|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1750495
銅および銅合金スクラップとリサイクル市場の機会、成長促進要因、産業動向分析、2025年~2034年の予測Copper And Copper Alloy Scrap and Recycling Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
|
|||||||
| 銅および銅合金スクラップとリサイクル市場の機会、成長促進要因、産業動向分析、2025年~2034年の予測 |
|
出版日: 2025年05月05日
発行: Global Market Insights Inc.
ページ情報: 英文 225 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
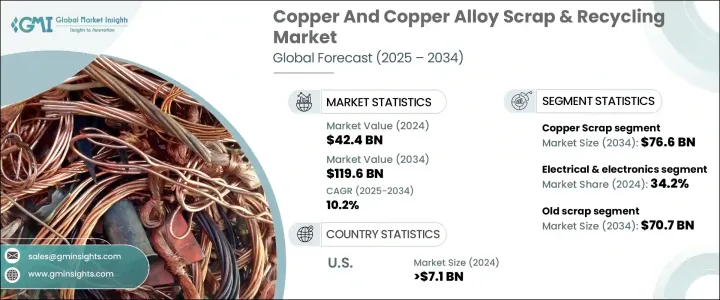
銅および銅合金スクラップとリサイクルの世界市場は、2024年には424億米ドルとなり、産業活動の高まりと持続可能性を求める世界の動きに後押しされ、CAGR 10.2%で成長し、2034年には1,196億米ドルに達すると予測されています。
循環型経済への注目は世界各国の政府にも支持され、銅スクラップやその合金の需要増につながっています。リサイクル銅は、その優れた導電性、リサイクル性、用途を問わない価値の高さから、電気から建築までさまざまな産業で不可欠な資源として重要性を増しています。
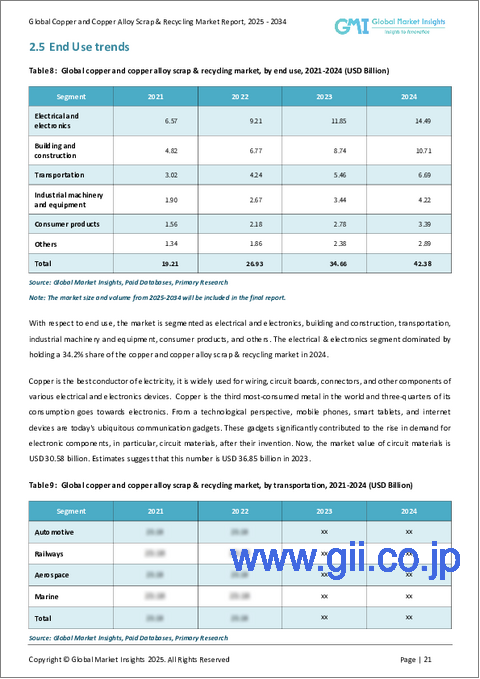
電気・電子部門は世界の銅の60%を消費しており、リサイクル銅の需要を牽引する極めて重要な役割を担っています。この分野では、その比類ない電気伝導性から、配線から回路基板まで、あらゆるものに銅が必要とされています。さらに、電気自動車や再生可能エネルギー、それに関連するインフラが台頭し、世界的に電化が進んでいるため、銅のリサイクルはサプライチェーンの重要な要素となっています。さらに、特にアジア太平洋や中東のような新興市場では、建築における銅の役割が拡大しており、配管、被覆、屋根、配線などに使われています。
| 市場範囲 | |
|---|---|
| 開始年 | 2024 |
| 予測年 | 2025-2034 |
| 開始金額 | 424億米ドル |
| 予測金額 | 1,196億米ドル |
| CAGR | 10.2% |
2024年に275億米ドルだった銅スクラップ分野は、2034年には766億米ドルに達し、大幅な成長が見込まれます。銅スクラップはリサイクル銅の一次情報源であり続け、その豊富さ、高い価値、優れた特性から、さまざまな産業で欠かせないものとなっています。銅の優れた導電性、耐腐食性、再利用の多用途性により、特に電気や建築などの分野で高い人気があります。産業界がより持続可能な解決策を求め続けるなか、銅スクラップの利用は銅の一次採掘の必要性を減らし、資源をリサイクルし最適化しようという世界の取り組みと一致します。
電気・電子部門が銅および銅合金スクラップとリサイクル市場を独占しており、2024年には34.2%のシェアを占める。銅は電気の信頼できる伝導体であるため、この業界では不可欠であり、一次銅とリサイクル銅の両方の需要を支えています。技術革新が進むにつれ、特に携帯電話やスマートデバイスの生産において、電子機器に使われる銅のニーズは高まり、銅スクラップ市場の成長をさらに後押しすることになります。
米国の銅および銅合金スクラップとリサイクル市場は、2024年には71億米ドルを生み出しました。企業や産業界がより環境にやさしいやり方を目指すようになるにつれ、銅のリサイクルも重視されるようになりました。銅は品質を落とすことなく何度でもリサイクルできることで知られ、再利用には理想的な素材です。これは新品の銅の需要を減らすだけでなく、廃棄物削減や資源保護の動向も後押ししています。
世界の銅および銅合金スクラップとリサイクル市場の主なプレーヤーは、Aurubis AG、Umicore、Commercial Metals Company、European Metal Recycling(EMR)、Sims Metal Managementなどです。これらの企業は、リサイクル能力の拡大、最先端技術への投資、サプライヤーや顧客との強固な関係構築など、市場での地位を強化するためにいくつかの戦略を採用しています。効率性の向上とリサイクル工程の強化に力を入れることで、これらの企業は世界の持続可能性の目標に沿いつつ、リサイクル銅の需要増に対応することを目指しています。さらに、新しい市場を開拓し、循環型経済における新たな機会を活用するために、地理的なフットプリントを広げています。
目次
第1章 調査手法と範囲
