
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1693942
大型衛星- 市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Large Satellites - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 大型衛星- 市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 193 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
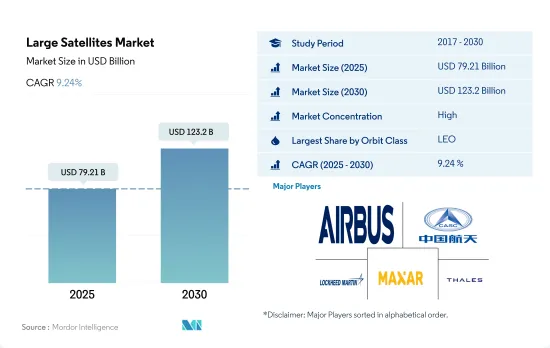
大型衛星市場規模は2025年に792億1,000万米ドルと予測され、2030年には1,232億米ドルに達し、予測期間中(2025~2030年)のCAGRは9.24%で成長すると予測されています。
LEOセグメントが2029年の市場シェア57.9%で市場成長をリード
- 過去10年間、大型衛星はGEOで打ち上げられてきました。2017年のGEOの市場シェアは79.8%でした。これらの衛星はコストが高く、寿命も長い方です。メーカーはこれらの衛星を打ち上げ、配備するために多額の資金を費やしました。しかし、技術の進歩に伴い、衛星の打ち上げと開発のコストは過去3~4年で削減されています。このため、LEOに大型衛星を打ち上げるメーカーの実行可能性も、はるかに大きなペースで高まっています。
- アプリケーションやミッションタイプに応じて、特定の衛星や衛星コンステレーション全体が異なるタイプの軌道で打ち上げられます。すべての地域で製造・打ち上げられる衛星は用途が異なります。例えば、2017~2022年の間に、打ち上げられた214機の大型衛星のうち、123機がGEO、71機がLEO、13機がMEO、7機が楕円軌道に配置されました。
- 市場シェアに関しては、LEOがこのセグメントをリードすると予想されており、2023年には50.5%のシェアを占め、2029年には57.1%に達すると予想されています。高い市場シェアは、その近接性と、技術開拓によってもたらされた他のいくつかの利点によるものです。GEOは2023年に44.3%のシェアを持ち、2029年には36.9%を占めると予想されています。
- そのため、電子情報、地球科学/気象学、レーザーイメージング、光学イメージング、気象学の各部門で衛星の利用が増加しており、予測期間中に衛星の開発需要が高まると予想されます。
寿命の長い人工衛星の増加により、アジア太平洋は大きな市場シェアを維持しています。
- 大型衛星は、通信、ナビゲーション、地球観測など幅広い用途に使用されています。こうした用途の需要が増え続けるなか、各社はこうしたニーズに応えるため、大型衛星の開発に研究開発費を投じています。
- 大型衛星は、主に運用目的で設計され、寿命が長い(5年から10年)。これらの衛星は主に、より大型のリモートセンシング・ペイロードや、より多数の中継器、通信用の大型アンテナを搭載するために使用されます。これらの運用衛星は、サブシステムの偶発的な故障に対応し、寿命を延ばすために、すべての主要なサブシステムに冗長性を持たせています。大型衛星は通常、放射線に強い宇宙仕様の電子機器で作られています。すべてのサブシステムとより大きな負荷をサポートするために、より大きな展開可能な太陽電池パネルでより多くの電力を生成します。大型衛星は太陽電池パネルと衛星本体が大きいため、大気抵抗が大きく、高出力の推進システムが必要となります。大型衛星は通常、軌道高度と姿勢補正のために化学推進システムを搭載しています。
- 2017~2022年の間に打ち上げられた約200以上の大型衛星は北米の組織が所有し、電子情報、地球科学/気象学、レーザーイメージング、電子情報、光学イメージング、気象学などの用途がありました。予測期間中、アジア太平洋が60%以上のシェアを占め、市場を独占すると予想されています。
世界の大型衛星市場動向
燃料効率と運用効率向上の動向
- 衛星の質量は打ち上げに大きな影響を与えます。衛星が重ければ重いほど、宇宙に打ち上げるために必要な燃料とエネルギーが増えるからです。衛星を打ち上げるには、地球の周回軌道に乗せるため、時速約2万8,000キロメートルという超高速まで加速する必要があります。この速度を達成するために必要なエネルギー量は、衛星の質量に比例します。
- Intelサットが開発した地域通信衛星ギャラクシー33とギャラクシー34は、2022年10月に米国で打ち上げられました。これらは世界で最も注目された人工衛星の開発と打ち上げのひとつです。同様に2022年3月には、ロッキード・マーティン社によって、高度気象衛星である静止能動環境衛星が打ち上げられました。欧州では2023年に衛星I-6 F2の打ち上げが予定されています。
- その結果、衛星が重くなると、宇宙に打ち上げるにはより大きなロケットとより多くの燃料が必要になります。その結果、打ち上げコストが上昇し、使用できるロケットタイプも制限されることになります。質量によって大きく分類すると、1,000kgを超える大型衛星となります。これらの大型衛星は、主に運用目的で設計されており、寿命も長いです。これらの衛星は、より大きなリモートセンシングのペイロード、より多くの中継器、通信目的のためのより大きなアンテナを搭載するために、様々な国によって採用されています。これらの運用衛星は、サブシステムの偶発的な故障に対応するため、すべての主要なサブシステムに冗長性を持たせています。大型衛星は通常、放射線に強い宇宙グレードの電子機器で作られています。2017~2022年の間に、世界中で約200以上の大型衛星が製造され、打ち上げられました。
さまざまな宇宙機関の世界の宇宙支出の増加は、大型衛星カテゴリーにプラスの影響を与えると予想されます。
- 大型衛星に対する研究開発費は、衛星産業における技術革新と技術開発を促進する重要な要因です。最近の大型衛星に対する研究開発費の世界の動向は、衛星技術、新材料、推進システム、エレクトロニクスの急速な進歩など、いくつかの要因によって上昇を続けており、これらの技術革新を利用できる大型衛星を設計・開発するための研究開発投資の必要性が高まっている
- 大型衛星は、通信、航法、地球観測など幅広い用途に利用されています。こうした用途の需要が伸び続ける中、企業はこうしたニーズに対応できる大型衛星を開発するための研究開発投資を進めています。現在、アジア太平洋では、中国、インド、日本が、完全なエンド・ツー・エンドの宇宙容量と宇宙インフラ、宇宙技術(通信衛星、地球観測衛星(EO)、航法衛星)、衛星製造、ロケット、宇宙港を保有しています。この地域の他の国々は、それぞれの宇宙計画を遂行するために国際協力に頼る必要があります。2022年6月、韓国はヌリ・ロケットを打ち上げ、6基の衛星を軌道に乗せ、世界で7番目に1トンを超えるペイロードを航空ロケットに搭載することに成功しました。
- 韓国政府は2022年度予算の中で、宇宙港の開発、衛星航法システムの構築、6G通信ネットワークの構築など、宇宙セグメントへの6億1,900万米ドルの投資を発表しました。同地域では、宇宙開発と研究助成金に対する支出が急増し、世界経済のあらゆる領域で同セグメントの重要性が高まることが予想されます。
大型衛星産業概要
大型衛星市場はかなり統合されており、上位5社で82.66%を占めています。この市場の主要企業は、Airbus SE、China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation(CASC)、Lockheed Martin Corporation、Maxar Technologies Inc.、Thalesです。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主要調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 衛星の質量
- 宇宙開発への支出
- 規制の枠組み
- 世界
- オーストラリア
- ブラジル
- カナダ
- 中国
- フランス
- ドイツ
- インド
- イラン
- 日本
- ニュージーランド
- ロシア
- シンガポール
- 韓国
- アラブ首長国連邦
- 英国
- 米国
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 用途
- 通信
- 地球観測
- ナビゲーション
- 宇宙観測
- その他
- 軌道クラス
- GEO
- LEO
- MEO
- エンドユーザー
- 商業
- 軍事・政府
- その他
- 推進技術
- 電気式
- ガス
- 液体燃料
- 地域
- アジア太平洋
- 欧州
- 北米
- その他
第6章 競合情勢
- 主要な戦略動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- Airbus SE
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation(CASC)
- Indian Space Research Organisation(ISRO)
- Information Satellite Systems Reshetnev
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Maxar Technologies Inc.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Thales
- The Boeing Company
第7章 CEOへの主要戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界のバリューチェーン分析
- 市場力学(DROs)
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表一覧
- 主要な洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
The Large Satellites Market size is estimated at 79.21 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 123.2 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 9.24% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

LEO segment leads the market's growth with a market share of 57.9% in 2029
- Over the past decade, large satellites have been launched in GEO. GEO occupied a market share of 79.8% in 2017. These satellites cost more, and their life span is on a higher side. Manufacturers spent large amounts of money to launch and deploy these satellites. However, with the advancements in technology, the cost of launching and developing satellites has been reduced over the past 3 to 4 years. Because of this, the viability of manufacturers to launch a large satellite in LEO also increased at a much larger pace.
- Depending on the type of application or mission, a particular satellite or entire satellite constellation is launched in different types of orbit. Different satellites manufactured and launched across all the regions have different applications. For instance, during 2017-2022, out of the 214 large satellites launched, 123, 71, 13, and 7 were placed in GEO, LEO, MEO, and elliptical orbits.
- With respect to the market shares, LEO is expected to lead the segment; it occupies a share of 50.5% in 2023, which is expected to reach 57.1% by 2029. The high market share is because of its proximity and several other advantages triggered by technological developments. GEO has a share of 44.3% in 2023 and is expected to occupy 36.9% in 2029.
