
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1851157
幼虫駆除剤:市場シェア分析、産業動向、統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Larvicides - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 幼虫駆除剤:市場シェア分析、産業動向、統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年06月05日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 120 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
概要
幼虫駆除剤市場規模は2025年に9億5,000万米ドルと推定され、予測期間中のCAGRは5.77%で、2030年には12億6,000万米ドルに達すると予測されます。
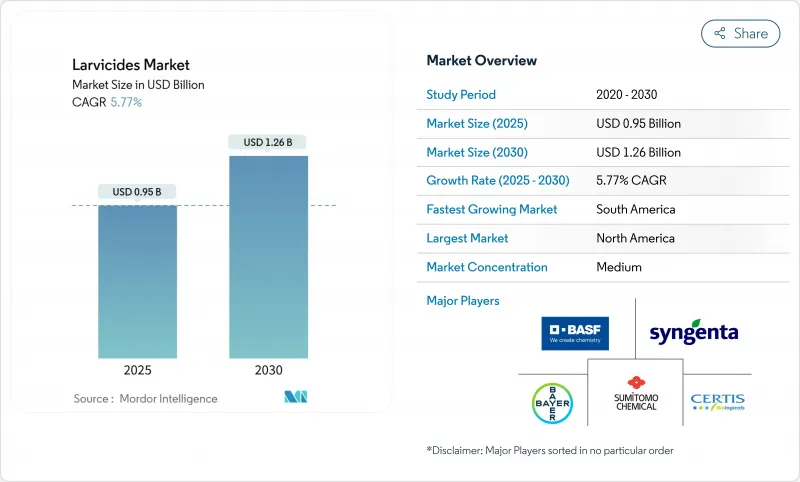
市場成長の原動力は、成虫駆除法の効果が低下したため幼虫期の蚊をターゲットにする必要性が高まっていること、南北アメリカにおけるヘルスケア予算の拡大、環境に適合した生物合理的製剤の継続的開発などです。さらに、温帯地域における蚊の繁殖期間の延長、熱帯都市部におけるデング熱の持続的な流行、養殖に適した安全な幼虫駆除剤を必要とする米と魚の統合養殖システムの採用の増加なども成長の原動力となっています。同市場は、生物学的製剤の生産コストの上昇、農村部における一貫性のない散布方法、処理効率を高めるためのGISベースのモニタリング・システムの必要性などの課題に直面しています。
世界の幼虫駆除剤市場の動向と洞察
殺虫剤抵抗性の成虫蚊の急増が幼虫段階への介入を加速
蚊は標的部位不感受性と代謝的解毒により殺虫剤に対する耐性を発達させる。アノフェレスやアエデス蚊は、遺伝的適応、行動変化、代謝抵抗性によって化学治療を回避します。現在、ベクターコントロール・プログラムでは、停滞した水域や都市部の貯水池など、繁殖場所にいる幼虫をターゲットにすることで、初期段階の個体数をコントロールすることに重点を置いています。このアプローチにより、蚊が成虫になるのを防ぎ、病気の伝播サイクルを遮断することができます。また害虫駆除プログラムでは、個々の薬剤に対する選択圧を減らすため、さまざまな有効成分をローテーションさせる統合戦略を実施することが増えています。この変化は、ピレスロイドの失敗によって緊急散布の予算が危うくなった地域で顕著であり、自治体は成虫の大群が出現する前に洪水プールや雨水排水溝を保護するシーズン中の幼虫駆除グリッドに投資するようになっています。
デング熱・チクングニア予防プログラムの展開
ラテンアメリカの大都市では、感染率の上昇と都市部の蚊の個体数の増加を受けて、デング熱とチクングニアの予防プログラムを強化しています。世界保健機関(WHO)は、特にボリビアとパラグアイで感染者が大幅に増加していると報告しています。予防戦略には、アカイエカの駆除、一般市民への啓発活動、衛生、都市計画、教育を組み合わせた統合的アプローチなどがあります。汎米保健機構(PAHO)は、疾病の感染を減らすための地域社会に根ざした対策の実施について、地域政府を指導しています。2024年にブラジルでデング熱が流行することを受け、世界蚊プログラム(WMP)はフィオクルスと提携し、ブラジル全土で蚊が媒介する疾病に取り組んでいます。WMPは、デング熱、ジカ熱、チクングニヤ熱の感染を防ぐため、イエネコ蚊に天然細菌を導入するウォルバキア法を拡大しています。
厳しい水生毒性閾値
2026年農薬一般許可では、地表水を処理する際、施用量、場所、非標的種のモニタリングを記録することを施用者に義務付けています。テメホスを含む有機リン剤の規制監督により、氾濫水湿地や都市の流域で使用できる製剤の選択肢が減少しました。コンプライアンスコストが増加したため、郡は価格が高いにもかかわらず、リスクの高い化学物質から生物学的代替物質に移行するようになりました。包括的な毒物学的データとデジタル散布記録を提供するサプライヤーは市場の優位性を維持しているが、参入障壁は小規模事業者に影響を与え、地域の化学幼虫駆除剤の流通を制限しています。
