|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1741579
スマート鉄道の世界市場:オファリング別(ソリューション、サービス)、地域別 - 2030年までの予測Smart Railways Market by Offering (Solutions (Rail Asset Management & Maintenance, Operation & Control, Communication & Networking, Security & Safety, and Rail Analytics) and Services (Professional and Managed)) Region - Global Forecast to 2030 |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
|
|||||||
| スマート鉄道の世界市場:オファリング別(ソリューション、サービス)、地域別 - 2030年までの予測 |
|
出版日: 2025年05月27日
発行: MarketsandMarkets
ページ情報: 英文 309 Pages
納期: 即納可能
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
スマート鉄道の市場規模は、2025年に364億9,000万米ドルと推定され、今後8.3%のCAGRで拡大し、2030年には543億1,000万米ドルに達すると予測されています。
クラウドコンピューティングとエッジコンピューティングへのシフトは、鉄道ネットワークの管理において革命的です。これらの技術により、鉄道事業者は信号、機関車、発券ゲートなど、より発生源に近い場所で膨大な量の運行データを処理できるようになり、同時にリアルタイムの意思決定や混乱への対応が可能になります。クラウドコンピューティングは、データ管理、ルート最適化、複数オペレーターの調整を可能にし、これは相互接続された鉄道ネットワークや国境を越えた鉄道ネットワークにおいて特に重要です。一方、エッジ・コンピューティングは、自動信号、監視、緊急対応システムなどのミッションクリティカルなアプリケーションの待ち時間を最小化します。この組み合わせにより、拡張性、サイバーセキュリティ、データ分析能力が向上します。スムーズで安全な旅を求める乗客の期待が高まり、各国政府が国家のデジタル化課題の一環として交通インフラのスマート化を推進する中、クラウドコンピューティングとエッジコンピューティングはスマート鉄道戦略に不可欠なものとなりつつあります。ベンダーは現在、鉄道事業者に特化したPlatform-as-a-Service(PaaS)とAIを搭載したエッジソリューションを提供しており、この動向は鉄道デジタル変革の中核となっています。
| 調査範囲 | |
|---|---|
| 調査対象年 | 2019年~2030年 |
| 基準年 | 2024年 |
| 予測期間 | 2025年~2030年 |
| 検討単位 | 米ドル(10億米ドル) |
| セグメント別 | オファリング別、地域別 |
| 対象地域 | 北米、欧州、アジア太平洋、中東・アフリカ、ラテンアメリカ |
トレーニング、サポート、保守サービスは、ユーザーや顧客が運用実務知識を習得するのに役立ちます。これらのサービスには、年中無休の顧客サポート、修理、アップグレード、スマート鉄道ソリューションの事前支援などが含まれるが、これらのサービスは、その利点を活用するために従業員が適切な訓練を受けない限り、最適なレベルで活用することはできません。トレーニングは組織にとってコストのかかるものですが、コラボレーション戦略の適切な実行に役立つため、従業員がアイデアを生み出し、集約できるようになり、従業員の生産性が向上します。さらに、厳しいトレーニングは、従業員がスマート鉄道ソリューションの様々な用途や利点を認識するようになるため、スマート鉄道ソリューションの採用拡大にも役立ちます。タイムリーなサポートとメンテナンスは、スマート鉄道ソリューションの全体的なパフォーマンスにおける問題の可能性を減らします。サポートとメンテナンス・サービスを提供するベンダーは、ソリューションの性能向上、資本支出(CAPEX)と運用支出(OPEX)の削減、エンド・ツー・エンドのスマート鉄道ソリューションの提供とマルチベンダー・サポートの確保に重点を置いています。サポート・メンテナンスチームは、政府や鉄道当局がスマート鉄道ソリューション導入への投資から利益を得られるよう支援します。
マルチメディア情報およびエンターテインメント・ソリューションは、列車での移動中に情報とエンターテインメントを求める乗客の需要を満たします。これらのソリューションは、あらゆる種類のデジタル・メディア・コンテンツを管理し、鉄道利用者に配信するための高度なソフトウェア・ソリューションとアプリケーションで構成され、快適な旅行体験を実現します。これらのソリューションはまた、旅行者が列車内でコミュニケーションを図り、旅行中の緊急事態に効率的に対応できるよう支援します。マルチメディア情報エンターテインメント・ソリューション分野の成長は、高解像度のデジタル・メディア・コンテンツや、列車の旅に関するリアルタイムの最新情報に対する需要の高まりによって特徴づけられます。
アジア太平洋のスマート鉄道市場は、予測期間中に最も速い成長を遂げると予想されます。この成長の原動力は、新興国による先進技術の積極的な導入とデジタルトランスフォーメーション構想への多額の投資です。中国、インド、韓国、シンガポール、オーストラリアなどの国々が最前線で、鉄道網の近代化に多額の資金を投じています。この地域では人口密度が高いため、輸送需要の増加に対応するために既存の鉄道インフラを拡張・改善することが急務となっています。加えて、スマートインフラとデジタル通信を支援する政府の計画が、市場成長の強力な促進要因となっています。様々な産業における貨物輸送量の増加、前向きな経済動向、支援的な規制環境は、予測期間中のアジア太平洋地域におけるスマート鉄道市場の急成長に寄与する主な要因です。日本や中国などの国々における自律走行列車やAI駆動型交通システムへの大規模な投資も、同地域の市場における地位を強化しています。
当レポートでは、世界のスマート鉄道市場について調査し、オファリング別、地域別動向、および市場に参入する企業のプロファイルなどをまとめています。
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 重要考察
第5章 市場概要
- イントロダクション
- 市場力学
- スマート鉄道の簡単な歴史
- エコシステム分析
- ケーススタディ分析
- サプライチェーン分析
- 関税と規制状況
- 規制状況
- 価格分析
- 技術分析
- 特許分析
- 2025年~2026年の主な会議とイベント
- ポーターのファイブフォースモデル
- 貿易分析
- 顧客のビジネスに影響を与える動向と混乱
- 主要な利害関係者と購入基準
- スマート鉄道市場におけるベストプラクティス
- スマート鉄道市場向け技術ロードマップ
- 投資と資金調達のシナリオ
- スマート鉄道のビジネスモデル
- スマート鉄道市場におけるAI/生成AIの影響
第6章 2025年の米国関税の影響- スマート鉄道市場
- イントロダクション
- 主要関税率
- 価格影響分析
- 国/地域への影響
- 米国
- 欧州
- アジア太平洋
- スマート鉄道市場セグメントへの影響
第7章 スマート鉄道市場、オファリング別
- イントロダクション
- ソリューション
- ソリューション:スマート鉄道市場促進要因
- 旅客情報システム
- 貨物管理システム
- セキュリティと安全ソリューション
- 鉄道通信ネットワークシステム
- スマートチケットシステム
- 鉄道分析システム
- 鉄道資産管理および保守ソリューション
- 鉄道運行・制御ソリューション
- サービス
- サービス:スマート鉄道市場促進要因
- 専門サービス
- マネージドサービス
第8章 スマート鉄道市場、地域別
- イントロダクション
- 北米
- 北米:PESTLE分析
- 北米:市場促進要因
- 北米:マクロ経済見通し
- 米国
- カナダ
- 欧州
- 欧州:市場促進要因
- 欧州:マクロ経済見通し
- 英国
- ドイツ
- フランス
- イタリア
- スペイン
- 北欧諸国
- その他
- アジア太平洋
- アジア太平洋:市場促進要因
- アジア太平洋:マクロ経済見通し
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- オーストラリアとニュージーランド(ANZ)
- 東南アジア
- その他
- 中東・アフリカ
- 中東・アフリカ:市場促進要因
- 中東・アフリカ:マクロ経済見通し
- 中東
- アフリカ
- ラテンアメリカ
- ラテンアメリカ:市場促進要因
- ラテンアメリカ:マクロ経済見通し
- ブラジル
- メキシコ
- その他
第9章 競合情勢
- イントロダクション
- 主要参入企業の戦略/強み、2022年~2025年
- 市場シェア分析、2024年
- 主要企業の収益分析(2020~2024年)
- ブランド/製品比較
- 企業評価と財務指標
- 企業評価マトリックス:主要参入企業、2024年
- 企業評価マトリックス:中小企業/スタートアップ、2024年
- 競合シナリオ
第10章 企業プロファイル
- 主要参入企業
- ALSTOM
- CISCO
- HITACHI
- WABTEC
- SIEMENS
- IBM
- HUAWEI
- INDRA SISTEMAS
- HONEYWELL
- ABB
- ADVANTECH
- FUJITSU
- TOSHIBA
- MOXA
- TELEVIC
- ALCATEL-LUCENT ENTERPRISE
- CONDUENT
- スタートアップ/中小企業
- EKE-ELECTRONICS
- AITEK S.P.A.
