|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1445785
糖尿病治療薬:日本市場シェア分析、業界動向と統計、成長予測(2024~2029年)Japan Diabetes Drugs - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 糖尿病治療薬:日本市場シェア分析、業界動向と統計、成長予測(2024~2029年) |
|
出版日: 2024年02月15日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 70 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
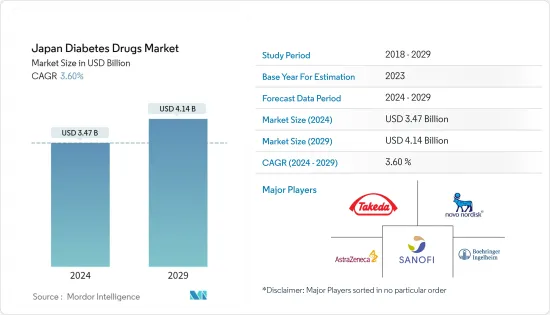
日本の糖尿病治療薬の市場規模は、2024年に34億7,000万米ドルと推定され、2029年までに41億4,000万米ドルに達すると予測されており、予測期間(2024年~2029年)中に3.60%のCAGRで成長する見込みです。
COVID-19のパンデミックは、糖尿病治療薬市場に大きな影響を与えています。COVID-19感染症で入院した患者における糖尿病の有病率と、血糖コントロールの改善により、SARS-CoV-2患者の転帰が改善し、入院期間が短縮される可能性があるという認識により、糖尿病治療機器の重要性が強調されています。米国糖尿病協会(ADA)の第81回バーチャル科学セッションで遡及的分析が発表され、糖尿病が日本のCOVID-19患者の重症化加速の主な危険因子であることが示されました。
パンデミックの間中、糖尿病はCOVID-19の重大な危険因子として存続しています。糖尿病とCOVID-19を患う入院患者では、10人に1人が入院後7日以内に死亡しました。
パンデミックはまた、ヘルスケア提供者と糖尿病患者との間の仮想協議や糖尿病テクノロジーの利用を通じて、糖尿病治療薬の提供におけるイノベーションを継続および拡大する機会を浮き彫りにしました。危機管理により、患者と医療提供者の両方から遠隔医療に対する前例のない関心が生まれ、長年にわたる多くの規制障壁が取り除かれました。このように、COVID-19の発生により、日本の糖尿病治療薬市場の成長が加速しました。
1型糖尿病は免疫系の機能不全によって引き起こされますが、2型糖尿病は座りっぱなしのライフスタイルを導くことに関連しており、その結果インスリンに対する固有の抵抗力が発現します。したがって、1型糖尿病はインスリン要求性糖尿病として特徴付けられ、2型糖尿病はインスリン依存性糖尿病として特徴付けられます。日本は世界でも有数の高齢者人口を抱えており、2型糖尿病を発症しやすい国です。日本では高齢化が進み、糖尿病の有病率も増加しています。心血管疾患、腎臓障害、その他多くの症状などの悪影響を回避するために、血糖値の監視と管理が増加しています。
したがって、前述の要因により、調査対象の市場は分析期間中に成長すると予想されます。
日本の糖尿病治療薬市場動向
経口糖尿病治療薬セグメントは、今年度の日本の糖尿病治療薬市場で最高の市場シェアを獲得
経口糖尿病治療薬セグメントは、今年の日本の糖尿病治療薬市場で約69%の最高の市場シェアを保持しています。
経口抗糖尿病治療薬は世界中で入手可能であり、ライフスタイル管理とともに2型糖尿病治療の段階的拡大が必要な場合の使用が推奨されています。経口剤は、有効性、安全性、作用機序が広範囲にわたるため、通常、2型糖尿病の治療に最初に使用される薬剤です。抗糖尿病治療薬は、糖尿病患者の状態をコントロールし、糖尿病合併症のリスクを下げるのに役立ちます。糖尿病患者は、血糖値をコントロールし、低血糖や高血糖を避けるために、生涯にわたって抗糖尿病治療薬を服用する必要がある場合があります。経口抗糖尿病治療薬には、管理が容易でコストが低いという利点があります。したがって、それらはより受け入れられやすく、治療遵守を高めるインスリンの魅力的な代替品となりました。
日本では糖尿病の有病率があらゆる年齢層で増加していますが、これは肥満人口の増加、不健康な食事、座りっぱなしのライフスタイルが原因と考えられます。糖尿病はその有病率の高さから広く懸念されており、その結果、医療機関、個人、政府の財政負担が増加します。日本のヘルスケア制度には、日本糖尿病教育・ケア協会が実施するいくつかの疾病管理プログラムが含まれています。日本は、糖尿病の公衆衛生政策において、アジア太平洋のリーダーの一つです。この国は国民の意識を高め、成人発症の糖尿病の可能性を減らすことができるライフスタイルと食事の調整に焦点を当てた予防政策を採用しています。
上記の要因により、市場は今後も成長する可能性があります。
ナトリウム-グルコース共輸送-2(SGLT-2)阻害剤セグメントは、予測期間中に日本の糖尿病治療薬市場で最高のCAGRで推移すると予想されます
ナトリウム-グルコース共輸送-2(SGLT-2)阻害剤セグメントは、予測期間中に日本の糖尿病治療薬市場で約8%という最高のCAGRで推移すると予想されます。