第2章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第3章 業界考察
- 市場概要およびダイナミクス
- 市場の定義と範囲
- 業界バリューチェーン分析
- 市場規模と成長予測(2025-2033)
- 市場の歴史的進化(2018-2024)
- 市場促進要因
- 再生可能エネルギーにおける銅の需要増加
- 循環型経済への注目の高まり
- リサイクル銅のコストメリット
- 成長する電気自動車市場
- 都市化とインフラ開発
- 市場抑制要因
- 銅市場の価格変動
- 収集と分類の課題
- リサイクル材料の品質のばらつき
- 技術的な制限
- サプライチェーンの混乱
- 市場機会
- リサイクルプロセスにおける技術の進歩
- 新興経済諸国の未開拓の潜在力
- 電子廃棄物リサイクルの拡大
- AIと自動化の統合
- 戦略的パートナーシップとコラボレーション
- 市場の課題
- 規制コンプライアンスの複雑さ
- 一次銅生産との競合
- リサイクル銅の汚染問題
- 初期投資額が高め
- 熟練労働者の不足
- PESTEL分析
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- トランプ政権による関税への影響
- 貿易への影響
- 貿易量の混乱
- 報復措置
- 業界への影響
- 供給側の影響(原材料)
- 主要原材料の価格変動
- サプライチェーン再構築
- 生産コストへの影響
- 需要側の影響(販売価格)
- 最終市場への価格伝達
- 市場シェアの動向
- 消費者の反応パターン
- 供給側の影響(原材料)
- 影響を受ける主要企業
- 戦略的業界対応
- サプライチェーンの再構成
- 価格設定と製品戦略
- 政策関与
- 展望と今後の検討事項
- 貿易への影響
- 貿易統計(HSコード)
- 主要輸出国、2021-2024
- 主要輸入国、2021-2024
- 銅リサイクルバリューチェーン分析
- 収集システムとインフラストラクチャ
- 正式な収集ネットワーク
- 非公式収集ネットワーク
- 預金システム
- 拡大生産者責任プログラム
- ソートと前処理
- 手動選別
- 自動選別技術
- 細断とサイズ縮小
- 分離技術
- 加工と精製
- 製錬事業
- 精製プロセス
- 品質管理措置
- 製品別回収
- 流通と最終市場
- 市場チャネル
- 価格決定メカニズム
- 品質基準と仕様
- 顧客の要件
- バリューチェーンの統合と最適化戦略
- バリューチェーンの課題とボトルネック
- バリューチェーンの将来的な進化
- 規制枠組みと政策分析
- 世界規制
- バーゼル条約
- 国際貿易規制
- 世界サステナビリティイニシアチブ
- 地域規制枠組み
- 北米
- 米国EPA規制
- 資源保全回収法(RCRA)
- 州レベルの規制
- 欧州連合
- 廃電気電子機器(WEEE)指令
- 使用済み自動車(ELV)指令
- 循環型経済行動計画
- REACH規制
- アジア太平洋地域
- 中国のスクラップ輸入政策
- 日本のリサイクル法
- インドの電子廃棄物管理規則
- 北米
- その他の地域規制
- 規制が市場力学に与える影響
- 業界関係者向けコンプライアンス戦略
- 将来の規制動向とその影響
- 世界規制
- 持続可能性と環境影響分析
- 銅リサイクルの環境的利点
- エネルギー節約
- 温室効果ガス排出削減
- 資源保全
- 廃棄物削減
- リサイクル銅と一次銅のライフサイクルアセスメント
- カーボンフットプリント分析
- 水の使用と管理
- 銅リサイクルにおける循環型経済の原則
- 企業の持続可能性への取り組み
- ESG(環境、社会、ガバナンス)の考慮
- 持続可能性の認証と基準
- 将来の持続可能性の動向と機会
- 銅リサイクルの環境的利点
- 技術的情勢とイノベーション分析
- 現在のリサイクル技術
- 収集および選別技術
- 処理技術
- 精製技術
- 新興技術とイノベーション
- 人工知能と機械学習のアプリケーション
- ロボット工学と自動化
- 高度なセンサー技術
- サプライチェーンのトレーサビリティのためのブロックチェーン
- 新しい冶金プロセス
- テクノロジー導入の動向
- 研究開発投資とイノベーションハブ
- 特許分析
- 技術成功事例のケーススタディ
- 将来の技術ロードマップ
- 現在のリサイクル技術
- 将来の市場動向と予測
- 短期市場見通し(1~2年)
- 中期市場予測(3~5年)
- 長期市場予測(6~8年)
- 新たな動向
- 都市鉱山
- リサイクルにおけるデジタル変革
- リサイクル事業の地域化
- 再生可能エネルギーシステムとの統合
- 高度な材料回収
- シナリオ分析
- 楽観的シナリオ
- 現実的なシナリオ
- 悲観的なシナリオ