- UPTAKE
- EUROTECH
- TEGO
- KONUX
- ASSETIC
- MACHINES WITH VISION
- DELPHISONIC
- PASSIO TECHNOLOGIES
- CLOUDMOYO
- CHEMITO
- RAILTEL
第11章 隣接市場/関連市場
- 制限事項
- 鉄道管理システム市場:2025年までの世界の予測
- 鉄道プラットフォームセキュリティ市場:2024年までの世界の予測
- デジタル鉄道市場:2024年までの世界の予測
第12章 付録
List of Tables
- TABLE 1 USD EXCHANGE RATES, 2020-2024
- TABLE 2 RISK ASSESSMENT
- TABLE 3 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET ECOSYSTEM
- TABLE 4 TARIFF RELATED TO AERIALS AND AERIAL REFLECTORS OF ALL KINDS (HSN: 853010), 2024
- TABLE 5 NORTH AMERICA: REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- TABLE 6 EUROPE: REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- TABLE 7 ASIA PACIFIC: REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- TABLE 8 REST OF THE WORLD: REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- TABLE 9 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE OF KEY PLAYERS, BY OFFERING
- TABLE 10 INDICATIVE PRICING ANALYSIS OF KEY PLAYERS, BY SOLUTION
- TABLE 11 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: LIST OF TOP PATENTS, 2024
- TABLE 12 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: LIST OF KEY CONFERENCES AND EVENTS
- TABLE 13 IMPACT OF EACH FORCE ON SMART RAILWAYS MARKET
- TABLE 14 INFLUENCE OF STAKEHOLDERS ON BUYING PROCESS FOR TOP THREE SOLUTIONS
- TABLE 15 KEY BUYING CRITERIA FOR TOP THREE SOLUTIONS
- TABLE 16 US ADJUSTED RECIPROCAL TARIFF RATES
- TABLE 17 EXPECTED CHANGE IN PRICES AND LIKELY IMPACT ON END-USE MARKET DUE TO TARIFF IMPACT
- TABLE 18 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY OFFERING, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 19 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY OFFERING, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 20 SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 21 SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 22 SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 23 SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 24 PASSENGER INFORMATION SYSTEM: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 25 PASSENGER INFORMATION SYSTEM: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 26 PASSENGER INFORMATION SYSTEM: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 27 PASSENGER INFORMATION SYSTEM: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 28 MULTIMEDIA INFORMATION AND ENTERTAINMENT: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 29 MULTIMEDIA INFORMATION AND ENTERTAINMENT: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 30 NETWORK CONNECTIVITY: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 31 NETWORK CONNECTIVITY: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 32 FREIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 33 FREIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 34 FREIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 35 FREIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 36 FREIGHT OPERATION MANAGEMENT: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 37 FREIGHT OPERATION MANAGEMENT: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 38 FREIGHT TRACKING: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 39 FREIGHT TRACKING: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 40 SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 41 SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 42 SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 43 SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 44 VIDEO SURVEILLANCE AND ANALYTICS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 45 VIDEO SURVEILLANCE AND ANALYTICS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 46 INTRUSION DETECTION: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 47 INTRUSION DETECTION: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 48 ACCESS CONTROL: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 49 ACCESS CONTROL: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 50 FIRE ALARM AND VOICE EVACUATION: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 51 FIRE ALARM AND VOICE EVACUATION: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 52 OTHER SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 53 OTHER SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 54 RAIL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING SYSTEM: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 55 RAIL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING SYSTEM: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 56 RAIL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING SYSTEM: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 57 RAIL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING SYSTEM: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 58 GROUND-TO-TRAIN COMMUNICATION: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 59 GROUND-TO-TRAIN COMMUNICATION: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 60 TRAIN-TO-TRAIN COMMUNICATION: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 61 TRAIN-TO-TRAIN COMMUNICATION: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 62 SMART TICKETING SYSTEM: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 63 SMART TICKETING SYSTEM: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 64 RAIL ANALYTICS SYSTEM: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 65 RAIL ANALYTICS SYSTEM: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 66 RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 67 RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 68 RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 69 RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 70 ASSET PLANNING AND SCHEDULING: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 71 ASSET PLANNING AND SCHEDULING: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 72 WORKFORCE MANAGEMENT AND OPTIMIZATION: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 73 WORKFORCE MANAGEMENT AND OPTIMIZATION: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 74 CONDITION-BASED MONITORING: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 75 CONDITION-BASED MONITORING: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 76 PREDICTIVE MAINTENANCE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 77 PREDICTIVE MAINTENANCE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 78 OTHER RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 79 OTHER RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 80 RAIL OPERATION AND CONTROL SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 81 RAIL OPERATION AND CONTROL SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 82 SERVICES: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 83 SERVICES: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 84 SERVICES: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 85 SERVICES: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 86 PROFESSIONAL SERVICES: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 87 PROFESSIONAL SERVICES: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 88 PROFESSIONAL SERVICES: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 89 PROFESSIONAL SERVICES: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 90 CONSULTING: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 91 CONSULTING: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 92 SYSTEM INTEGRATION AND DEPLOYMENT: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 93 SYSTEM INTEGRATION AND DEPLOYMENT: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 94 TRAINING, SUPPORT, AND MAINTENANCE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 95 TRAINING, SUPPORT, AND MAINTENANCE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 96 MANAGED SERVICES: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 97 MANAGED SERVICES: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 98 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 99 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 100 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY OFFERING, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 101 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY OFFERING, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 102 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SOLUTIONS, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 103 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SOLUTIONS, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 104 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PASSENGER INFORMATION SYSTEM, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 105 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PASSENGER INFORMATION SYSTEM, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 106 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY FREIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 107 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY FREIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 108 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 109 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 110 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING SYSTEM, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 111 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING SYSTEM, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 112 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 113 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 114 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SERVICES, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 115 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SERVICES, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 116 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 117 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 118 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 119 NORTH AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 120 US: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY OFFERING, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 121 US: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY OFFERING, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 122 US: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SOLUTIONS, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 123 US: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SOLUTIONS, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 124 US: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PASSENGER INFORMATION SYSTEM, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 125 US: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PASSENGER INFORMATION SYSTEM, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 126 US: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY FREIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 127 US: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY FREIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 128 US: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 129 