グリフロジンとも呼ばれるSGLT-2阻害剤は、2型糖尿病患者の高血糖レベルを下げるために使用される医薬品の一種です。SGLT-2阻害剤は、膵臓のベータ細胞の機能とは独立して作用します。SGLT-2薬は、血圧、心機能、抗炎症作用などの心血管危険因子を大幅に管理します。SGLT-2阻害薬は、ヘモグロビンA1cレベルを低下させ、体重減少を改善するのに効果的です。低血糖症のリスクは低く、通常は忍容性が良好です。
この間に技術の進歩が進み、SGLT-2阻害剤や開発中の製剤にいくつかの変更が加えられました。糖尿病は世界の流行として出現しました。IDF 2021データによると、日本には約1,100万人の糖尿病患者がいます。糖尿病は厚生労働省によって重点ヘルスケアとして位置づけられています。2型糖尿病の罹患率の高さは、重大な経済的負担と関連しています。糖尿病の費用は、高血圧や高脂血症などの併存疾患がある患者や合併症を発症した患者では増加します。合併症の数が増えると費用も増加します。日本では、医療保険制度が整備され、糖尿病の医療費は全額負担され、糖尿病患者は自由に医師の診察を受けることができます。このような利点により、日本市場でのこれらの製品の採用が増加しました。
日本の糖尿病治療薬業界の概要
日本の糖尿病治療薬市場は適度に統合されており、Eli Lilly、Sanofi、Novo Nordisk、AstraZenecaなどの大手メーカーがこの地域で存在感を示しています。市場の主要なシェアは、戦略に基づいたM&A業務を並行し、新たな収益源を生み出し、既存の収益源を拡大するために常に市場に参入しているメーカーによって占められています。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3か月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場の定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場力学
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- 市場抑制要因
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 消費者の交渉力
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 代替製品やサービスの脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係の激しさ
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- インスリン
- 基礎インスリンまたは持効性インスリン
- ランタス(インスリングラルギン)
- レベミル(インスリンデテミル)
- トウジョ(インスリングラルギン)
- トレシーバ(インスリンデグルデク)
- バサグラー(インスリングラルギン)
- ボーラスまたは速効型インスリン
- ノボラピッド/ノボログ(インスリンアスパルト)
- ヒューマログ(インスリンリスプロ)
- アピドラ(インスリングルリシン)
- 従来のヒトインスリン
- ノボリン/アクタピッド/インシュラタード
- フムリン
- インスマン
- バイオシミラーインスリン
- インスリングラルギンバイオシミラー
- ヒトインスリンバイオシミラー
- 基礎インスリンまたは持効性インスリン
- 経口糖尿病治療薬
- ビグアニデス
- メトホルミン
- α-グルコシダーゼ阻害剤
- α-グルコシダーゼ阻害剤
- ドーパミンD2受容体作動薬
- ブロモクリプチン
- SGLT-2阻害剤
- インボカナ(カナグリフロジン)
- ジャディアンス(エンパグリフロジン)
- フォシーガ/フォシーガ(ダパグリフロジン)
- スーグラ(イプラグリフロジン)
- DPP-4阻害剤
- オングリザ(サクサグリプチン)
- トラジェンタ(リナグリプチン)
- Vipidia/Nesina(アログリプチン)
- ガルバス(ビルダグリプチン)
- スルホニル尿素
- スルホニル尿素
- メグリチニド
- メグリチニド
- ビグアニデス
- 非インスリン注射薬
- GLP-1受容体アゴニスト
- ビクトーザ(リラグルチド)
- バイエッタ(エクセナチド)
- ビデュレオン(エクセナチド)
- トルリシティ(デュラグルチド)
- リクスミア(リクシセナチド)
- アミリン類似体
- シムリン(プラムリンタイド)
- GLP-1受容体アゴニスト
- 配合剤
- インスリンの組み合わせ
- ノボミックス(二相性インスリンアスパルト)
- Ryzodeg(インスリンデグルデクおよびインスリンアスパルト)
- Xultophy(インスリンデグルデクおよびリラグルチド)
- 経口併用療法
- ジャヌメット(シタグリプチンおよびメトホルミン)
- インスリンの組み合わせ
第6章 市場指標
- 1型糖尿病人口
- 2型糖尿病人口
第7章 競合情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- Novo Nordisk A/S
- Takeda
- Pfizer
- Eli Lilly
- Janssen Pharmaceuticals
- Astellas
- Boehringer Ingelheim
- Merck And Co.
- AstraZeneca
- Bristol Myers Squibb
- Novartis
