|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1295360
シンチレーター市場-2023年から2028年までの予測Scintillator Market - Forecasts from 2023 to 2028 |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
|
|||||||
| シンチレーター市場-2023年から2028年までの予測 |
|
出版日: 2023年06月07日
発行: Knowledge Sourcing Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 125 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
- 全表示
- 概要
- 目次
シンチレーター市場は、2021年の7億59万7,000米ドルから2028年には9億7,407万6,000米ドルへと、CAGR 4.82%で成長すると予測されています。
シンチレーターは、研究者が多数の放射線や粒子を見つけることを可能にします。光電子増倍管とフォトダイオードは、後の工程で粒子を用いて同時に検出されます。粒子がシンチレーターに当たると、シンチレーターは粒子のエネルギーを吸収して発光します。シンチレーターは、一般的に水晶のような透明な材料で構成されていますが、重元素を含んでいる方がより良い性能を発揮しやすくなります。これは、シンチレーターが物質からのガンマ線を吸収できるようになるためです。このように、シンチレーターは一度に多くのラベリング実験ができることが、普及の原動力となっています。
さらに、主要メーカーによる技術改良への注力、アジア諸国における原子力発電所の増加、幅広い最終用途でのシンチレーターの使用拡大が、シンチレーターの市場成長につながっています。
さらに、シンチレーターの医療スキャンやその他の放射線用途における使用の増加、心臓病や神経疾患の有病率の増加が、シンチレーターの市場価値を押し上げるでしょう。研究開発のコストは上昇し、シンチレーター市場の拡大に道を開きます。
技術進歩の拡大が市場成長を後押ししています。
技術進歩の高まりと、さまざまな用途に向けた斬新な技術が市場を牽引しています。様々な組織がこの技術を調査しており、例えば国土安全保障省国内核検知局は、分光式個人用放射線検出器の新技術を探求しようとしています。この研究は、より優れた検出システムを開発するだけでなく、核物質や放射性物質を特定・認識しようとするものです。この努力によって生み出された技術は、真新しいハンドヘルド型ガジェットと組み合わされ、通常の活動に使用される可能性があります。DHSが核の脅威を認識し、封じ込める能力を向上させるために不可欠な、核・放射性物質検出能力の強化に力を入れています。
パッシブ高速移動中性子検出ソリューションは、様々な能動的検出方法にわたって遮蔽された固有の核物質の検出を増加させ、特定の核物質、特に兵器級プルトニウムの存在を示す可能性のある指標となります。さらに、シンチレーターの高精度、有効性、さらに低レベルの放射線を検出する能力といった魅力的な特性は、さまざまな産業で数多くの進歩を引き寄せています。
さらに、PETスキャナでシンチレーション材料を使用する習慣の拡大は、主要国の医療機器の収益を増加させている医療イメージング技術の発展に大きく貢献すると期待されています。例えば、国際貿易局の2020年報告書によると、米国の医療機器の収益は2019年の1,980億米ドルから2020年には2,090億米ドルに増加しました。
医療業界での応用がシンチレーター市場の需要を押し上げます。
シンチレーターは、平面X線イメージング、X線コンピュータ断層撮影(X線CT)、SPECT、PETスキャンなど、さまざまな医療用画像診断装置の製造に使用されています。シンチレーターとシンチレーション材料は、ガンマ線とX線の正確な位置、放出時間、変換時間に関する関連情報を提供し、正確な画像を撮影するのに役立つため、画像診断装置に使用されています。そのため、腫瘍や怪我などの慢性疾患の増加による診断画像への需要の高まりが、このセグメントの成長を牽引しています。最近のNHSレポートによると、イングランドでは2022年に4,400万件の画像検査が記録され、前年の3,490万件から26%増加しました。最も一般的なのはX線検査で、2,180万件(前年比30%増)、次いで超音波検査が1,010万件(同23%増)、コンピュータ断層撮影が670万件(同21%増)、磁気共鳴画像装置(MRI)が380万件(同28%増)でした。
