
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1693943
MEO衛星- 市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)MEO Satellite - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| MEO衛星- 市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 168 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
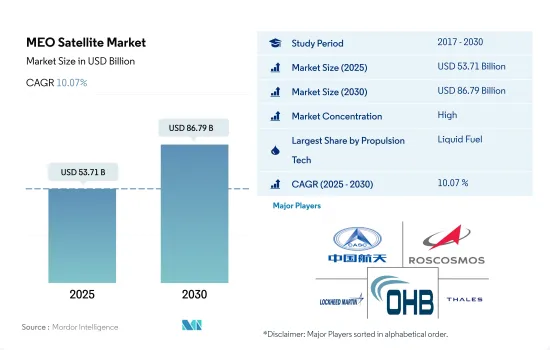
MEO衛星市場規模は2025年に537億1,000万米ドルと予測され、2030年には867億9,000万米ドルに達し、予測期間(2025~2030年)のCAGRは10.07%で成長すると予測されます。
液体燃料推進システムセグメントが市場の成長を牽引
- 衛星の推進システムは、宇宙船を軌道に推進し、軌道上の宇宙船の位置を調整するために一般的に使用されます。液体推進剤または液体ロケットは、液体推進剤を使用するロケットエンジンを使用します。気体推進剤も使用できるが、密度が低く、従来の圧送方法を適用するのが難しいため、一般的ではないです。液体燃料推進システムは、密度と比推力が高いため、3つの推進タイプの中で最も採用されています。2023年には73.3%の市場シェアを占め、2029年には69.5%に達すると予想されます。
- 電気推進は2番目に多く採用されている推進システムで、商業通信衛星のステーション保持に一般的に使用されています。電気推進はその高い比インパルスにより、一部の宇宙科学ミッションの主推進力となっています。ノースロップ・グラマン社、ムーグ社、シエラネバダ社、スペースX、ブルーオリジン社などが、推進システムの主要プロバイダです。人工衛星の新規打ち上げにより、予測期間中の市場成長は加速すると予想されます。
- 移動を可能にするガスベースの推進システムは、効率性と信頼性が実証されています。これらには、ヒドラジンシステム、その他のシングルまたはツイン推進システム、ハイブリッドシステム、冷温風システム、固体推進剤などが含まれます。通常、これらのシステムは、強い推力や急速な操縦が必要な場合に使用されます。そのため、総インパルス容量がミッション要件を満たすのに十分な場合には、ガスベースのシステムが宇宙推進技術として選択され続けるケースもあります。コールド・ガス・スラスターは低コストで複雑なため小型衛星には適しているが、大型衛星には不向きです。
欧州では大幅な新製品開発により、新たなビジネス機会が広がると期待されています。
- 中軌道(MEO)衛星の研究開発費は、衛星産業における技術革新と技術開発を促進する重要な要因です。MEO衛星は、全地球測位システム(GPS)サービスの提供など、特殊な用途に使用されることが多いです。こうした用途が社会にとってより重要になるにつれ、MEO衛星の性能や能力を向上させるための研究開発投資が増える可能性があります。
- ロシアの衛星産業は、世界で最も活発で先進的な産業の1つです。ISS Reshetnevは、ロシアのMEO衛星市場を独占しています。ISSレシェトネフはロシアを代表する衛星メーカーで、ロシアのMEO衛星のほとんどを開発・製造しています。ロシアのMEO衛星市場におけるISSレシェトネフの最も顕著な貢献は、グロナスシリーズです。GLONASSシステムは、アメリカのGPSシステムに対抗するロシアのシステムで、世界中のユーザーに全地球測位サービスを提供しています。これらの衛星はすべてGLONASSシリーズで、ISSレシェトネフ社によって製造・打ち上げられました。
- 中国はこの構想の一環として、すでに多くのMEO衛星を打ち上げており、今後数年間でさらに多くの衛星を打ち上げると予想されています。例えば、2017~2022年*の間に、政府や軍事目的のために、それぞれ800kgの重さの24基のナビゲーション衛星と全地球測位衛星がMEOに配置されました。これらの衛星は、中国の世界ナビゲーションシステムであるBeiDou Navigation Satellite System(BDS)の一部として、中国の宇宙技術研究院(CASCの一部)によって打ち上げられました。予測期間中はアジア太平洋が優位を占めると予想されます。
世界のMEO衛星市場動向
燃料効率と運用効率向上のための衛星小型化が市場で見られる
- MEO衛星はLEOとGEOの中間に位置し、通常は高度約2,000~3万6,000km(1,242~2万2,369マイル)にあります。MEOは、全地球測位システム(GPS)などの衛星ナビゲーションシステムに一般的に使用されています。MEO衛星の質量も用途によって異なるが、一般に高度が低いためGEO衛星よりも軽いです。
- 衛星の質量は打ち上げに大きな影響を与えます。衛星が重ければ重いほど、宇宙に打ち上げるのに必要な燃料やエネルギーが増えるからです。人工衛星を打ち上げるには、地球の周回軌道に乗せるために、時速約2万8,000キロメートルという超高速まで加速する必要があります。この速度を達成するのに必要なエネルギー量は、衛星の質量に比例します。
- 衛星の質量は打ち上げに大きな影響を与えます。実際、衛星が重ければ重いほど、宇宙に打ち上げるために必要な燃料とエネルギーは多くなります。この速度を達成するために必要なエネルギー量は、衛星の質量に比例します。材料、製造技術、技術の開発により、より軽量で効率的な衛星部品の開発が可能になりました。その結果、衛星の性能を維持あるいは向上させながら、衛星の質量を減らすことができるようになりました。2017~2022年の間に、世界全体で約55機の衛星がMEOに打ち上げられました。
さまざまな宇宙機関による支出の増加は、MEO衛星セグメントにプラスの影響を与えると予想されます。
- MEO衛星に対する研究開発費の世界の動向は、LEO衛星やGEO衛星の動向ほど明確ではないです。というのも、MEO衛星はLEO衛星やGEO衛星ほど広く利用されておらず、その用途も欧州ではやや限定的だからです。英国宇宙庁は、同国の宇宙産業を後押しする18のプロジェクトを支援するため、650万ユーロの資金を提供すると発表しました。この資金援助は、インパクトのある地元主導の計画や宇宙クラスター開発マネージャーを支援することで、英国の宇宙産業の成長を刺激することを目的としています。18のプロジェクトは、公共サービスを強化するための地球観測(EO)データの活用など、地域の問題に対処するためのさまざまな革新的宇宙技術を開拓します。2022年11月、スペイン政府は、今後5年間でESAに15億ユーロを割り当てると発表しました。