- 外部要因の影響
- 経済的要因
- 技術開発
- 規制の変更
- 環境問題
- 社会と人口の変化
- 投資分析と市場機会
- 銅リサイクルへの投資動向
- ベンチャーキャピタルおよびプライベートエクイティ活動
- 合併と買収の情勢
- 投資収益率分析
- 地域別投資ホットスポット
- 投資リスクと軽減戦略
- 将来の投資機会
- ステークホルダー分析
- 主要な利害関係者グループ
- リサイクル会社
- 銅生産者
- 最終用途産業
- テクノロジープロバイダー
- 規制機関
- 投資家と金融機関
- 調査・学術機関
- 業界団体
- ステークホルダーの利益と影響力の分析
- ステークホルダーエンゲージメント戦略
- コラボレーションの機会
- 主要な利害関係者グループ
- 戦略的提言
- リサイクル会社向け
- テクノロジー導入戦略
- 市場拡大の機会
- 運用効率の改善
- 戦略的パートナーシップ
- 最終用途産業向け
- 調達戦略
- 持続可能性の統合
- サプライチェーンの最適化
- 投資家向け
- 潜在的投資分野
- リスク評価フレームワーク
- ポートフォリオ分散戦略
- 政策立案者向け
- 規制枠組みの強化
- インセンティブプログラム
- インフラ開発支援
- テクノロジープロバイダー向け
- イノベーションの重点分野
- 市場浸透戦略
- 共同研究開発の機会
- リサイクル会社向け
第4章 競合情勢
- 市場シェア分析
- 市場集中分析
- 競合ポジショニングマトリックス
- 主要企業プロファイル
- Aurubis AG
- 会社概要
- 財務実績
- 製品ポートフォリオ
- 戦略的取り組み
- SWOT分析
- Umicore
- Commercial Metals Company
- European Metal Recycling (EMR)
- Sims Metal Management
- Dowa Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Schnitzer Steel Industries
- Kuusakoski Oy
- Nucor Corporation
- The David J. Joseph Company
- その他の主要企業
- Aurubis AG
- 競争戦略
- 合併と買収
- ジョイントベンチャーとパートナーシップ
- 容量拡張
- 技術革新
- 市場参入戦略
- 最近の動向とその影響
第5章 市場規模・予測:タイプ別、2021年~2034年
- 主要動向
- 銅スクラップ
- むき出しの明るい銅スクラップ
- 銅スクラップNo.1
- 銅スクラップ2号
- その他の銅スクラップ
- 銅合金スクラップ
- 真鍮
- 青銅
- 白銅
- その他の銅合金
第6章 市場規模・予測:排出源別、2021年~2034年
- 主要動向
- 古いスクラップ(使用済み)
- 廃車
- 電子廃棄物
- 建築廃棄物
- 産業機械
- その他の使用済み資源
- 新しいスクラップ(プレコンシューマー/産業用)
- 製造工程の廃棄物
- 生産残渣
- 規格外材料
- その他の排出源
第7章 市場規模・予測:最終用途別、2021年~2034年
- 主要動向
- 電気・電子工学
- 建築・建設
- 輸送機関
- 自動車
- 鉄道
- 航空宇宙
- 海洋
- 産業機械および装置
- 消費財
- その他
第8章 市場規模・予測:加工方法別、2021年~2034年
- 主要動向
- 機械加工
- 乾式冶金処理
- 湿式冶金処理
- 電気冶金処理
- その他の処理方法
第9章 市場規模・予測:地域別、2021年~2034年
- 主要動向
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- 欧州
- 英国
- ドイツ
- フランス
- イタリア
- スペイン
- オランダ
- アジア太平洋地域
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- 韓国
- オーストラリア
- ラテンアメリカ
- ブラジル
- メキシコ
- アルゼンチン
- 中東・アフリカ
- 南アフリカ
- サウジアラビア
- アラブ首長国連邦
第10章 企業プロファイル
- Aurubis AG
- Umicore
- Commercial Metals Company
- European Metal Recycling(EMR)
- Sims Metal Management
- Dowa Holdings
- Schnitzer Steel Industries
- Kuusakoski Oy
- Nucor Corporation
- The David J. Joseph Company
The Global Copper And Copper Alloy Scrap & Recycling Market was valued at USD 42.4 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 10.2% to reach USD 119.6 billion by 2034, driven by rising industrial activities and a global push for sustainability. The focus on a circular economy, supported by governments worldwide, has resulted in increased demand for copper scrap and its alloys. Recycled copper is gaining importance as an essential resource in various industries, from electrical to construction, due to its excellent conductivity, recyclability, and high value across applications.

The electrical and electronics sector plays a pivotal role in driving the demand for recycled copper, as it consumes 60% of the world's copper. This sector requires copper for everything from wiring to circuit boards due to its unmatched electrical conductivity. Additionally, as the world continues to undergo significant electrification, spurred by the rise of electric vehicles, renewable energy, and related infrastructure, copper recycling has become a key component of the supply chain. Furthermore, copper's role in construction, especially in emerging markets like Asia-Pacific and the Middle East, is expanding, where it's used in plumbing, cladding, roofing, and wiring.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $42.4 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $119.6 Billion |
| CAGR | 10.2% |
The copper scrap segment, which was valued at USD 27.5 billion in 2024, is anticipated to experience substantial growth, reaching USD 76.6 billion by 2034. Copper scrap remains a primary source of recycled copper, making it essential across various industries due to its abundance, high value, and superior properties. Copper's excellent conductivity, resistance to corrosion, and versatility for reuse make it highly sought after, particularly in sectors like electrical and construction. As industries continue to demand more sustainable solutions, the use of copper scrap helps reduce the need for primary copper mining, aligning with global efforts to recycle and optimize resources.