US: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 130 US: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING SYSTEM, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 131 US: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING SYSTEM, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 132 US: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 133 US: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 134 US: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SERVICES, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 135 US: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SERVICES, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 136 US: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 137 US: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 138 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY OFFERING, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 139 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY OFFERING, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 140 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SOLUTIONS, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 141 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SOLUTIONS, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 142 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PASSENGER INFORMATION SYSTEM, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 143 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PASSENGER INFORMATION SYSTEM, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 144 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY FREIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 145 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY FREIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 146 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 147 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 148 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING SYSTEM, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 149 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING SYSTEM, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 150 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 151 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 152 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SERVICES, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 153 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SERVICES, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 154 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 155 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 156 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 157 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 158 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY OFFERING, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 159 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY OFFERING, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 160 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SOLUTIONS, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 161 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SOLUTIONS, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 162 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PASSENGER INFORMATION SYSTEM, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 163 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PASSENGER INFORMATION SYSTEM, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 164 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY FREIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 165 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY FREIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 166 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 167 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 168 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING SYSTEM, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 169 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING SYSTEM, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 170 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 171 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 172 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SERVICES, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 173 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SERVICES, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 174 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 175 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 176 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 177 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 178 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY OFFERING, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 179 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY OFFERING, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 180 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SOLUTIONS, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 181 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SOLUTIONS, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 182 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PASSENGER INFORMATION SYSTEM, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 183 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PASSENGER INFORMATION SYSTEM, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 184 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY FREIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 185 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY FREIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 186 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 187 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 188 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING SYSTEM, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 189 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING SYSTEM, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 190 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 191 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 192 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SERVICES, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 193 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SERVICES, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 194 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 195 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 196 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 197 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 198 MIDDLE EAST: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 199 MIDDLE EAST: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 200 AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 201 AFRICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 202 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY OFFERING, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 203 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY OFFERING, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 204 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SOLUTIONS, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 205 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SOLUTIONS, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 206 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PASSENGER INFORMATION SYSTEM, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 207 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PASSENGER INFORMATION SYSTEM, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 208 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY FREIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 209 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY FREIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 210 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 211 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 212 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING SYSTEM, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 213 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING SYSTEM, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 214 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 215 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 216 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SERVICES, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 217 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY SERVICES, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 218 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 219 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 220 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2019-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 221 LATIN AMERICA: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 222 OVERVIEW OF STRATEGIES DEPLOYED BY KEY MARKET PLAYERS, 2022-2025
- TABLE 223 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: DEGREE OF COMPETITION
- TABLE 224 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: REGION FOOTPRINT
- TABLE 225 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: OFFERING FOOTPRINT
- TABLE 226 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: LIST OF KEY STARTUPS/SMES
- TABLE 227 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING OF KEY STARTUPS/SMES
- TABLE 228 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: PRODUCT LAUNCHES, JANUARY 2019-MAY 2025
- TABLE 229 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: DEALS, JANUARY 2019-MAY 2025
- TABLE 230 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: OTHER DEVELOPMENTS, JANUARY 2019-MAY 2025
- TABLE 231 ALSTOM: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 232 ALSTOM: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 233 ALSTOM: DEALS
- TABLE 234 ALSTOM: OTHER DEVELOPMENTS
- TABLE 235 CISCO: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 236 CISCO: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 237 CISCO: DEALS
- TABLE 238 HITACHI: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 239 HITACHI: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 240 HITACHI: PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- TABLE 241 HITACHI: DEALS
- TABLE 242 HITACHI: OTHER DEVELOPMENTS
- TABLE 243 WABTEC: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 244 WABTEC: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 245 WABTEC: PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- TABLE 246 WABTEC: DEALS
- TABLE 247 SIEMENS: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 248 SIEMENS: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 249 WABTEC: PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- TABLE 250 SIEMENS: DEALS
- TABLE 251 SIEMENS: OTHER DEVELOPMENTS
- TABLE 252 IBM: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 253 IBM: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 254 IBM: DEALS
