|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1474077
リチウムイオン電池用ハロゲン化物固体電解質:特許情勢の分析 (2024年)Halide Solid Electrolytes for Li-ion Batteries Patent Landscape Analysis 2024 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| リチウムイオン電池用ハロゲン化物固体電解質:特許情勢の分析 (2024年) |
|
出版日: 2024年05月07日
発行: KnowMade
ページ情報: 英文 PDF >90 slides, Excel file >300 patent families
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
当レポートでは、リチウムイオン電池用ハロゲン化物固体電解質に関する特許出願・公開の動きについて分析し、特許公開件数の推移 (国別・特許権者別) や、セグメント別の主な特許権者や新規参入企業、主要企業のポジショニングと特許ポートフォリオの拡充度、材料構成別・技術課題別の特許一覧、主要企業のIPプロファイル (特許ポートフォリオの概要、技術的カバー率、地理的カバー率、主要特許ほか) などを調査すると共に、分析対象特許 (全330件以上) の概略を取りまとめたExcelファイルを添付してお届けいたします。
ハロゲン化物固体電解質:固体電池の有望な選択肢
固体リチウムイオン電池は、安全性と高エネルギー密度の可能性という特筆すべき利点があるため、ここ数十年で大きな注目を集めています。この有望な次世代リチウム電池の実用化には、迅速なイオン輸送と優れた安定性を有する固体電解質 (SE) が不可欠です。そのため、硫化物系電解質や酸化物系電解質など、無機固体電解質の研究が盛んに行われてきました。しかし、両者とも導電性と安定性の最適なバランスをとることはできていません。酸化物は粒界のインピーダンスが高く、硫化物は安定性が低いです。しかし、ハロゲン化物系固体電解質は、室温でのイオン伝導度 (>10-3 S.cm-1)、酸化物正極材料との良好な相溶性、優れた化学的安定性・拡張性を備えているため、固体リチウムイオン電池の最も有望な選択肢の1つとして認識されつつあります。
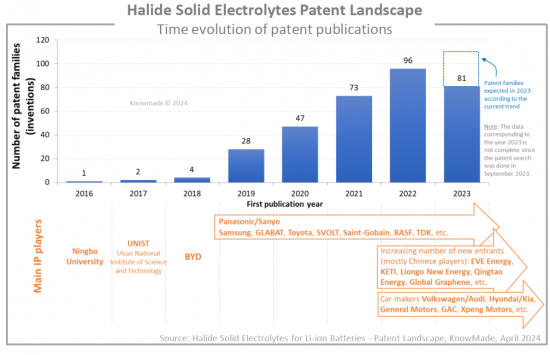
ハロゲン化物固体電解質への関心が高まっていることは、固体リチウムイオン電池に関する特許のモニターからも確認されています。2023年9月現在、リチウムイオン電池用ハロゲン化物固体電解質材料に関する特許は330件以上公開されています。固体電池業界で事業を展開する企業にとって、技術、競合、知的財産 (IP) の観点からこれらの新興材料を精査することは、今や極めて重要です。
特許技術とは?
当レポートでは、特許ポートフォリオの強さ、主要な特許権者 (特許譲受人) 企業の主な技術と活用領域を分析します。また、特許技術とその利用の現状と動向についても概観しています。さらに、この分野の大手企業と新規参入企業の戦略的・技術的方向性についても検証しています。
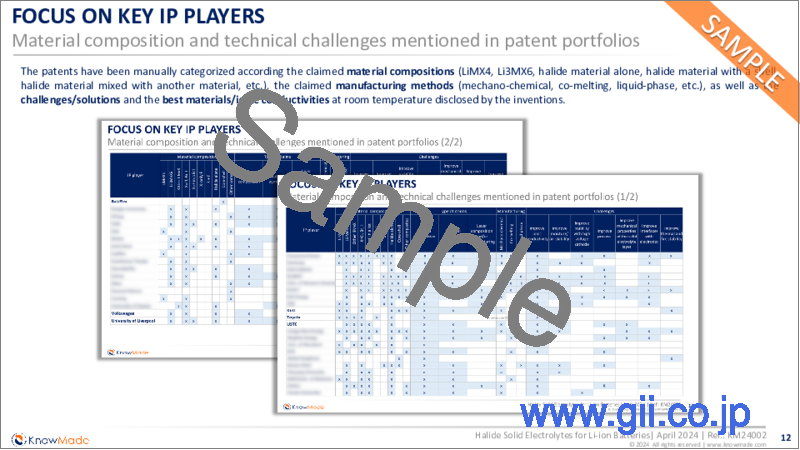
特許は、請求大賞の材料組成 (LiMX4、Li3MX6、ハロゲン化物材料単独、シェルを有するハロゲン化物材料、他の材料と混合されたハロゲン化物材料)、特許請求対象の製造方法 (メカノケミカル、共溶融、液相)、および課題/解決策、発明によって開示された室温での最良の材料/イオン伝導度に従って、手作業で分類されています。
少数のIPリーダーと多数のIP新規参入企業
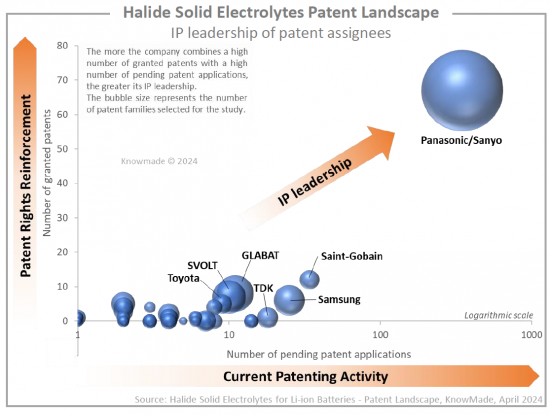
Panasonic/Sanyoがハロゲン化物固体電解質の特許をリードしており、Samsung、GLABAT、SVOLT、Saint-Gobain、TDKがこれに対抗しています。さらに、IP分析により、2022年以降に最初のハロゲン化物関連特許を出願した60以上のIP新規参入企業を特定することができました:EVE Energy、Korea Electronics Technology Institute (KETI)、Liongo New Energy、Qingtao Energy Development、Global Grapheneなどです。特許の新規参入者の80%は中国からです。専用セクションでは、主要企業 (Panasonic、Samsung、Saint-Govain、GLABAT、SVOLT、EVE Energy、University of Western Ontario、TDK、Toyotaなど) が保有するIPポートフォリオに焦点を当てています。それぞれについて、ハロゲン化物固体電解質に関連する特許ポートフォリオの概要と、主要な特許技術の説明を提供します。
便利なExcel特許データベース
当レポートには、分析対象の全ての特許を含む広範なExcelデータベースも含まれています。この便利な特許データベースは、多基準検索が可能で、特許公開番号、更新されたオンラインデータベースへのハイパーリンク (原文、法的ステータスなど)、優先日、タイトル、要約、特許譲受人、セグメント (課題/解決策、材料組成、ハロゲン化物処方、合成方法など) を含んでいます。
報告書に記載された企業 (一部)