- Sanofi Aventis
- 企業シェア分析
- Novo Nordisk A/S
- Sanofi Aventis
- Eli Lilly
- Merck And Co.
- Others
第8章 市場機会と将来の動向
The Japan Diabetes Drugs Market size is estimated at USD 3.47 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 4.14 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 3.60% during the forecast period (2024-2029).

The COVID-19 pandemic has had a substantial impact on the diabetes drugs market. The prevalence of diabetes in people hospitalized with COVID-19 infection and the recognition that improved glycemic control might improve outcomes and reduce the length of stay in patients with SARS-CoV-2 have underlined the importance of diabetes care devices. A retrospective analysis was presented at the virtual 81st Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) which showed diabetes was the main risk factor for the accelerated advancement to a severe state in Japanese COVID-19 patients.
Throughout the pandemic, diabetes has persisted as a significant risk factor for COVID-19. In hospitalized patients with diabetes and COVID-19, one in 10 people died within seven days of admission.
The pandemic also highlighted opportunities for continuing and expanding innovations in the delivery of diabetes drugs, through virtual consultations between healthcare providers and people with diabetes, and the use of diabetes technology. Crisis management has created unprecedented interest in remote care from both patients and providers and removed many long-standing regulatory barriers. Thus, the COVID-19 outbreak increased the Japanese diabetes drugs market's growth.
While Type 1 diabetes is caused by an immune system malfunction, Type 2 diabetes is linked to leading a sedentary lifestyle, which results in the development of inherent resistance to insulin. Hence, Type 1 diabetes can be characterized as insulin-requiring, while Type 2 diabetes can be characterized as insulin-dependent diabetes. Japan has one of the largest elderly populations in the world which is more susceptible to the onset of type 2 diabetes. As Japan's population continues to age, the prevalence of diabetes increases as well. The monitoring and management of blood glucose levels are on the rise, to avoid negative consequences, such as cardiovascular diseases, kidney disorders, and many other conditions.