- TABLE 255 HUAWEI: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 256 HUAWEI: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 257 HUAWEI: PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- TABLE 258 HUAWEI: DEALS
- TABLE 259 INDRA SISTEMAS: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 260 INDRA SISTEMAS: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 261 INDRA SISTEMAS: DEALS
- TABLE 262 HONEYWELL: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 263 HONEYWELL: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 264 HONEYWELL: DEALS
- TABLE 265 ABB: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 266 ABB: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 267 ABB: DEALS
- TABLE 268 RAILWAY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM MARKET SIZE, BY OFFERING, 2016-2019 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 269 RAILWAY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM MARKET SIZE, BY OFFERING, 2019-2025 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 270 RAILWAY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM MARKET SIZE, BY SERVICE, 2016-2019 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 271 RAILWAY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM MARKET SIZE, BY SERVICE, 2019-2025 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 272 RAILWAY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2016-2019 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 273 RAILWAY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2019-2025 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 274 RAILWAY PLATFORM SECURITY MARKET SIZE, BY COMPONENT, 2017-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 275 SOLUTIONS: RAILWAY PLATFORM SECURITY MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2017-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 276 SERVICES: RAILWAY PLATFORM SECURITY MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2017-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 277 PROFESSIONAL SERVICES: RAILWAY PLATFORM SECURITY MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2017-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 278 RAILWAY PLATFORM SECURITY MARKET SIZE, BY APPLICATION, 2017-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 279 RAILWAY PLATFORM SECURITY MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2017-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 280 DIGITAL RAILWAY MARKET SIZE, BY SOLUTION, 2017-2024 (USD BILLION)
- TABLE 281 DIGITAL RAILWAY MARKET SIZE, BY SERVICE, 2017-2024 (USD BILLION)
- TABLE 282 PROFESSIONAL SERVICES: DIGITAL RAILWAY MARKET SIZE, BY TYPE, 2017-2024 (USD BILLION)
- TABLE 283 DIGITAL RAILWAY MARKET SIZE, BY APPLICATION, 2017-2024 (USD BILLION)
- TABLE 284 DIGITAL RAILWAY MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2017-2024 (USD BILLION)
List of Figures
- FIGURE 1 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: RESEARCH DESIGN
- FIGURE 2 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: TOP-DOWN AND BOTTOM-UP APPROACHES
- FIGURE 3 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION METHODOLOGY-APPROACH 1 (SUPPLY SIDE): REVENUE OF VENDORS IN SMART RAILWAYS MARKET
- FIGURE 4 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION METHODOLOGY-APPROACH 2 (DEMAND SIDE): SMART RAILWAYS MARKET
- FIGURE 5 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION METHODOLOGY: DEMAND-SIDE ANALYSIS
- FIGURE 6 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION USING BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
- FIGURE 7 DATA TRIANGULATION
- FIGURE 8 RAILWAY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM EVOLUTION
- FIGURE 9 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SIZE, 2023-2030
- FIGURE 10 LARGEST SEGMENTS IN SMART RAILWAYS MARKET, 2025
- FIGURE 11 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET ANALYSIS
- FIGURE 12 NEED FOR EFFICIENCY IN RAIL OPERATIONS TO DRIVE MARKET DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 13 SOLUTIONS SEGMENT AND UK TO HOLD LARGEST MARKET SHARES IN EUROPE DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 14 SOLUTIONS SEGMENT AND CHINA TO HOLD LARGEST MARKET SHARES IN ASIA PACIFIC DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 15 DRIVERS, RESTRAINTS, OPPORTUNITIES, AND CHALLENGES: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET
- FIGURE 16 BRIEF HISTORY OF SMART RAILWAYS
- FIGURE 17 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: ECOSYSTEM
- FIGURE 18 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: SUPPLY CHAIN ANALYSIS
- FIGURE 19 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE OF KEY PLAYERS, BY OFFERING
- FIGURE 20 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: PATENTS APPLIED AND GRANTED, 2015-2024
- FIGURE 21 PORTER'S FIVE FORCES ANALYSIS
- FIGURE 22 EXPORTS OF PARTS SUITABLE FOR ELECTRICAL SIGNALING, SAFETY, OR TRAFFIC CONTROL EQUIPMENT FOR RAILWAYS, TRAMWAYS, AND ROADS, BY COUNTRY, 2017-2024 (USD MILLION)
- FIGURE 23 IMPORTS OF PARTS SUITABLE FOR ELECTRICAL SIGNALING, SAFETY, OR TRAFFIC CONTROL EQUIPMENT FOR RAILWAYS, TRAMWAYS, AND ROADS, BY COUNTRY, 2017-2024 (USD MILLION)
- FIGURE 24 TRENDS AND DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMER BUSINESS
- FIGURE 25 INFLUENCE OF STAKEHOLDERS ON BUYING PROCESS FOR TOP THREE SOLUTIONS
- FIGURE 26 KEY BUYING CRITERIA FOR TOP THREE SOLUTIONS
- FIGURE 27 INVESTMENT IN LEADING GLOBAL SMART RAILWAYS, BY NUMBER OF INVESTORS AND FUNDING (USD MILLION)
- FIGURE 28 USE CASES OF GENERATIVE AI IN SMART RAILWAYS
- FIGURE 29 SERVICES SEGMENT TO GROW AT HIGHER CAGR DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 30 RAIL ANALYTICS SYSTEM SEGMENT TO GROW AT HIGHEST CAGR DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 31 MULTIMEDIA INFORMATION AND ENTERTAINMENT SEGMENT TO GROW AT HIGHER CAGR DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 32 FREIGHT TRACKING SEGMENT TO GROW AT HIGHER CAGR FROM 2025 TO 2030
- FIGURE 33 VIDEO SURVEILLANCE AND ANALYTICS SEGMENT TO GROW AT HIGHEST CAGR DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 34 TRAIN-TO-TRAIN COMMUNICATION SEGMENT TO GROW AT HIGHER CAGR FROM 2025 TO 2030
- FIGURE 35 PREDICTIVE MAINTENANCE SEGMENT TO GROW AT HIGHEST CAGR FROM 2025 TO 2030
- FIGURE 36 MANAGED SERVICES TO GROW AT HIGHER CAGR FROM 2022 TO 2027
- FIGURE 37 TRAINING, SUPPORT, AND MAINTENANCE SEGMENT TO GROW AT HIGHEST CAGR DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 38 EUROPE TO BE LARGEST MARKET DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 39 EUROPE: MARKET SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 40 ASIA PACIFIC: MARKET SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 41 SHARES OF LEADING COMPANIES IN SMART RAILWAYS MARKET, 2024
- FIGURE 42 REVENUE ANALYSIS OF TOP 5 PLAYERS, 2020-2024
- FIGURE 43 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: BRAND/PRODUCT COMPARISON
- FIGURE 44 COMPANY VALUATION: 2025
- FIGURE 45 FINANCIAL METRICS OF KEY VENDORS: 2025
- FIGURE 46 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX (KEY PLAYERS), 2024
- FIGURE 47 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: COMPANY FOOTPRINT
- FIGURE 48 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET: COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX (STARTUPS/SMES), 2024
- FIGURE 49 ALSTOM: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 50 CISCO: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 51 HITACHI: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 52 WABTEC: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 53 SIEMENS: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 54 IBM: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 55 HUAWEI: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 56 INDRA SISTEMAS: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 57 HONEYWELL: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 58 ABB: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
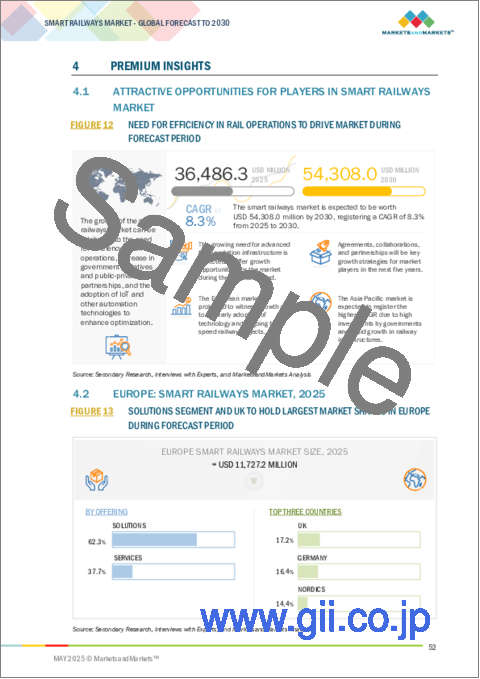
The smart railways market is estimated to be USD 36.49 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 54.31 billion by 2030 at a CAGR of 8.3%. The shift toward cloud and edge computing is revolutionary in the management of railway networks. These technologies enable rail operators to process huge amounts of operational data closer to the source, such as signals, locomotives, or ticketing gates, while enabling real-time decision-making and response to disruptions. Cloud computing allows data management, route optimization, and multi-operator coordination, which is especially important in interconnected or cross-border rail networks. Meanwhile, edge computing minimizes latency in mission-critical applications such as automatic signaling, surveillance, and emergency response systems. This combination improves scalability, cybersecurity, and data analytics capacities. With increasing passenger expectations for smooth and safe journeys and governments pushing for smarter transportation infrastructure as part of their national digitalization agendas, cloud and edge computing are becoming integral to smart rail strategies. Vendors are now providing platform-as-a-service (PaaS) and AI-powered edge solutions focused on rail operators, which makes this trend the core of the digital rail transformation.
| Scope of the Report | |
|---|---|
| Years Considered for the Study | 2019-2030 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2030 |
| Units Considered | USD (Billion) |
| Segments | By Offering and Region |
| Regions covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and Latin America |
"Training, support, and maintenance services segment will witness the highest growth during the forecast period" Training, support, and maintenance services help users or customers gain operational working knowledge. These services include 24/7 customer support, repairs, upgrades, and proactive assistance of smart railway solutions, which cannot be utilized to the optimum level until employees are trained properly to leverage their benefits. Training is a costly affair for an organization, but it helps in the proper execution of the collaboration strategy and thus increases employee productivity by enabling employees to generate and consolidate ideas. Furthermore, rigorous training also helps in the increased adoption of smart railway solutions, as employees become aware of their various uses and benefits. Timely support and maintenance reduce the chances of issues in the overall performance of smart railway solutions. Vendors offering support and maintenance services focus on improving the performance of the solutions, reducing Capital Expenditure (CAPEX) and Operational Expenditure (OPEX), and ensuring end-to-end smart railway solution delivery and multi-vendor support. The support and maintenance teams help government and railway authorities reap benefits from their investments in implementing smart railway solutions.