- Therefore, the increasing use of satellites in electronic intelligence, Earth science/meteorology, laser imaging, optical imaging, and meteorology departments is expected to drive the demand for the development of satellites during the forecast period.
The increasing number of satellites with long lifespans helps the Asia-Pacific region maintain a substantial market share
- Large satellites are used for a wide range of applications, including communication, navigation, and Earth observation. As the demand for these applications continues to increase, companies are investing in R&D to develop large satellites to meet these needs.
- Large satellites are designed primarily for operational purposes with a long lifespan (between five and 10 years). These satellites are mainly used to carry larger remote sensing payloads or larger numbers of transponders and larger antennas for communication purposes. These operational satellites have redundancy for all major subsystems to support accidental failures in subsystems and extend lifespan. Larger satellites are typically built with radiation-hardened space-grade electronics. They generate more power with larger deployable solar panels to support all subsystems and larger loads. Since large satellites have large solar panels and bodies, they face greater atmospheric drag, generating the need for high-powered propulsion systems. Large satellites generally carry a chemical propulsion system for orbital elevation and attitude correction.
- During 2017-2022, around 200+ large satellites launched were owned by North American organizations and had applications such as electronic intelligence, Earth science/meteorology, laser imaging, electronic intelligence, optical imaging, and meteorology. Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate the market during the forecast period, with a share of more than 60%.
Global Large Satellites Market Trends
Trend for better fuel and operational efficiency has been witnessed
- The mass of a satellite has a significant impact on the launch of the satellite. This is because the heavier the satellite, the more fuel and energy are required to launch it into space. The launch of a satellite involves accelerating it to a very high speed, typically around 28,000 kilometers per hour, in order to place it in orbit around the Earth. The amount of energy required to achieve this speed is proportional to the mass of the satellite.
- Galaxy 33 and Galaxy 34, local communications satellites developed by Intelsat, were launched in October 2022 in the United States. These were among the world's most notable development and launches of satellites. Similarly, in March 2022, a Geostationary Active Environmental Satellite was launched by Lockheed Martin, which is an advanced weather satellite. In Europe, satellite I-6 F2 is planned to be launched in 2023.
