|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1444102
畜産・食肉:市場シェア分析、業界動向と統計、成長予測(2024~2029年)Livestock and Meat - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 畜産・食肉:市場シェア分析、業界動向と統計、成長予測(2024~2029年) |
|
出版日: 2024年02月15日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 185 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
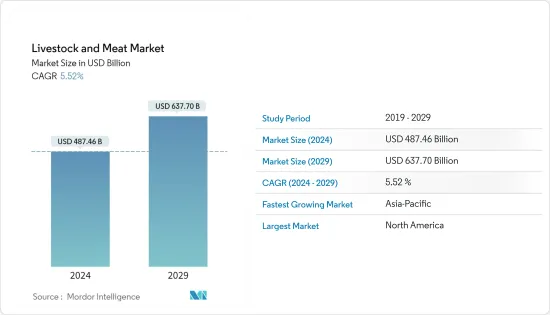
畜産・食肉の市場規模は、2024年に4,874億6,000万米ドルと推定され、2029年までに6,377億米ドルに達すると予測されており、予測期間(2024年から2029年)中に5.52%のCAGRで成長します。
動物飼料の生産に利用できる土地と水の資源が限られていることと、これらの資源の食品への利用が増加していることにより、食肉業界全体で動物飼料の需要が高まっています。インド、中国、ブラジル、ロシアなどの国々は、世界で最も急速に成長している経済国の一つです。一人当たりの収入の増加により、食事の好みはタンパク質が豊富な食事へと移行すると予想されます。
しかし、各国の文化、宗教、その他の消費者の嗜好要因により、肉の消費パターンは世界各地で依然として大きく異なると予想されます。
世界的には、人口増加動向も世界の肉および魚介類市場の成長を支えています。食生活パターンの変化、タンパク質摂取量の増加、都市化、人口、経済成長により、アジア太平洋地域とラテンアメリカ地域での肉消費量の最も高い伸びが予想されています。たとえば、OECD農業統計 2022年報告書によると、世界的に、鶏肉、豚肉、牛肉、羊肉からのタンパク質の入手可能量は、2031年までにそれぞれ16%、17%、8%、16%増加すると予測されています。
畜産・食肉市場の動向
動物性タンパク質の需要の増加
WHOによると、年間の食肉生産量は、主に世界中の消費者の健康意識の高まりによってタンパク質が豊富な食品への需要が高まっているため、1997年から1999年の2億1,800万トンから2030年までに3億7,600万トンに増加すると予測されています。動物性タンパク質の需要の高まりと、低脂肪・高タンパク質の食事に対する消費者の嗜好の高まりにより、世界中で動物性タンパク質の消費量が顕著に増加しています。
この傾向は、アフリカ、アジア太平洋、特に中東における西洋料理の影響によって推進されてきました。 OECD-FAO農業見通し2022報告書によると、家禽肉の消費量は予測期間中に世界全体で1億5,400万トンに増加すると予測されており、これは追加で消費される肉のほぼ半分を占めます。一人当たりの家禽消費量のこうした堅調な伸び率は、中国、インド、インドネシア、マレーシア、パキスタン、ペルーなどを含む人口の多い新興諸国の国民食において鶏肉が果たす重要な役割を反映しています。
アジア太平洋は市場で最も急速に成長している
アジア太平洋の発展途上国における食肉生産の増加は、畜産・食肉産業全体の高い成長につながっています。中国は世界最大の食肉生産国で、次いで米国、欧州連合、ブラジル、ロシアが続きます。世界的には、特に新興諸国において、より統合されたシステムに向けた生産単位の規模拡大と統合によって家畜の拡大が促進される可能性があります。
この傾向は、多忙なライフスタイルと可処分所得の増加による中国人消費者の食生活の変化によるものです。加工肉の消費は所得の増加に伴い着実に増加しており、国内の食肉市場を牽引しています。
家禽肉は引き続き食肉生産の主な原動力となり、2031年までに16%を記録する可能性があります。他の反芻動物と比べて肉と飼料の価格比率が有利であり、生産サイクルが短いため、家禽生産者は市場のシグナルに迅速に対応しながら、課題に取り組むことができます。遺伝学、動物の健康、給餌方法の急速な改善に取り組みます。中国、インド、インドネシアでは持続的な生産性向上により生産が拡大する可能性があります。
中国の食品と肉の需要は、量と質の面で増加し続けています。土地、飼料、水、サプライチェーンの問題により地元の食肉供給が制限されているため、中国は食肉のかなりの部分をオーストラリア、ブラジル、ウルグアイ、アルゼンチンから輸入しなければならないです。中国全土で近代化と都市化が進む中、ベーコンやハム製品など、西洋の影響を受けた低温食肉製品の需要が食肉市場を牽引しています。
羊肉の生産量の増加は、中国、インド、パキスタンを筆頭にアジアで始まる可能性が高いです。しかし、アフリカ、特にサハラ以南アフリカの後発開発途上国でも大幅な増加が見込まれています。一部の国では都市化、砂漠化、飼料の入手可能性に関連した制限があるにもかかわらず、羊とヤギはその大規模な生産システムによってその地域によく適応しています。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3か月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場の定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場力学
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- 市場抑制要因
- 畜産・食肉産業のバリューチェーン
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 畜産活動
- ライブアニマル取引
- 食用肉
- 牛肉
- 家禽
- 豚肉
- マトン
- その他
- 肉副産物
- 内臓肉
- 脂肪
- 畜産物
- 生乳
- 卵
- 天然蜂蜜
- 蜜蝋
- 羊毛
- 生皮・皮
- 地域
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- メキシコ
- その他北米
- 欧州
- ドイツ
- 英国
- フランス
- スペイン
- ロシア
- イタリア
- その他欧州
- アジア太平洋
- 中国
- インド
- オーストラリア
- 日本
- その他アジア太平洋
- 南米
- ブラジル
- アルゼンチン
- その他南米
- 中東とアフリカ
- サウジアラビア
- 南アフリカ
- その他中東とアフリカ
- 北米
第6章 市場機会と将来の動向
The Livestock and Meat Market size is estimated at USD 487.46 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 637.70 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 5.52% during the forecast period (2024-2029).