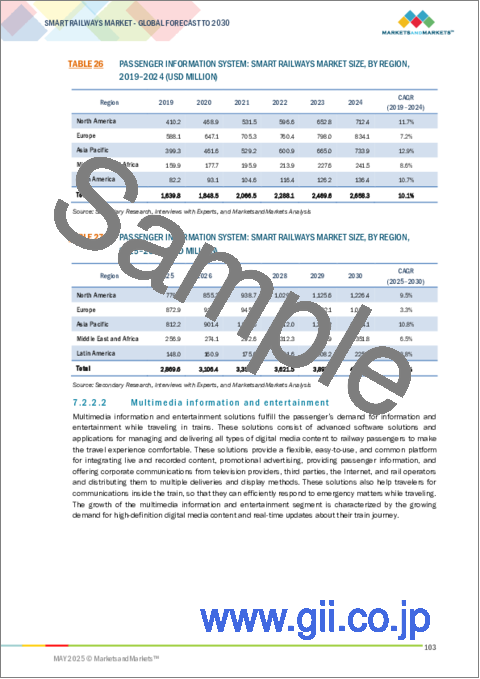
"Multimedia information and entertainment solution segment is expected to have the largest market size during the forecast period" Multimedia information and entertainment solutions fulfill the passenger's demand for information and entertainment while traveling in trains. These solutions consist of advanced software solutions and applications for managing and delivering all types of digital media content to railway passengers to make the travel experience comfortable. These solutions also help travelers communicate inside the train so that they can efficiently respond to emergency matters while traveling. The growth of the multimedia information and entertainment solutions segment is characterized by the growing demand for high-definition digital media content and real-time updates about train journeys.
"Asia Pacific is expected to record the highest growth rate during the forecast period"
The smart railway market in the Asia Pacific region is expected to experience the fastest growth during the forecast period. This growth is driven by the aggressive implementation of advanced technologies and significant investments in digital transformation initiatives by emerging economies. Countries such as China, India, South Korea, Singapore, and Australia are at the forefront, dedicating substantial funds to modernizing their rail networks. The high population density in this region increases the urgent need to expand and improve the existing rail infrastructure to meet the rising demands for transportation. In addition, government schemes to support smart infrastructure and digital communications are serving as powerful drivers of market growth. The increasing freight traffic across various industries, along with positive economic trends and a supportive regulatory environment, are key factors contributing to the smart railways market's rapid growth in the Asia Pacific region during the projected period. Major investments in autonomous trains and AI-driven traffic systems in countries such as Japan or China also strengthen the region's position in the market.
Breakdown of Primaries
The study contains insights from various industry experts, from solution vendors to Tier 1 companies. The break-up of the primaries is as follows:
- By Company Type: Tier 1 - 35%, Tier 2 - 39%, and Tier 3 - 26%
- By Designation: C-level -33%, D-level - 25%, and Others - 42%
- By Region: North America - 38%, Europe - 20%, Asia Pacific - 30%, Rest of the World - 12%
The major players in the smart railways market include Alstom (France), Cisco (US), Wabtec (US), ABB (Switzerland), IBM (US), Hitachi (Japan), Huawei (China), Indra Sistemas (Spain), Siemens (Germany), Honeywell (US), Thales (France), Advantech (Taiwan), Fujitsu (Japan), Toshiba (Japan), Alcatel-Lucent Enterprise (France), Moxa (Taiwan), EKE-Electronics (Finland), Televic (Belgium), Uptake (US), Eurotech (Italy), Tego (US), KONUX (Germany), Aitek S.p.A (Italy), Assetic (Australia), Machines With Vision (UK), Delphisonic (US), Passio Technologies (US), CloudMoyo (US), Conduent (US), RailTel (India), and Chemito (India). These players have adopted various growth strategies, such as partnerships, agreements, collaborations, product launches/enhancements, and acquisitions, to expand their market footprint.
Research Coverage
- The market study covers the market size of smart railways and their growth potential across different segments, including offerings and regions. The offerings are sub-segmented into solutions and services. The solutions studied under the smart railways market include passenger information systems (multimedia information and entertainment, network connectivity), freight management systems (freight operation management, freight tracking), security and safety solutions (video surveillance and analytics, intrusion detection, access control, fire alarm and voice evacuation, others (imaging and scanning solutions and security information management)), rail communication and networking systems (ground-to-train communication, train-to-train communication), smart ticketing systems, rail analytics systems, rail asset management and maintenance solutions (asset planning and scheduling, workforce management and optimization, condition-based monitoring, predictive maintenance, others (incident management, warranty management, and material management)), and rail operation and control solutions. The services studied under the smart railways market include professional services (consulting, system integration and deployment, training support and maintenance) and managed services. The regional analysis of the smart railways market covers North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, the Middle East & Africa, and Latin America.
Key Benefits of Buying the Report
The report will help market leaders and new entrants with information on the closest approximations of the global smart railways market's revenue numbers and subsegments. It will also help stakeholders understand the competitive landscape, gain insights, and plan suitable go-to-market strategies. Moreover, the report will provide insights for stakeholders to understand the market's pulse and provide them with information on key market drivers, restraints, challenges, and opportunities.
The report provides the following insights.
1. Analysis of key drivers (rise in need for efficiency in rail operations, rapid urbanization results in increased need for efficient railway systems, government initiatives and increased number of public-private partnership projects in rail industry, adoption of IoT and other automation technologies for process optimization, technological advancements targeted toward enhancement of customer experience), restraints (high initial cost of deployment), opportunities (increase in globalization and need for advanced transportation infrastructure, rise in demand for cloud-based services), and challenges (integration of advanced and complex systems with legacy infrastructure, disruption in logistics and supply chain of IoT devices, disruption in logistics and supply chain of IoT devices) influencing the growth of the smart railways market
2. Product Development/Innovation: Detailed insights on upcoming technologies, research & development activities, and new product & service launches in the smart railways market
3. Market Development: The report provides comprehensive information about lucrative markets, analyzing the smart railways market across various regions.
4. Market Diversification: Comprehensive information about new products and services, untapped geographies, recent developments, and investments in the smart railways market.
5. Competitive Assessment: In-depth assessment of market shares, growth strategies, and service offerings of leading players: Alstom (France), Cisco (US), Wabtec (US), ABB (Switzerland), IBM (US), Hitachi (Japan), Huawei (China), Indra Sistemas (Spain), Siemens (Germany), Honeywell (US), Thales (France), Advantech (Taiwan), Fujitsu (Japan), Toshiba (Japan), Alcatel-Lucent Enterprise (France), Moxa (Taiwan), EKE-Electronics (Finland), Televic (Belgium), Uptake (US), Eurotech (Italy), Tego (US), KONUX (Germany), Aitek S.p.A. (Italy), Assetic (Australia), Machines With Vision (UK), Delphisonic (US), Passio Technologies (US), CloudMoyo (US), Conduent (US), RailTel (India), and Chemito (India).