Baoneng Group、Baowu Steel Group、BASF、Beijing Institute of Technology、BYD、China Automotive Battery Research Institute、China Electrics、Corning、EVE Energy、FAW (China First Automobile Works)、Global Graphene、GRINM (General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals) / GRIMAT、GRIREM Advanced Materials、GTC Power、Guolian Automobile Power Battery Research Institute (GLABAT)、Guoxuan High Tech Power Energy / Gotion、Hanyang University、Hyundai / Kia、Institute of Chemistry - Chinese Academy of Sciences、Korea Electronics Technology Institute (KETI)、Liongo New Energy Technology、Nankai University、Nanmu Nanotechnology、Nichia、Panasonic / Sanyo、QingTao Energy Development、Rare Earth Functional Materials Innovation Center、Saint-Gobain、Samsung、Shenzhen University、Silver Leaf Element、Solvay、South University of Science & Technology of China (SUSTech)、SVOLT / Fengchao Energy Technology、TDK、Toyota、Tsinghua Shenzhen International Graduate School、University of Maryland、University of Waterloo、University of Western Ontario、University of Science and Technology of China (USTC)、Xi'an Jiaotong University、Yonsei University、Zengzhou New Century Materials Genome Institute、Zhejiang University、など。
目次
イントロダクション
ハイライト
特許情勢の概要
- 特許の公開件数:時系列的変化
- 特許の出願件数:国別
- 特許権者の類型
- 主なIP企業:国別・類型別
- スタートアップと専業企業
- 主な特許権者
- 最も活発なIP企業 (2022~2023年)
- IP企業のタイムライン
- 新規参入のIP企業
- 現在の特許の法的地位
- IPリーダーシップ:国別
- IPリーダーシップ:特許権者別
- 主要企業の特許の法的地位と活動地域
- 存続特許の地域分布
- 主要なIP企業とそのIPポジション
- 特許譲受人のIP妨害の可能性
- 特許譲受人のIPの強み
主要なIP企業の分析
- 表:特許権者の特許ポートフォリオに記載されている材料構成と技術的課題
- 主要企業のIPプロファイル (IPポートフォリオの概要と主要な特許技術) :
- Panasonic/Sanyo
- Samsung
- Saint-Gobain
- Guolian Automobile Power Battery Res. Inst. (GLABAT)
- University of Western Ontario
- SVOLT
- EVE Energy
- TDK
- KETI (Korea Electronics Technology Institute)
- Toyota
- USTC (University of Science and Technology of China)
- Liongo New Energy Technology
- Qingtao Energy Development
- University of Maryland
- BYD
- Global Graphene
- Baowu Steel Group
- Hanyang University
- BASF / University of Waterloo
- Guoxuan High Tech Power Energy / Gotion
- Yonsei University
- BattFlex
- Ningbo University
- XPeng
- FAW
- GAC
- Nichia
- Aichi Steel
- Fujifilm
- Sumitomo/ Tanaka
- Hyundai/Kia
- Solvay
- Sidus
- General Motors
- Corning
- University of Dayton
- Volkswagen
- University of Liverpool
付録
- 特許の基礎知識
- 用語
- 主要なIP企業:定義と事例
- 固体電池の基礎知識
- 参考文献
KnowMadeのプレゼンテーション
KEY FEATURES
- PDF >90 slides
- Excel file >300 patent families
- Global patenting trends, including time evolution of patent publications, countries of patent filings, etc.