The electrical & electronics sector dominates the Copper And Copper Alloy Scrap & Recycling Market, holding a 34.2% share in 2024, driven by copper's crucial role in mobile phones, smart tablets, computers, and other modern electronics, where it is used extensively for wiring, circuit boards, and connectors. Copper's role as a reliable conductor of electricity makes it indispensable in this industry, supporting the demand for both primary and recycled copper. As technological innovation continues, especially in mobile and smart device production, the need for copper in electronics is set to rise, further bolstering the growth of the copper scrap market.
United States Copper And Copper Alloy Scrap & Recycling Market generated USD 7.1 billion in 2024, underpinned by the country's increasing focus on sustainability and the circular economy. As businesses and industries move toward more environmentally friendly practices, the emphasis on recycling copper has intensified. Copper is known for its ability to be recycled multiple times without losing quality, making it an ideal material for reuse. This not only reduces the demand for virgin copper but also supports the growing trend of waste reduction and resource conservation.
Key players in the Global Copper And Copper Alloy Scrap & Recycling Market Include Aurubis AG, Umicore, Commercial Metals Company, European Metal Recycling (EMR), and Sims Metal Management. These companies have adopted several strategies to strengthen their positions in the market, including expanding their recycling capacities, investing in state-of-the-art technologies, and building strong relationships with suppliers and customers. By focusing on efficiency improvements and enhancing their recycling processes, these firms aim to meet the growing demand for recycled copper while aligning with global sustainability goals. Additionally, they are expanding their geographic footprints to tap into new markets and leverage emerging opportunities in the circular economy.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology & Scope
- 1.1 Market scope & definition
- 1.2 Base estimates & calculations
- 1.3 Forecast calculation
- 1.4 Data sources
- 1.4.1 Primary
- 1.4.2 Secondary
- 1.4.2.1 Paid sources
- 1.4.2.2 Public sources
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry synopsis, 2021-2034
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Market Overview and Dynamics
- 3.1.1 Market Definition and Scope
- 3.1.2 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 3.1.3 Market Size and Growth Projections (2025-2033)
- 3.1.4 Historical Market Evolution (2018-2024)
- 3.1.5 Market Drivers
- 3.1.5.1 Rising Demand for Copper in Renewable Energy
- 3.1.5.2 Increasing Focus on Circular Economy
- 3.1.5.3 Cost Advantages of Recycled Copper
- 3.1.5.4 Growing Electric Vehicle Market
- 3.1.5.5 Urbanization and Infrastructure Development
- 3.1.6 Market Restraints
- 3.1.6.1 Price Volatility in Copper Markets
- 3.1.6.2 Collection and Sorting Challenges
- 3.1.6.3 Quality Inconsistencies in Recycled Materials
- 3.1.6.4 Technological Limitations
- 3.1.6.5 Supply Chain Disruptions
- 3.1.7 Market Opportunities
- 3.1.7.1 Technological Advancements in Recycling Processes
- 3.1.7.2 Untapped Potential in Developing Economies
- 3.1.7.3 E-Waste Recycling Expansion
- 3.1.7.4 Integration of AI and Automation
- 3.1.7.5 Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
- 3.1.8 Market Challenges
- 3.1.8.1 Regulatory Compliance Complexity
- 3.1.8.2 Competition from Primary Copper Production
- 3.1.8.3 Contamination Issues in Recycled Copper
- 3.1.8.4 High Initial Investment Requirements
- 3.1.8.5 Skilled Labor Shortages