シンチレーターは、平面X線イメージング、X線コンピュータ断層撮影(X線CT)、SPECT、PETスキャンなど、さまざまな医療用イメージング装置の製造に使用されています。シンチレーターとシンチレーション材料は、ガンマ線とX線の正確な位置、放出時間、変換時間に関する関連情報を提供し、正確な画像を撮影するのに役立つため、画像診断装置に使用されています。そのため、腫瘍や怪我などの慢性疾患の増加による診断画像への需要の高まりが、このセグメントの成長を牽引しています。最近のNHSレポートによると、イングランドでは2022年に4,400万件の画像検査が記録され、前年の3,490万件から26%増加しました。プレーンX線撮影が最も多く、2,180万件(前年比30%増)、次いで診断用超音波検査が1,010万件(同23%増)、コンピューター断層撮影が670万件(同21%増)、磁気共鳴画像法(MRI、380万件、同28%増)となっています。
慢性疾患の増加やパンデミック(世界的大流行)のような状況により、最新の診断医療機器を開発するための研究や開発が活発化しており、ヘルスケア分野におけるシンチレーターの成長を牽引しています。例えば、2023年5月、フロリダ州立大学の科学者グループは、CTスキャン、X線装置、その他の放射線検出およびイメージング技術の画質を向上させる可能性のある新世代の有機-無機ハイブリッド材料を開発しました。化学・生化学科のBiwu Ma教授らは、この新しい材料を開発しました。X線やその他の高エネルギー放射線に曝されると、これらの材料は発光します。
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 市場概要
- 市場の定義
- 調査範囲
- 市場セグメンテーション
- 通貨
- 前提条件
- 基準年と予測年のタイムライン
第2章 調査手法
- 調査データ
- 前提条件
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
- 調査ハイライト
第4章 市場力学
- 市場促進要因
- 市場抑制要因
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 業界バリューチェーン分析
第5章 シンチレーター市場:材質別の分析
- イントロダクション
- 有機
- 無機
第6章 シンチレーター市場:製品別の分析
- イントロダクション
- ポケットサイズ装置
- ハンドヘルド式装置
- 固定型・据置型システム
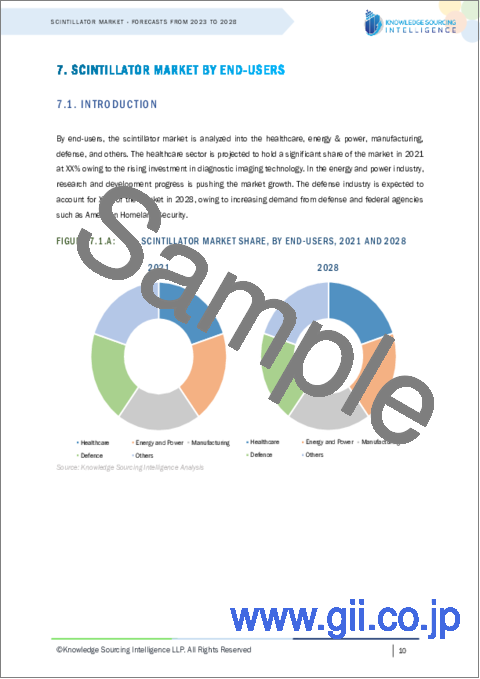
第7章 シンチレーター市場:エンドユーザー産業別の分析
- イントロダクション
- 医療
- エネルギー・電力
- 製造業
- 防衛
- その他
第8章 シンチレーター市場:地域別分析
- イントロダクション
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- メキシコ
- 南米
- ブラジル
- その他
- 欧州
- 英国
- ドイツ
- フランス
- その他
- 中東・アフリカ
- サウジアラビア
- イスラエル
- その他
- アジア太平洋
- 日本
- 中国
- 韓国
- インド
- インドネシア
- 台湾
- その他
第9章 競合環境と分析
- 主要企業と戦略分析
- 新興企業と市場収益性
- 合併、買収、合意およびコラボレーション
- ベンダー競争力マトリックス
第10章 企業プロファイル
- Applied Scintillation Technologies Ltd.
- Argus Imaging Bv Inc.
- Hamamatsu Photonics K.K.
- Radiation Monitoring Devices Inc
- Hitachi Metal Ltd.
- Mirion Technologies
- Siemens
- Zecotek Photonics Inc
- Ludlum Measurements
- Amcrys
- Saint Gobain
- Zecotek Photonics Inc.
The scintillator market is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 4.82% from US$700.597 million in 2021 to US$974.076 million by 2028.