- Main patent assignees and IP newcomers in the different segments of the supply chain.
- Key players' IP position and the relative strength of their patent portfolio.
- Patents categorized by material composition and technical challenges.
- IP profile of key players (patent portfolio overview, technical coverage, geographical coverage, key patents, etc.)
- Excel database containing all patents analyzed in the report, including patent segmentations and hyperlinks to an updated online database.
Halide solid electrolytes are promising options for solid-state batteries
Solid-state Li-ion batteries have garnered significant attention in recent decades due to their notable advantages of safety and potential for high energy density. Solid electrolytes (SE) with rapid ionic transport and excellent stability are essential for the commercialization of this promising next-generation of Lithium batteries. Hence, there has been extensive exploration of inorganic solid electrolytes, including sulfide- and oxide-based electrolytes. Unfortunately, both have been unable to strike an optimal balance between conductivity and stability. Oxides suffer from high impedance of grain boundaries, while sulfides experience poor stability. However, halide-based solid electrolytes are increasingly being recognized as one of the most promising options for solid-state Li-ion batteries, owing to their decent room temperature ionic conductivity (>10-3 S.cm-1), good compatibility with oxide cathode materials, excellent chemical stability, and scalability.
The increasing interest in halide solid electrolytes has been observed while monitoring patents on solid-state Li-ion batteries. As of September 2023, over 330 patent families have been published on halide solid electrolyte materials for Li-ion batteries. It is now crucial for companies operating in the solid-state battery industry to closely examine these emerging materials from technological, competitive, and intellectual property (IP) perspectives.
In this context, Knowmade is releasing a new patent landscape report that focuses on halide solid electrolyte materials for Li-ion batteries. In this report, Knowmade's analysts have selected and analyzed over 860 patents and patent applications from more than 330 patent families (inventions) filed by 110+ different entities. The report provides a detailed analysis of the IP landscape and noteworthy patents concerning halide solid electrolyte materials. This new IP report is complementary to our previous patent landscape reports and patent monitors on solid-state batteries.

Understanding the main trends, the key players' IP position and IP strategy
IP competition analysis should reflect the vision of players with a strategy to enter and develop their business in the solid-state Li-ion battery market. In this report, Knowmade's analysts provide a comprehensive overview of the competitive IP landscape and latest technological developments in this field. The report covers IP dynamics and key trends in terms of patents applications, patent assignees, filing countries, and patented technologies. It also identifies the IP leaders, most active patent applicants, and new entrants in the IP landscape. The report also sheds light on under-the-radar companies and new players in this field.
What are the patented technologies?

In this report, we analyze the strength of patent portfolios and the technology and application focus of key patent assignees. An overview of the current status and trends of patented technologies and their applications is also provided. Furthermore, the report examines the strategic and technological directions of both leading companies and newcomers in the field.
The patents have been manually categorized according the claimed material compositions (LiMX4, Li3MX6, halide material alone, halide material with a shell, halide material mixed with another material), the claimed manufacturing methods (mechano-chemical, co-melting, liquid-phase), as well as the challenges/solutions and the best materials/ionic conductivities at room temperature disclosed by the inventions.