- 3.1.9 PESTLE Analysis
- 3.1.10 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 3.2 Trump Administration Tariffs
- 3.2.1 Impact on Trade
- 3.2.1.1 Trade Volume Disruptions
- 3.2.1.2 Retaliatory Measures
- 3.2.2 Impact on the Industry
- 3.2.2.1 Supply-Side Impact (Raw Materials)
- 3.2.2.1.1 Price Volatility in Key Materials
- 3.2.2.1.2 Supply Chain Restructuring
- 3.2.2.1.3 Production Cost Implications
- 3.2.2.2 Demand-Side Impact (Selling Price)
- 3.2.2.2.1 Price Transmission to End Markets
- 3.2.2.2.2 Market Share Dynamics
- 3.2.2.2.3 Consumer Response Patterns
- 3.2.2.1 Supply-Side Impact (Raw Materials)
- 3.2.3 Key Companies Impacted
- 3.2.4 Strategic Industry Responses
- 3.2.4.1 Supply Chain Reconfiguration
- 3.2.4.2 Pricing and Product Strategies
- 3.2.4.3 Policy Engagement
- 3.2.5 Outlook and Future Considerations
- 3.2.1 Impact on Trade
- 3.3 Trade statistics (HS Code)
- 3.3.1 Major Exporting Countries, 2021-2024 (USD Mn)
- 3.3.2 Major Importing Countries, 2021-2024 (USD Mn)
Note: The above trade statistics will be provided for key countries only
- 3.4 Copper Recycling Value Chain Analysis
- 3.5 Collection Systems and Infrastructure
- 3.5.1 Formal Collection Networks
- 3.5.2 Informal Collection Networks
- 3.5.3 Deposit Systems
- 3.5.4 Extended Producer Responsibility Programs
- 3.6 Sorting and Pre-processing
- 3.6.1 Manual Sorting
- 3.6.2 Automated Sorting Technologies
- 3.6.3 Shredding and Size Reduction
- 3.6.4 Separation Technologies
- 3.7 Processing and Refining
- 3.7.1 Smelting Operations
- 3.7.2 Refining Processes
- 3.7.3 Quality Control Measures
- 3.7.4 By-product Recovery
- 3.8 Distribution and End Markets
- 3.8.1 Market Channels
- 3.8.2 Pricing Mechanisms
- 3.8.3 Quality Standards and Specifications
- 3.8.4 Customer Requirements
- 3.9 Value Chain Integration and Optimization Strategies
- 3.10 Value Chain Challenges and Bottlenecks
- 3.11 Future Evolution of the Value Chain
- 3.12 Regulatory Framework and Policy Analysis
- 3.12.1 Global Regulations
- 3.12.1.1 Basel Convention
- 3.12.1.2 International Trade Regulations
- 3.12.1.3 Global Sustainability Initiatives
- 3.12.2 Regional Regulatory Frameworks
- 3.12.2.1 North America
- 3.12.2.1.1 U.S. EPA Regulations
- 3.12.2.1.2 Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA)
- 3.12.2.1.3 State-Level Regulations
- 3.12.2.2 European Union
- 3.12.2.2.1 Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive
- 3.12.2.2.2 End-of-Life Vehicles (ELV) Directive
- 3.12.2.2.3 Circular Economy Action Plan
- 3.12.2.2.4 REACH Regulations
- 3.12.2.3 Asia-Pacific
- 3.12.2.3.1 China's Policies on Scrap Imports
- 3.12.2.3.2 Japan's Recycling Laws
- 3.12.2.3.3 India's E-Waste Management Rules
- 3.12.2.1 North America
- 3.12.3 Other Regional Regulations
- 3.12.4 Impact of Regulations on Market Dynamics
- 3.12.5 Compliance Strategies for Industry Participants
- 3.12.6 Future Regulatory Trends and Their Implications
- 3.12.1 Global Regulations
- 3.13 Sustainability and Environmental Impact Analysis
- 3.13.1 Environmental Benefits of Copper Recycling
- 3.13.1.1 Energy Savings
- 3.13.1.2 Greenhouse Gas Emission Reductions
- 3.13.1.3 Resource Conservation
- 3.13.1.4 Waste Reduction
- 3.13.2 Life Cycle Assessment of Recycled vs. Primary Copper
- 3.13.3 Carbon Footprint Analysis
- 3.13.4 Water Usage and Management
- 3.13.5 Circular Economy Principles in Copper Recycling
- 3.13.6 Corporate Sustainability Initiatives
- 3.13.7 ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) Considerations
- 3.13.8 Sustainability Certifications and Standards
- 3.13.9 Future Sustainability Trends and Opportunities
- 3.13.1 Environmental Benefits of Copper Recycling