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 STUDY OBJECTIVES
- 1.2 MARKET DEFINITION
- 1.3 STUDY SCOPE
- 1.3.1 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 1.3.2 INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS
- 1.3.3 YEARS CONSIDERED
- 1.4 CURRENCY CONSIDERED
- 1.5 STAKEHOLDERS
- 1.6 SUMMARY OF CHANGES
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 RESEARCH DATA
- 2.1.1 SECONDARY DATA
- 2.1.2 PRIMARY DATA
- 2.1.2.1 Primary interviews with experts
- 2.1.2.2 Breakdown of primaries
- 2.1.2.3 Key industry insights
- 2.2 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION
- 2.2.1 TOP-DOWN APPROACH
- 2.2.2 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
- 2.2.3 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET ESTIMATION: DEMAND-SIDE ANALYSIS
- 2.3 MARKET BREAKDOWN AND DATA TRIANGULATION
- 2.4 RISK ASSESSMENT
- 2.5 RESEARCH ASSUMPTIONS
- 2.6 RESEARCH LIMITATIONS
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 PREMIUM INSIGHTS
- 4.1 ATTRACTIVE OPPORTUNITIES FOR PLAYERS IN SMART RAILWAYS MARKET
- 4.2 EUROPE: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET, 2025
- 4.3 ASIA PACIFIC: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET, 2025
5 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 5.1 INTRODUCTION
- 5.2 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.2.1 DRIVERS
- 5.2.1.1 Rise in need for efficiency in rail operations
- 5.2.1.2 Rapid urbanization results in increased need for efficient railway systems
- 5.2.1.3 Government initiatives and increased number of public-private partnership projects in rail industry
- 5.2.1.4 Adoption of IoT and other automation technologies for process optimization
- 5.2.1.5 Technological advancements targeted toward enhancement of customer experience
- 5.2.2 RESTRAINTS
- 5.2.2.1 High initial cost of deployment
- 5.2.3 OPPORTUNITIES
- 5.2.3.1 Increased globalization and need for advanced transportation infrastructure
- 5.2.3.2 Rise in demand for cloud-based services
- 5.2.4 CHALLENGES
- 5.2.4.1 Integration of advanced and complex systems with legacy infrastructure
- 5.2.4.2 Disruption in logistics and supply chain of IoT devices
- 5.2.4.3 Data security and privacy issues related to IoT devices
- 5.2.1 DRIVERS
- 5.3 BRIEF HISTORY OF SMART RAILWAYS
- 5.3.1 1980S-1990S: FOUNDATION LAYING
- 5.3.2 2000S: RISE OF INTELLIGENT INFRASTRUCTURE
- 5.3.3 2010S: DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION AND CONNECTIVITY
- 5.3.4 2020S-PRESENT: AI-DRIVEN AND AUTONOMOUS RAILWAYS
- 5.4 ECOSYSTEM ANALYSIS
- 5.5 CASE STUDY ANALYSIS
- 5.5.1 CASE STUDY 1: LUXEMBOURG RAILWAYS EQUIPPED 34 NEW CORADIA TRAINS WITH ALSTOM'S AUTOMATIC TRAIN OPERATION SYSTEM
- 5.5.2 CASE STUDY 2: VTG RAIL EUROPE COLLABORATED WITH SIEMENS TO INNOVATE RAIL FREIGHT TRANSPORT
- 5.5.3 CASE STUDY 3: UPTAKE AUTOMATED MAINTENANCE WORK ORDER OF A NORTH AMERICAN FREIGHT RAILWAY COMPANY
- 5.5.4 CASE STUDY 4: THALES PROVIDED TRAIN-TO-GROUND BROADBAND DATA COMMUNICATION SOLUTION TO BRESCIA METRO
- 5.5.5 CASE STUDY 5: COMBOIOS DE PORTUGAL IMPLEMENTED SOLUTIONS BY FUJITSU TO INNOVATE ITS TICKETING INFRASTRUCTURE
- 5.5.6 CASE STUDY 6: SIEMENS PROVIDED MAINTENANCE SERVICES TO GOVIA THAMESLINK RAILWAY
- 5.5.7 CASE STUDY 7: ASSETIC HELPED SYDNEY TRAINS VISUALIZE RAIL ASSETS FOR OPTIMIZED ASSET MANAGEMENT
- 5.6 SUPPLY CHAIN ANALYSIS
- 5.7 TARIFF AND REGULATORY LANDSCAPE
- 5.7.1 TARIFF DATA (HSN: 853010) - ELECTRICAL SIGNALING, SAFETY, OR TRAFFIC CONTROL EQUIPMENT FOR RAILWAYS AND TRAMWAYS
- 5.8 REGULATORY LANDSCAPE
- 5.8.1 REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- 5.8.2 KEY REGULATIONS, BY REGION
- 5.8.2.1 North America
- 5.8.2.1.1 US
- 5.8.2.1.2 Canada
- 5.8.2.2 Europe
- 5.8.2.2.1 Germany
- 5.8.2.2.2 UK
- 5.8.2.2.3 UK
- 5.8.2.3 Asia Pacific
- 5.8.2.3.1 China
- 5.8.2.3.2 India
- 5.8.2.3.3 Japan
- 5.8.2.4 Rest of the World
- 5.8.2.4.1 Qatar
- 5.8.2.4.2 Mexico
- 5.8.2.1 North America
- 5.8.3 REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- 5.8.4 ISO
- 5.8.4.1 ISO/IEC JTC 1
- 5.8.4.2 ISO/IEC 27001
- 5.8.4.3 ISO/IEC 19770-1
- 5.8.4.4 ISO/IEC JTC 1/SWG 5
- 5.8.4.5 ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 31
- 5.8.4.6 ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 27
- 5.8.4.7 ISO/IEC JTC 1/WG 7 sensors
- 5.8.5 GDPR
- 5.8.6 FMCSA
- 5.8.7 FHWA
- 5.8.8 MARAD
- 5.8.9 FAA
- 5.8.10 FRA
- 5.8.11 IEEE-SA
- 5.8.12 CEN/ISO
- 5.8.13 CEN/CENELEC
- 5.8.14 ETSI
- 5.8.15 ITU-T
- 5.9 PRICING ANALYSIS
- 5.9.1 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE OF KEY PLAYERS, BY OFFERING
- 5.9.1.1 Indicative pricing analysis of key players, by solution
- 5.9.1 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE OF KEY PLAYERS, BY OFFERING
- 5.10 TECHNOLOGY ANALYSIS
- 5.10.1 KEY TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.10.1.1 Internet of Things (IoT)
- 5.10.1.2 Big data analytics and cloud computing
- 5.10.1.3 Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML)
- 5.10.1.4 Advanced signaling systems
- 5.10.1.5 Communication-based train control (CBTC)
- 5.10.2 ADJACENT TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.10.2.1 Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR)
- 5.10.2.2 Blockchain
- 5.10.2.3 Drones
- 5.10.3 COMPLEMENTARY TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.10.3.1 Edge computing
- 5.10.3.2 Digital twin
- 5.10.3.3 Cybersecurity
- 5.10.3.4 5G and wireless communication networks
- 5.10.1 KEY TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.11 PATENT ANALYSIS
- 5.12 KEY CONFERENCES AND EVENTS, 2025-2026
- 5.13 PORTER'S FIVE FORCES MODEL
- 5.13.1 THREAT OF NEW ENTRANTS
- 5.13.2 THREAT OF SUBSTITUTES
- 5.13.3 BARGAINING POWER OF BUYERS
- 5.13.4 BARGAINING POWER OF SUPPLIERS
- 5.13.5 INTENSITY OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY
- 5.14 TRADE ANALYSIS
- 5.14.1 EXPORT SCENARIO OF PARTS SUITABLE FOR ELECTRICAL SIGNALING, SAFETY, OR TRAFFIC CONTROL EQUIPMENT FOR RAILWAYS, TRAMWAYS, AND ROADS
- 5.14.2 IMPORT SCENARIO OF ELECTRICAL SIGNALING, SAFETY, OR TRAFFIC CONTROL EQUIPMENT FOR RAILWAYS, TRAMWAYS, AND ROADS
