM(設計・調達・建設管理)(EPCM)市場は、多数のプレイヤーを抱える断片的な状況です。有力企業は存在するもの、市場は細分化されており、特に専門分野や地域市場では、多くの中小企業が積極的に参入しています。この分野で著名な企業には、Larsen &Toubro(L&T)、Tata Projects Limited、Punj Lloyd Group、Reliance Infrastructure Limited、GMR Groupなどがあります。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリスト・サポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の成果
- 調査の前提
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場力学
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- 再生可能エネルギープロジェクト
- 政府の取り組み
- 市場抑制要因
- 規制と官僚的ハードル
- 建設資材コストの上昇
- 市場機会
- スマートインフラ技術の採用
- バリューチェーン/サプライチェーン分析
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 買い手/消費者の交渉力
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係の強さ
- PESTLE分析
- 市場における技術革新の洞察
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- サービス別
- 設計
- 調達
- 建設
- その他サービス
- セクター別
- 住宅産業、インフラ(運輸)、エネルギー・公益事業
- 産業
- インフラ(運輸)
- エネルギー・公益事業
第6章 競合情勢
- Market Concetration Overview
- 企業プロファイル
- Larsen & Toubro(L&T)
- Tata Projects Limited
- Punj Lloyd Group
- Reliance Infrastructure Limited
- GMR Group
- Afcons Infrastructure Limited
- Hindustan Construction Company(HCC)
- NCC Limited(Nagarjuna Construction Company)
- IVRCL Limited
- KEC International
- Gammon India Limited
- Simplex Infrastructures Limited
- Rays Power Infra Limited
- Megha Engineering & Infrastructures Ltd
- Salasar Techno Engineering Ltd(STEL)
第7章 今後の動向
The India Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management Market size is estimated at USD 69.28 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 126.91 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 12.87% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- India's engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) market is pivotal in the nation's infrastructure landscape. This market presents a spectrum of trends, challenges, and opportunities spanning diverse industries. India's EPC market has grown robustly and is fueled by ambitious infrastructure blueprints and industrial advancements. Bolstered by governmental impetus and private investments, the market's compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is poised to maintain its vigor in the coming years. Noteworthy investments are channeled into the Bharatmala project for road construction, the modernization of the railway network, and initiatives like the Smart Cities Mission. In addition, there is a notable surge in renewable energy projects, spanning solar, wind, and other avenues.
- The nation is also witnessing the development and expansion of thermal, hydroelectric, and nuclear power plants alongside a bolstered power transmission network. Key initiatives such as the Smart Cities Mission, AMRUT, and Bharatmala underscore India's commitment to infrastructure growth. Furthermore, the nation's rapid industrialization and urbanization fuel an escalating demand for enhanced infrastructure. Lastly, the liberalization of FDI policies is drawing in international EPC players, who are also embracing cutting-edge construction technologies and project management tools.
India Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) Market Trends
Infrastructure Development Driving Demand For EPC Services
The Indian government has embarked on ambitious infrastructure programs, notably the Smart Cities Mission, Bharatmala Pariyojana for highways, and the Sagarmala Project for ports. The Smart Cities Mission aims to elevate cities by enhancing core infrastructure, ensuring a high quality of life, fostering a clean and sustainable environment, and implementing 'Smart' Solutions. Emphasizing sustainable and inclusive growth, the mission focuses on compact areas, aiming to create a replicable model to guide other cities. This initiative is not just about transforming individual cities but about catalyzing a nationwide movement toward smarter urban centers.
These initiatives underscore India's commitment to infrastructure development, presenting significant opportunities for EPCM services. With urbanization surging, there is a critical need for upgraded urban infrastructure, from metro rail systems to airports and smart city projects. In tandem, the "Make in India" campaign, aimed at bolstering manufacturing, is spurring the construction of new plants and industrial facilities, further driving the demand for EPCM services.
The global launch of the "Make in India" initiative marked India's renewed focus on manufacturing. The primary goal of this initiative is to position India as the top choice for global manufacturing. Since its inception, the Indian government has spearheaded numerous reforms to bolster manufacturing, design, innovation, and startups. Amidst a globally subdued economic landscape, India has emerged as the fastest-growing economy, boasting a growth rate of 7.5% that continues to accelerate. Initiatives like "Make in India," "Digital India," "100 Smart Cities," and "Skill India" have played a pivotal role in driving this growth.
"Make in India" specifically targets integrating India into the global supply chain, emphasizing the need for Indian companies to excel on a global stage. India has significantly liberalized its economy, opening sectors like defense, railways, construction, insurance, pension funds, and medical devices to foreign direct investment (FDI). This move has positioned India as one of the most open economies worldwide. To further enhance the business environment, the Indian government has prioritized improving the ease of doing business. The focus is on simplifying regulations to foster a conducive environment for businesses. Leveraging technology, the government has integrated 14 services into the eBiz portal, streamlining clearances from various government agencies. The impact of "Make in India" is already evident.
Overall, India is witnessing tangible outcomes from its "Make in India" initiative, with economic indicators on the rise, foreign investments increasing, and the manufacturing sector expanding. The concerted efforts of the Smart Cities Mission, Bharatmala Pariyojana, Sagarmala Project, and Make in India are reshaping India's infrastructure. This ambitious agenda bolsters urban and industrial capabilities and opens up significant avenues for engineering, procurement, and construction management services. With India's deepening integration into global supply chains and ongoing efforts to improve its business environment, the nation is on track to emerge as a pivotal manufacturing and infrastructure hub, setting the stage for sustained economic growth and development.