- 3.14 Technological Landscape and Innovation Analysis
- 3.14.1 Current Recycling Technologies
- 3.14.1.1 Collection and Sorting Technologies
- 3.14.1.2 Processing Technologies
- 3.14.1.3 Refining Technologies
- 3.14.2 Emerging Technologies and Innovations
- 3.14.2.1 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications
- 3.14.2.2 Robotics and Automation
- 3.14.2.3 Advanced Sensor Technologies
- 3.14.2.4 Blockchain for Supply Chain Traceability
- 3.14.2.5 Novel Metallurgical Processes
- 3.14.3 Technology Adoption Trends
- 3.14.4 R&D Investments and Innovation Hubs
- 3.14.5 Patent Analysis
- 3.14.6 Case Studies of Technological Success Stories
- 3.14.7 Future Technology Roadmap
- 3.14.1 Current Recycling Technologies
- 3.15 Future Market Trends and Forecasts
- 3.15.1 Short-term Market Outlook (1–2 Years)
- 3.15.2 Medium-term Market Projections (3–5 Years)
- 3.15.3 Long-term Market Forecasts (6–8 Years)
- 3.15.4 Emerging Trends
- 3.15.4.1 Urban Mining
- 3.15.4.2 Digital Transformation in Recycling
- 3.15.4.3 Localization of Recycling Operations
- 3.15.4.4 Integration with Renewable Energy Systems
- 3.15.4.5 Advanced Material Recovery
- 3.15.5 Scenario Analysis
- 3.15.5.1 Optimistic Scenario
- 3.15.5.2 Realistic Scenario
- 3.15.5.3 Pessimistic Scenario
- 3.15.6 Impact of External Factors
- 3.15.6.1 Economic Factors
- 3.15.6.2 Technological Developments
- 3.15.6.3 Regulatory Changes
- 3.15.6.4 Environmental Concerns
- 3.15.6.5 Social and Demographic Shifts
- 3.16 Investment Analysis and Market Opportunities
- 3.16.1 Investment Trends in Copper Recycling
- 3.16.2 Venture Capital and Private Equity Activities
- 3.16.3 Mergers and Acquisitions Landscape
- 3.16.4 Return on Investment Analysis
- 3.16.5 Investment Hotspots by Region
- 3.16.6 Investment Risks and Mitigation Strategies
- 3.16.7 Future Investment Opportunities
- 3.17 Stakeholder Analysis
- 3.17.1 Key Stakeholder Groups
- 3.17.1.1 Recycling Companies
- 3.17.1.2 Copper Producers
- 3.17.1.3 End-Use Industries
- 3.17.1.4 Technology Providers
- 3.17.1.5 Regulatory Bodies
- 3.17.1.6 Investors and Financial Institutions
- 3.17.1.7 Research and Academic Institutions
- 3.17.1.8 Industry Associations
- 3.17.2 Stakeholder Interests and Influence Analysis
- 3.17.3 Stakeholder Engagement Strategies
- 3.17.4 Collaborative Opportunities
- 3.17.1 Key Stakeholder Groups
- 3.18 Strategic Recommendations
- 3.18.1 For Recycling Companies
- 3.18.1.1 Technology Adoption Strategies
- 3.18.1.2 Market Expansion Opportunities
- 3.18.1.3 Operational Efficiency Improvements
- 3.18.1.4 Strategic Partnerships
- 3.18.2 For End-Use Industries
- 3.18.2.1 Sourcing Strategies
- 3.18.2.2 Sustainability Integration
- 3.18.2.3 Supply Chain Optimization
- 3.18.3 For Investors
- 3.18.3.1 High-Potential Investment Areas
- 3.18.3.2 Risk Assessment Framework
- 3.18.3.3 Portfolio Diversification Strategies
- 3.18.4 For Policy Makers
- 3.18.4.1 Regulatory Framework Enhancements
- 3.18.4.2 Incentive Programs
- 3.18.4.3 Infrastructure Development Support
- 3.18.5 For Technology Providers
- 3.18.5.1 Innovation Focus Areas
- 3.18.5.2 Market Penetration Strategies
- 3.18.5.3 Collaborative R&D Opportunities
- 3.18.1 For Recycling Companies
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Market Share Analysis
- 4.2 Market Concentration Analysis
- 4.3 Competitive Positioning Matrix
- 4.4 Key Player Profiles
- 4.4.1 Aurubis AG
- 4.4.1.1 Company Overview
- 4.4.1.2 Financial Performance
- 4.4.1.3 Product Portfolio
- 4.4.1.4 Strategic Initiatives
- 4.4.1.5 SWOT Analysis
- 4.4.2 Umicore
- 4.4.3 Commercial Metals Company
- 4.4.4 European Metal Recycling (EMR)
- 4.4.5 Sims Metal Management
- 4.4.6 Dowa Holdings Co., Ltd.