- 5.15 TRENDS AND DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMER BUSINESS
- 5.16 KEY STAKEHOLDERS AND BUYING CRITERIA
- 5.16.1 KEY STAKEHOLDERS IN BUYING PROCESS
- 5.16.2 BUYING CRITERIA
- 5.17 BEST PRACTICES IN SMART RAILWAYS MARKET
- 5.18 TECHNOLOGY ROADMAP FOR SMART RAILWAYS MARKET
- 5.18.1 SHORT-TERM ROADMAP (2023-2025)
- 5.18.2 MID-TERM ROADMAP (2026-2028)
- 5.18.3 LONG-TERM ROADMAP (2029-2030)
- 5.19 INVESTMENT AND FUNDING SCENARIO
- 5.20 BUSINESS MODELS OF SMART RAILWAYS
- 5.20.1 CURRENT BUSINESS MODELS
- 5.20.2 EMERGING BUSINESS MODELS
- 5.21 IMPACT OF AI/GENERATIVE AI ON SMART RAILWAYS MARKET
- 5.21.1 USE CASES OF GENERATIVE AI IN SMART RAILWAYS
6 IMPACT OF 2025 US TARIFF - SMART RAILWAYS MARKET
- 6.1 INTRODUCTION
- 6.2 KEY TARIFF RATES
- 6.3 PRICE IMPACT ANALYSIS
- 6.4 IMPACT ON COUNTRY/REGION
- 6.4.1 US
- 6.4.2 EUROPE
- 6.4.3 ASIA PACIFIC
- 6.5 IMPACT ON SMART RAILWAYS MARKET SEGMENTS
7 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET, BY OFFERING
- 7.1 INTRODUCTION
- 7.2 SOLUTIONS
- 7.2.1 SOLUTIONS: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET DRIVERS
- 7.2.2 PASSENGER INFORMATION SYSTEM
- 7.2.2.1 Rising demand for real-time passenger information systems
- 7.2.2.2 Multimedia information and entertainment
- 7.2.2.3 Network connectivity
- 7.2.3 FREIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
- 7.2.3.1 Rapid digitalization and adoption of advanced technologies
- 7.2.3.2 Freight operation management
- 7.2.3.3 Freight tracking
- 7.2.4 SECURITY AND SAFETY SOLUTIONS
- 7.2.4.1 Use of AI and IoT in railway security
- 7.2.4.2 Video surveillance and analytics
- 7.2.4.3 Intrusion detection
- 7.2.4.4 Access control
- 7.2.4.5 Fire alarm and voice evacuation
- 7.2.4.6 Other security and safety solutions
- 7.2.5 RAIL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING SYSTEM
- 7.2.5.1 Emerging requirements for IT and networking in railways
- 7.2.5.2 Ground-to-train communication
- 7.2.5.3 Train-to-train communication
- 7.2.6 SMART TICKETING SYSTEM
- 7.2.6.1 Need for convenience
- 7.2.7 RAIL ANALYTICS SYSTEM
- 7.2.7.1 Rapid adoption of AI-powered solutions in various countries across globe
- 7.2.8 RAIL ASSET MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS
- 7.2.8.1 Increased use of sensors in rail asset maintenance
- 7.2.8.2 Asset planning and scheduling
- 7.2.8.3 Workforce management and optimization
- 7.2.8.4 Condition-based monitoring
- 7.2.8.5 Predictive maintenance
- 7.2.8.6 Other railway asset management and maintenance solutions
- 7.2.9 RAIL OPERATION AND CONTROL SOLUTIONS
- 7.2.9.1 Need to compete with other modes of transportation
- 7.3 SERVICES
- 7.3.1 SERVICES: SMART RAILWAYS MARKET DRIVERS
- 7.3.2 PROFESSIONAL SERVICES
- 7.3.2.1 Fast digitalization in railway industry and growing need for personnel training
- 7.3.2.2 Consulting
- 7.3.2.3 System integration and deployment
- 7.3.2.4 Training, support, and maintenance
- 7.3.3 MANAGED SERVICES
- 7.3.3.1 Increased requirement for competent personnel for technical assistance
8 SMART RAILWAYS MARKET, BY REGION
- 8.1 INTRODUCTION
- 8.2 NORTH AMERICA
- 8.2.1 NORTH AMERICA: PESTLE ANALYSIS
- 8.2.2 NORTH AMERICA: MARKET DRIVERS
- 8.2.3 NORTH AMERICA: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 8.2.4 US
- 8.2.4.1 Government initiatives to drive market in US
- 8.2.5 CANADA
- 8.2.5.1 Increase in number of passengers and higher freight traffic to drive market in Canada
- 8.3 EUROPE
- 8.3.1 EUROPE: MARKET DRIVERS
- 8.3.2 EUROPE: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 8.3.3 UK
- 8.3.3.1 Need to improve efficiency of existing railway infrastructure to boost market
- 8.3.4 GERMANY
- 8.3.4.1 Significant adoption of IoT technologies and analytics in railway sector to propel market
- 8.3.5 FRANCE
- 8.3.5.1 High investment by railway operators to drive market
- 8.3.6 ITALY
- 8.3.6.1 Advancement in railway mobility through smart and integrated solutions to drive market
- 8.3.7 SPAIN
- 8.3.7.1 Modernization of railway infrastructure with cutting-edge technology and strategic investment to drive market
- 8.3.8 NORDIC COUNTRIES
- 8.3.8.1 Focus on sustainable innovation and autonomous rail operations to drive market
- 8.3.9 REST OF EUROPE
- 8.4 ASIA PACIFIC
- 8.4.1 ASIA PACIFIC: MARKET DRIVERS
- 8.4.2 ASIA PACIFIC: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 8.4.3 CHINA
- 8.4.3.1 High government investments in railway infrastructure and rapid growth in railways to drive market
- 8.4.4 INDIA
- 8.4.4.1 Investments in smart city projects by government to spur market growth
- 8.4.5 JAPAN
- 8.4.5.1 Rise in adoption of railway technologies to boost market
- 8.4.6 AUSTRALIA & NEW ZEALAND (ANZ)
- 8.4.6.1 Rising infrastructure investments to drive market
- 8.4.7 SOUTHEAST ASIA
- 8.4.7.1 Increasing investment in rail infrastructure modernization to drive market
- 8.4.8 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC
- 8.5 MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA
- 8.5.1 MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA: MARKET DRIVERS
- 8.5.2 MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 8.5.3 MIDDLE EAST
- 8.5.3.1 UAE
- 8.5.3.1.1 Technological advancements and growing economy to drive market
- 8.5.3.2 KSA
- 8.5.3.2.1 Strengthening of freight network through strategic rail innovation and partnerships to drive market
- 8.5.3.3 Turkey
- 8.5.3.3.1 Focus on boosting regional connectivity and internationally funded high-speed rail expansion to drive market
- 8.5.3.4 Rest of Middle East
- 8.5.3.1 UAE
- 8.5.4 AFRICA
- 8.5.4.1 Nigeria
- 8.5.4.1.1 Government initiatives combined with increased cooperation with other countries to drive market
- 8.5.4.2 South Africa
- 8.5.4.2.1 Increased demand for transportation services to support regional trade requirements to propel market growth
- 8.5.4.3 Rest of Africa
- 8.5.4.1 Nigeria
- 8.6 LATIN AMERICA
- 8.6.1 LATIN AMERICA: MARKET DRIVERS
- 8.6.2 LATIN AMERICA: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 8.6.3 BRAZIL