India's Energy And Utilities Segment Experiencing Surge in Demand, Driven by Increased Investments and Initiatives
India still grapples with an unreliable power grid, leaving a significant portion of its populace unconnected and facing daily power outages. The country's power sector stands out globally for its diverse energy sources. India harnesses traditional avenues like coal, natural gas, oil, and nuclear power alongside newer options such as wind, solar, hydropower, municipal waste, and biomass. Driven by a commitment to transition to clean energy, the Indian government is spearheading a substantial industry overhaul. This includes revamping infrastructure and channeling investments into green energy, notably wind and solar power.
Recognizing the pivotal role of private investment, the Indian government has rolled out several incentive schemes to bolster the sector. Setting ambitious targets, India aims to slash carbon emissions by 45% by the end of the decade, source 50% of its electricity from renewables by 2030, and ultimately achieve carbon neutrality by 2070. These targets and India's robust and consistent economic growth present lucrative prospects for energy companies.
India's vision for 2030 includes a 500 GW clean energy capacity, with a significant 280 GW from solar power. As of February 2023, India's total generation capacity stood at 412.21 GW, with approximately 100 GW attributed to clean sources. Notably, India boasts the second-highest wind power capacity in Asia, trailing only China. It also holds the title of the world's fifth-fastest-growing solar energy market and the most cost-efficient producer of solar power.
On the global stage, India ranks fourth in renewable energy generation. The government has earmarked a substantial USD 42 billion over the next five years to foster innovation and scale up the energy sector. India's commitment to enhancing its energy landscape is underscored by its impressive score of 89.4 in the World Bank's 2019 Ease of Doing Business - Getting Electricity survey. This score evaluates the ease of connecting to the grid, supply reliability, tariff transparency, and electricity pricing. For context, Denmark secured a slightly higher score of 90.2.
Looking ahead, India has laid out ambitious plans for offshore wind energy, aiming to establish 5 GW of projects by 2022 and a substantial 30 GW by 2030. The "Grid Connected Solar Rooftop Program" is set on achieving a 40 GW capacity for rooftop solar (RTS) projects by 2022. The key focus is on research, development, and demonstration (RD&D) to bolster the adoption of new and renewable energy. The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) actively promotes R&D to advance energy technologies, materials, and local production capabilities.
Overall, India's power sector is undergoing a significant transformation, a diverse energy mix, and a notable focus on clean energy. This shift is spurring substantial infrastructure enhancements and drawing in considerable investments. With clear targets to slash carbon emissions, ramp up renewable energy capacity, and ultimately achieve carbon neutrality, India emerges as an attractive prospect for energy firms. The government's proactive steps bolstered this appeal, such as generous funding and supportive policies, which nurture innovation and foster sectoral growth. As India fortifies its energy landscape and embraces more renewables, the country is on track to cement its position as a global frontrunner in sustainable energy. This promises a more dependable power supply for its citizens and underscores India's commitment to worldwide environmental objectives.
India Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) Industry Overview
The Indian engineering, procurement, and construction management (EPCM) market features a fragmented landscape, hosting numerous players. Although dominant players exist, the market is fragmented, with many small to mid-sized companies actively participating, especially in specialized sectors or regional markets. Prominent entities in this sector include Larsen & Toubro (L&T), Tata Projects Limited, Punj Lloyd Group, Reliance Infrastructure Limited, and GMR Group.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Deliverables
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
- 1.3 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Renewable Energy Projects
- 4.2.2 Government Initiatives
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Regulatory and Bureaucratic Hurdles
- 4.3.2 Increase in Cost of Construction Material
- 4.4 Market Opportunities
- 4.4.1 Adoption of Smart Infrastructure Technologies
- 4.5 Value Chain/Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.7 PESTLE Analysis
- 4.8 Insights into Technology Innovation in the Market
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Service
- 5.1.1 Engineering
- 5.1.2 Procurement
- 5.1.3 Construction
- 5.1.4 Other Services
- 5.2 By Sectors
- 5.2.1 Residential Industrial, Infrastructure (Transportation), and Energy and Utilities
- 5.2.2 Industrial
- 5.2.3 Infrastructure (Transportation)
- 5.2.4 Energy and Utilities
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concetration Overview
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Larsen & Toubro (L&T)
- 6.2.2 Tata Projects Limited
- 6.2.3 Punj Lloyd Group
- 6.2.4 Reliance Infrastructure Limited
- 6.2.5 GMR Group
- 6.2.6 Afcons Infrastructure Limited
- 6.2.7 Hindustan Construction Company (HCC)
- 6.2.8 NCC Limited (Nagarjuna Construction Company)
- 6.2.9 IVRCL Limited
- 6.2.10 KEC International
- 6.2.11 Gammon India Limited
- 6.2.12 Simplex Infrastructures Limited
- 6.2.13 Rays Power Infra Limited
- 6.2.14 Megha Engineering & Infrastructures Ltd
- 6.2.15 Salasar Techno Engineering Ltd (STEL)