- 北米では、宇宙計画のための政府支出が2021年に約220億米ドルと過去最高を記録しました。この地域は、世界最大の宇宙機関であるNASAが存在する、宇宙イノベーションと研究の中心地です。2022年、米国政府は宇宙プログラムに約620億米ドルを支出し、世界的に宇宙開発への支出額が最も高い国となりました。米国では、連邦政府機関が政府から毎年323億3,000万米ドル相当の資金を受け取っています。
- MEO衛星の研究開発費は、特定の用途や利用可能な資金によって多少不規則になることがあります。しかし、他の衛星技術と同様に、研究開発への継続的な投資は、さまざまな用途をサポートし、予測期間中の産業の成長を促進することができる、新しく改良されたMEO衛星技術の開発につながる可能性が高いです。
MEO衛星産業概要
MEO衛星市場はかなり統合されており、上位5社が100%を占めています。この市場の主要企業は、China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation(CASC)、Information Satellite Systems Reshetnev、Lockheed Martin Corporation、OHB SE、Thalesです。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主要調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 衛星の質量
- 宇宙開発への支出
- 規制の枠組み
- 世界
- オーストラリア
- ブラジル
- カナダ
- 中国
- フランス
- ドイツ
- インド
- イラン
- 日本
- ニュージーランド
- ロシア
- シンガポール
- 韓国
- アラブ首長国連邦
- 英国
- 米国
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 用途
- 通信
- 地球観測
- ナビゲーション
- その他
- 衛星質量
- 100~500kg
- 500~1,000kg
- 1,000kg以上
- エンドユーザー
- 商業
- 軍事・政府
- その他
- 推進技術
- 電気式
- ガス
- 液体燃料
- 地域
- アジア太平洋
- 欧州
- 北米
- その他
第6章 競合情勢
- 主要な戦略動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation(CASC)
- Information Satellite Systems Reshetnev
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- OHB SE
- Thales
第7章 CEOへの主要戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界のバリューチェーン分析
- 市場力学(DROs)
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表一覧
- 主要な洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
The MEO Satellite Market size is estimated at 53.71 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 86.79 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 10.07% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

The liquid fuel propulsion system segment leads the market's growth
- A satellite's propulsion system is commonly used to propel a spacecraft into orbit and to coordinate the position of the spacecraft in orbit. Liquid propellants or liquid rockets use rocket engines that use liquid propellants. Gas propellants can also be used but are not common due to their low density and difficulty in applying conventional pumping methods. The liquid fuel propulsion system is the most adopted one of the three propulsion types because of its high density and specific impulse. It is expected to occupy a market share of 73.3% in 2023, which is anticipated to reach 69.5% in 2029.
- Electric propulsion is the second most adopted type of propulsion system, and it is commonly used to hold stations for commercial communication satellites. It is the main propulsion of some space science missions due to its high specific impulses. Northrop Grumman Corporation, Moog Inc., Sierra Nevada Corporation, SpaceX, and Blue Origin are some of the major providers of propulsion systems. The new launch of satellites is expected to accelerate market growth over the forecast period.
- Gas-based propulsion systems that enable movements have been proven efficient and reliable. These include hydrazine systems, other single or twin propulsion systems, hybrid systems, cold/hot air systems, and solid propellants. Typically, these systems are used when strong thrust or rapid maneuvering is required. Therefore, in some cases, gas-based systems continue to be the space propulsion technology of choice when their total impulse capacity is sufficient to meet the mission requirements. Cold gas thrusters are suitable for small satellites because of their low cost and complexity, but they are not ideal for large satellites.
Europe is expected to open new scope of opportunities with significant new product developments in the region
- R&D expenditure on medium Earth orbit (MEO) satellites is an important factor in driving innovation and technology development in the satellite industry. MEO satellites are often used for specialized applications, such as providing global positioning system (GPS) services. As these applications become more critical to society, there may be more R&D investment to improve MEO satellite performance and capabilities.
- The Russian satellite industry is one of the most active and advanced in the world. ISS Reshetnev dominates the MEO satellite market in Russia. ISS Reshetnev is a leading Russian satellite manufacturer responsible for developing and producing most of the country's MEO satellites. ISS Reshetnev's most notable contribution to the MEO satellite market in Russia is its GLONASS series. The GLONASS system is a Russian counterpart to the American GPS system and provides global positioning services to users worldwide. All of these satellites are of the GLONASS series and were manufactured and launched by ISS Reshetnev.
- China has already launched a number of MEO satellites as part of this initiative and is expected to launch many more in the coming years. For instance, during 2017-2022*, 24 navigation and global positioning satellites weighing 800 kg each were placed in MEO for government and military purposes. These satellites were launched by China's Space Technology Research Institute (part of CASC) as part of China's BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS), China's global navigation system. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to dominate during the forecast period.
Global MEO Satellite Market Trends
Satellite miniaturization for better fuel and operational efficiency witnessed in the market
- MEO satellites are located between LEO and GEO, typically at an altitude of about 2,000 to 36,000 kilometers (1,242 to 22,369 miles). MEO is commonly used for satellite navigation systems such as the Global Positioning System (GPS). The mass of MEO satellites can also vary depending on their specific applications, but they are generally lighter than GEO satellites due to their lower altitude.
- The mass of a satellite has a significant impact on its launch. This is because the heavier the satellite, the more fuel and energy will be required to launch it into space. The launch of a satellite involves accelerating it to a very high speed, typically around 28,000 kilometers per hour, in order to place it in orbit around the Earth. The amount of energy required to achieve this speed is proportional to the mass of the satellite.
- The mass of a satellite has a significant impact on its launch. Indeed, the heavier the satellite, the more fuel and energy it will need to be launched into space. The amount of energy required to achieve this speed is proportional to the mass of the satellite. Advancements in materials, manufacturing techniques, and technology have enabled the development of lighter and more efficient satellite components. This has resulted in a reduction in satellite mass while maintaining or even improving performance. During 2017-2022, around 55 satellites were launched into MEO globally.
Increasing expenditure by different space agencies is expected to positively impact the MEO satellites segment
- The global trend in R&D expenditure on MEO satellites is not as well-defined as that for LEO or GEO satellites. This is because MEO satellites are not as widely used as LEO or GEO satellites, and their applications are somewhat limited in Europe. The UK Space Agency announced that it would be funding EUR 6.5 million to support 18 projects to boost its space industry. The funding aims to stimulate growth in the UK space industry by supporting high-impact, locally-led schemes and space cluster development managers. The 18 projects will pioneer various innovative space technologies to combat local issues, such as utilizing Earth observation (EO) data to enhance public services. In November 2022, the Government of Spain announced that it would allocate EUR 1.5 billion to the ESA over the next five years, which will reinforce Spain's leadership in space.
- In North America, government expenditure for space programs hit a record of approximately USD 22 billion in 2021. The region is the epicenter of space innovation and research, with the presence of the world's biggest space agency, NASA. In 2022, the US government spent nearly USD 62 billion on its space programs, making it the highest spender on space globally. In the United States, federal agencies receive funds worth USD 32.33 billion from the government every year.
- R&D spending on MEO satellites can be somewhat irregular depending on specific applications and available funding. However, as with other satellite technologies, continued investment in R&D will likely lead to the development of new and improved MEO satellite technologies that can support different applications and promote industry growth over the forecast period.
MEO Satellite Industry Overview
The MEO Satellite Market is fairly consolidated, with the top five companies occupying 100%. The major players in this market are China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), Information Satellite Systems Reshetnev, Lockheed Martin Corporation, OHB SE and Thales (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Satellite Mass
- 4.2 Spending On Space Programs
- 4.3 Regulatory Framework
- 4.3.1 Global
- 4.3.2 Australia
- 4.3.3 Brazil
- 4.3.4 Canada
- 4.3.5 China
- 4.3.6 France
- 4.3.7 Germany
- 4.3.8 India
- 4.3.9 Iran
- 4.3.10 Japan
- 4.3.11 New Zealand
- 4.3.12 Russia
- 4.3.13 Singapore
- 4.3.14 South Korea
- 4.3.15 United Arab Emirates
- 4.3.16 United Kingdom
- 4.3.17 United States
- 4.4 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Application
- 5.1.1 Communication
- 5.1.2 Earth Observation
- 5.1.3 Navigation
- 5.1.4 Others
- 5.2 Satellite Mass
- 5.2.1 100-500kg
- 5.2.2 500-1000kg
- 5.2.3 above 1000kg
- 5.3 End User
- 5.3.1 Commercial
- 5.3.2 Military & Government
- 5.3.3 Other
- 5.4 Propulsion Tech
- 5.4.1 Electric
- 5.4.2 Gas based
- 5.4.3 Liquid Fuel
- 5.5 Region
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.3 North America
- 5.5.4 Rest of World
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC)
- 6.4.2 Information Satellite Systems Reshetnev
- 6.4.3 Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 6.4.4 OHB SE
- 6.4.5 Thales
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SATELLITE CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms


