
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1911305
日本の医薬品3PL市場:市場シェア分析、業界動向、統計、成長予測(2026年~2031年)Japan Pharmaceutical 3PL - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 日本の医薬品3PL市場:市場シェア分析、業界動向、統計、成長予測(2026年~2031年) |
|
出版日: 2026年01月12日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 150 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
概要
日本の医薬品3PL市場は、2025年の42億5,000万米ドルから2026年には44億4,000万米ドルへ成長し、2026年から2031年にかけてCAGR4.55%で推移し、2031年までに55億5,000万米ドルに達すると予測されています。
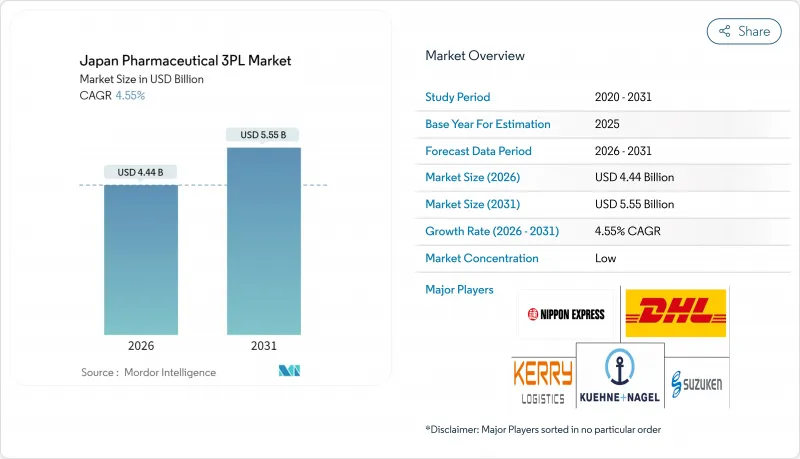
日本の厳格な適正流通基準(GDP)規制、生物学的製剤への依存度が高い高齢化社会、ならびに細胞・遺伝子治療への需要増加が、製薬企業を外部物流パートナーへの依存へと導いております。-196℃から常温までの温度管理輸送、リアルタイム出荷監視、全国的な規制対応ノウハウを提供できる事業者がシェアを拡大しております。サービスの差別化は現在、AIを活用したルート計画、コールドチェーンの完全性を検証するIoTセンサー、そして日本の2050年脱炭素化目標に沿ったカーボンニュートラルな倉庫ソリューションに依存しています。横浜、大阪、福岡周辺におけるバイオ医薬品工場への投資が活発化していることで、国内輸送量は高水準を維持すると同時に、臨床試験用資材や高付加価値の完成医薬品といった越境物流の二桁成長を促進しています。卸売業者間の談合事件後の規制当局の監視強化によりコンプライアンスコストは上昇しましたが、一方で監査記録に問題のない物流専門業者に対する顧客の選好も強まっています。
日本の医薬品3PL市場の動向と洞察
温度管理を要するバイオ医薬品・ワクチンの需要拡大
バイオ医薬品は現在、低分子医薬品を上回る収益成長率を示しており、出荷元は工場から患者まで有効性を確保する超低温包装の導入を迫られています。AGCバイオロジクスの細胞治療専用横浜工場(3億5,050万米ドル)は、既に国内幹線ルートにおける-80℃保管およびドライベーパーデュワー容器の契約を促進しています。パナソニックのVIXELLコンテナは、-70℃以下での18日間の安定性が認証されており、ANAカーゴなどの航空会社がIATA CEIV Pharma認証を取得することを可能にしております。これは、世界の生物製剤輸送の前提条件となっております。逸脱を記録するリアルタイムセンサーは分析エンジンに情報を提供し、運送業者は腐敗が発生する前にルートを調整することが可能となります。その結果、コールドチェーンのプレミアム料金は常温輸送料金を20~30%上回る場合が多く、GDPライセンシングを受けた3PL業者の利益率向上に寄与しています。
日本の製薬メーカーにおけるアウトソーシングの動向
政府の価格改革により生産者の利益率が圧迫される中、ジェネリック企業における品質管理の不備が自社物流管理のリスクを高めました。包装・保管・コンプライアンス対応輸送を3PLに委託する動きを受け、日本CMO協会の会員数は2021年以降倍増しています。明治製菓がインド工場から年間30億錠を輸出する一方でGDP認定の日本拠点を利用する決定は、新たな複数拠点モデルを象徴しています。資本効率の高い戦略により、監査対応可能な文書化を保証しつつ研究開発予算を解放できるため、既存ブランド企業とバイオシミラー参入企業の双方において、アウトソーシングが標準となっています。
GDP準拠コストと有資格者不足
PMDA監査では検証済みチャンバー、非常用発電機、文書化された標準作業手順書(SOP)が要求され、中規模施設の場合、初期投資額が約1,200万米ドルに膨らみます。GDP訓練を受けた技術者の不足により、年間賃金の中央値は一般倉庫スタッフより18%高くなっています。小規模な地域3PL事業者は模擬検査に不合格となることが多く、合併や撤退を余儀なくされ、ニッチ分野での競合が緩和されています。
セグメント分析
2025年、国内輸送管理は日本の医薬品3PL市場全体の42.15%を占めました。これは関東・関西に密集する生産拠点が、全国8,000以上の病院および59,000の薬局と結びついているためです。日本の医薬品3PL市場の規模は日々の補充サイクルに依存しているため、運送会社はリアルタイムGPSとドアセンサーを装備した温度区画式ボックストラックを運用しています。当日配送が標準化され、規制要件により各配送拠点で改ざん防止ラベルを発行する車載プリンターの維持が義務付けられています。
国際輸送管理は規模こそ小さいもの、日本の製薬企業が世界の臨床試験やバイオ医薬品輸入を拡大するにつれ、CAGR5.25%で増加しています。このセグメントの高付加価値は、二重包装、冗長データロガー、EU GDPおよび米国CFR-21への準拠に由来します。日本通運は25カ国に36ヶ所のGDP認証ステーションをネットワーク化し、フライト予約前に輸送経路の温度プロファイルを調整することで逸脱リスクを最小化しています。こうした能力は、1回の逸脱で50万米ドル相当のバッチ全体が無効となる治験用細胞療法を輸送するスポンサー企業を惹きつけています。
2025年時点で、製薬メーカーは日本の医薬品3PL(サードパーティ・ロジスティクス)市場の44.10%を占めており、従来からの優位性と卸売業者への大量流通ニーズが継続していることを示しています。シリアル化とリコール対応準備の重要性が高まる中、バッチ追跡可能性を確保する外部3PLの必要性は不可欠となり、包装・倉庫保管・リバースロジスティクスを包括する複数年契約のマスターサービス契約が締結されています。
バイオテクノロジー及びバイオシミラーメーカーは、再生医療に対する政府の優遇措置を反映し、CAGR6.55%で最も急成長している顧客層を形成しています。自社物流機能を持たないスタートアップ企業は、資産を最小限に抑えたパートナーシップを好み、アイデンティティの連鎖記録を確保するため、第I相試験段階から3PLを活用するケースが増えています。臨床研究スポンサー、専門薬局、患者向け直接販売プラットフォームは、マイクロフルフィルメント能力の需要を増加させており、これにより俊敏なプロバイダーの収益基盤が拡大しています。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- アナリストサポート(3ヶ月間)
よくあるご質問
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場の定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- 温度管理が必要な生物製剤・ワクチンに対する需要の増加
- 日本の製薬メーカーにおけるアウトソーシング動向
- 医薬品電子商取引の急増とラストマイル・コールドチェーン需要の拡大
- ドローンを活用した地方配送のパイロット事業
- カーボンニュートラルなコールドチェーンへの投資
- AIを活用した廃棄削減と配送ルート最適化
- 市場抑制要因
- GDPコンプライアンスコストと熟練労働者不足
- 都市部における冷蔵倉庫用不動産の不足状況とコスト
- 超低温倉庫における電気料金の上昇
- 災害リスク保険及び緊急時対応費用
- 価値/バリューチェーン分析
- 規制情勢
- テクノロジーの展望
- ポーターのファイブフォース
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 買い手の交渉力
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係
- 日本の医薬品電子商取引市場
- 医薬品包装の注目点- 世界の及び日本の動向
- COVID-19および地政学的イベントが市場に与える影響
第5章 市場規模と成長予測
- サービスタイプ別
- 国内輸送管理(DTM)
- 道路
- 鉄道
- 航空路
- 水運
- 国際輸送管理(ITM)
- 道路
- 鉄道
- 航空路
- 水運
- 付加価値型倉庫・物流サービス(VAWD)
- 国内輸送管理(DTM)
- 温度タイプ別
- コールドチェーン
- 非冷蔵チェーン
- エンドユーザー別
- 製薬メーカー
- バイオテクノロジー及びバイオシミラー製造メーカー
- 臨床調査・試験スポンサー
- 病院・小売薬局
- ヘルスケア卸売業者・流通業者
- オンライン薬局・患者様向け直接サービス
- その他
- 製品タイプ別
- 処方薬
- 一般用医薬品・消費者向け健康製品
- バイオ医薬品・バイオシミラー(CGTを除く)
- 細胞・遺伝子治療
- ワクチン・血液由来製品
- 動物用医薬品・動物用衛生製品
- 医療機器、診断薬及び複合製品
- 臨床試験用医薬品(治験薬)
- その他
- 地域別(日本)
- 北海道・東北
- 関東
- 中部
- 関西
- 中国・四国
- 九州・沖縄
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度
- 戦略的動き(M&A、合弁事業、投資)
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業プロファイル
- Nippon Express
- DHL Logistics
- Kuehne+Nagel
- Kerry Logistics
- CEVA Logistics
- FedEx
- Yusen Logistics
- LOGISTEED
- Yamato Transport
- Sagawa Express
- Nissin Corporation
- Suzuyo Co.
- Mitsubishi Logistics
- Sankyu Inc.
- Kintetsu World Express(KWE)
- NNR Global Logistics
- Suzuken Group
- Itochu Logistics
- Nichirei Logistics Group
- Kokusai Express