Scintillators enable researchers to find numerous radiation and particles. The photomultipliers and photodiodes are simultaneously detected using the particles in a later step. When a particle strikes a scintillator, the scintillator emits luminesce by absorbing the energy of the particle. Scintillators, which typically consist of water-clear crystalline materials, are more likely to perform better if they contain heavy elements. This is since it enables the scintillators to absorb gamma radiation from the substance. The scintillators' capacity to conduct many labeling experiments at once is what is driving their wider use.
Further, expanding focus on technological improvements by the major producers, rising the number of nuclear power plants in Asian countries, and the expanding use of scintillators for a broad range of end-use applications are leading to the market growth of scintillators.
Moreover, the increasing use of scintillators in medical scanning and other radiological applications in medicine, as well as the rising prevalence of heart and neurological illnesses, will boost the scintillator market value. The cost of conducting research and development will rise, which will pave the way for the market for scintillators to expand.
Increasing technological advancements to boost market growth.
Growing technical advancement and novel technologies for a variety of uses is driving the market. Various organizations are researching this technology such as The Domestic Nuclear Detection Office of the Department of Homeland Security, which is trying to explore new technologies for Spectroscopic Personal Radiation Detectors. The study attempts to locate and recognize nuclear or radioactive sources as well as develop better detection systems. The technologies created through this effort could be combined with brand-new handheld gadgets and used in regular activities. It is putting a lot of effort into enhancing nuclear and radiological detection capabilities, which is essential to improving the DHS's capacity to recognize and contain nuclear threats.
The passive fast-moving neutron detection solution, which in turn increases the detection of shielded unique nuclear material across various active detection methods, is a possible indicator of the presence of certain nuclear materials, notably weapons-grade plutonium. Further, the enticing characteristics of scintillators, such as high precision, effectiveness, and the capacity to detect even lower radiation levels, are drawing numerous advancements in a variety of industries.
Additionally, the expanding practice of using scintillating materials in PET scanners is expected to significantly contribute to the development of medical imaging techniques which has increased the revenue for medical devices in major countries. For instance, as per the 2020 report of International Trade Administration, the revenue of medical devices in America increased from US$198 billion in 2019 to US$209 billion in 2020.
Application in the medical industry to boost the demand for the scintillators market.
Scintillators are used in the production of a wide variety of medical imaging devices such as planar x-ray imaging, x-ray computed tomography (x-ray CT), SPECT and PET scan. Scintillators and scintillating materials are used in imaging devices as they provide relevant information regarding the exact position, emission time and time of conversion of each gamma and X ray which help in taking precise images. Therefore, growing demand for diagnostic images because of rising prevalence of chronic disease such as tumors or injuries is driving the growth of this segment. According to a recent NHS report, in England, 44.0 million imaging tests were recorded in 2022, up from 34.9 million the previous year, representing a 26 per cent rise. Plain radiography or X-ray was the most common, accounting for 21.8 million treatments, an increase of 30 per cent from previous year followed by Diagnostic Ultrasonography with 10.1 million scans, an increase of 23 per cent), Computerized Axial Tomography recorded 6.7 million scans, representing an increase of 21 per cent, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI, 3.8 million, an increase of 28%).
Scintillators are used in the production of a wide variety of medical imaging devices such as planar x-ray imaging, x-ray computed tomography (x-ray CT), SPECT and PET scan. Scintillators and scintillating materials are used in imaging devices as they provide relevant information regarding the exact position, emission time and time of conversion of each gamma and X ray which help in taking precise images. Therefore, growing demand for diagnostic images because of rising prevalence of chronic disease such as tumors or injuries is driving the growth of this segment. According to a recent NHS report, in England, 44.0 million imaging tests were recorded in 2022, up from 34.9 million the previous year, representing a 26 per cent rise. Plain radiography or X-ray was the most common, accounting for 21.8 million treatments, an increase of 30 per cent from previous year followed by Diagnostic Ultrasonography with 10.1 million scans, an increase of 23 per cent), Computerized Axial Tomography recorded 6.7 million scans, representing an increase of 21 per cent, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI, 3.8 million, an increase of 28%).
Rising prevalence of chronic disease and pandemic like situations have led to increased research and trails to develop latest diagnostic medical devices, driving the growth of scintillators in the healthcare sector. For instance, in May 2023, a group of Florida State University scientists has developed a new generation of organic-inorganic hybrid materials that potentially improve picture quality in CT scans, X-Ray machines, and other radiation detection and imaging technologies. Professor Biwu Ma of the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry and his colleagues developed these novel materials, which may be used as scintillators. When exposed to X-Rays and other high-energy radiations, these materials emit light.