- 4.4.7 Schnitzer Steel Industries
- 4.4.8 Kuusakoski Oy
- 4.4.9 Nucor Corporation
- 4.4.10 The David J. Joseph Company
- 4.4.11 Other Notable Players
- 4.4.1 Aurubis AG
- 4.5 Competitive Strategies
- 4.5.1 Mergers and Acquisitions
- 4.5.2 Joint Ventures and Partnerships
- 4.5.3 Capacity Expansions
- 4.5.4 Technological Innovations
- 4.5.5 Market Entry Strategies
- 4.6 Recent Developments and Their Impact
Chapter 5 Market Size and Forecast, By Type, 2021-2034 (USD Million) (Tons)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Copper scrap
- 5.2.1 Bare bright copper scrap
- 5.2.2 #1 copper scrap
- 5.2.3 #2 copper scrap
- 5.2.4 Other copper scrap
- 5.3 Copper alloy scrap
- 5.3.1 Brass
- 5.3.2 Bronze
- 5.3.3 Cupronickel
- 5.3.4 Other copper alloys
Chapter 6 Market Size and Forecast, By Source, 2021-2034 (USD Million) (Tons)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Old scrap (post-consumer)
- 6.2.1 End-of-life vehicles
- 6.2.2 Electronic waste
- 6.2.3 Building and construction waste
- 6.2.4 Industrial machinery
- 6.2.5 Other post-consumer sources
- 6.3 New scrap (pre-consumer/industrial)
- 6.3.1 Manufacturing process waste
- 6.3.2 Production residues
- 6.3.3 Off-specification materials
- 6.3.4 Other industrial sources
Chapter 7 Market Size and Forecast, By End Use, 2021-2034 (USD Million) (Tons)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Electrical and electronics
- 7.3 Building and construction
- 7.4 Transportation
- 7.4.1 Automotive
- 7.4.2 Railways
- 7.4.3 Aerospace
- 7.4.4 Marine
- 7.5 Industrial machinery and equipment
- 7.6 Consumer products
- 7.7 Others
Chapter 8 Market Size and Forecast, By Processing Method, 2021-2034 (USD Million) (Tons)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 Mechanical processing
- 8.3 Pyrometallurgical processing
- 8.4 Hydrometallurgical processing
- 8.5 Electrometallurgical processing
- 8.6 Other processing methods
Chapter 9 Market Size and Forecast, By Region, 2021-2034 (USD Million) (Tons)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 North America
- 9.2.1 U.S.
- 9.2.2 Canada
- 9.3 Europe
- 9.3.1 UK
- 9.3.2 Germany
- 9.3.3 France
- 9.3.4 Italy
- 9.3.5 Spain
- 9.3.6 Netherlands
- 9.4 Asia Pacific
- 9.4.1 China
- 9.4.2 India
- 9.4.3 Japan
- 9.4.4 South Korea
- 9.4.5 Australia
- 9.5 Latin America
- 9.5.1 Brazil
- 9.5.2 Mexico
- 9.5.3 Argentina
- 9.6 MEA
- 9.6.1 South Africa
- 9.6.2 Saudi Arabia
- 9.6.3 UAE
Chapter 10 Company Profiles
- 10.1 Aurubis AG
- 10.2 Umicore
- 10.3 Commercial Metals Company
- 10.4 European Metal Recycling (EMR)
- 10.5 Sims Metal Management
- 10.6 Dowa Holdings
- 10.7 Schnitzer Steel Industries
- 10.8 Kuusakoski Oy
- 10.9 Nucor Corporation
- 10.10 The David J. Joseph Company