セグメント分析
2024年の幼虫駆除剤市場シェアの45%は合成幼虫駆除剤が占めています。市場でのリーダーシップは、コストの優位性と確立された調達契約に起因します。生物学的製品はCAGR 8.4%という高い成長率で伸びており、統合的なベクター管理アプローチを推進する政府のイニシアティブに支えられています。バチルス・チューリンゲンシス・イスラエレンシス(Bti)は、蚊の幼虫、クロバエ、カビブヨに特異的な毒性を示します。2023年、カトマンズ・メトロポリタン市(KMC)は、蚊の幼虫を対象としたバイオ殺虫プログラムを実施し、デング熱の発生を防いです。この有機溶液は、蚊の幼虫の消化器官を破壊することで蚊の幼虫を駆除し、他の生物は温存します。
後期試験段階にあるRNAi酵母幼虫駆除剤の市場開拓は、非標的種に影響を与えることなく遺伝子特異的な制御を提供する、潜在的な市場シフトを示しています。メーカーは製品の寿命と使いやすさを向上させるためにマイクロカプセル化技術を改良しています。2024年の調査では、作物保護における植物性幼虫駆除剤の有効性、特にマリーゴールド抽出物の有効性が実証されました。バンガロールのPES大学が実施した研究により、Tagetes erectaとTagetes patulaにはチオフェン類が含まれており、作物の害虫Spodoptera lituraとCorcyra cephalonicaに対して顕著な殺幼虫効果を示すことが明らかになりました。このような技術的改良は、環境的に持続可能な製品に対する政府のインセンティブと相まって、生物学的幼虫駆除剤がより多くの自治体との契約を確保することを可能にしています。
昆虫成長調節剤(IGR)は、特に従来の殺虫剤に対する抵抗性の高まりに対応して、効果的な幼虫駆除方法として登場しました。IGRは脱皮、繁殖、変態を阻害することで蚊の発育を阻害し、幼虫が成虫になるのを防ぐ。化学接触殺虫剤は2024年の売上高の55%を占めるが、現場調査では耐性発達による効果の低下が指摘されています。主要なIGR化合物であるメトプレンは、10 ppb未満の濃度で有効性を示し、水中での移動性は最小限です。
害虫駆除プログラムでは、ピレスロイドや有機リン酸塩に対する代謝抵抗性や行動抵抗性が広まっているため、ピリプロキシフェンやメトプレンを含むIGRベースのソリューションの採用が増加しています。IGRは残効性が長く、環境への影響が少なく、耐性菌発生リスクが低いため、持続可能な蚊の駆除プログラムに不可欠な要素となっています。
地域別分析
北米は2024年に最大の売上を計上した地域であり、これは構造化されたベクター・マネジメントの枠組みや、西ナイルや東部ウマ脳炎に対する関心の高まりに支えられています。米国は北米における蚊と幼虫駆除のための幼虫駆除剤の主要ユーザーです。米国疾病予防管理センター(CDC)と地域の蚊防除地区が、全国で媒介蚊防除プログラムを実施しています。これらのプログラムでは、西ナイルウイルスやジカ熱などの蚊が媒介する病気を予防するために、統合蚊管理(IMM)戦略の中に幼虫駆除剤が組み込まれています。
環境保護庁(EPA)は、初期の未熟な蚊を対象とした複数の幼虫駆除法を推奨しています。幼虫の消化を阻害する細菌性殺虫剤(Bacillus thuringiensis israelensisおよびBacillus sphaericus)- 発育を妨げるメトプレンなどの昆虫成長阻害剤- 幼虫を溺死させる表面油やフィルム。環境問題への懸念から、特定の防除方法、特に有機リン系殺虫剤の使用を中止しています。すべての防除方法は、脆弱な個体群を保護するための規制に従わなければならないです。EPAの2026年農薬一般許可(Pesticide General Permit)は、地表水への農薬散布に関する厳しい要件を定めており、これが北米全体の製品開発を形作っています。
アジアでは、中国とインドが農薬散布による生産量を確保する一方、東南アジアの市場では、コメと魚のシステムに生物学的な幼虫駆除剤を義務付ける補助金を活用しています。同時に、イエネコが有機リン剤とピレスロイド剤に抵抗性を示すため、インドネシアの議会はIGRとBtiの組み合わせのローテーションを余儀なくされており、これが販売量の増加を支えています。アジアに帰属する幼虫駆除剤の市場シェアは毎年拡大するが、いくつかの国では価格に敏感であるため、マージンは圧縮されたままとなる可能性があります。
南米は、デング熱とチクングニアの流行に関連する公衆衛生上の危機が原動力となって、最も高い成長率を示しています。ブラジルでは、2024年にデング熱患者が725万人に達し、2023年に記録された数の2倍に達しました。都市衛生部門は、発生源削減イニシアチブと週1回の幼虫駆除剤散布を組み合わせ、流通業者の在庫レベルを維持する安定した製品需要を確保しています。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月のアナリストサポート
よくあるご質問
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場の定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- 殺虫剤耐性成蚊の急増
- デング熱およびチクングニア予防プログラムの展開
- 気候による蚊の繁殖期の拡大
- 米魚一貫養殖に対する政府補助金
- 幼虫駆除剤に関する規制政策
- ドローンを用いた幼虫駆除剤の空中散布の急速な拡大
- 市場抑制要因
- 厳しい水生毒性基準値による化学製剤の制限
- GIS育種サイトマッピングの低採用が商業的販売を抑制
- バチルス発酵培地のサプライチェーン変動性
- 合成ベクターコントロール化合物に対する世論の圧力
- バリュー/サプライチェーン分析
- 規制情勢
- テクノロジーの展望
- ポーターズファイブフォース
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 買い手の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係
第5章 市場規模と成長予測
- 製品タイプ別
- 合成幼虫駆除剤
- 生物学幼虫駆除剤
- 制御方法別
- 化学薬品
- 生物防除剤
- 昆虫成長調節剤(IGR)
- 対象昆虫別
- 蚊
- ハエ
- 甲虫
- アリ
- 用途別
- 農業
- 非農業
- 剤形別
- 顆粒
- 液体と懸濁液
- ペレットと錠剤
- パウダーおよびウェッタブルダスト
- 地域別
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- メキシコ
- その他北米地域
- 南米
- ブラジル
- アルゼンチン
- その他南米
- 欧州
- 英国
- ドイツ
- フランス
- イタリア
- スペイン
- その他欧州地域
- アフリカ
- 南アフリカ
- ナイジェリア
- エジプト
- その他アフリカ
- 中東
- サウジアラビア
- アラブ首長国連邦
- カタール
- その他中東
- アジア太平洋地域
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- オーストラリア
- その他アジア太平洋地域
- 北米
第6章 競合情勢
- 戦略的動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業プロファイル
- BASF SE
- Bayer AG
- Syngenta AG
- Sumitomo Chemical Co.
- Clarke Mosquito Control Products Inc.
- Central Life Sciences
- Certis Biologicals
- UPL Ltd.
- FMC Corporation
- Russell IPM