- 8.6.3.1 Significant scope for development of advanced railway infrastructure to boost market growth
- 8.6.4 MEXICO
- 8.6.4.1 Increased demand for improved transportation infrastructure to fuel market growth
- 8.6.5 REST OF LATIN AMERICA
9 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 9.1 INTRODUCTION
- 9.2 KEY PLAYER STRATEGIES/RIGHT TO WIN, 2022-2025
- 9.3 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS, 2024
- 9.4 REVENUE ANALYSIS OF LEADING PLAYERS, 2020-2024
- 9.5 BRAND/PRODUCT COMPARISON
- 9.6 COMPANY VALUATION AND FINANCIAL METRICS
- 9.7 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- 9.7.1 STARS
- 9.7.2 EMERGING LEADERS
- 9.7.3 PERVASIVE PLAYERS
- 9.7.4 PARTICIPANTS
- 9.7.5 COMPANY FOOTPRINT: KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- 9.7.5.1 Company footprint
- 9.7.5.2 Region footprint
- 9.7.5.3 Offering footprint
- 9.8 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: SME/STARTUPS, 2024
- 9.8.1 PROGRESSIVE COMPANIES
- 9.8.2 RESPONSIVE COMPANIES
- 9.8.3 DYNAMIC COMPANIES
- 9.8.4 STARTING BLOCKS
- 9.8.5 COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING: STARTUPS/SMES, 2024
- 9.8.5.1 Detailed list of key startups/SMEs
- 9.8.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of key startups/SMEs
- 9.9 COMPETITIVE SCENARIO
- 9.9.1 PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- 9.9.2 DEALS
- 9.9.3 OTHER DEVELOPMENTS
10 COMPANY PROFILES
- 10.1 MAJOR PLAYERS
- 10.1.1 ALSTOM
- 10.1.1.1 Business overview
- 10.1.1.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 10.1.1.3 Recent developments
- 10.1.1.3.1 Deals
- 10.1.1.3.2 Other developments
- 10.1.1.4 MnM view
- 10.1.1.4.1 Key strengths
- 10.1.1.4.2 Strategic choices
- 10.1.1.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 10.1.2 CISCO
- 10.1.2.1 Business overview
- 10.1.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 10.1.2.3 Recent developments
- 10.1.2.3.1 Deals
- 10.1.2.4 MnM view
- 10.1.2.4.1 Key strengths
- 10.1.2.4.2 Strategic choices
- 10.1.2.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 10.1.3 HITACHI
- 10.1.3.1 Business overview
- 10.1.3.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 10.1.3.3 Recent developments
- 10.1.3.3.1 Product Launches
- 10.1.3.3.2 Deals
- 10.1.3.3.3 Other developments
- 10.1.3.4 MnM view
- 10.1.3.4.1 Key strengths
- 10.1.3.4.2 Strategic choices
- 10.1.3.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 10.1.4 WABTEC
- 10.1.4.1 Business overview
- 10.1.4.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 10.1.4.3 Recent developments
- 10.1.4.3.1 Product launches
- 10.1.4.3.2 Deals
- 10.1.4.4 MnM view
- 10.1.4.4.1 Key strengths
- 10.1.4.4.2 Strategic choices
- 10.1.4.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 10.1.5 SIEMENS
- 10.1.5.1 Business overview
- 10.1.5.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 10.1.5.3 Recent developments
- 10.1.5.3.1 Product launches
- 10.1.5.3.2 Deals
- 10.1.5.3.3 Other developments
- 10.1.5.4 MnM view
- 10.1.5.4.1 Key strengths
- 10.1.5.4.2 Strategic choices
- 10.1.5.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 10.1.6 IBM
- 10.1.6.1 Business overview
- 10.1.6.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 10.1.6.3 Recent developments
- 10.1.6.3.1 Deals
- 10.1.6.4 MnM view
- 10.1.6.4.1 Key strengths
- 10.1.6.4.2 Strategic choices
- 10.1.6.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 10.1.7 HUAWEI
- 10.1.7.1 Business overview
- 10.1.7.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 10.1.7.3 Recent developments
- 10.1.7.3.1 Product launches
- 10.1.7.3.2 Deals
- 10.1.8 INDRA SISTEMAS
- 10.1.8.1 Business overview
- 10.1.8.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 10.1.8.3 Recent developments
- 10.1.8.3.1 Deals
- 10.1.9 HONEYWELL
- 10.1.9.1 Business overview
- 10.1.9.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 10.1.9.3 Recent developments
- 10.1.9.3.1 Deals
- 10.1.10 ABB
- 10.1.10.1 Business overview
- 10.1.10.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 10.1.10.3 Recent developments
- 10.1.10.3.1 Deals
- 10.1.11 ADVANTECH
- 10.1.12 FUJITSU
- 10.1.13 TOSHIBA
- 10.1.14 MOXA
- 10.1.15 TELEVIC
- 10.1.16 ALCATEL-LUCENT ENTERPRISE
- 10.1.17 CONDUENT
- 10.1.1 ALSTOM
- 10.2 STARTUPS/SMES
- 10.2.1 EKE-ELECTRONICS
- 10.2.2 AITEK S.P.A.
- 10.2.3 UPTAKE
- 10.2.4 EUROTECH
- 10.2.5 TEGO
- 10.2.6 KONUX
- 10.2.7 ASSETIC
- 10.2.8 MACHINES WITH VISION
- 10.2.9 DELPHISONIC
- 10.2.10 PASSIO TECHNOLOGIES
- 10.2.11 CLOUDMOYO
- 10.2.12 CHEMITO
- 10.2.13 RAILTEL
11 ADJACENT/RELATED MARKETS
- 11.1 LIMITATIONS
- 11.2 RAILWAY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM MARKET - GLOBAL FORECAST TO 2025
- 11.2.1 MARKET DEFINITION
- 11.2.2 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 11.2.3 RAILWAY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM MARKET, BY OFFERING
- 11.2.4 RAILWAY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM MARKET, BY SERVICE
- 11.2.5 RAILWAY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM MARKET, BY REGION
- 11.3 RAILWAY PLATFORM SECURITY MARKET - GLOBAL FORECAST TO 2024
- 11.3.1 MARKET DEFINITION
- 11.3.2 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 11.3.3 RAILWAY PLATFORM SECURITY MARKET, BY COMPONENT
- 11.3.4 RAILWAY PLATFORM SECURITY MARKET, BY SOLUTION
- 11.3.5 RAILWAY PLATFORM SECURITY MARKET, BY SERVICE
- 11.3.6 RAILWAY PLATFORM SECURITY MARKET, BY PROFESSIONAL SERVICE
- 11.3.7 RAILWAY PLATFORM SECURITY MARKET, BY APPLICATION
- 11.3.8 RAILWAY PLATFORM SECURITY MARKET, BY REGION
- 11.4 DIGITAL RAILWAY MARKET - GLOBAL FORECAST TO 2024
- 11.4.1 MARKET DEFINITION
- 11.4.2 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 11.4.3 DIGITAL RAILWAY MARKET, BY SOLUTION
- 11.4.4 DIGITAL RAILWAY MARKET, BY SERVICE
- 11.4.5 DIGITAL RAILWAY MARKET, BY PROFESSIONAL SERVICE
- 11.4.6 DIGITAL RAILWAY MARKET, BY APPLICATION
- 11.4.7 DIGITAL RAILWAY MARKET, BY REGION
12 APPENDIX
- 12.1 DISCUSSION GUIDE
- 12.2 KNOWLEDGESTORE: MARKETSANDMARKETS' SUBSCRIPTION PORTAL
- 12.3 CUSTOMIZATION OPTIONS
- 12.4 RELATED REPORTS
- 12.5 AUTHOR DETAILS