The limited availability of land and water resources for animal feed production and the increasing use of these resources for food are boosting the demand for animal feed in the overall meat industry. Countries such as India, China, Brazil, and Russia are among the world's fastest-growing economies. A rise in per capita income is expected to shift dietary preferences toward protein-rich diets.
However, meat consumption patterns are expected to remain significantly different in various parts of the world because of cultural, religious, and other consumer preference factors in different countries.
Globally, increasing population trends also support the growth of the world's meat and seafood market. The highest growth in meat consumption is expected from the Asia-Pacific and Latin American regions due to changing diet patterns, higher protein intake, urbanization, population, and economic growth. For instance, according to the OECD Agriculture Statistics 2022 Report, globally, protein availability from poultry, pork, beef, and sheep meat is projected to grow by 16%, 17%, 8%, and 16%, respectively, by 2031.
Livestock & Meat Market Trends
Increasing Demand for Animal Proteins
According to the WHO, annual meat production is projected to increase from 218.0 million metric ton in 1997-1999 to 376.0 million metric ton by 2030 due to the growing demand for protein-rich food, primarily driven by the rising health consciousness among consumers globally. The increasing demand for animal protein, along with the growing consumer preference for low-fat and high-protein diets, has led to a remarkable rise in the consumption of animal protein across the world.
This trend has been driven by the influence of western cuisines across Africa, Asia-Pacific, and especially the Middle East. As per the OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2022 Report, the consumption of poultry meat is projected to increase globally to 154 million metric ton over the forecast period, accounting for nearly half of the additional meat consumed. On a per capita basis, these robust growth rates in poultry consumption reflect the significant role it plays in the national diets of several populous developing countries, including China, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Pakistan, Peru, and others.
Asia-Pacific is the Fastest Growing in the Market
The growing meat production in the developing nations of Asia-Pacific is leading to high growth in the overall livestock and meat industry. China is the world's largest meat producer, followed by the United States, the European Union, Brazil, and Russia. Globally, livestock expansion is likely to be facilitated by the increasing size and consolidation of production units toward more integrated systems, especially in emerging developing countries.
This trend is due to changes in the dietary patterns of Chinese consumers due to busy lifestyles and rising disposable incomes. The consumption of processed meat has been steadily increasing, in line with income growth, thus driving the meat market in the country.
Poultry meat may continue to be the primary driver of meat production, registering a 16% by 2031. With favorable meat-to-feed price ratios compared to other ruminants and a short production cycle, poultry producers can respond quickly to market signals while taking on board rapid improvements in genetics, animal health, and feeding practices. Production may expand from sustained productivity gains in China, India, and Indonesia.
China's demand for food and meat continues to rise in terms of quantity and quality. With local meat supplies limited by land, feed, water, and supply chain issues, China has to import a significant proportion of the meat from Australia, Brazil, Uruguay, and Argentina. With increasing modernization and urbanization across China, demand for western-influenced low-temperature meat products, such as bacon and ham products, is driving the meat market.
The growing sheep meat production will likely originate in Asia, led by China, India, and Pakistan. However, significant increases are also projected in Africa, particularly in the least developed countries of Sub-Saharan Africa. Despite limitations linked to urbanisation, desertification, and the availability of feed in some countries, sheep and goats are well adapted to the region with their extensive production systems.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.4 Value Chain of Livestock and Meat Industry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Livestock Activity
- 5.1.1 Live Animals Trade
- 5.1.2 Edible Meat
- 5.1.2.1 Beef
- 5.1.2.2 Poultry
- 5.1.2.3 Pork
- 5.1.2.4 Mutton
- 5.1.2.5 Other Edible Meat
- 5.1.3 Meat Byproducts
- 5.1.3.1 Meat Offal
- 5.1.3.2 Fats
- 5.1.4 Livestock Products
- 5.1.4.1 Raw Milk
- 5.1.4.2 Eggs
- 5.1.4.3 Natural Honey
- 5.1.4.4 Beeswax
- 5.1.4.5 Wool
- 5.1.4.6 Raw Hides and Skin
- 5.2 Geography
- 5.2.1 North America
- 5.2.1.1 United States
- 5.2.1.2 Canada
- 5.2.1.3 Mexico
- 5.2.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.2.2 Europe
- 5.2.2.1 Germany
- 5.2.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.2.2.3 France
- 5.2.2.4 Spain
- 5.2.2.5 Russia
- 5.2.2.6 Italy
- 5.2.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.2.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.2.3.1 China
- 5.2.3.2 India
- 5.2.3.3 Australia
- 5.2.3.4 Japan
- 5.2.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.2.4 South America
- 5.2.4.1 Brazil
- 5.2.4.2 Argentina
- 5.2.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.2.5 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.2.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.2.5.2 South Africa
- 5.2.5.3 Rest of Middle-East and Africa
- 5.2.1 North America