- As a result, a heavier satellite requires a larger rocket and more fuel to launch it into space. This, in turn, increases the cost of the launch and can also limit the types of launch vehicles that can be used. The major classification types according to mass are large satellites that are more than 1,000 kg. These large satellites are majorly designed for operational purposes with a long lifespan. These satellites are being adopted by various countries to carry larger remote sensing payloads, larger numbers of transponders, and larger antennas for communication purposes. These operational satellites have redundancy for all major subsystems to support accidental failures in subsystems. Larger satellites are typically built with radiation-hardened space-grade electronics. During the period 2017-2022, around 200+ large satellites were manufactured and launched globally.
Increasing space expenditures of different space agencies globally is expected to positively impact the large satellites category
- R&D expenditure on large satellites is an important factor in driving innovation and technology development in the satellite industry. In recent years, the global trend in R&D expenditure on large satellites continues to rise, owing to several factors, including rapid advancements in satellite technology, new materials, propulsion systems, and electronics, which are driving the need for R&D investment to design and develop large satellites that can take advantage of these innovations.
- Large satellites are used for a wide range of applications, including communication, navigation, and Earth observation. As the demand for these applications continues to grow, companies are investing in R&D to develop large satellites that can meet these needs. Currently, in the Asia-Pacific region, China, India, and Japan possess a complete end-to-end space capacity and space infrastructure, space technology (communication, Earth observation (EO), and navigation satellites), satellite manufacturing, rockets, and spaceports. Other countries in the region are required to rely on international cooperation to carry out their respective space programs. In June 2022, the Nuri rocket was launched by South Korea, putting six satellites into orbit, making it the seventh country in the world to successfully launch a payload weighing more than one ton onto an air launch vehicle.
- The South Korean government, in its 2022 budget, announced an investment of USD 619 million in the space segment, which includes the development of a spaceport, the construction of a satellite navigation system, and a 6G communications network. The spending on space and research grants is expected to surge in the region, thereby increasing the sector's importance in every domain of the global economy..
Large Satellites Industry Overview
The Large Satellites Market is fairly consolidated, with the top five companies occupying 82.66%. The major players in this market are Airbus SE, China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), Lockheed Martin Corporation, Maxar Technologies Inc. and Thales (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Satellite Mass
- 4.2 Spending On Space Programs
- 4.3 Regulatory Framework
- 4.3.1 Global
- 4.3.2 Australia
- 4.3.3 Brazil
- 4.3.4 Canada
- 4.3.5 China
- 4.3.6 France
- 4.3.7 Germany
- 4.3.8 India
- 4.3.9 Iran
- 4.3.10 Japan
- 4.3.11 New Zealand
- 4.3.12 Russia
- 4.3.13 Singapore
- 4.3.14 South Korea
- 4.3.15 United Arab Emirates
- 4.3.16 United Kingdom
- 4.3.17 United States
- 4.4 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Application
- 5.1.1 Communication
- 5.1.2 Earth Observation
- 5.1.3 Navigation
- 5.1.4 Space Observation
- 5.1.5 Others
- 5.2 Orbit Class
- 5.2.1 GEO
- 5.2.2 LEO
- 5.2.3 MEO
- 5.3 End User
- 5.3.1 Commercial
- 5.3.2 Military & Government
- 5.3.3 Other
- 5.4 Propulsion Tech
- 5.4.1 Electric
- 5.4.2 Gas based
- 5.4.3 Liquid Fuel
- 5.5 Region
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.3 North America
- 5.5.4 Rest of World
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 Airbus SE
- 6.4.2 China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC)
- 6.4.3 Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
- 6.4.4 Information Satellite Systems Reshetnev
- 6.4.5 Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 6.4.6 Maxar Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.7 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- 6.4.8 Thales
- 6.4.9 The Boeing Company
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SATELLITE CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms


