
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1550143
インドネシアの衛星通信:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2024年~2029年)Indonesia Satellite Communications - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| インドネシアの衛星通信:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2024年~2029年) |
|
出版日: 2024年09月02日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 120 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
概要
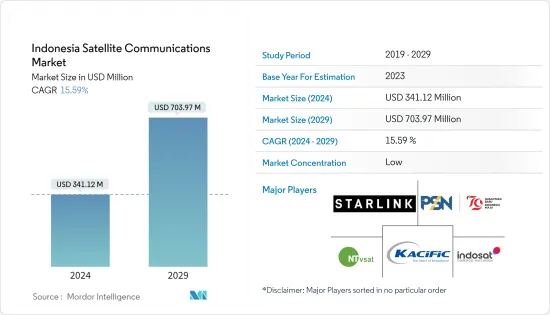
インドネシアの衛星通信市場は予測期間中にCAGR 10%を記録する見込み
主なハイライト
- インドネシアの衛星通信市場は、同国特有の地理的課題に後押しされ、広範な通信インフラに不可欠な要素となっています。17,000以上の島々からなる群島であるため、従来の地上ネットワークでは全国的な接続性を確保するには不十分です。その結果、衛星通信は、都心部と遠隔地との間のデジタルデバイドを埋める重要なソリューションとして浮上してきました。
- インドネシア政府と民間セクターは、通信、放送、インターネット・サービスなどさまざまなアプリケーションをサポートするため、衛星技術に多額の投資を行ってきました。例えば、2024年5月、イーロン・マスクはインドネシアでスペースX社のスターリンク衛星インターネット・サービスを正式に開始しました。打ち上げイベントはバリのコミュニティ・ヘルスセンターで行われ、マスク氏は、特に接続が重要なライフラインとして機能する遠隔地の診療所にとって、インターネットアクセスを変革するプロジェクトの可能性を強調しました。
- 同市場は、国内外のプレーヤーが混在しているのが特徴です。国営企業であるPT Telekomunikasi Indonesia(Telkom)は主要企業で、Telkomシリーズを含む複数の衛星を運用しています。国内事業者に加えて、SESやIntelsatといった国際衛星サービス・プロバイダーも市場で大きな存在感を示しており、現地のサービスを補完するサービスを提供しています。こうした提携により、特にサービスが行き届いていない地域でのサービス提供が強化されています。
- さらに、インドネシアの衛星通信市場の形成には、規制の枠組みや政府のイニシアチブが極めて重要な役割を果たしています。政府は、より広範なデジタル経済戦略の一環として、衛星技術の開発と展開を促進する政策を実施しています。パラパ・リング・プロジェクトのようなプログラムは、国全体のブロードバンド・インフラを改善することを目的としており、衛星は最も遠隔の地域に到達するために不可欠です。政府はまた、民間セクターの参加と投資を促進するため、規制プロセスを合理化しました。
- さらに、技術の進歩も市場の成長を後押ししています。高スループット衛星(HTS)や今後の低軌道(LEO)衛星コンステレーションなどの衛星技術の革新は、通信容量の増強と遅延の低減を約束し、より良いサービス品質を提供します。高速で信頼性の高いインターネット・アクセスが多くの地域で課題となっているインドネシアにとって、これらの進歩は特に重要です。これらの技術の採用により、市場の拡大と接続性の向上がさらに促進されると期待されます。
インドネシアの衛星通信市場動向
5G衛星通信の拡大が市場を牽引
- 5G衛星通信の拡大が、調査対象市場の成長を大きく牽引しています。この開発は、地上インフラが不足しがちな群島国家における接続性の課題に対処する上で極めて重要です。5G技術により、衛星通信は遠隔地やサービスが行き届いていない地域でも高速インターネットアクセスを提供し、デジタル経済へのより良い統合を促進し、多くのインドネシア人の生活の質を向上させる。
- インドネシアの通信セクターにおける投資と戦略的パートナーシップの増加が、5Gインフラの成長を促進しています。例えば、PT Telkom Indonesia Groupは2023年度末時点で、合計約4万3047基の通信タワーを保有していると報告しています。業界のリーダーたちは、5Gの広帯域幅と低遅延の要件を満たすために不可欠な先進的衛星技術の導入に協力しています。こうした投資は、消費者の接続性を高めるだけでなく、輸送、物流、航空などのセクターを強化し、市場の範囲と影響力を拡大しています。
- さらに、SATRIA-1衛星の打ち上げなどのインドネシア政府のイニシアチブは、国家発展のために5G衛星通信を活用するというコミットメントを強調しています。SATRIA-1は2024年初頭に運用を開始しました。SATRIA-1は、遠隔地を広範囲にカバーし、高速インターネットを提供することで、デジタルデバイドを縮小することが期待されています。政府が支援するこのプロジェクトは、より広範な社会経済目標の達成における衛星通信の戦略的重要性を浮き彫りにしています。
- インドネシアの衛星通信市場は急速に進化しており、特に低軌道(LEO)衛星の統合など、先進技術の採用へと大きくシフトしています。LEO衛星は地球に近い位置にあり、特に遅延を最小限に抑え、サービス品質を向上させることで、5Gアプリケーションに明確な利点を提供します。LEO衛星へのトランスミッションは、通信ネットワークを強化し、IoT機能を強化し、リアルタイムのデータ伝送を効率化します。
その他の地域セグメントが大きな成長を遂げている
- インドネシアの衛星通信は、主にスラウェシ、パプア、マルク、バリ、ヌサ・トゥンガラといった地域に後押しされ、需要が高まっています。これらの地域は課題が多い地形で知られ、強固な地上通信ネットワークの構築と維持に苦慮しています。インドネシアの広大な群島は、遠隔地で人口もまばらな島が多いため、大規模な光ファイバーや地上ベースの通信システムを導入するのは、実現可能性と費用対効果が厳しく制限されます。したがって、衛星通信は、こうした遠隔地の接続ギャップを埋める極めて重要かつ効率的なソリューションです。
- スラウェシ島、パプア島、マルク島では、かなりの人口が、地上ネットワークが整備されていない遠隔地に居住しています。衛星通信は、接続を容易にし、教育、ヘルスケア、緊急援助などの重要なサービスへのアクセスを可能にする、極めて重要なソリューションとして浮上しています。これらの地域は、地震、津波、火山活動などの自然災害が頻発しやすく、陸上インフラがしばしば破壊されます。対照的に、衛星ネットワークは回復力に優れ、特に危機的な状況下でも中断のない通信チャネルを保証します。
- バリ島やヌサ・トゥンガラ島は、この地域ではより発展した人気の観光地であるが、特に小さな島や農村部では、地上通信が不十分であるという課題に依然として直面しています。観光が重要な経済牽引力であることを考えると、これらの地域は強固な通信ネットワークに大きく依存しています。これらのネットワークは、ホスピタリティ、輸送サービス、緊急対応に不可欠です。そのため、衛星通信は、観光客や企業が途切れることなく接続を確保し、旅行体験と業務効率の両方を向上させる上で重要な役割を果たしています。
- さらに、インドネシア政府はデジタル・インクルージョンとコネクティビティに積極的な姿勢を示しています。衛星通信の戦略的重要性を認識した政府は、パラパ・リング・プロジェクトのようなイニシアティブを開始しました。このプロジェクトは、遠隔地や十分なサービスを受けていない地域に高速インターネット・アクセスを拡大することを目的としており、多くの場合、地上波ネットワークを補完するために衛星技術を利用しています。このような政府の取り組みは、これらの地域における衛星通信サービスの需要を大幅に押し上げています。
インドネシアの衛星通信産業の概要
インドネシアの衛星通信市場は細分化されており、多数の主要企業が競合他社を凌駕するために継続的にサービスを強化しています。これらの企業は、先端技術の導入やサービス品質の向上のため、研究開発に多額の投資を行っています。市場のプレゼンスと顧客基盤の拡大を目指すため、戦略的提携や合併も一般的です。
- 2024年3月:世界の衛星通信事業者であるインテルサットは、ユーテルサットのOneWeb LEO衛星コンステレーションから追加容量を取得することで合意したと発表。この戦略的な動きは、インテルサットのマルチオービット・ビジネスモデルを強化し、LEO接続に対する需要の増加を活用することを目的としています。
- 2024年2月地球観測とデータ分析で著名なBlackSkyは、インドネシア共和国に衛星画像サービスと画像処理宇宙船を提供する5,000万米ドルの契約を締結したと発表。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリスト・サポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場洞察
- 市場概要
- 業界利害関係者分析
- マクロ経済動向の影響
第5章 市場力学
- 市場促進要因
- 5G衛星通信の拡大
- 低軌道(LEO)衛星の成長
- 市場の課題
- 熟練人材の不足
- 技術動向
- 主な使用事例
第6章 市場セグメンテーション
- 衛星質量別
- 10-100 Kg
- 100-500 Kg
- 500-1000 Kg
- 10Kg未満
- 1000Kg以上
- 軌道クラス別
- GEO
- LEO
- MEO
- 通信タイプ別
- 放送
- 移動体通信
- 衛星電話
- その他の通信タイプ
- エンドユーザー別
- 商業
- 軍事・政府
- 地域別
- ジャワ島
- スマトラ
- カリマンタン
- その他の地域(スラウェシ、パプア&マルク、バリ&ヌサ・トゥンガラ)
第7章 競合情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- Pasifik Satelit Nusantara
- Thales Alenia Space
- PT Telekomunikasi Indonesia(Telkom)
- Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison
- Bank Rakyat Indonesia(BRI)
- Thaicom
- SES SA
- Intelesat
- Viasat
- Inmarsat
第8章 投資分析
第9章 市場機会と今後の動向
目次
Product Code: 50002703
The Indonesia Satellite Communications Market is expected to register a CAGR of 10% during the forecast period.

Key Highlights
- Indonesia's satellite communications market is an essential component of its broader telecommunications infrastructure, driven by the country's unique geographic challenges. As an archipelago with over 17,000 islands, traditional terrestrial networks are insufficient to ensure nationwide connectivity. Consequently, satellite communication has emerged as a critical solution to bridge the digital divide between urban centers and remote regions.
- The Indonesian government and private sector have invested significantly in satellite technology to support various applications, including telecommunication, broadcasting, and internet services. For instance, in May 2024, Elon Musk officially launched SpaceX's Starlink satellite internet services in Indonesia, representing a significant milestone in the nation's efforts to enhance internet connectivity in remote regions. The launch event occurred at a community health center in Bali, where Musk emphasized the project's potential to transform internet access, particularly for remote medical clinics where connectivity can serve as a critical lifeline.
- The market is characterized by a mix of domestic and international players. PT Telekomunikasi Indonesia (Telkom), the state-owned enterprise, is a major player, operating several satellites, including the Telkom series. In addition to domestic operators, international satellite service providers like SES and Intelsat also have a significant presence in the market, offering services that complement local offerings. These collaborations have enhanced service delivery, particularly in underserved areas.
- Moreover, regulatory frameworks and government initiatives play a pivotal role in shaping the satellite communications market in Indonesia. The government has implemented policies to promote the development and deployment of satellite technology as part of its broader digital economy strategy. Programs such as the Palapa Ring Project aim to improve broadband infrastructure across the country, with satellites being integral to reaching the most remote regions. The government has also streamlined regulatory processes to encourage private sector participation and investment.
- Furthermore, technological advancements are also driving growth in the market. Innovations in satellite technology, such as high-throughput satellites (HTS) and the upcoming low earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellations, promise to enhance capacity and reduce latency, offering better service quality. These advancements are particularly relevant for Indonesia, where high-speed, reliable internet access remains a challenge in many areas. The adoption of these technologies is expected to further boost the market's expansion and improve connectivity.
Indonesia Satellite Communications Market Trends
Expansion of 5G Satellite Communication is Driving the Market
- The expansion of 5G satellite communication is significantly driving the growth of the market studied. This development is pivotal in addressing the connectivity challenges in the archipelagic nation, where terrestrial infrastructure often falls short. With 5G technology, satellite communication offers high-speed internet access even in remote and underserved areas, facilitating better integration into the digital economy and enhancing the quality of life for many Indonesians.
- Increased investments and strategic partnerships in Indonesia's telecom sector are driving the growth of 5G infrastructure. For instance, at the end of the 2023 fiscal year, PT Telkom Indonesia Group reported a total of approximately 43,047 telecommunications towers. Industry leaders are collaborating to deploy advanced satellite technologies, which are essential for meeting 5G's high bandwidth and low latency requirements. These investments are not only enhancing consumer connectivity but also strengthening sectors such as transportation, logistics, and aviation, thereby expanding the market's reach and impact.
- Furthermore, the Indonesian government's initiatives, such as launching the SATRIA-1 satellite, underscore the commitment to leveraging 5G satellite communication for national development. SATRIA-1 became operational in early 2024. It is expected to provide extensive coverage and high-speed internet to remote areas, thereby reducing the digital divide. This government-backed project highlights the strategic importance of satellite communication in achieving broader socio-economic goals.
- The Indonesian satellite communication market is rapidly evolving, with a significant shift toward embracing advanced technology, notably the integration of low earth orbit (LEO) satellites. LEO satellites, positioned closer to Earth, offer distinct advantages for 5G applications, notably by minimizing latency and elevating service quality. This transition to LEO satellites is poised to bolster communication networks, bolster IoT capabilities, and streamline real-time data transmission, all pivotal for contemporary digital services.
Other Regional Segment is Experiencing Major Growth
- Satellite communication in Indonesia is witnessing heightened demand, primarily propelled by regions like Sulawesi, Papua, Maluku, Bali, and Nusa Tenggara. These areas, known for their challenging terrains, struggle to establish and sustain robust terrestrial communication networks. Given Indonesia's vast archipelago comprising numerous remote and sparsely populated islands, the feasibility and cost-effectiveness of deploying extensive fiber-optic or ground-based communication systems are severely limited. Hence, satellite communication is the pivotal and efficient solution to bridge connectivity gaps in these remote locales.
- In Sulawesi, Papua, and Maluku, a substantial population resides in remote, underserved regions lacking terrestrial network coverage. Satellite communication emerges as a pivotal solution, facilitating connectivity and granting access to vital services such as education, healthcare, and emergency aid. These areas are also prone to frequent natural calamities, including earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic activities, often disrupting land-based infrastructure. In contrast, satellite networks exhibit greater resilience, guaranteeing uninterrupted communication channels, especially in times of crisis.
- While Bali and Nusa Tenggara are more developed and popular tourist destinations in their region, they still face challenges with inadequate terrestrial communication, particularly on smaller islands and in rural areas. Given that tourism is a critical economic driver, these regions rely heavily on robust communication networks. These networks are essential for hospitality, transportation services, and emergency responses. Satellite communications, therefore, play a crucial role in ensuring uninterrupted connectivity for tourists and businesses, enhancing both travel experiences and operational efficiencies.
- Moreover, the Indonesian government has taken a proactive stance on digital inclusion and connectivity. Recognizing the strategic importance of satellite communications, the government has launched initiatives like the Palapa Ring project. This project aims to extend high-speed internet access to remote and underserved areas, often utilizing satellite technology to complement terrestrial networks. Such governmental initiatives are significantly boosting the demand for satellite communication services in these regions.
Indonesia Satellite Communications Industry Overview
The Indonesian satellite communications market features a fragmented landscape, with numerous key players continually enhancing their offerings to outpace competitors. These companies invest heavily in research and development to introduce advanced technologies and improve service quality. Strategic partnerships and mergers are common as firms seek to expand their market presence and customer base.
- March 2024: The global satellite operator Intelsat announced an agreement to acquire additional capacity from Eutelsat's OneWeb LEO satellite constellation. This strategic move aims to enhance Intelsat's multi-orbit business model and leverage the increasing demand for LEO connectivity.
- February 2024: BlackSky, a prominent Earth observation and data analytics firm, announced a USD 50 million contract to deliver satellite imagery services and imaging spacecraft to the Republic of Indonesia.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Stakeholder Analysis
- 4.3 Impact of Macroeconomic Trends
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Expansion of 5G Satellite Communication
- 5.1.2 Growth of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellites
- 5.2 Market Challenges
- 5.2.1 Shortfall of Skilled Resource
- 5.3 Technology Trends
- 5.4 Key Use Cases
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Satellite Mass
- 6.1.1 10-100 Kg
- 6.1.2 100-500 Kg
- 6.1.3 500-1000 Kg
- 6.1.4 Below 10 Kg
- 6.1.5 Above 1000 Kg
- 6.2 By Orbit Class
- 6.2.1 GEO
- 6.2.2 LEO
- 6.2.3 MEO
- 6.3 By Communication Type
- 6.3.1 Broadcasting
- 6.3.2 Mobile Communication
- 6.3.3 Satellite Phone
- 6.3.4 Other Communication Types
- 6.4 By End User
- 6.4.1 Commercial
- 6.4.2 Military & Government
- 6.5 By Geography
- 6.6 Java
- 6.7 Sumatra
- 6.8 Kalimantan
- 6.9 Other Regions (Sulawesi, Papua & Maluku, and Bali & Nusa Tenggara)
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 Pasifik Satelit Nusantara
- 7.1.2 Thales Alenia Space
- 7.1.3 PT Telekomunikasi Indonesia (Telkom)
- 7.1.4 Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison
- 7.1.5 Bank Rakyat Indonesia (BRI)
- 7.1.6 Thaicom
- 7.1.7 SES SA
- 7.1.8 Intelesat
- 7.1.9 Viasat
- 7.1.10 Inmarsat