Key Developments
- In August 2020, researchers from Florida State University created eco-friendly X-ray Scintillators with High Efficiency that are less expensive and environmentally hazardous than current technology.
- in November 2022, Canon Medical Systems Corporation (Canon Medical), a subsidiary of Canon Inc., has created the first photon-counting CT system using scintillators in the United States that incorporates Redlen's sophisticated technology. This system was deployed at Japan's National Cancer Centre Exploratory Oncology Research & Clinical Trial Centre, where it is now employed for research into the clinical uses of PCCT.
Segmentation:
By Material Type
- Organic
- Inorganic
By Product
- Pocket-Size Instruments
- Hand-Held Instruments
- Fixed or Installed Systems
By End-User Industry
- Healthcare
- Energy and Power
- Manufacturing
- Defense
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- USA
- Canada
- Others
- South America
- Brazil
- Others
- Europe
- UK
- Germany
- France
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- Israel
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Indonesia
- Taiwan
- Others
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. INTRODUCTION
- 1.1. Market Overview
- 1.2. Market Definition
- 1.3. Scope of the Study
- 1.4. Market Segmentation
- 1.5. Currency
- 1.6. Assumptions
- 1.7. Base, and Forecast Years Timeline
2. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1. Research Data
- 2.2. Assumptions
3. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- 3.1. Research Highlights
4. MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1. Market Drivers
- 4.2. Market Restraints
- 4.3. Porter's Five Force Analysis
- 4.3.1. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.3.2. Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.3.3. Threat of New Entrants
- 4.3.4. Threat of Substitutes
- 4.3.5. Competitive Rivalry in the Industry
- 4.4. Industry Value Chain Analysis
5. SCINTILLATOR MARKET ANALYSIS BY MATERIAL TYPE
- 5.1. Introduction
- 5.2. Organic
- 5.3. Inorganic
6. SCINTILLATOR MARKET ANALYSIS BY PRODUCT
- 6.1. Introduction
- 6.2. Pocket-Size Instruments
- 6.3. Hand-Held Instruments
- 6.4. Fixed or Installed Systems
7. SCINTILLATOR MARKET ANALYSIS BY END-USER INDUSTRY
- 7.1. Introduction
- 7.2. Healthcare
- 7.3. Energy and Power
- 7.4. Manufacturing
- 7.5. Defense
- 7.6. Others
8. SCINTILLATOR MARKET ANALYSIS BY GEOGRAPHY
- 8.1. Introduction
- 8.2. North America
- 8.2.1. United States
- 8.2.2. Canada
- 8.2.3. Mexico
- 8.3. South America
- 8.3.1. Brazil
- 8.3.2. Others
- 8.4. Europe
- 8.4.1. UK
- 8.4.2. Germany
- 8.4.3. France
- 8.4.4. Others
- 8.5. Middle East and Africa
- 8.5.1. Saudi Arabia
- 8.5.2. Israel
- 8.5.3. Others
- 8.6. Asia Pacific
- 8.6.1. Japan
- 8.6.2. China
- 8.6.3. South Korea
- 8.6.4. India
- 8.6.5. Indonesia
- 8.6.6. Taiwan
- 8.6.7. Others
9. COMPETITIVE ENVIRONMENT AND ANALYSIS
- 9.1. Major Players and Strategy Analysis
- 9.2. Emerging Players and Market Lucrativeness
- 9.3. Mergers, Acquisitions, Agreements, and Collaborations
- 9.4. Vendor Competitiveness Matrix
10. COMPANY PROFILES
- 10.1. Applied Scintillation Technologies Ltd.
- 10.2. Argus Imaging Bv Inc.
- 10.3. Hamamatsu Photonics K.K.
- 10.4. Radiation Monitoring Devices Inc
- 10.5. Hitachi Metal Ltd.
- 10.6. Mirion Technologies
- 10.7. Siemens
- 10.8. Zecotek Photonics Inc
- 10.9. Ludlum Measurements
- 10.10. Amcrys
- 10.11. Saint Gobain
- 10.12. Zecotek Photonics Inc.