Therefore, owing to the aforementioned factors the studied market is anticipated to witness growth over the analysis period.
Japan Diabetes Drugs Market Trends
The oral anti-diabetic drugs segment holds the highest market share in the Japan Diabetes Drugs Market in the current year
The oral anti-diabetic drugs segment holds the highest market share of about 69% in the Japan Diabetes Drugs Market in the current year.
Oral Anti-Diabetic Drugs are available internationally and are recommended for use when escalation of treatment for type 2 diabetes is required along with lifestyle management. Oral agents are typically the first medications used in treating type 2 diabetes due to their wide range of efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of action. Anti-diabetic drugs help diabetes patients control their condition and lower the risk of diabetes complications. People with diabetes may need to take anti-diabetic drugs for their whole lives to control their blood glucose levels and avoid hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Oral anti-diabetic agents present the advantages of easier management and lower cost. So they became an attractive alternative to insulin with better acceptance, which enhances adherence to the treatment.
The prevalence of diabetes is growing among all ages in Japan, which can be attributed to the growing obese population, unhealthy diets, and sedentary lifestyles. Diabetes mellitus is of wide concern with its high prevalence, resulting in increased financial burdens for clinical systems, individuals, and governments. The Japanese healthcare system includes a few disease management programs conducted by the Japan Association for Diabetes Education and Care. Japan is one of the regional leaders in Asia-Pacific in terms of diabetic public health policies. The country promotes public awareness and embraces preventive policies focusing on lifestyle and dietary adjustments, which can lessen the likelihood of adult-onset diabetes.
Owing to the above factors, the market will likely continue to grow.
Sodium-glucose cotransport -2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor segment is expected to register the highest CAGR in the Japan Diabetes Drugs Market over the forecast period
Sodium-glucose cotransport -2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor segment is expected to register the highest CAGR of about 8% in the Japan Diabetes Drugs Market over the forecast period.
SGLT-2 inhibitors, also called gliflozins, are a medicine class used to lower high blood glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes. SGLT-2 inhibitors act independently of beta-cell function in the pancreas. SGLT-2 drugs significantly manage cardiovascular risk factors, including blood pressure, cardiac function, and antiinflammatory activity.SGLT-2 inhibitors are effective at lowering hemoglobin A1c levels and improving weight loss. They include a low risk of hypoglycemia and are usually well tolerated.
Technological advancements increased over the period leading to several modifications in the SGLT-2 inhibitors or the formulations being developed. Diabetes emerged as a global epidemic. Japan contains around 11 million people with diabetes, according to IDF 2021 data. Diabetes is identified as a healthcare priority by the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare. The high prevalence of type 2 diabetes is associated with a significant economic burden. The costs of diabetes are increased in patients with co-morbidities such as hypertension and hyperlipidemia and in patients who develop complications. Costs increase with an increasing number of complications. Well-organized medical insurance systems cover all medical fees for diabetes mellitus, and people with diabetes can visit doctors freely in Japan. Such advantages helped the increased adoption of these products in the Japanese market.
Japan Diabetes Drugs Industry Overview
The Japan Diabetes Drugs Market is moderately consolidated, with major manufacturers, namely Eli Lilly, Sanofi, Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca, and other generic players, holding a presence in the region. A major share of the market is held by manufacturers concomitant with strategy-based M&A operations and constantly entering the market to generate new revenue streams and boost existing ones.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products and Services
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Insulins
- 5.1.1 Basal or Long Acting Insulins
- 5.1.1.1 Lantus (Insulin Glargine)
- 5.1.1.2 Levemir (Insulin Detemir)
- 5.1.1.3 Toujeo (Insulin Glargine)
- 5.1.1.4 Tresiba (Insulin Degludec)
- 5.1.1.5 Basaglar (Insulin Glargine)
- 5.1.2 Bolus or Fast Acting Insulins
- 5.1.2.1 NovoRapid/Novolog (Insulin Aspart)
- 5.1.2.2 Humalog (Insulin Lispro)
- 5.1.2.3 Apidra (Insulin Glulisine)
- 5.1.3 Traditional Human Insulins
- 5.1.3.1 Novolin/Actrapid/Insulatard
- 5.1.3.2 Humulin
- 5.1.3.3 Insuman
- 5.1.4 Biosimilar Insulins
- 5.1.4.1 Insulin Glargine Biosimilars
- 5.1.4.2 Human Insulin Biosimilars
- 5.1.1 Basal or Long Acting Insulins
- 5.2 Oral Anti-diabetic drugs
- 5.2.1 Biguanides
- 5.2.1.1 Metformin
- 5.2.2 Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
- 5.2.2.1 Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
- 5.2.3 Dopamine D2 receptor agonist
- 5.2.3.1 Bromocriptin
- 5.2.4 SGLT-2 inhibitors
- 5.2.4.1 Invokana (Canagliflozin)
- 5.2.4.2 Jardiance (Empagliflozin)
- 5.2.4.3 Farxiga/Forxiga (Dapagliflozin)
- 5.2.4.4 Suglat (Ipragliflozin)
- 5.2.5 DPP-4 inhibitors
- 5.2.5.1 Onglyza (Saxagliptin)
- 5.2.5.2 Tradjenta (Linagliptin)
- 5.2.5.3 Vipidia/Nesina(Alogliptin)
- 5.2.5.4 Galvus (Vildagliptin)
- 5.2.6 Sulfonylureas
- 5.2.6.1 Sulfonylureas
- 5.2.7 Meglitinides
- 5.2.7.1 Meglitinides
- 5.2.1 Biguanides
- 5.3 Non-Insulin Injectable drugs
- 5.3.1 GLP-1 receptor agonists
- 5.3.1.1 Victoza (Liraglutide)
- 5.3.1.2 Byetta (Exenatide)
- 5.3.1.3 Bydureon (Exenatide)
- 5.3.1.4 Trulicity (Dulaglutide)
- 5.3.1.5 Lyxumia (Lixisenatide)
- 5.3.2 Amylin Analogue
- 5.3.2.1 Symlin (Pramlintide)
- 5.3.1 GLP-1 receptor agonists
- 5.4 Combination drugs
- 5.4.1 Insulin combinations
- 5.4.1.1 NovoMix (Biphasic Insulin Aspart)
- 5.4.1.2 Ryzodeg (Insulin Degludec and Insulin Aspart)
- 5.4.1.3 Xultophy (Insulin Degludec and Liraglutide)
- 5.4.2 Oral Combinations
- 5.4.2.1 Janumet (Sitagliptin and Metformin)
- 5.4.1 Insulin combinations
6 MARKET INDICATORS
- 6.1 Type-1 Diabetic Population
- 6.2 Type-2 Diabetic Population
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 COMPANY PROFILES
- 7.1.1 Novo Nordisk A/S
- 7.1.2 Takeda
- 7.1.3 Pfizer
- 7.1.4 Eli Lilly
- 7.1.5 Janssen Pharmaceuticals
- 7.1.6 Astellas
- 7.1.7 Boehringer Ingelheim
- 7.1.8 Merck And Co.
- 7.1.9 AstraZeneca
- 7.1.10 Bristol Myers Squibb
- 7.1.11 Novartis
- 7.1.12 Sanofi Aventis
- 7.2 COMPANY SHARE ANALYSIS
- 7.2.1 Novo Nordisk A/S
- 7.2.2 Sanofi Aventis
- 7.2.3 Eli Lilly
- 7.2.4 Merck And Co.
- 7.2.5 Others