A few IP leaders and numerous IP newcomers
Panasonic/Sanyo is leading the halide solid electrolytes patent landscape, challenged by Samsung, GLABAT, SVOLT, Saint-Gobain, and TDK. Additionally, the IP analysis allowed us to pinpoint over 60 IP newcomers who filed their first halide-related patents in 2022 or after: EVE Energy, Korea Electronics Technology Institute (KETI), Liongo New Energy, Qingtao Energy Development, Global Graphene, etc. 80% of new entrants in the patent landscape come from China. In a dedicated section, we focus on the IP portfolios held by key players (Panasonic, Samsung, Saint-Gobain, GLABAT, SVOLT, EVE Energy, University of Western Ontario, TDK, Toyota, etc.). For each, we provide an overview of their patent portfolio related to halide solid electrolytes and a description of their key patented technologies.
Useful Excel patent database
This report also includes an extensive Excel database with all patents analyzed in this study. This useful patent database allows for multi-criteria searches and includes patent publication numbers, hyperlinks to an updated online database (original documents, legal status, etc.), priority date, title, abstract, patent assignees, and segments (challenges/solutions, material composition, halide formula, synthesis methods, etc.).
Companies mentioned in the report (non-exhaustive)
Baoneng Group, Baowu Steel Group, BASF, Beijing Institute of Technology, BYD, China Automotive Battery Research Institute, China Electrics, Corning, EVE Energy, FAW (China First Automobile Works), Global Graphene, GRINM (General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals) / GRIMAT, GRIREM Advanced Materials, GTC Power, Guolian Automobile Power Battery Research Institute (GLABAT), Guoxuan High Tech Power Energy / Gotion, Hanyang University, Hyundai / Kia, Institute of Chemistry - Chinese Academy of Sciences, Korea Electronics Technology Institute (KETI), Liongo New Energy Technology, Nankai University, Nanmu Nanotechnology, Nichia, Panasonic / Sanyo, QingTao Energy Development, Rare Earth Functional Materials Innovation Center, Saint-Gobain, Samsung, Shenzhen University, Silver Leaf Element, Solvay, South University of Science & Technology of China (SUSTech), SVOLT / Fengchao Energy Technology, TDK, Toyota, Tsinghua Shenzhen International Graduate School, University of Maryland, University of Waterloo, University of Western Ontario, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), Xi'an Jiaotong University, Yonsei University, Zengzhou New Century Materials Genome Institute, Zhejiang University, and more.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
- Context and objectives of the report
- Scope of the report
- Methodology for patent search, selection, and analysis
- Halide Solid Electrolytes
- Chemical composition
- Room temperature ionic conductivity of main halide solid electrolyte materials
- Main properties, advantages and drawbacks
- Challenges and envisioned solutions for main halide solid electrolyte materials
- Main manufacturing methods
HIGHLIGHTS
PATENT LANDSCAPE OVERVIEW
- Time evolution of patent publications
- Patent filings by country
- Typology of patent assignees
- Main IP players per country and typology
- Startups and pure players
- Main patent assignees
- Most active IP players in 2022-2023
- Timeline of IP players
- IP newcomers
- Current legal status of patents
- IP leadership of countries
- IP leadership of patent assignees
- Main players' patent legal status and geographical coverage
- Geographical distribution of alive patents
- Key IP players and their IP position
- IP blocking potential of patent assignees
- IP strength of patent assignees
FOCUS ON KEY IP PLAYERS
- Table showing material compositions and technical challenges mentioned in patent portfolios of patent assignees
- IP profile of key players (IP portfolio overview and key patented technologies):
- Panasonic/Sanyo
- Samsung
- Saint-Gobain
- Guolian Automobile Power Battery Res. Inst. (GLABAT)
- University of Western Ontario
- SVOLT
- EVE Energy
- TDK
- KETI (Korea Electronics Technology Institute)
- Toyota
- USTC (University of Science and Technology of China)
- Liongo New Energy Technology
- Qingtao Energy Development
- University of Maryland
- BYD
- Global Graphene
- Baowu Steel Group
- Hanyang University
- BASF / University of Waterloo
- Guoxuan High Tech Power Energy / Gotion
- Yonsei University
- BattFlex
- Ningbo University
- XPeng
- FAW
- GAC
- Nichia
- Aichi Steel
- Fujifilm
- Sumitomo/ Tanaka
- Hyundai/Kia
- Solvay
- Sidus
- General Motors
- Corning
- University of Dayton
- Volkswagen
- University of Liverpool
ANNEX
- Basic knowledge of patents
- Terminology
- Key IP players: definition and examples
- Essentials on Solid-state Batteries
- Definitions
- Impact of main bulk solid-state battery technical issues on its performances
- Challenges and improvement solutions for bulk solid-state lithium battery
- Overview of main technical issues for bulk solid-state lithium batteries
- Categories of solid electrolytes
- Properties of each solid electrolyte categories
- Overview of main inorganic solid electrolyte materials
- Ionic conductivities of main other inorganic solid electrolyte materials
- Properties of main other inorganic solid electrolyte materials
- Bibliographic references